Cervical Spine Muscles
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Sternocleidomastoid Action
Bilateral Contraction:
forward translation of C-spine (protraction)
flexion of lower C-spine
Unilateral Contraction:
contralateral rotation of upper & lower C-spine
ipsilateral flexion of lower C-spine
Extension of upper C-spine
What does the SCM resist?
forceful extension & backward movements of C-spine (whiplash)
Is the SCM usually under or over active?
Overactive
Does forward head posture (protraction) which we are usually in
If the SCM is over active, what can also be over active?
Upper Traps and Levator Scapulae
Are overactive to prevent your head from falling forward
Scalenes Action
Bilateral Contraction:
synergist to C-spine flexion when ribs are fixed
Unilateral Contraction:
ipsilateral lateral flexion with slight contralateral rotation when ribs are fixed
Accessory muscle of respiration:
elevate 1st/2nd rib

What do the scalenes resist?
prevent excessive posterior shear forces
Are the scalenes usually under or over active?
Overactive
Phasic muscle
Longus Colli/Capitus Action
Deep anterior neck flexors
primary anterior stabilizers of upper and lower c-spine bc they are closest to the vertebrae
Chin tucks make this more active
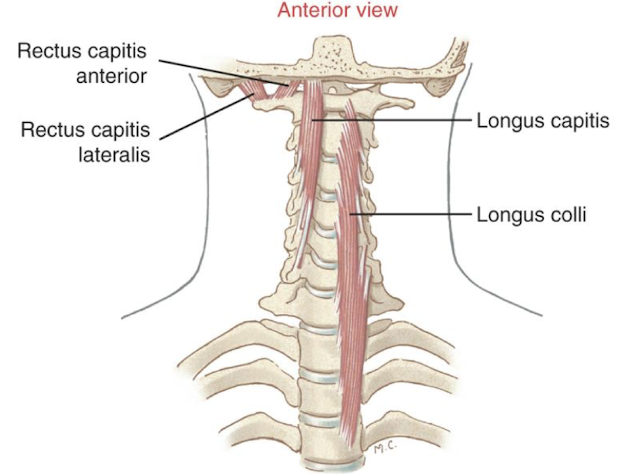
How do the longus colli/capitis increase C-spine stability?
provide increase compression force between the vertebrae
Rectus Capitis Anterior/Lateral Action
Limited to the OA joint and have separate roles
RCA= flexor of OA joint
RCL= lateral flexor of OA joint
large proprioceptive input to position of head & neck
Upper Trapezius Action
Scapula:
elevation & upward rotation
C-spine:
ipsilateral lateral flexion, extension, and contralateral rotation
Dynamic stabilizer of the C-spine & scapula during UE tasks
What is the passive insufficiency position of the upper traps?
Contralateral lateral flexion + ipsilateral rotation + downward rotation of scapula + depress scapula (put hand behind back/under butt)
Levator Scapulae Action
Scapula:
elevation & downward rotation
C-spine:
ipsilateral lateral flexion & slight ipsilateral rotation
some neck extension
‘bring your nose to your clavicle’
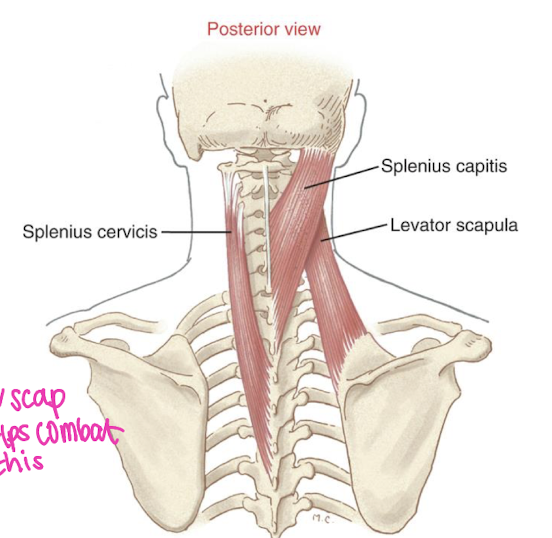
What does the Levator Scapulae resist?
Resists anterior shear forces due to natural lordosis of C-spine
Provides a posterior shear force on vertebrae
What is the passive insufficiency position of Levator Scapulae?
Neck flexion + contralateral lateral flexion + contralateral rotation + depression + upward rotation (put hand behind your head)
Splenius Capitis/Cervisis Action
Bilateral contraction:
extension of the head/neck
Unilateral contraction:
ipsilateral lateral flexion and ipsilateral rotation of c-spine
similar to lev scap
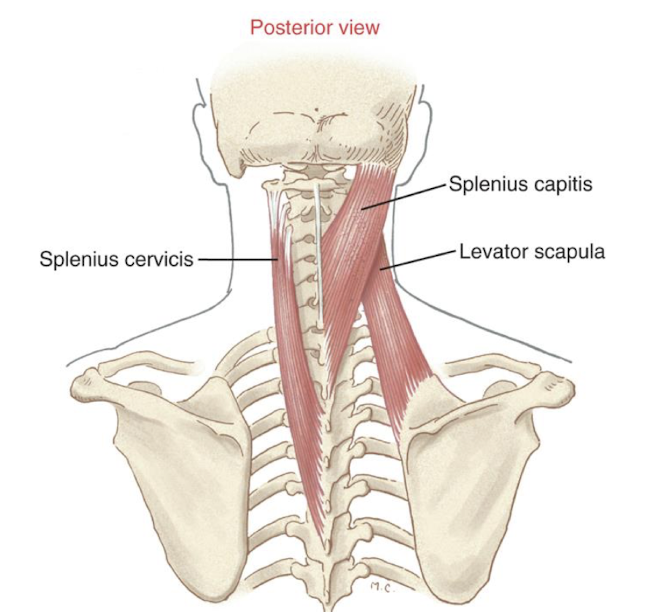
What is the passive insufficiency position of the splenius capitis/cervicis?
