MGMT 343: Exam 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/129
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:47 PM on 4/5/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
1
New cards
What is the order of work analysis & design?
1. Work Analysis Flow
2. Job Analysis
3. Job Description
2
New cards
____ is considered the “bedrock” of human resources management, as it lays the groundwork for all other HR activities
* Job Analysis
3
New cards
Job
* Collection of tasks, duties, and responsibilities (TDRs)
4
New cards
Work
* Broad, includes TDRs + **skills & knowledge**
5
New cards
Why is the concept of a job in work design'/analysis up for debate?
* Because of rapid technology, work is becoming more important than jobs
6
New cards
Work Analysis
* Defining & codifying tasks + duties → Job Description
* Includes job analysis + task/skill analysis
* Includes job analysis + task/skill analysis
7
New cards
One of the give major variables in strategy implementation is
* Job Design
8
New cards
How did companies in the United States shift from a mechanistic approach (assembly lines) to self-directed work teams?
* Volvo
* Charifman of Volvo - “'I want the people in a team to be able to go home at night and really say, 'I built that car,”
* Motivational approach to work design
* **The** ***Volvo*** **Way is based on the conviction that every individual has the capability and the determination to improve our business**
* Charifman of Volvo - “'I want the people in a team to be able to go home at night and really say, 'I built that car,”
* Motivational approach to work design
* **The** ***Volvo*** **Way is based on the conviction that every individual has the capability and the determination to improve our business**
9
New cards
Work-Flow Design
* **process of analyzing the tasks necessary for the production of a product or service**
* **prior** to **allocating and assigning these tasks to a particular job category or person**
* Bundling tasks → jobs
* **prior** to **allocating and assigning these tasks to a particular job category or person**
* Bundling tasks → jobs
10
New cards
Organization Structure
* Stable and formal network of vertical and horizontal interconnections among jobs that constitute the organization
* Understand how jobs at different levels relate
* Understand how jobs at different levels relate
11
New cards
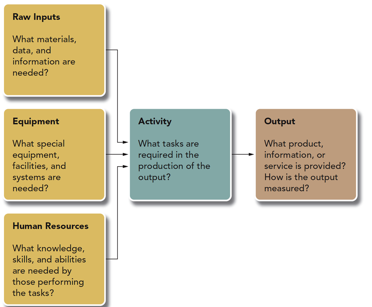
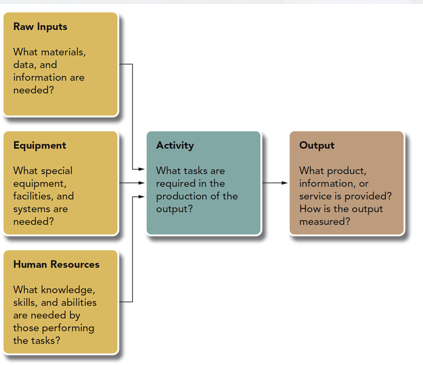
The picture below is an example of
Work-Unit Activity Analysis
12
New cards
For a Work Unit Activity Analysis, you:
* Start at the Outputs, then end with the input
13
New cards
Raw Materials
* consist of the materials that will be converted into the work unit’s product
* KSAO’s are **not** raw materials/input
* KSAO’s are **not** raw materials/input
14
New cards
Equipment
* refers to the technology and machinery necessary to transform the raw materials into the product
15
New cards
Human Skills
* Final inputs in the work-flow process
16
New cards
How is the work-unit activity analysis important to HR?
* Must understand the qualifications for the job to recruit & retain talent
\
\
17
New cards
Work Outputs
* Can be a product/service
* Must also specify standards for quantity or quality of outputs:
* Can create challenges for how to process inputs to generate outputs efficiently.
* Must decided whether to produce whole output or just parts.
* Must also specify standards for quantity or quality of outputs:
* Can create challenges for how to process inputs to generate outputs efficiently.
* Must decided whether to produce whole output or just parts.
18
New cards
Work Processes
* Determine how output is generated (operating procedures).
* Team-based job design.
* Becoming increasingly popular - back each other up, catch errors, etc.
\
* Efficiency experts can improve work-flow processes.
\
* Lean production.
* Team-based job design.
* Becoming increasingly popular - back each other up, catch errors, etc.
\
* Efficiency experts can improve work-flow processes.
\
* Lean production.
