A&P 100 Chapter 6 - Skeletal System: Bone Tissue
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
The 6 key functions of the skeletal system
1. support
2. protection
3. movement
4. control of mineral content
5. hemopoesis
6. triglycerides storage
strength in our skeleton comes from the microscopic lattice of _____________ and ______________
calcium, phosphate
the skeleton allows for movement but also ________ movement at joints at the same time
limits
the skeleton is the major storage reservoir for ________
calcium
the skeleton also serves as a storage reservoir for __________ & ___________
phosphorus, iron
within certain bones is ________ bone marrow, responsible for blood cell production
red
blood cell production is called _____________
hemopoesis
triglycerides (lipids & fats) are stored and release within the ________ bone marrow
yellow
the main portion of the bone, long, tubular, cylindrical - tends to be predominantly made of compact bone is the ________________
diaphysis
the ends of the bones, proximal & distal portions - tends to have projections & fossas that contributes to articulations with other bones is called the _____________
epiphysis
portion b/w the diaphysis and epiphysis is called the ___________
metaphysis
the metaphysis also contains the ___________ growth plate which later becomes the ___________ line (approx age 20)
epiphyseal
the skin surrounding bones, made of dense irregular connective tissue is called _______________
periosteum
the periosteum merges with _________ and contains many sensory nerve endings and is held in place by perforating __________ fibers that mesh with bone matrix
tendons, sharpey's
the cartilaginous tissue found at the ends of bones, covers the epiphysis and reduces friction, allows movement at joints is called ___________ _____________
articular cartilage
the central cavity within the bone is called the __________ cavity, also called the marrow cavity
medullary
the medullary cavity is the location of the ___________ bone marrow
yellow
the medullary inner membrane is called ____________
endosteum
the 1st hardest material in the body is __________ and the 2nd is ____________ extracellular matrix.
enamel, bone (lamellae)
the extracellular matrix of bone is made up of 3 main ingredients, they are....
(WCC)
water 15%
collagen fibers 30%
crystallized mineral salts 55%
what is the percentage of water in bone extracellular matrix?
15%
what is the percentage of collagen fibers in bone extracellular matrix?
30%
what is the percentage of crystallized mineral salts in bone extracellular matrix?
55%
the most abundant compound in bone extracellular matrix is ___________ ____________
calcium phosphate
the 2nd most abundant compound in bone extracellular matrix is ___________ ____________
calcium hydroxide
calcium phosphate + calcium hydroxide = ______________
hydroxyappatite
hydroxyapatite + fluoride, potassium, sulphate and iron = _________________
calcification
the 4 main types of cells in bone are:
osteogenic cells
osteoblasts
