AP Micro: Lesson 3.5 - Profit Maximization
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
How do you calculate economic profit?
TR - TC
How do you calculate TR?
TR = P • Q
What does breaking even mean?
Making normal profit. Economic profit = 0
Is breaking even a bad thing for a firm? Explain
No. It means a firm is doing just as well operating the business as they would doing another job
No other job will make you do as well as you are doing now
How do you find the optimal quantity using total benefit vs. TC?
Total benefit = TR for producers
Optimal choice is when difference between TR (total benefit) and TC is the greatest (TR > TC)
How do you find the optimal quantity using MB vs. MC?
MB = marginal revenue for producers
Optimal choice is when MB = MC
What is marginal revenue (MR)? and formula
The additional revenue from selling an additional unit of output
MR = change TR ÷ change Q
MR is the derivative of TR (tracks the slope)
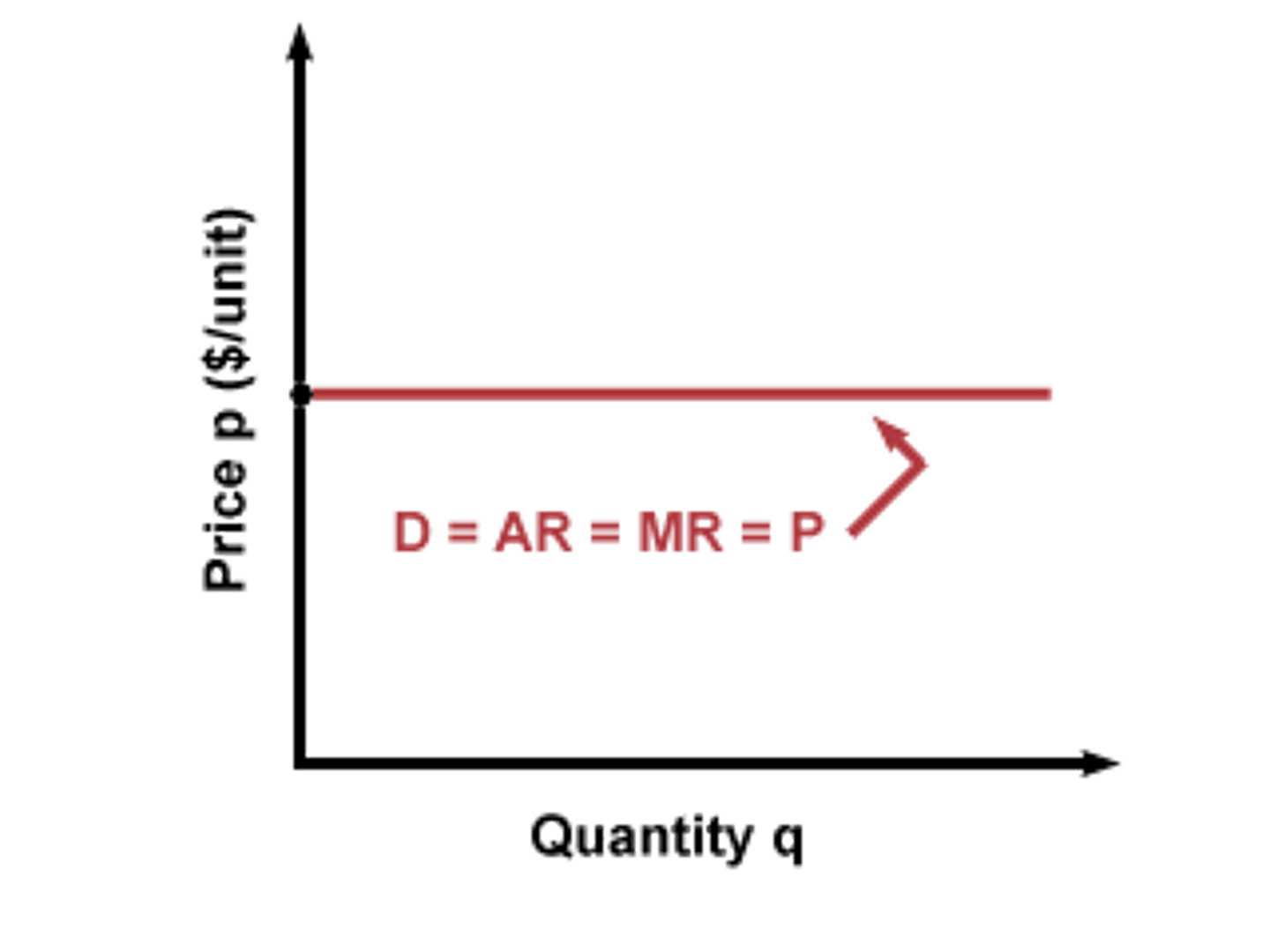
What does MR look like when demand is perfectly elastic?
