ESCI 204 final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/68
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 4:34 AM on 3/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
1
New cards
diatoms
2 shapes, often form long chains, .1 mm

2
New cards
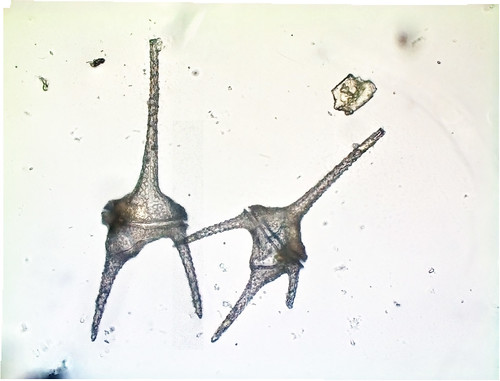
dinoflagellates
5 mm- largest phytoplankton, 2 flagella for movement
3
New cards
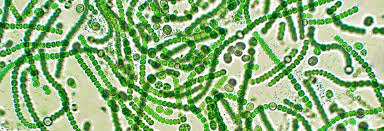
cyanobacteria
.00005 mm-.04 mm, photosynthetic
4
New cards
microflagellates
.01 mm, many other groups of flagellated phytoplankton

5
New cards
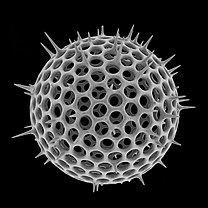
radiolarian
silica shells
6
New cards
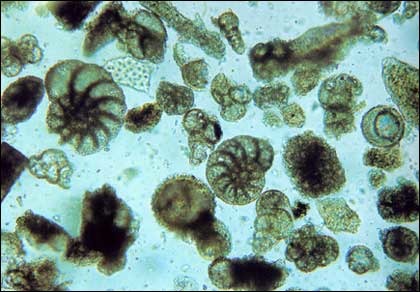
foraminifera
calcium carbonate shells
7
New cards
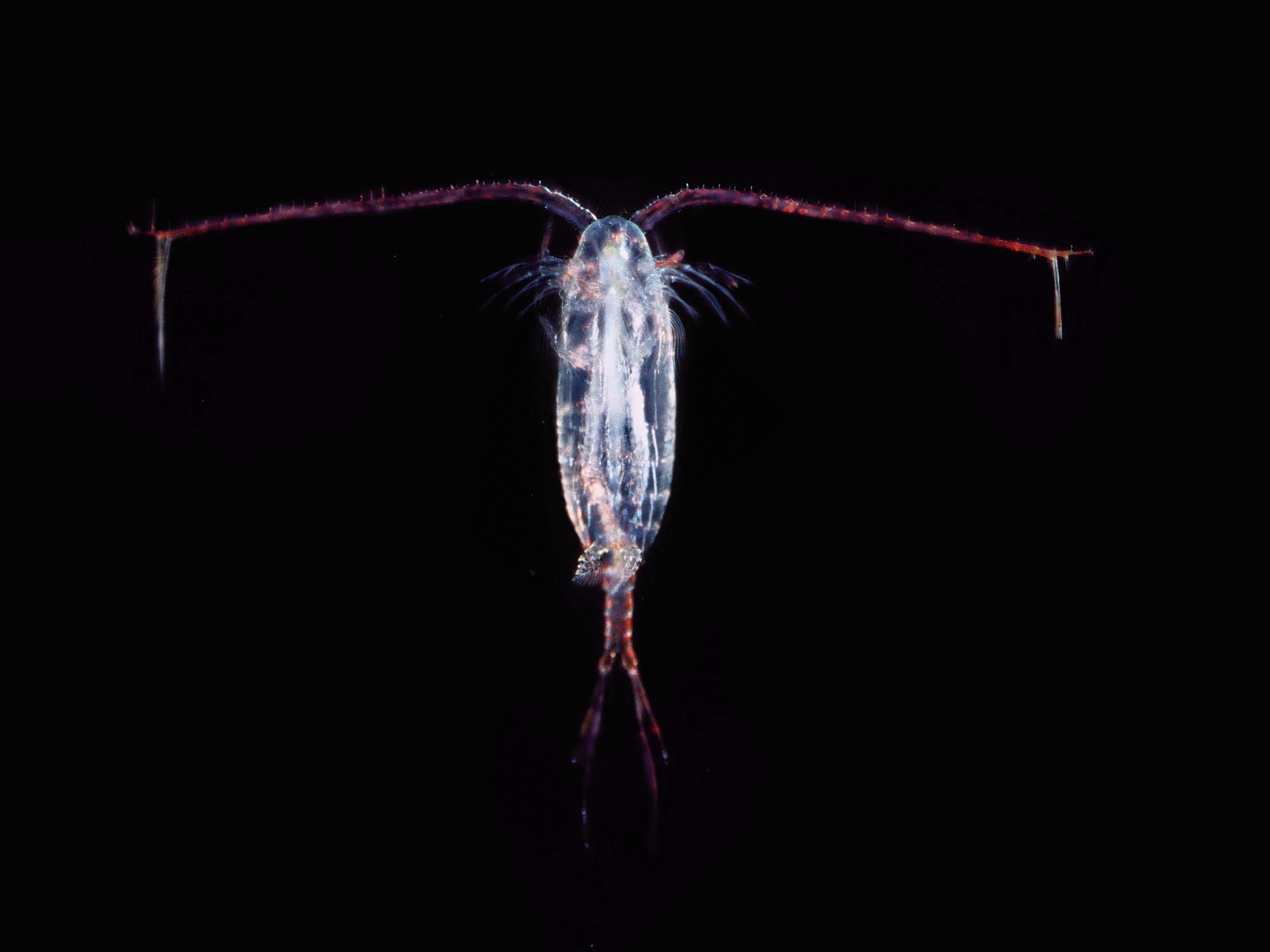
copepods
phytoplankton grazers, “smell” chemical plumes