osteocytes
osteoclasts
the unspecialized stem cells derived from mesenchyme cells are called _____________ cells
osteogenic
can osteogenic cells undergo cell division/mitosis?
yes
the bone builders called ____________ synthesize __________ fibers and initiate calcification
osteoblasts, collagen
osteoblasts take ____________ from blood and put it into bone
calcium (Ca2)
cells that destroy bone are called ____________
osteoclasts
osteoclasts take __________ from bone and put it into the blood
calcium
osteoblasts are responsible for bone ____________, the laying down of minerals and collagen fibers to create the extracellular matrix
deposition
osteoclasts are responsible for bone ____________, the breakdown of bone extracellular matrix
resorption
deposition and resorption are processes in bone ___________
remodeling
mature bone cells, which maintain daily metabolic activities of the bone cell such as exchange of nutrients, removal of wastes are called _________________
osetocytes
the two major portions/types of bone are ___________ bone & ___________ bone
compact, spongy (cancellous)
compact bone is made up of ____________, _____________ & ____________ and has little or no space b/w cells
calcium, phosphate & collagen (and other minerals)
the matrix of compact bone is called _____________ and is a ________ ________ connective tissue
lamellae, dense irregular
the 3 types of lamellae are ___________, ____________ & __________ lamellae
concentric, interstitial, circumferential
rings of hard, extracellular matrix surrounding each central canal called __________ __________
concentric lamellae
located b/w osteons but not part of an osteon are called _________ ___________
interstitial lamellae
surround the medullary cavity or lie underneath the periosteum, along the superficial edge of the bone is the ___________ ____________
circumferential lamellae
the perpendicular canals that run superficial to deep that carry blood & lymphatic vessels and nerves that penetrate from the periosteum are called __________ canals or ____________ canals
perforating, volkmann's
the parallel canals that run deep & longitudinally along the shaft of the bone, also carrying blood & lymph vessels as well as nerves are called ___________ canals or ___________ canals
central, haversian
spaces within lamellae where osteocytes can be found, also called "little lakes" ___________
lacunae
small channels that radiate in all directions from each lacunae, filled with ECF, also called little canals ____________
canaliculi
the repeating units of all components of compact bone around 1 central canal is called ___________ system or __________
haversian, osteon
bone that has the appearance of lattice, irregular pattern of bone tissue distribution, air/fluid filled is referred to as ______________ bone
spongy
Bone diagram
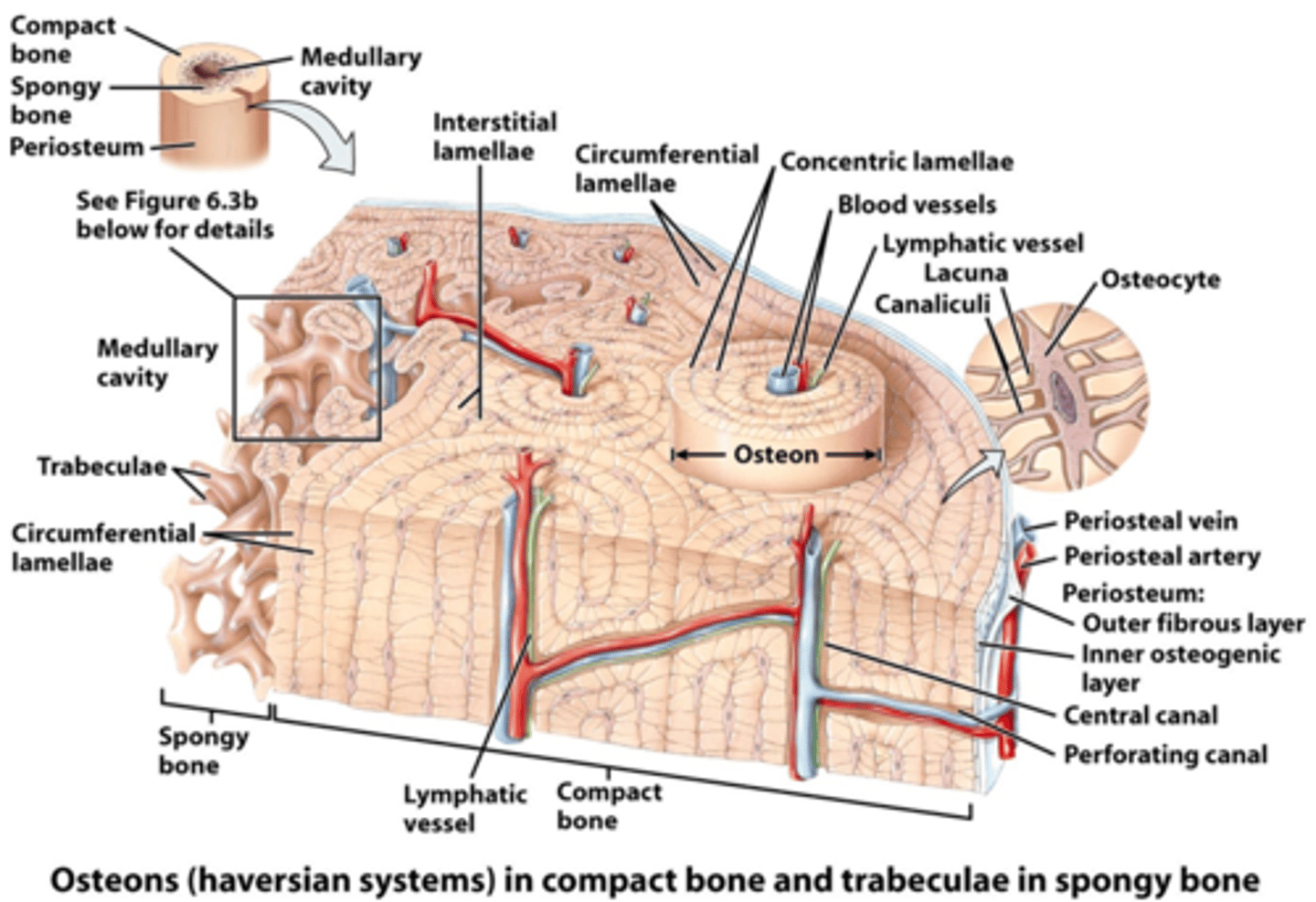
true/false, spongy bone has no osteons?
true
spongy bone is a greater/lesser blood supply?
greater
spongy bone requires more blood because what is produced there?