MR is perfectly elastic (same as demand)
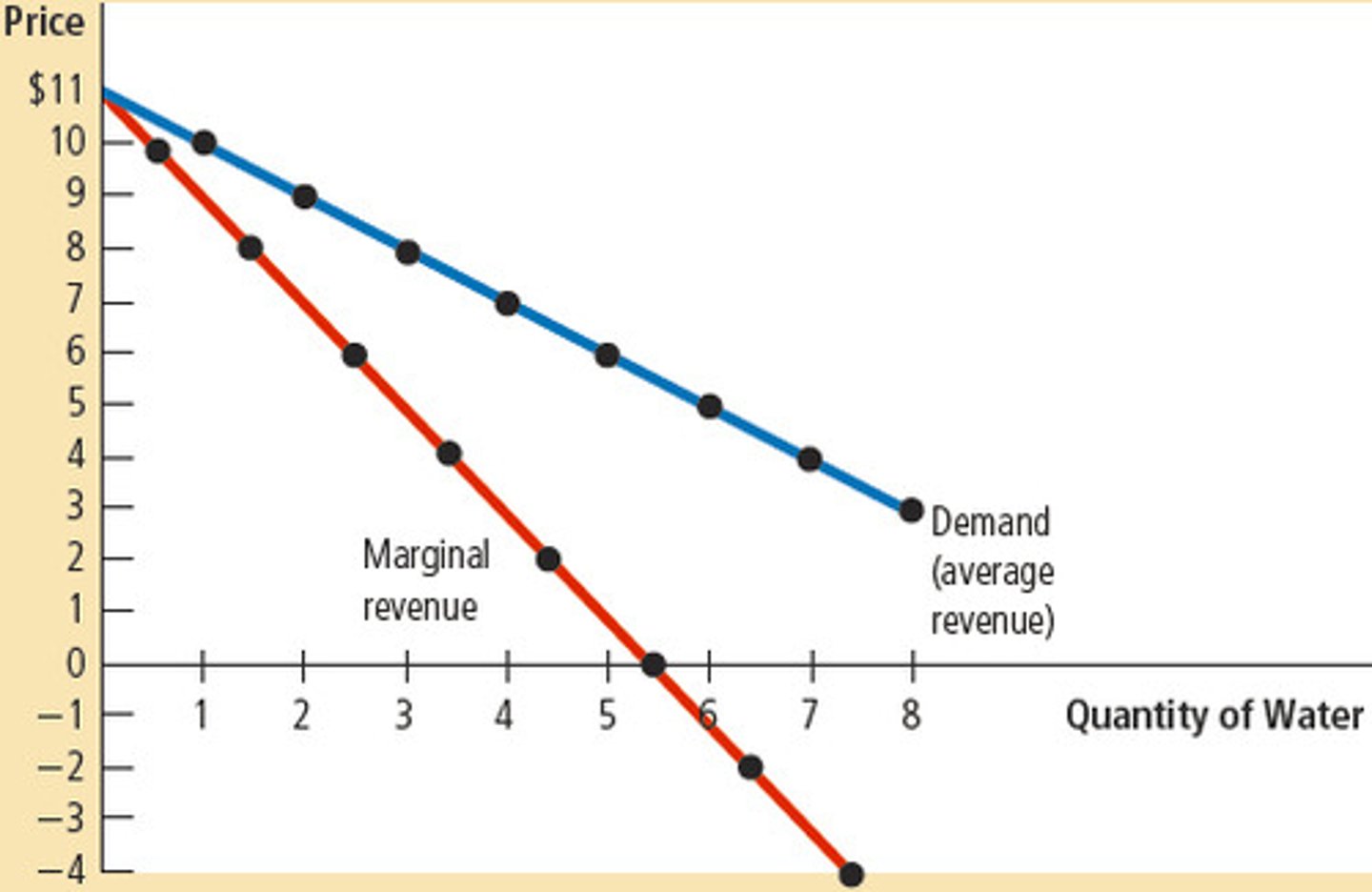
What does MR look like when demand is downward sloping?