8
New cards
euphausiids
small crustaceans, zooplankton, krill- light sensitive

9
New cards
chaetognaths
predatory worms
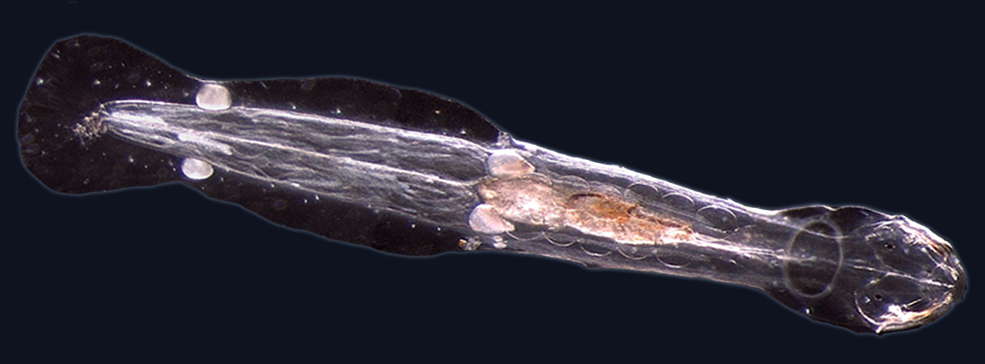
10
New cards
ctenophores
engulf prey using their sticky cells
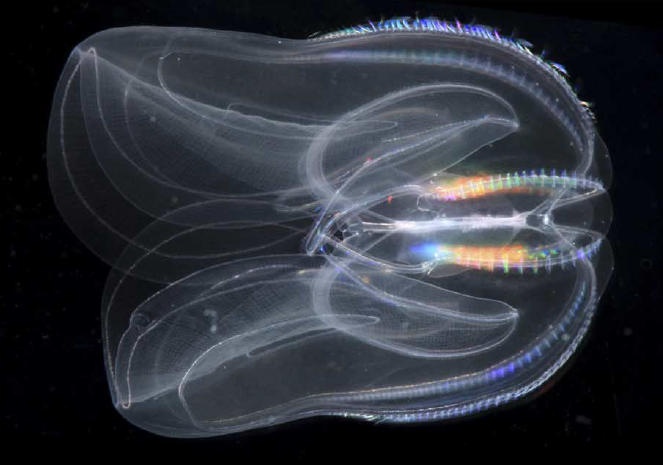
11
New cards
salps
tunicates- enclosed in a tunic with openings at either side, pump water thru gelatinous bodies