RBC, WBC & platelets
once RBC's, WBC's & platelets are produced in spongy bone tissue, they are deposited into the bloodstream to migrate to the s_______ and other l______ tissue where they are stored until reaching maturity.
spleen, lymph
the matrix or lamellae of spongy bone is called __________ and has a coral reef appearance
trabeculae
___________ bones have spongy bone throughout but more concentrated in the ends
long
bones that are predominantly spongy bone
flat, some irregular and all cuboidal
bone formation, also known as _____________ and _____________
Ossification, Osteogenesis
bone formation begins in the ________ week of development
6th
the 2 types of bone formation are ___________ and __________
Intramembranous, endochondral
bone formation that begins b/w 2 membranes, used by flat & skull bones and mandible
intramembranous
bone formation that replaces cartilage, more common in long bones
endochondral
intramembranous bone formation (4)
1. development of ossification center
2. calcification
3. formation of trabeculae
4. development of periosteum
step ___ of intramembranous bone formation; chemical messages cause mesenchymal cells to cluster and develop into osteoblasts, which secrete bone extracellular matrix. ____________________________________
1
development of ossification center
step ___ of intramembranous bone formation; osteoblasts become osteocytes, which extend projections into canaliculi; calcium and minerals are deposited and the matrix hardens. _____________________
2
calcification
step ___ of intramembranous bone formation; matrix continues to harden and forms trabeculae that fuse with one another to form spongy bone, blood vessels & connective tissue enter spaces and red bone marrow is formed. _________________________________
3
formation of trabeculae
step ___ of intramembranous bone formation; outer layer of mesenchyme develops into the periosteum; compact bone replaces spongy bone on cortex of bone, spongy bone remains in the middle; eventually bone conforms into adult size and shape. ____________________
4
development of periosteum
endochondral bone formation (6)
1. development of cartilage model
2. growth of cartilage model
3. development of primary ossification center
4. development of marrow cavity
5. development of secondary ossification center
6. formation of articular cartilage and epiphyseal growth plate
step ___ of endochondral bone formation; chemical messages initiate the mesenchymal cells to develop into chondroblasts, which begins cartilage extracellular matrix formation. cartilage is formed w/ perichondrium membrane surrounding the entire model. ________________________________
1
development of the cartilage model
step ___ of endochondral bone formation; chondroblasts develop into chondrocytes, with further deposition of cartilage extracellular matrix. 2 types, interstitial & appositional growth. _______________________________
2
growth of the cartilage model
step ___ of endochondral bone formation; nutrient artery penetrates into the middle of the cartilage initiating activity of osteoblasts; perichondrium becomes periosteum; local cartilage calcifies into bone. ______________________________
3
development of the primary ossification center
step ___ of endochondral bone formation; osteoclastic activity cause a marrow cavity to form with in the shaft of the diaphysis. ________________________________
4
development of marrow cavity
step ___ of endochondral bone formation; epiphyseal plate is formed from penetration of epiphyseal arteries; growth occurs outwards from the epiphysis, cartilage continues to be converted into bone. __________________________________
5
development of secondary ossification center
step ___ of endochondral bone formation; final stage of ossification where hyaline cartilage becomes the articular cartilage we see in adulthood. _________________________________
6
formation of articular cartilage and epiphyseal plate
replication of chondrocytes accompanying new matrix, results in __________________ growth.
interstitial (length)
deposition of extracellular matrix on cartilage surface and periphery results in __________________ growth.