It is a decreasing line (goes negative when TR decreases)
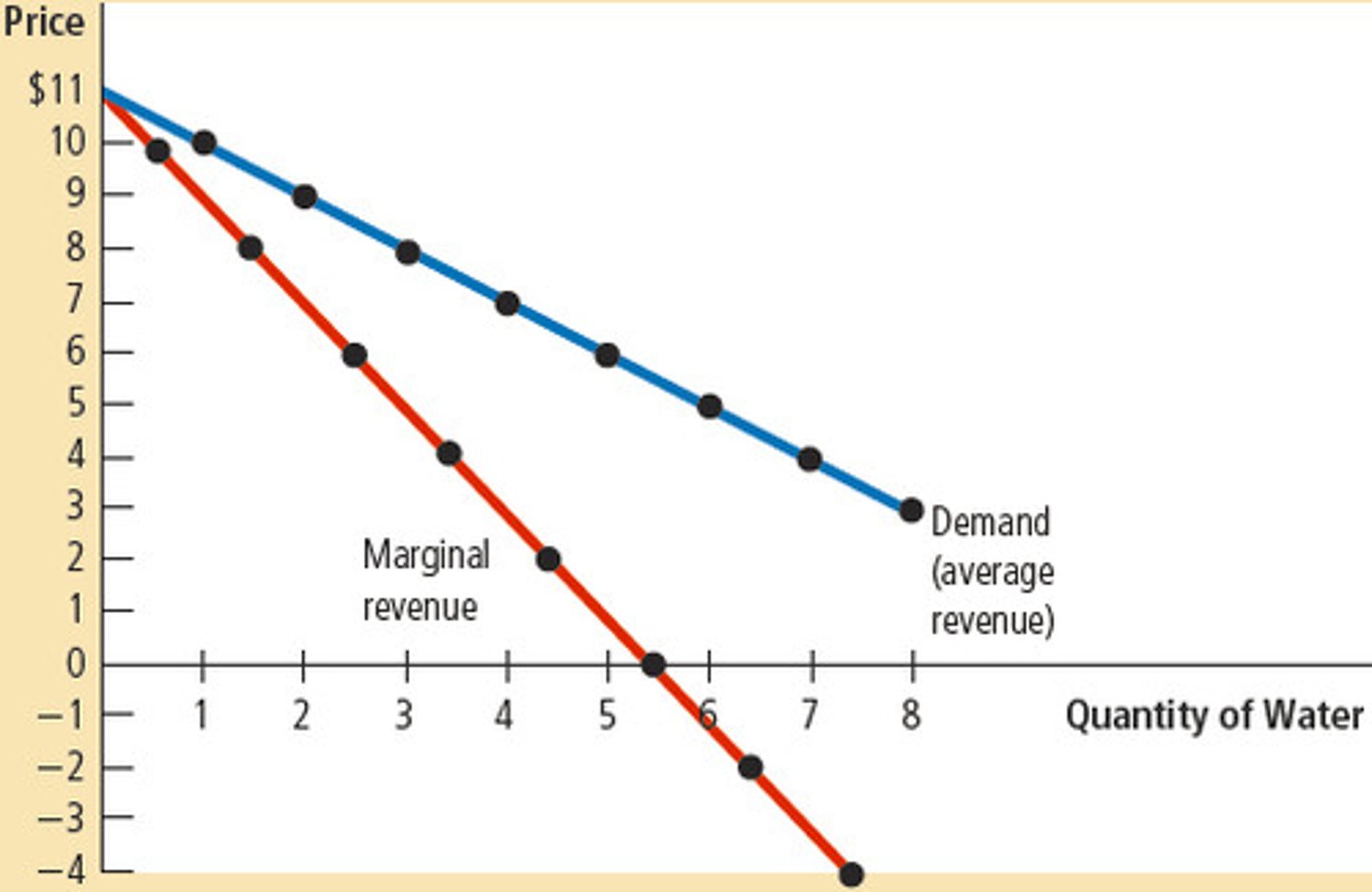
What is the relationship between price and demand?
Demand = price
Define average revenue (and formula)
AR = TR ÷ Q
What is the relationship between P and AR?
