Unit 3, Concept 1: Enzymes and Biochemical Reactions
4.0(3)
Card Sorting
1/21
Last updated 2:48 AM on 11/21/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
1
New cards
chemical reactions
the creation or breaking of bonds
2
New cards
activation energy
the amount of energy needed to start a chemical reaction
3
New cards
reactants
substrate- substances that are changed during a reaction
4
New cards
products
substances that are made by a chemical reaction
5
New cards
endothermic
absorbs energy (energy is stored as sugar, therefore endothermic)
6
New cards
exothermic
releases energy ie cellular respiration (energy is released when sugar is broken down, there fore exothermic reactions)
7
New cards
enzyme
type of protein that speeds up biochemical reactions, they are specialized molecules that bind to substrates and help to break or form bonds
8
New cards
active site
site on the enzyme where the reaction takes place
9
New cards
denaturation
enzymes active site gets deformed and loses its specific shape causing a loss of biological activity
10
New cards
function of enzymes
speeds up biochemical reactions
11
New cards
photosynthesis
6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6 + 6O2
12
New cards
cellular respiration
C6H12O6 + 6O2 -> 6CO2 + 6H2O
13
New cards
endothermic diagram
energy starts low and then gains energy for a process and ends with more energy than before
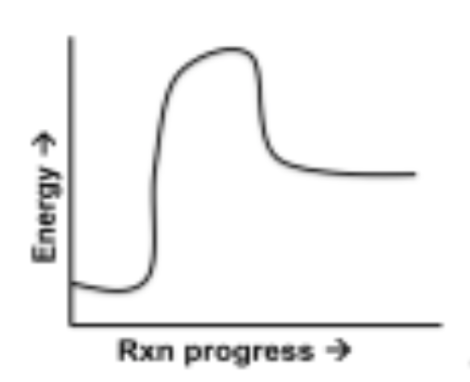
14
New cards
exothermic diagram
energy starts high and increases for a process then decreases as it is released
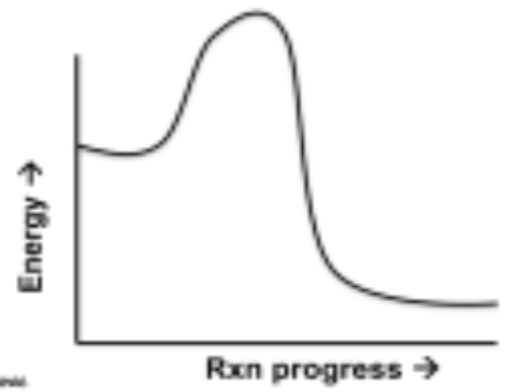
15
New cards
what are the 5 things that affect the rate of a chemical reaction
temperature, pH, substrate concentration, catalysts, and competitive inhibitors
16
New cards
temperature
higher X increases the rate of reaction as molecules move faster more collisions occur
17
New cards
pH
how acidic a solution is; most enzymes only work at a specific X
18
New cards
substrate concentration
more X means faster reaction because there are more particle collisions
19
New cards
catalysts
speed up reactions (like enzymes)
20
New cards
competitive inhibitors
slow down reactions
21
New cards
lock and key model
enzymes can break bonds in a substrate to form two products or make bonds between substrates to from one product
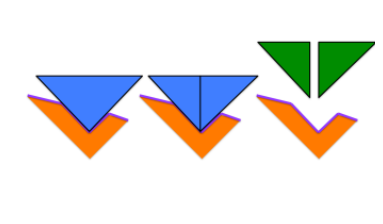
22
New cards
describe the lock and key model
the substrate enters the enzymes activation site and comes out as the product