Bio 1-Review Chapter 5
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/57
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
1
New cards
what are the five phases of the cell cycle?
Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase
2
New cards
What three phases make up interphase?
G1 phase, S phase, and G2 phase
3
New cards
What happens in the G1 phase?
First gap phase, cell grows physically larger
4
New cards
What happens in the S phase?
the cell synthesizes a complete copy of the DNA in its nucleus
5
New cards
What happens in the G2 phase?
Second gap phase, cell grows more, makes proteins and organelles. It ends when Mitosis begins
6
New cards
What is mitosis?
when the cell separates its DNA into 2 sets and divides its cytoplasm, forming into new cells.
7
New cards
What is cytokinesis?
When the cytoplasm of the cell is split in 2, making 2 new cells. It usually begins when mitosis is ending. Takes place differently in plant and animal cells.
8
New cards
What are the three checkpoints of the cell cycle?
Grow, Copy genetic material DNA, Physically split into 2 daughter cells.
9
New cards
What type of cells in all organisms has the greatest need for a rapid cell cycle? Why?
embryonic, the cells need to multiply for the formation of the embryo
10
New cards
What is GO?
This is the resting phase, a cell is not actively preparing to divide, it is just doing its job.
11
New cards
what is a chromosome?
an entire structure that contains the chromatid and chromatin
12
New cards
What is a chromatid?
the threadlike strand that contains a double helix of DNA
13
New cards
what is chromatin?
the loose combination of DNA and proteins that looks like spaghetti.
14
New cards
What protein does the DNA wrap itself around which helps to organize and condense it?
Histones
15
New cards
What is the goal of mitosis and cytokinesis?
to make sure the two daughter cells inherit an equal and
identical amount of chromosomes.
identical amount of chromosomes.
16
New cards
What happens in Prophase?
chromosomes condense and spindle fibers form. Nuclear envelope breaks down
17
New cards
What happens in Metaphase?
chromosomes line up in the middle of the cell
18
New cards
What happens in the Anaphase?
sister chromatids separate to opposite sides of the cell
19
New cards
What happens in the Telophase?
the new nuclei form and chromosomes begin to coil
20
New cards
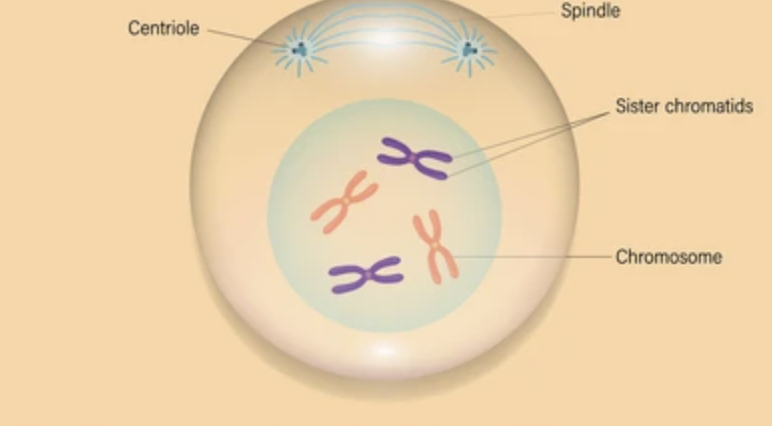
What phase is this?
prophase
21
New cards
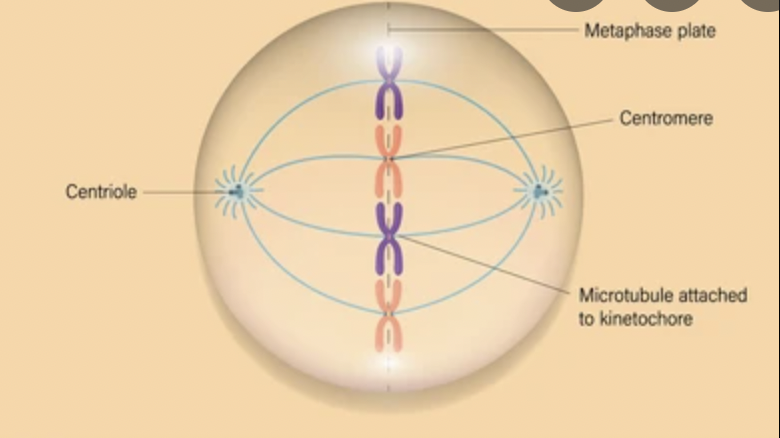
What phase is this?