12
New cards
appendicularians (oikopleura)
mucus house builders
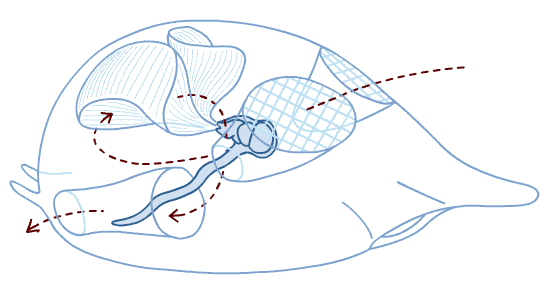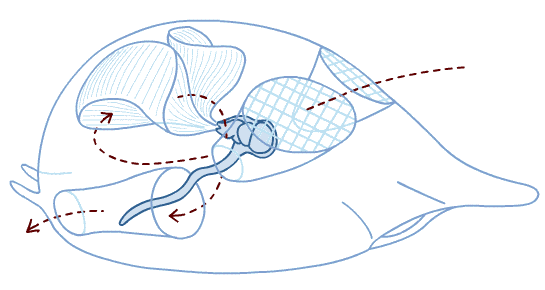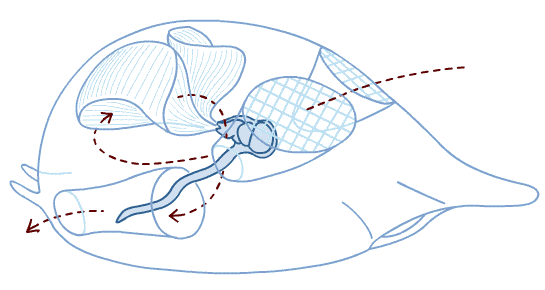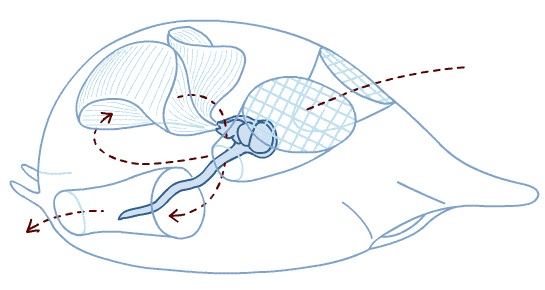
13
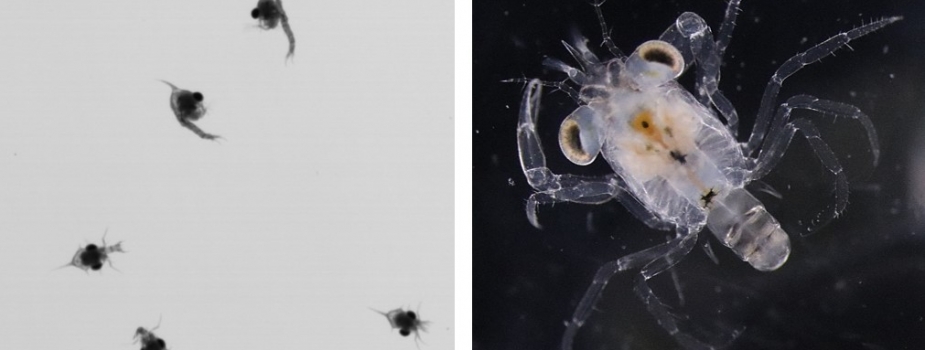
New cards
crab larvae
14
New cards
polychaete larvae

15
New cards
barnacle cyprid
last larval stage before adulthood, its role is to find a suitable place for settlement

16
New cards
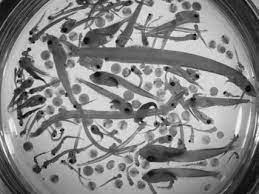
ichtyoplankton
eggs and larvae of fish
17
New cards
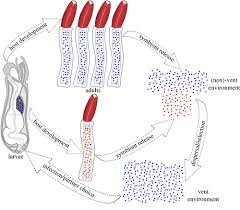
riftia larvae
giant tubeworm larval stage
18
New cards
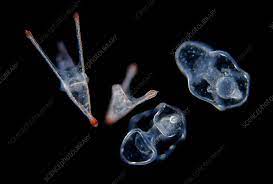
echinoderm larvae
bilaterally symmetrical
19
New cards
barnacles