neck flexion + contralateral lateral flexion + contralateral rotation
Semispinalis capitis/cervicis Action
Primary C-spine extensors!! Always active during extension, just might not have the largest MA
maintains the lordosis of C-spine
Semispinalis Cervicis= primary stabilizer of upper c-spine so that suboccipital muscles can function at the AA joint (more precise flexion)
What do semispinalis capitis/cervicis resist?
resists excessive anterior shear forces
Longissimus Capitis/Cervicis Action
stabilization of the head/neck in the frontal plane
ipsilateral lateral flexors of c-spine
small MA to produce cervical extension & ipsilateral rotation
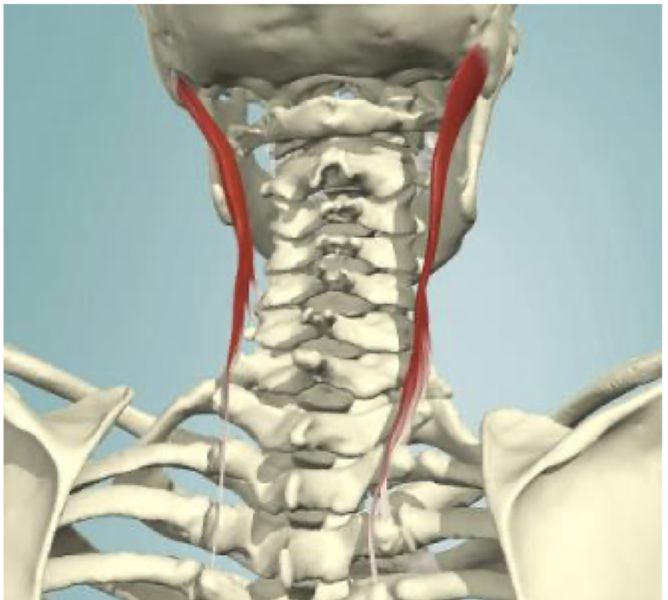
Suboccipital Muscles Action
Movement of the OA & AA joints independent of the C-spine
Proprioception of head/neck & rate of movement
sensations needed for balance, equilibrium, and head-eye coordination
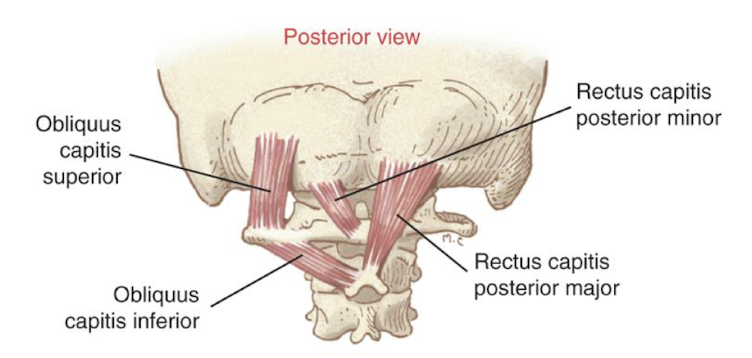
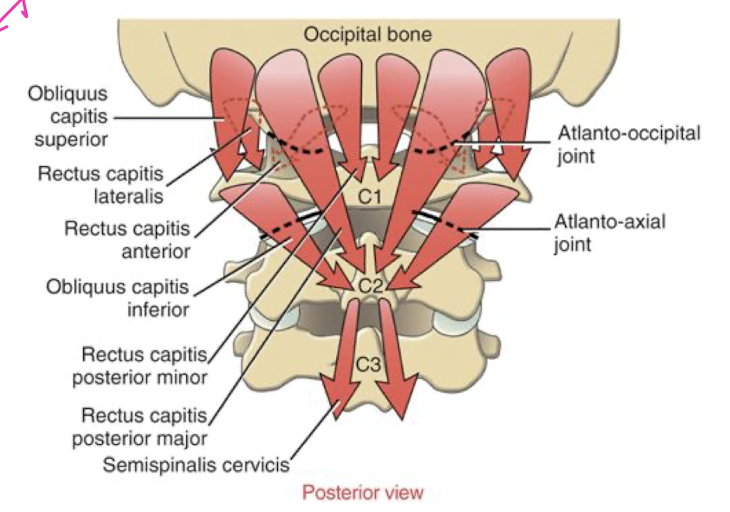
What are the big takeaways from this image?
majority of your suboccipitals are NOT doing rotation EXCEPT for Obliquus Capitis Inferior
the rest are contributing to upper c-spine extension