19
New cards
When efficiency experts visit a company, they are looking for 3 different kinds of waste:
(1) movement that creates no value
(2) the overburdening of specific people or machines
(3) inconsistent production that creates excessive inventories
(2) the overburdening of specific people or machines
(3) inconsistent production that creates excessive inventories
20
New cards
Lean Production
* Developed in Japan
* Leverage technology + skilled personnel
* Emphasizing manufacturing goods with a minimum amount of time, materials, money, and people
* Leverage technology + skilled personnel
* Emphasizing manufacturing goods with a minimum amount of time, materials, money, and people
21
New cards
What is the downside to “just-in-time” inventory management practices?
* Efficiency gained from maintaining an inventory (measured in days rather than weeks) → creates a lack of flexibility
22
New cards
True or False: Identifying outputs is the final stage of Work-Unit Activity Analysis?
* False
* It is the first step
* It is the first step
23
New cards
Job Analysis
* Process of analyzing various aspects of work so as to come about a job description
* Important in design/redesigning work
* Important in design/redesigning work
24
New cards
What are potential uses of job analysis?
1. Organization Deisgn
2. HR managmeent
3. Work design
25
New cards
Organization design
* Smaller companies tend to have more open-ended approaches to job design because they need employees to be more flexible & do more tasks
* Larger organizations, which tend to be more specialized, usually have more formality
* Larger organizations, which tend to be more specialized, usually have more formality
26
New cards
Task
* Distinct work activity with a specific purpose
27
New cards
Job
* Collection of tasks
28
New cards
Job Family
* Group of jobs with similar characteristics
29
New cards
Occupation
* Higher level than a job, a profession
30
New cards
True or False: accoutning and laborers are both occupations
* True
* If it can be high-level and include a variety of different types of jobs (ex. auditor, analyst, etc.) it is an occupation
* If it can be high-level and include a variety of different types of jobs (ex. auditor, analyst, etc.) it is an occupation
31
New cards
What are the 2 job analysis techniques?
* O\*Net
* Position Analysis Questionnaire
* Position Analysis Questionnaire
32
New cards
Task inventory approach
* Focuses on collecting information about the tasks that need to be done to perform a job
* Subject matter experts generate statements about the tasks needed to perform the job
* Job incumbents put a checkmark next to the statements that they feel describe their job
* Subject matter experts generate statements about the tasks needed to perform the job
* Job incumbents put a checkmark next to the statements that they feel describe their job
33
New cards
True or False:
Small companies and startups tend to have more narrow or closed approaches to job design because they have fewer tasks or moving pieces relative to large companies.
Small companies and startups tend to have more narrow or closed approaches to job design because they have fewer tasks or moving pieces relative to large companies.
* False
34
New cards
True or False: TDRs are observable actions
* True
35
New cards
Job Description
* a list of the tasks, duties, and responsibilities (TDRs) that a job entails
* Balance breadth and specificity when constructiong
* Balance breadth and specificity when constructiong
36
New cards
What elements do job description have? (5)
1. Job Title
2. Job Activities & Procedures
3. Working Conditions & Physical Environment
4. Social Environment
5. Conditions of Employment
\
37
New cards
Job Specification
* is a list of the knowledge, skills, abilities, and other characteristics (KSAOs) that an individual must have to perform the job
38
New cards
Knowledge
factual (declarative) knowledge or procedural information that is necessary for successfully performing a task
39
New cards
Skill
* individual’s level of proficiency at performing a particular task
40
New cards
Ability
* refers to a more general enduring capability that an individual possesses
41
New cards
True or False:
Under KSOAs - A skill is an individual's level of proficiency when performing a specific task.
Under KSOAs - A skill is an individual's level of proficiency when performing a specific task.
* True
42
New cards
Position Analysis Questionnaire (PAQ)
* 194 items about work behaviors, work conditions, job characteristics
* Most commonly used P
* Generalized across variety of jobs
* Fixed job titles, narrow task descriptions
* Difficult to make job description
* Requires trained employee
* Most commonly used P
* Generalized across variety of jobs
* Fixed job titles, narrow task descriptions
* Difficult to make job description
* Requires trained employee
43
New cards
Occupational Information Network (O\*NET)
* 1000 - describe the qualifications, work styles, activities and contexts relevant to broadly defined occupations
* Uses common language, various occupations, broadly defined
* May generalize across countries (developed in the U.S.)
* Transition from DOT
* Uses common language, various occupations, broadly defined
* May generalize across countries (developed in the U.S.)