20
New cards
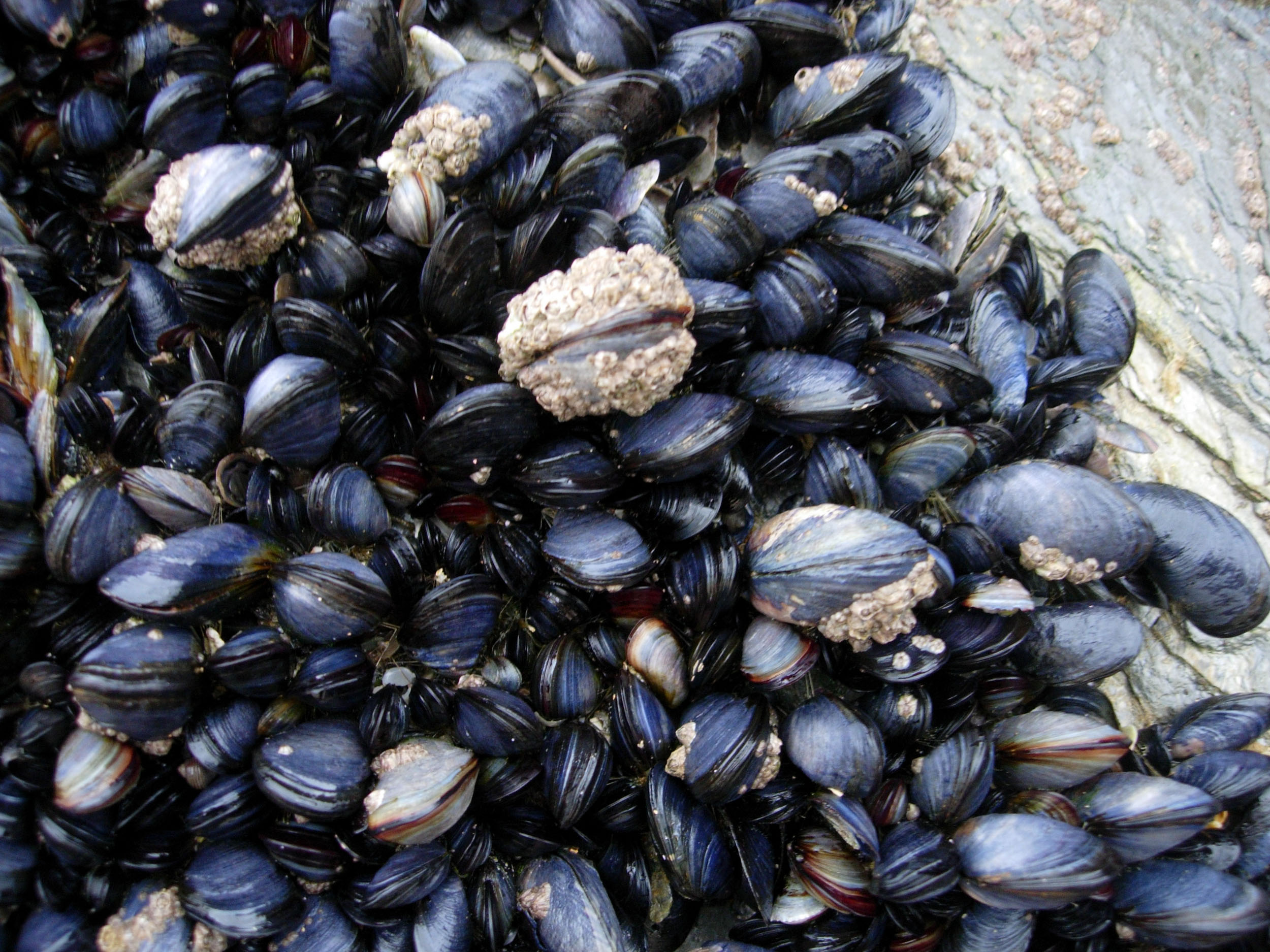
mussels

21
New cards
sea stars

22
New cards
anemone

23
New cards
sea urchins

24
New cards
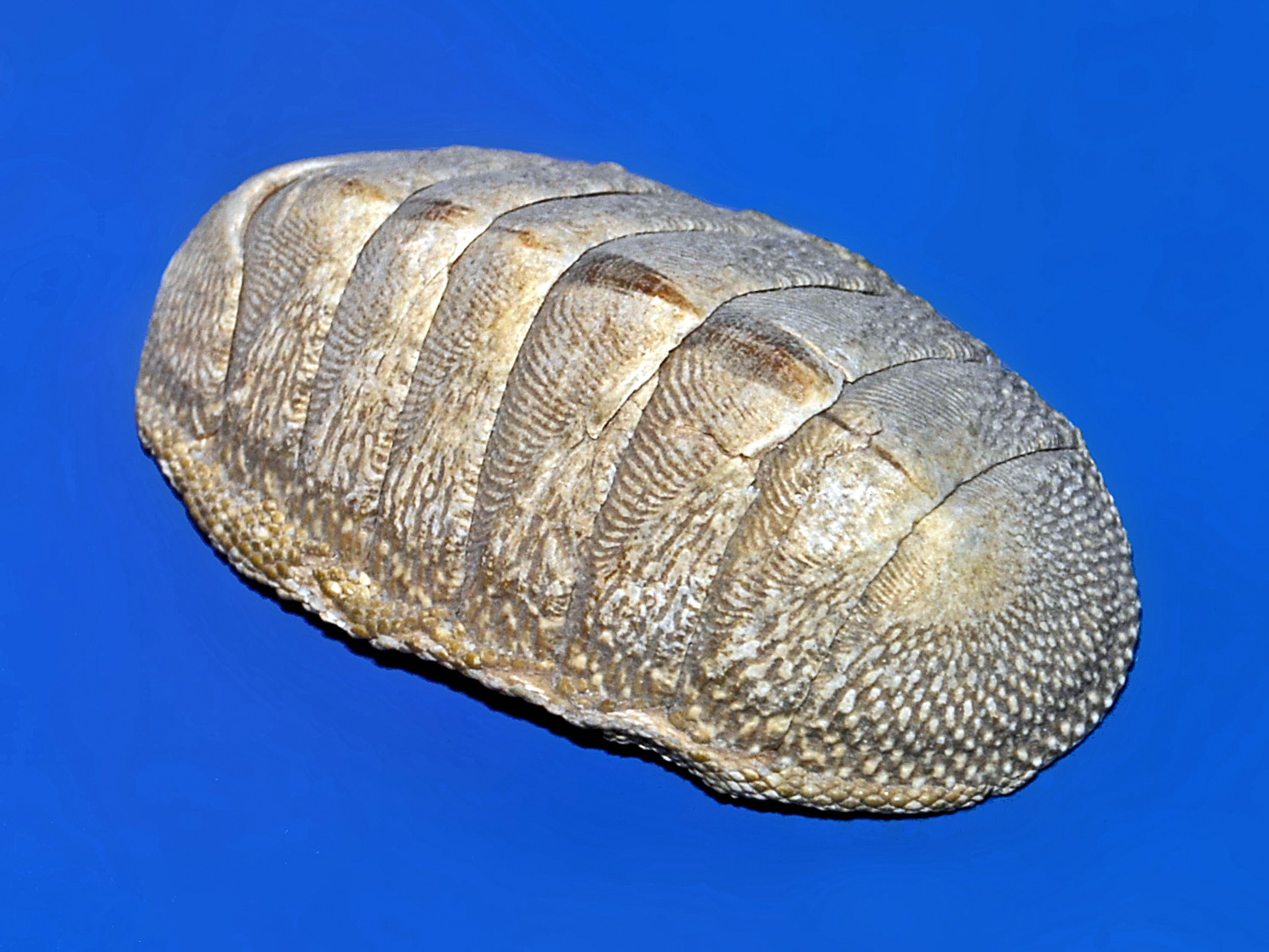
chitons

25
New cards