metaphase
22
New cards
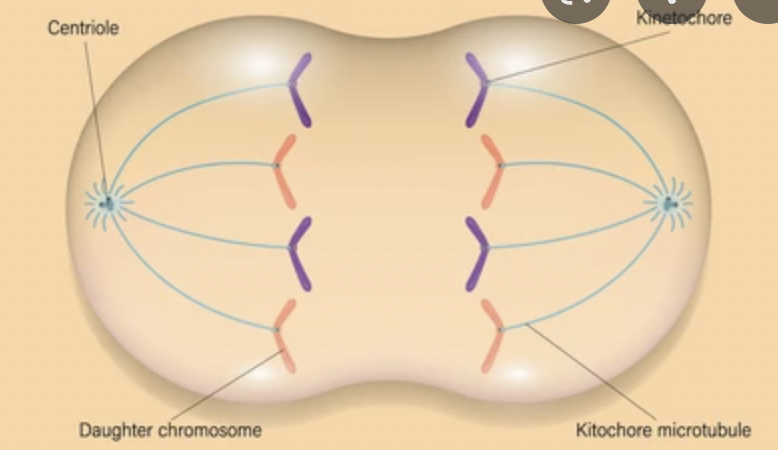
What phase is this?
anaphase
23
New cards
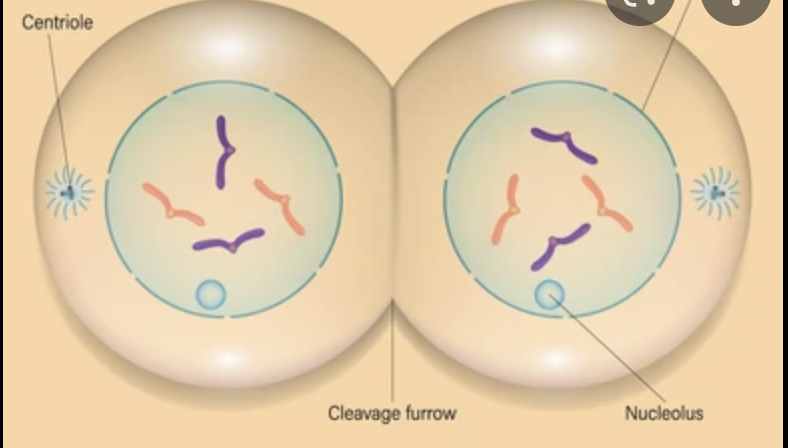
What phase is this?
telophase
24
New cards

What phase is this?
cytokinesis
25
New cards
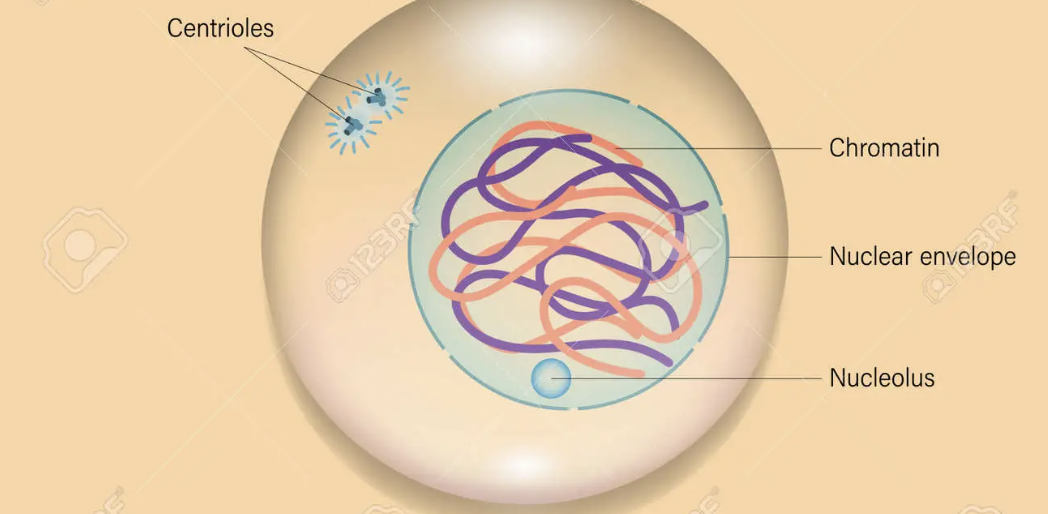
What phase is this
interphase
26
New cards
What are the signals that regulate cell division? Give examples of each.