* Transition from DOT
44
New cards
The PAQ has 6 sections:
* i**nformation input, relationships, mental processes, job context, work output and other characteristics**
45
New cards
O-NET is most usefel in:
* A rapidly changing, incrqasingly complex, global economy
46
New cards
Job Design
* Process of defining how work will be performed and the tasks that will be required in a given job
47
New cards
Job redesign
* changing the tasks or the way work is performed in an existing job
* one must have a complete understanding of the job – through job analysis – and its relevance for work-flow
* one must have a complete understanding of the job – through job analysis – and its relevance for work-flow
48
New cards
Mechanistic Approach
* “identifying the simplest way to structure work that maximizes efficiency”
* Specialization
* Skill variety
* Work methods autonomy
* Specialization
* Skill variety
* Work methods autonomy
49
New cards
___ is one of the earliest mechanistic approaches that sought to identify the one best way to perform the job through the use of time-and-motion studies.
Scientific management
50
New cards
Motivational Approach
* job characteristics that affect the psychological meaning + motivational potential
* views attitudinal variables as the most important outcomes of job design
* Decision-making autonomy
* Task significance
* Interdependence
* views attitudinal variables as the most important outcomes of job design
* Decision-making autonomy
* Task significance
* Interdependence
51
New cards
Job Characteristics Model (5)
\
* ***Skill variety*** is the extent to which the job requires a variety of skills to carry out the tasks.
\
* ***Task identity*** is the degree to which a job requires completing a “whole” piece of work from beginning to end.
\
* ***Autonomy*** is the degree to which the job allows an individual to make decisions about the way the work will be carried out.
\
* ***Feedback*** is the extent to which a person receives clear information about performance effectiveness from the work itself.
\
* **Task significance** is the extent to which the job has an important impact on the lives of other people.
* ***Skill variety*** is the extent to which the job requires a variety of skills to carry out the tasks.
\
* ***Task identity*** is the degree to which a job requires completing a “whole” piece of work from beginning to end.
\
* ***Autonomy*** is the degree to which the job allows an individual to make decisions about the way the work will be carried out.
\
* ***Feedback*** is the extent to which a person receives clear information about performance effectiveness from the work itself.
\
* **Task significance** is the extent to which the job has an important impact on the lives of other people.
52
New cards
Biological Approach
* identify clearly the outputs of work, to specify the quality and quantity standards for those outputs, and to analyze the processes and inputs necessary for producing outputs that meet the quality standards
\
\
* Physical demands
* Ergonomics
* Work conditions
\
\
* Physical demands
* Ergonomics
* Work conditions
53
New cards
Perceptual Motor Approach
* Roots in the human‑factors literature and focuses on human mental capabilities and limitations
* The goal is to design jobs in a way that ensures that they do not exceed people's mental capabilities
* Job complexity
* Information processing
* quipment use
* The goal is to design jobs in a way that ensures that they do not exceed people's mental capabilities
* Job complexity
* Information processing
* quipment use
54
New cards
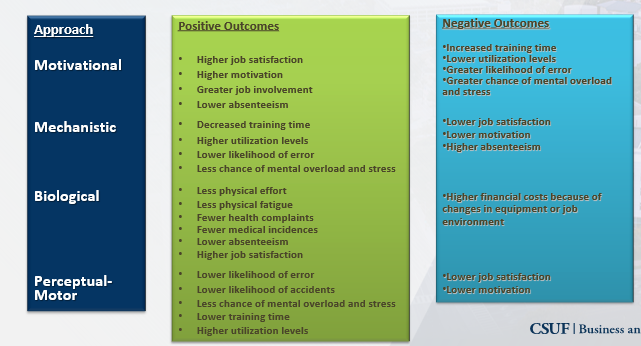
Trade Offs Among Job Design Approaches
.
55
New cards
According to the BCG video, What are the key HR issues folks are concerned about?
* Talent Management
* Leaders
* Engagement
* Workforce planning
* Leaders
* Engagement
* Workforce planning
56
New cards
According to the BCG video, why are workforce planning + recruiting increasingly important to the future?
* Retiring baby boomers
* Growth in employability issues
* Growth in employability issues
57
New cards
In the BCG video, what does the speaker mean by “strategic workforce planning”, and how is this relevant to the importance of HR as a business function?
* Labor Supply & Demand
* shortage/surplus of labor
* Competitive advantage
* shortage/surplus of labor
* Competitive advantage
58
New cards
HR Planning
* Must follow EEO requirements, be effective/efficient, support the KSAs of employees, & within operating budgets
* Processes + practices used to ensure individuals with the KSAOs meet an organization at it’s current & future labor force needs
* including *talent inventories*, *workforce forecasts*, *action plans* and *program evaluations*
* Processes + practices used to ensure individuals with the KSAOs meet an organization at it’s current & future labor force needs
* including *talent inventories*, *workforce forecasts*, *action plans* and *program evaluations*
59
New cards
How is HR planning part of the strategic management process?