P = AR
TR = P • Q, so P = TR ÷ Q (same as AR: AR = TR ÷ Q)
Explain D = AR = P
Occurs when demand is downward sloping
D = P
AR = TR ÷ Q
P = TR ÷ Q
So... D = AR = P
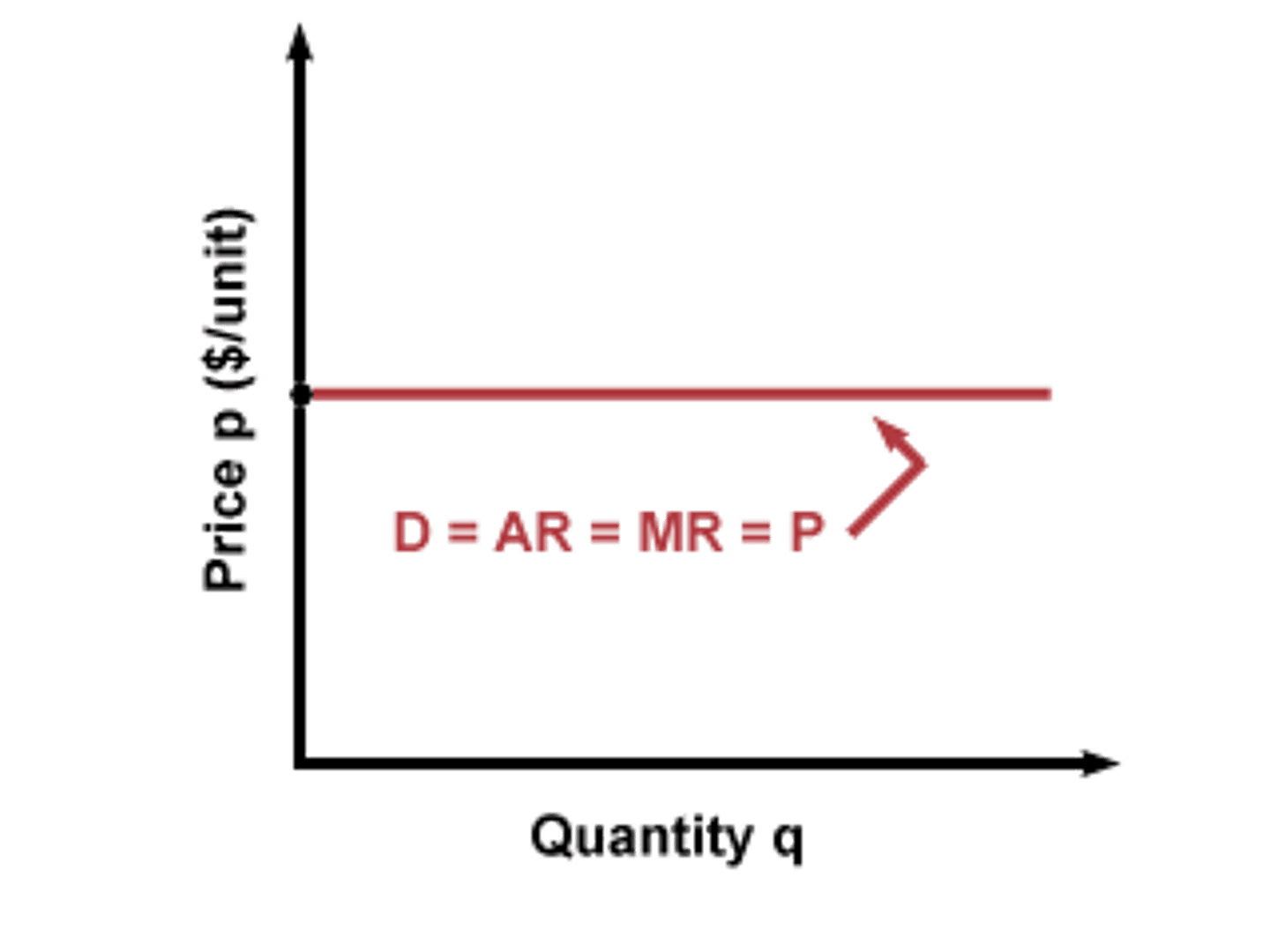
Explain MR = D = AR = P
Occurs when D is perfectly elastic
MR is perfectly elastic when D is perfectly elastic, so MR = D
D = P
P = TR ÷ Q
AR = TR ÷ Q
So... MR = D = AR = P
How is MR vs MC similar to MB vs MC? How do you find the optimal choice using MR vs. MC?
MR = MB for producers. They are the same thing
Optimal choice when MR = MC (profit-maximizing rule)