Physical and chemical signals, ex. Growth factors are proteins that stimulate cell division.
27
New cards
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death
28
New cards
How is the normal division of cells controlled?
Proteins stimulate cell division, and internal enzymes such as kinesis and cyclins are triggered by External factors that affect the cell cycle
29
New cards
Cancer arises from the __________ of a normal gene.
damage
30
New cards
Mutated genes are called_____________________.
gene variants
31
New cards
What are 3 ways that mutations occur in genes? Know examples
Can result from errors in DNA replication during cell division, exposure to mutagens or a viral
infection.
infection.
32
New cards
What is a tumor?
Disorganized clumps formed by cancer cells.
33
New cards
What is a malignant tumor?
Tumors that metastasize or break away and can form more tumors
34
New cards
What is a benign tumor?
Tumors that remain clustered and can be removed.
35
New cards
Carcinogen
Substances known to promote cancer
36
New cards
What are the 2 treatments that are localized for fighting cancer?
Radiation therapy is the use of radiation to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. Surgery is another
way to remove cancer in one certain area.
way to remove cancer in one certain area.
37
New cards
What are the treatments that are systemic for fighting cancer?
Chemotherapy uses certain drugs, often in combination, to kill actively dividing cells. Hormone therapies, Immunotherapies
and Targeted therapies are also used.
and Targeted therapies are also used.
38
New cards
What is gene therapy?
A medical approach that treats or prevents disease by correcting the underlying genetic problem. Techniques allow doctors to treat a disorder by altering a person’s genetic makeup instead of using drugs or surgery.
39
New cards
What is the difference between asexual and sexual reproduction?
Asexual reproduction is the creation of offspring from a single parent while sexual reproduction
requires 2 parents.
requires 2 parents.
40
New cards
What are the 4 types of asexual reproduction?
Binary fission, budding, fragmentation, parthenogenesis
41
New cards
Binary Fission
a microorganism splits in two equal halves, such as amoebas
42
New cards
Budding
new organism develops from an outgrowth or bud due to cell division at one particular
site, Bacteria, yeast, corals, flatworms, Jellyfish and sea anemones
site, Bacteria, yeast, corals, flatworms, Jellyfish and sea anemones
43
New cards
Fragmentation
a body breaks into several fragments, which later develop into complete organisms
44
New cards
Parthenogenesis
growth and development of embryos occur in a gamete without combining with another gamete occurs in vertebrae species such as some fish and lizards.
45
New cards
What are advantages in asexual reproduction?
is an advantage in consistantly favorable conditions
46
New cards
What are advantages in sexual reproduction?
is an advantage in changing conditions.
47
New cards
What are the levels of organization in multicellular organisms?
Cells --> Tissues --> Organs --> Organ system --> Organism
48
New cards
What is cell differentiation?
When cells develop into their mature forms.
49
New cards
What are stem cells?
a unique type of body cell that can (1) divide and renew themselves for long periods of time, (2) remain undifferentiated in form, and (3) differentiate into a variety of specialized cell types.
50
New cards
Pluripotent
growing into any cell type but a totipotent cell
51
New cards
Multipotent
growing into cells of a closely related cell family
52
New cards
What is the advantage of using adult stem cells?
they can be taken from a patient, grown in culture,
and put back into the patient.
and put back into the patient.
53
New cards
What are the disadvantages of using adult stem cells?
They can be hard to isolate and grow.
54
New cards
Where do embryonic cells come from?
Most come from donated embryos grown in a clinic.
55
New cards
What is the advantage of using embryonic stem cells?
Because they are pluripotent, they can form any of the 200 cell types of the body. They can also be grown indefinitely in culture.
56
New cards
What is the disadvantage of using embryonic stem cells?
They raise ethical issues and patients' bodies also may reject them causing a tumor to form.
57
New cards
What is the Catholic Church’s stand on stem cell research?
They allow the use of adult stem cells, but do not support stem cells from embryos.
58
New cards
What are some current and potential uses for stem cells?
Treatment for leukemia and lymphoma ,May cure diseases or replace damaged organs, May revolutionize the drug development process