* Forecasting labor demand (external analysis, which is part of SWOT)
60
New cards
What are the 3 stages in the HR planning process?
1. Forecasting - make useful predictions about where there will be future labor surpluses and shortages
\
2. Goal Setting & Strategic Planning - set specific, quantitative goals for increasing or decreasing human resource units
\
3. Program Implementation & Evaluation - expansion into new markets, mergers & acquisitions, industry trends
61
New cards
Determining Labor Demand
•derived from product/service demanded
•***externa****l* in nature
•multiple methods and various levels of sophistication (statistical analysis, judgement)
•indicators
62
New cards
Determining Labor Supply
•***Internal*** movements caused by transfers, promotions, turnover, retirements, etc.
•**transitional matrices** identify employee movements in different job categories over time to chart historical trends in company’s labor supply
•Succession planning
•useful for **AA / EEO** purposes
63
New cards
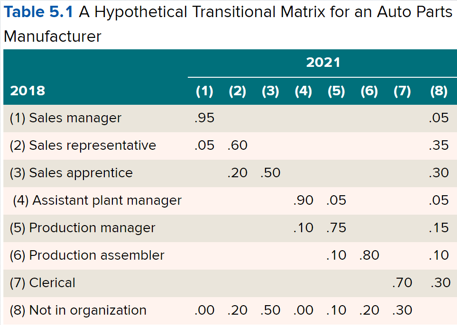
What is a workforce utilization review?
* comparison of the proportion of a firm’s workers in a particular subgroup within a particular job or occupation with the relevant outside labor market to determine if persons in that subgroup (e.g., Hispanics or Women) are being under-utilized
64
New cards
True or False:
Succession plans with internally sourced candidates are generally cheaper than those with externally sourced candidates?
Succession plans with internally sourced candidates are generally cheaper than those with externally sourced candidates?
* True
65
New cards
In the War for Talent video, what is the shift from HR being 1.0 → 3.0?
1\.0:
* HR = personnel, transactional
\
3\.0:
* Transofrmational
* CEOs demand HR is good at business
* HR = personnel, transactional
\
3\.0:
* Transofrmational
* CEOs demand HR is good at business
66
New cards
In the War for Talent video. what does Richards mean when he says “The - War for Talent is over and talent won”?
* Employers are facing a shortage for talented workers & have trouble getting large pool of applicants
67
New cards
What is the global average of talent shortage around the world?
* 75%
68
New cards
Job Choice
* An individual’s decision to accept an offer of employment
69
New cards
Personnel Policies
•Organizational decisions that affect the nature of the vacancies for which people are recruited.
70
New cards
•**Personnel Policies vary:**
\
\
* **Internal versus external recruiting**
* Internal Job ladders
* **Extrinsic versus intrinsic rewards**
* **Employment-at-will policies**
* **Image advertising**
71
New cards
Internal Recruitment
* Gives opportunities for promotion to employees
* Lateral move - try something new/develop new skills
* Vertical move - promotions
* Word of mouth, employee inventory, previous performance appraisals
\
* Pros: Most cost-effective, employees already know company, managers have access to past performance
\
* Cons: Companies want new ideas, difficult for diversity
* Lateral move - try something new/develop new skills
* Vertical move - promotions
* Word of mouth, employee inventory, previous performance appraisals
\
* Pros: Most cost-effective, employees already know company, managers have access to past performance
\
* Cons: Companies want new ideas, difficult for diversity
72
New cards
73
New cards
External Recruitment
* Source should be dictated by nature of the job, location, and skill level needed
* Relevant labor market: location in which one can reasonably expect to find a sufficient supply of qualified applicants
* Relevant labor market: location in which one can reasonably expect to find a sufficient supply of qualified applicants
74
New cards
Why are informal sources of external recruiting important?
* Word of mouth, referrals
* Applicant will have a more realistic sense of what it may look like to work at firm
* Ex. , **Sprint saw their proportion of new hires grow from 8% to 34% recently**
* Applicant will have a more realistic sense of what it may look like to work at firm
* Ex. , **Sprint saw their proportion of new hires grow from 8% to 34% recently**
75
New cards
Advertising
* Newspapers, bulletin boards and the Internet
* Websites can help firms determine the extent to which a individual might actually be a good fit for a position
* Websites can help firms determine the extent to which a individual might actually be a good fit for a position
76
New cards
College Recruiting
•Sending recruiters to college campuses to attract employees right out of college
•Recruiters usually have multiple openings
•May speak to student organizations or alumni groups
•Internships are sometimes offered to evaluate performance and allow student to get to know organization
77
New cards
Employment Agencies & Search Firms
•May benefit small HR departments to make recruiting process more efficient
•Public employment agencies provide career guidance, testing, training, and placement for free
•Private employment agencies provide job search assistance for a fee
78
New cards
True or False: recruiters have a large impact on job choice
* False
79
New cards
What are ways a recruiter is likely to be perceived as more credible?