hydrothermal vent giant tubeworms

26
New cards
pompeii worms
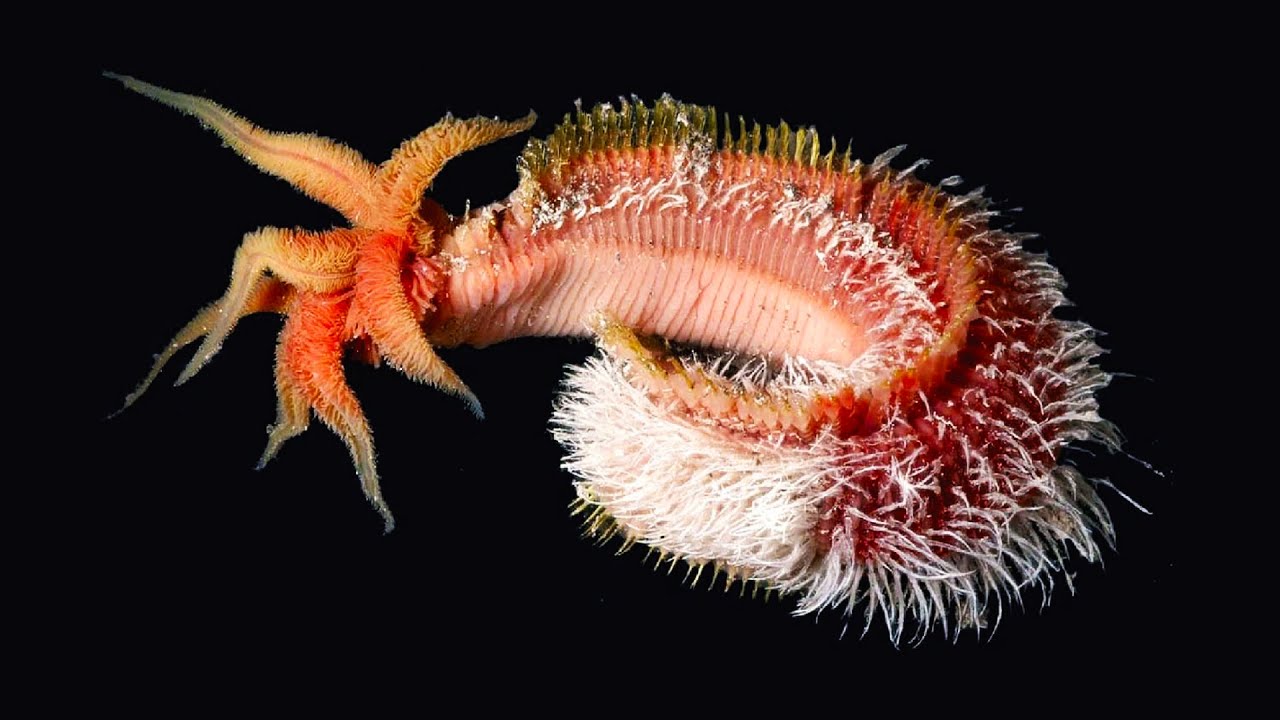

27
New cards
hagfish
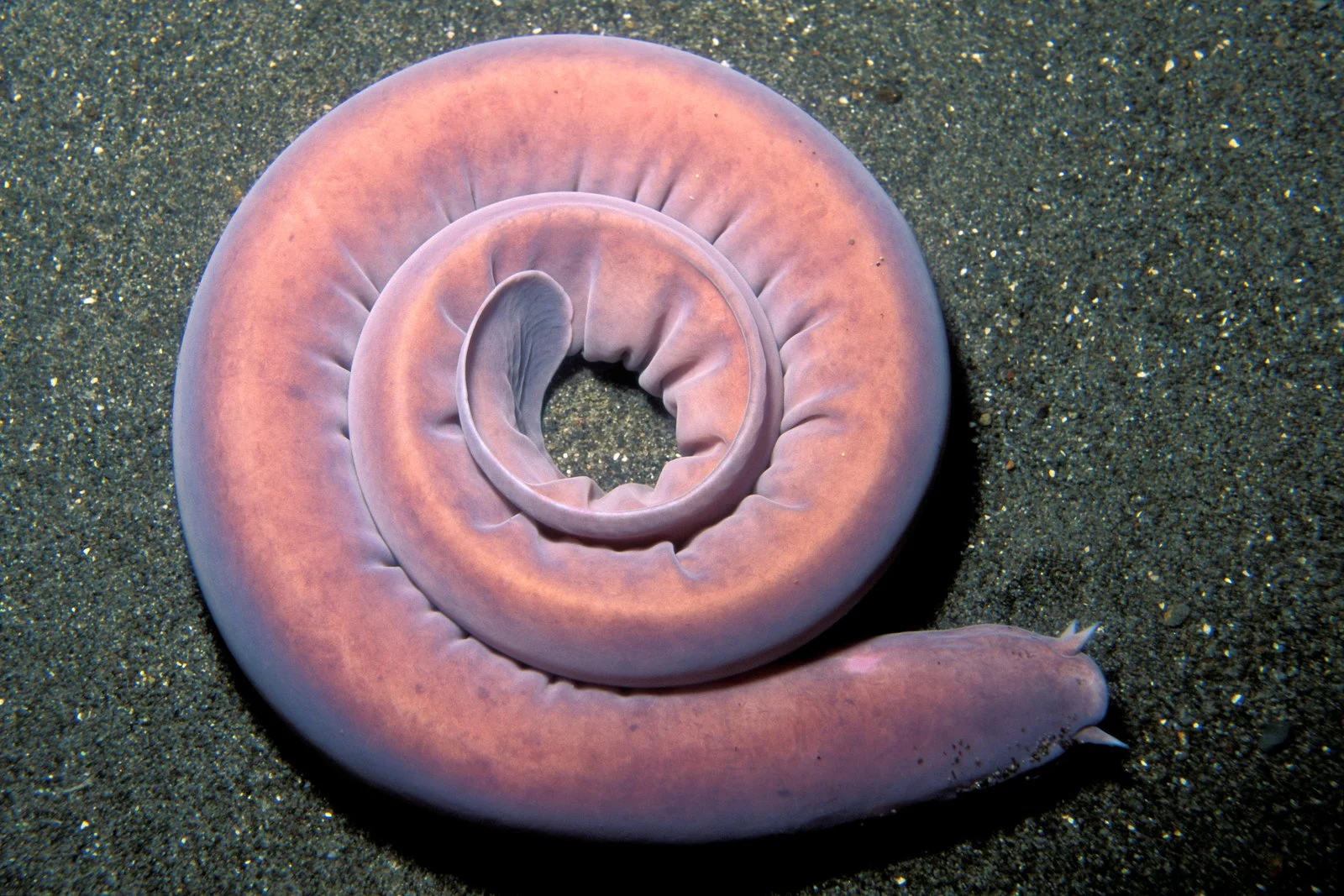

28
New cards
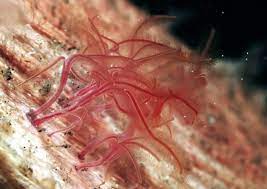