appositional (width/thickness)
Bone Growth Model
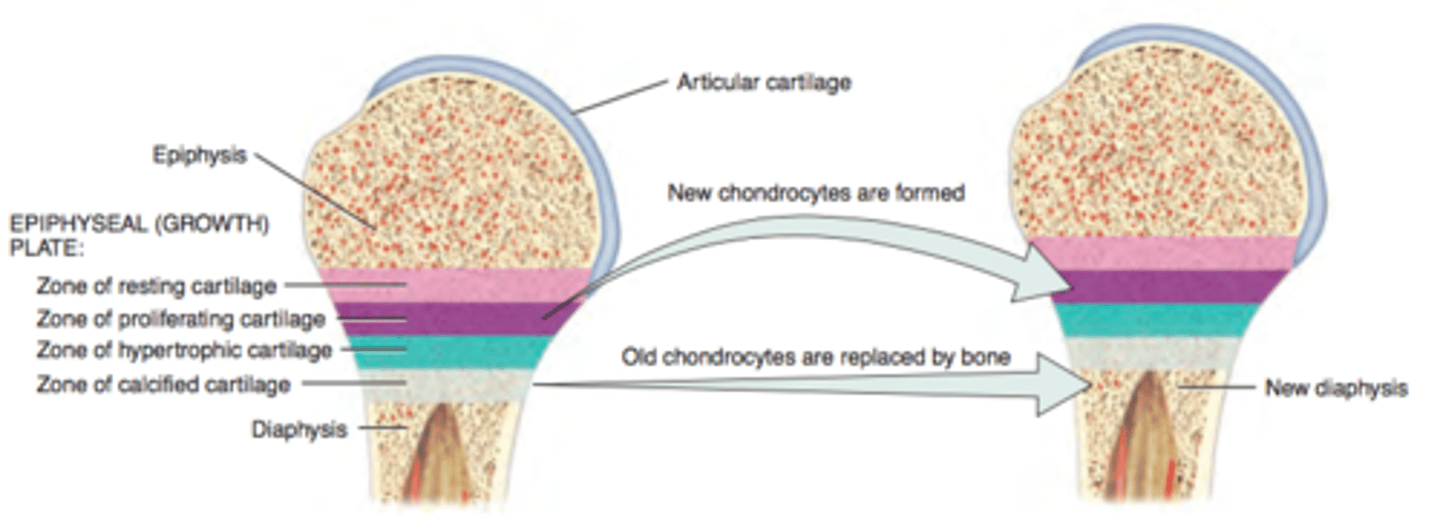
____________ plate - hyaline layer of cartilage in the metaphysis that consists of 4 main zones, from which new bone is laid down. This becomes the _______________ line after the person has stopped growing in length
epiphyseal
step ___ of bone growth; _______________ cartilage zone. the layer nearest to the epiphysis; consists of small chondrocytes that anchor the epiphyseal plate to the bone. the cells are not involved in bone growth.
1
resting
step ___ of bone growth; _______________ cartilage zone. large chondrocytes that replicate and divide to replace old/dying chondrocytes
2
proliferating
step ___ of bone growth; _______________ cartilage zone. large mature chondrocytes situated in columns
3
hypertrophic
step ___ of bone growth; _______________ cartilage zone. mostly dead chondrocytes, areas is calcified and osteoblasts invade to lay down new extracellular bone matrix to convert it from calcified cartilage to new diaphysis and new blood vessels are formed
4
calcified
bone tissue will lay down along lines of _________. also known as ___________ law
stress, wolf's
examples of bone stress
trauma
infection
cancer
aging
factors that affect bone growth
minerals
vitamins
hormones
minerals
calcium
phosphorus
fluoride
magnesium
manganese
vitamins
vitamin A
Vitamin C
Vitamin D
Vitamin B12/K
promotes osteoblAsts
Vit A
needed for Collagen formation
Vit C
helps with absorption of calcium in GI tract
Vit D (Digestive)
Vit D converted in Calcitriol by Kidneys
helps build bone proteins
Vit K & B12
hormones: from thyroid & insulin like growth factors, in response to human growth hormone, help to promote bone growth
T3 & T4
(Thyroid Hormone)
Arterial bone-blood supplies
periosteal artery - thru volkmann's / perforating
nutrient/diaphyseal artery
metaphyseal artery
epiphyseal artery
importance of calcium
- chemical reactions
- blood clotting
- muscle contractions
concentration of calcium in body must remain b/w:
9-11 mg/100ml
too much Ca2+ and heart __________
stops (stays contracted)
too little Ca2+ and respiration ___________
stops (not enough muscle fibers are stimulated)
too little Calcium: ___________
too much Calcium: ___________
Hypocalcemia
Hypercalcemia