1. From the same functional area the applicant is being considered for
2. Give a realistic job preview, are warm, informative, & honest
80
New cards
How to enhance a recruiter’s impact?
1\.**Provide timely feedback**
2\.**Include line personnel**
**3. Recruit in teams**
81
New cards
What are the arugments against using personality yesting in selection? (3)
1. ***people can fake their answers***
***2. tests are inaccurate***
***3. personality changes from situation to situation***
82
New cards
Reliability
* degree to which a measure of physical or cognitive abilities or traits is free from random error. Reliability is “the extent of unsystematic variation of one individual’s scores
83
New cards
What is the test-retest reliability method?
* the degree to which a measure correlates with itself at two different times
* Is a correlation coefficient (perfect = +1.0, negative = -1.0r
* Is a correlation coefficient (perfect = +1.0, negative = -1.0r
84
New cards
Whats is internal consistency reliability?
* the extent to which different items in the same test are consistent with one another
85
New cards
Correlation Coefficient Guide
0\.10 are trivial
0\.10 to 0.29 are small
30 to 0.49 are moderate
0\.50 and above are considered large
0\.10 to 0.29 are small
30 to 0.49 are moderate
0\.50 and above are considered large
86
New cards
Validity
* extent to which a performance measure assesses all the relevant—and only the relevant- aspects of a criterion such as job performance
* Quality & accuracy of inferences made from the test
* Quality & accuracy of inferences made from the test
87
New cards
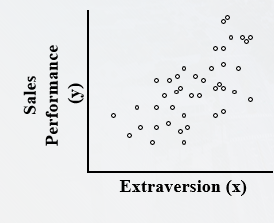
What kind of correlation is this?
* Positive
* As extraversion goes up, so does sales performance
* As extraversion goes up, so does sales performance
88
New cards
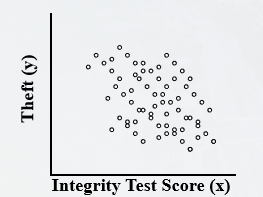
What kind of correlation is this?
* Negative
* As x goes up, y goes down
* As x goes up, y goes down
89
New cards
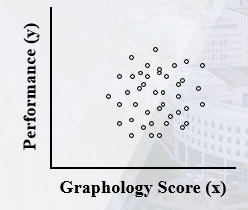
What kind of correlation is this?
* Zero
* do not change each other, & cannot be predicted from each other
* do not change each other, & cannot be predicted from each other
90
New cards
Content Validation
* a test-validation strategy performed by demonstrating that the items, questions, or problems posed by a test are a representative sample of the kinds of situations or problems that occur on the job
91
New cards
Criterion-Related Validity
* demonstrate the extent to which a given measure (X) is predictive of some criterion (Y)
* Job performance = ultimate criterion in personnel
* Job performance = ultimate criterion in personnel
92
New cards
Concurrent Validation
* Less time consuming + less resource intensive as predictive validation
93
New cards
Predictive validity
* Measuring all applicants, correlating scores on the test pre-hiring with job performance scores post-hiring
* Limitations:
* Needs more time/effort
* Not often done in business organizations
* Limitations:
* Needs more time/effort
* Not often done in business organizations
94
New cards
Generalizability
* the degree to which the validity of a selection method established in one context extends to other contexts
* Contexts include:
* different situations (jobs or organizations)
* different samples of people
* different time periods
* Contexts include:
* different situations (jobs or organizations)
* different samples of people
* different time periods
95
New cards
___ is impacted by reliability, validity, and generalizability
* Utility
96
New cards
Utility
* degree to which information (provided by selection methods) enhances the effectiveness of selecting personnel
97
New cards
Verbal Comprehension
* person’s capacity to understand & use written/spoken language
98
New cards
Quantitative Ability
* Speed & accuracy w/ one can solve arithmetic problems
99
New cards
Reasoning Ability
* Person’s capacity to invent solutions to diverse problems
100
New cards
How does IQ predict/relate job performance?
* Rapid learning & job knowledge when info is complex
* 0.60 - 0.70
* 0.60 - 0.70