osedax
bone boring worm
29
New cards
brain coral
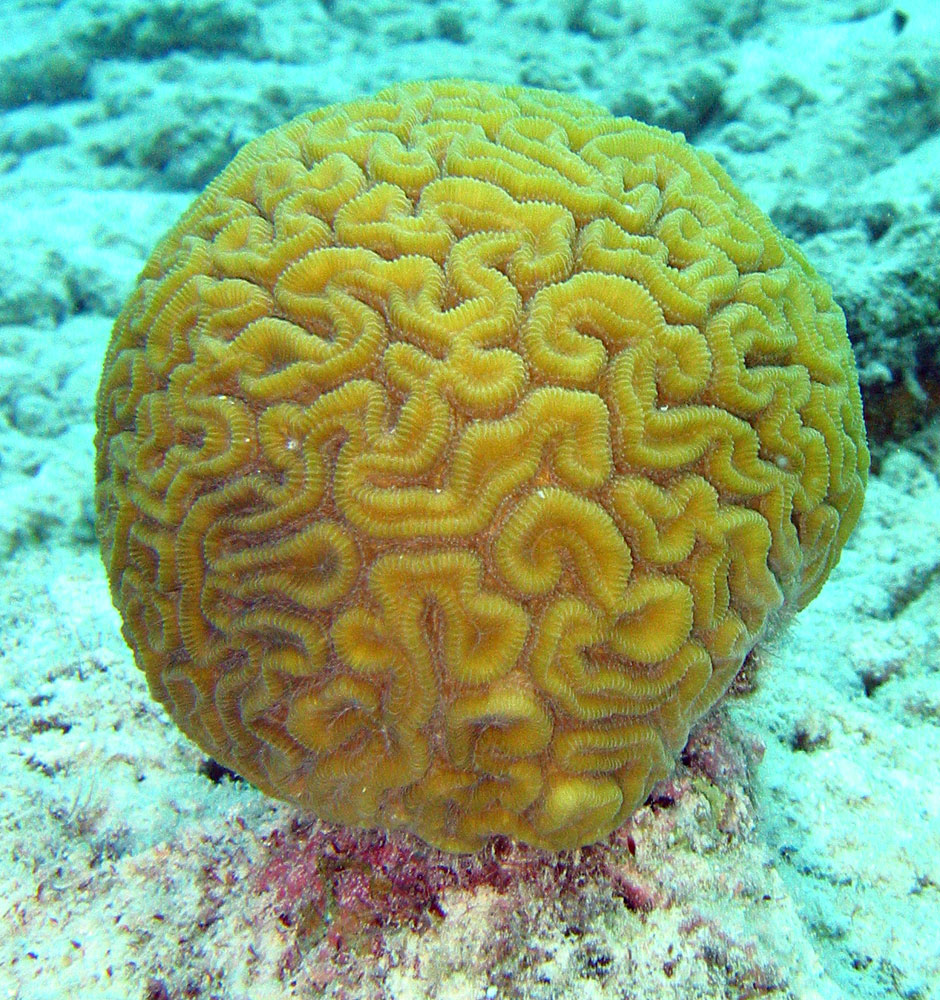

30
New cards
branching coral
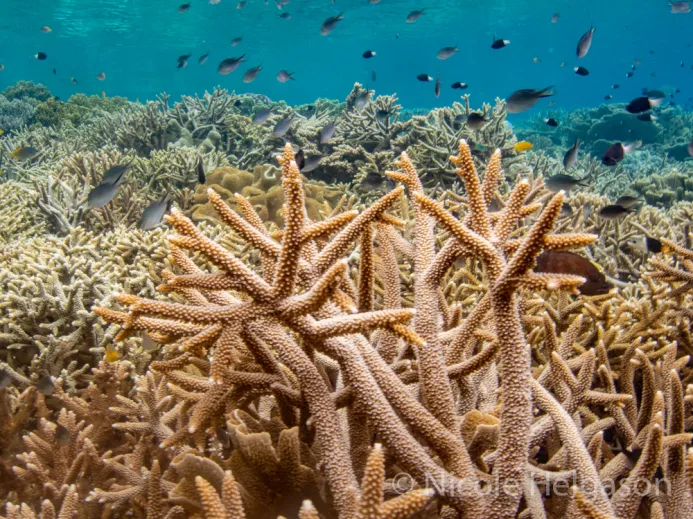

31
New cards
salmon
32
New cards
flounder

33
New cards
sculpin
rocky intertidal type of fish

34
New cards
ratfish

35
New cards
shark
elasmobranch fish characterized by cartilaginous skeleton, 5-7 gill slits, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head

