rRNA and tRNA processing
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
rRNA genes have _______ built in
redundancy
clusters of rRNA in the nucleus are called ______ _______ ________
nucleolar organizing regions
rRNA and tRNA are more _______ and _______ than mRNA
stable, longer lived
rRNA appears in _______ ________ that are 43 kb long
repeating units
humans have _______ copies of rRNA genes
400
human rRNA gene clusters are usually at the ______ of chromosomes
ends
rRNA’s and tRNA’s first appear as ________
precursors
rRNA/tRNA have sequences that must be _______
removed
vertabrate pre-rRNAs have ______, ______, and _______ sequence
28S, 18S, 5.8S
the 28S, 18S, and 5.8S sequence are located between ______ ____ __________
transcribed spacer regions
rRNA processing occurs in the ________
nucleolus
in rRNA, sequences can be __________ or ___________
transcribed, non-transcribed
transcribed sequences can be ________ or _________
imbedded, external
as rRNA is processed, it gets ________
smaller
at the end of rRNA processing, the ______ and ________ pieces are connected
28S, 5.8S
the 18S piece goes into the ________ subunit
small
the 18S and 5.8S piece goes into the _______ subunit
large
Eukaryotes process rRNA by ________ bases
modifying
snoRNP stands for _______ ________ _________
small nucleolar ribonuclear protein
Eukaryotes modify bases using ________
snoRNP
snoRNP is made using ________
snoRNA
snoRNA are _______ to the rRNA
complimentary
snoRNP’s are located at the _________
nucleolus
snoRNP's use a _________ __________ to _________ introns and exons
methylation pattern, sort
Two ribosome subunits: _________ and ________
large, small
the large subunit is _______ size
60S
the small subunit is _________ size
40S
in prokaryotes, tRNA starts as a ________ ________
large precursor
in prokaryotes, tRNA is cleaved at _____ ________
both ends
prokaryotic pre-rRNAs often contain __________ with ___________
tRNA's, 3 rRNA's
rRNA's are released from pre-rRNAS by ___________ and __________
RNase 3, RNase E
RNase 3 does __________ __________ to separate ___________ ___________
first cleavage, large rRNA's
pre-tRNA has extra ___ and ____ __________
5', 3' pieces
3/4 rRNA products come from the ________ __________
same gene
the main rRNA gene must be cut into __________ _________ to be functional
small pieces
in eukaryotes, the pieces are ________, _________, and __________
28S, 18S, 5.8S
in prokaryotes the pieces are _______, ________, and ________
16S, 23S, 5S
in prokaryotic tRNA processing __________ recognizes the ____ end of tRNA precursors
RNase P, 5'
____________ and ____________ cleave the 5' end of pre-tRNA
RNase P, RNase D
____________ cleaves the 3' end of pre-tRNA
endonuclease
____________ removes the additional bases on the ends of pre-tRNA
Rnase D
in prokaryotes, after the 3' and 5' ends are cleaved, we locate the ________ sequence on the ___ end
CCA, 3'
CCA sequence
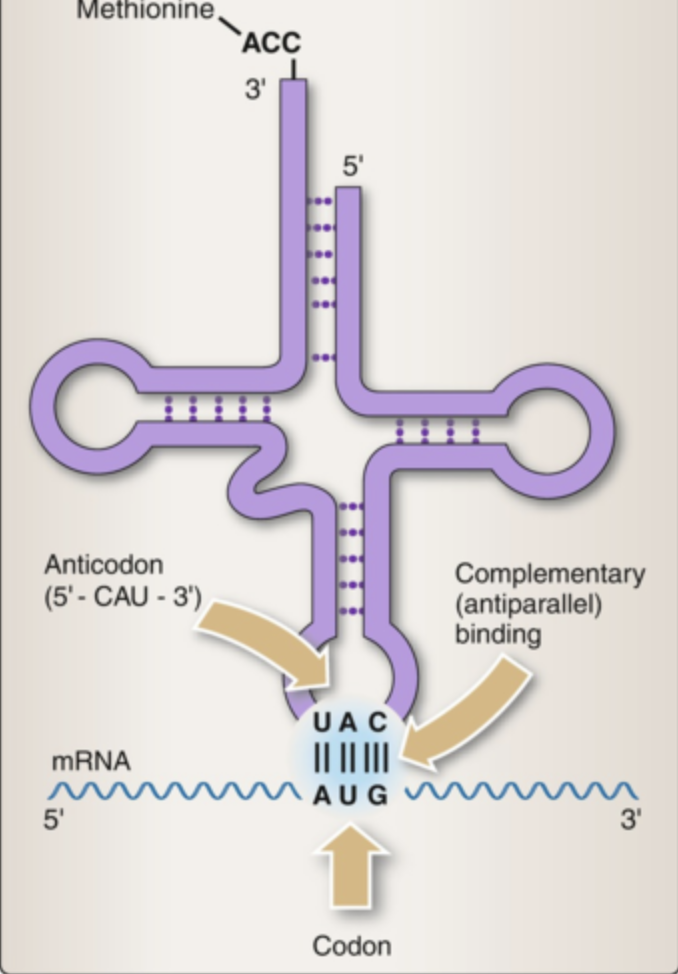
after the CCA sequence is found or added, tRNA can be ____________
modified
we have identified more than _________ nucleotide modification identified in prokaryotic tRNA
60
____________ enzymes modify bases
multiple
research suggests that modified forms are ____________
required
tRNA structure includes ________ _________ regions
four stem-loop
tRNA structure
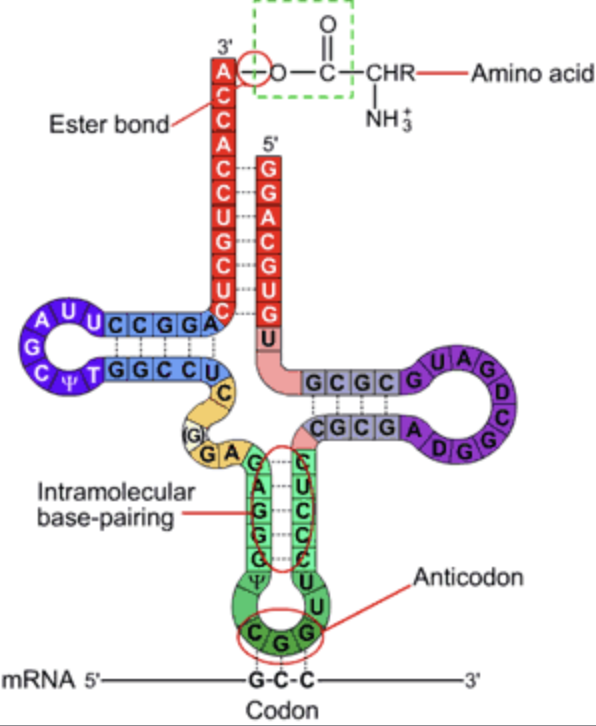
four consistent regions of tRNA:
acceptor stem, D loop, anticodon loop, T psi C loop
the ___________ __________ is an additional region that may or may not be present
variable loop
The acceptor stem has the _______ on the ___
CCA, 3'
the D loop has ____ ___________
D nucleotides
the anticodon loops matches with _________
mRNA
the T psi C loop contains psi, a modified __________
uracil
the variable loop varies in __________ and __________
length, presence
some tRNA’s have “_______”
introns
introns in tRNA can be located between __________ and __________ __________
anticodon, variable loop
tRNA's use the ____________ and ____________ ___________ to remove "introns"
cleavage, ligation system