36
New cards
rockfish
cod fish of the Salish Sea

37
New cards
sea otter
exclusively marine

38
New cards
river otter
endemic to North america

39
New cards
blue whale
baleen- largest animal that exists

40
New cards
orca
largest oceanic dolphin

41
New cards
narwhal
small arctic whale, male has a horn

42
New cards
sea lion
pinnipeds- external ear flaps, ability to walk on all fours, short/thick hair, big chest/belly

43
New cards
harbor seal
pinniped species- no visible ears

44
New cards
walrus
large pinniped mammal

45
New cards
manatee
herbivorous sea cows

46
New cards
why is there so much phytoplankton diversity?
there is variation in the types of nutrients they require, preferred temp, different levels etc, different phytoplankton thrive in different areas
47
New cards
why are small phytoplankton better?
sink slower, more efficient photosynthesis, more rapid reproduction
48
New cards
why is Puget Sound so productive?
balance of mixing/stratification, nutrients from inflow of rivers, lots of upwelling
49
New cards
How can you estimate phytoplankton population and zooplankton grazing with the dilution method?
increasing dilution separates the phytoplankton, makes it harder for zooplankton to graze and makes it possible to calculate grazing rate per capita
50
New cards
Why do zooplankton perform diel vertical migration?
during the night they eat at the surface, during the day they avoid predation at the bottom
51
New cards
what causes vertical zonation patterns of benthos on rocky intertidal shorelines?
biological stress vs physical stress-higher on the shoreline means less water access, but the lower you go the more predators there are
52
New cards
How do whale falls serve as stepping stones for the dispersal of hydrothermal vent organisms?
large sources of nutrients- hydrothermal vent organisms use them as a temporary feeding place for larva to catapult the next generation closer to another hydrothermal vent
53
New cards
Why else are whale carcasses important to the deep sea?
they serve as nutrients and food sources in the deep sea
54
New cards
why is deep sea benthic species diversity so high?
long lived, stable habitat, large habitat area, intermediate predation, high level of food, highly complex habitat, heterogeneous food resources
55
New cards
what roles do microbes and viruses play in marine ecosystems?
they act as decomposers; they alter interactions within ecosystems/further natural selection
56
New cards
what is the microbial loop and how does it affect carbon transfer to higher trophic levels and the cycling of nutrients?
a trophic pathway where dissolved organic carbon is returned to higher trophic levels via its incorporation into bacterial biomass, and then coupled with the classic food chain formed by phytoplankton-zooplankton-nekton
57
New cards
explain how the processes of stratification and upwelling influence ocean productivity.
limits productivity, increases productivity
58
New cards
marine food webs structure
bottom up and top down processes
59
New cards
feeding patterns of seals
eats herring in the winter+spring, salmon in summer+fall
60
New cards
Identify sources and sinks of plastics in the open ocean and PCBs in the Salish Sea
61
New cards
causes and consequences of global warming and ocean acidification on marine ecosystems
fossil fuels release CO2, which is taken into the ocean and becomes carbonic acid that releases ions. ions cause the acidity of the ocean to increase which causes coral bleaching and lower aragonite levels. this negatively affects calcifiers who rely on CaCO3 to build shells, in environments without CaCO3 shells deteriorate.
62
New cards
feeding patterns of sea lions
eat everything from fish to octopi to bivalves, they will station themselves below dams at salmon output areas
63
New cards
feeding patterns of orcas
eat everything, but especially salmon, determined by location
64
New cards
feeding patterns of manatees
eat sea grass, completely herbivorous
65
New cards
feeding patterns of dugongs
eat eelgrass, completely herbivorous
66
New cards
bottom up food web
more dependent on the lowest trophic level to be sustained
67
New cards
top down food web
not as reliant on lower trophic levels to be sustained
68
New cards
why are fish and whale communities bottom up?
they rely heavily on phytoplankton communities to thrive
69
New cards
which top predatory animals exert top down control?
orcas, sea otters