Cognitive Theories of Moral Development: Piaget and Kohlberg
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
Premoral Stage
Ages 0-5, little concern for rules.
Moral Realism
Ages 5-11, respect for rules, inflexible application.
Moral Absolutism
Belief in absolute right or wrong.
Imminent Justice
Belief that rule deviation leads to punishment.
Egocentrism
Inability to see others' perspectives.
Morality of Reciprocity
Ages 11+, rules can be questioned and altered.
Justice and Equality
Belief in fairness for all individuals.
Intentions in Punishment
Punishment relates to intentions and transgressions.
Cross-Cultural Variation
Differences in moral development stages across cultures.
Underestimated Abilities
Piaget underestimated young children's moral reasoning.
Mixed Action Outcome
Confusion between action consequences and actor's intention.
Kohlberg's Dilemma
Moral dilemmas used to study moral development.
Heinz's Dilemma
Scenario exploring moral reasoning about stealing.
Moral Reasoning
The process of determining right from wrong.
Developmental Sequence
General progression of moral reasoning stages.
Consequential Evaluation
Assessing morality based on outcomes of actions.
Psychologist Lawrence Kohlberg
Developer of a theory on moral development.
Moral Dilemmas
Situations requiring moral judgment and reasoning.
Reasoning Behind Choices
Focus on rationale, not just the decision.
Childhood Moral Development
Evolution of moral understanding from childhood.
Pre-conventional level
Moral reasoning based on avoiding punishment and gaining rewards.
Stage 1: Obedience Orientation
Focus on avoiding punishment through obedience.
Stage 2: Instrumental Orientation
Behavior driven by self-interest and rewards.
Conventional Level
Moral decisions based on social norms and expectations.
Stage 3: Good-boy Morality
Moral behavior driven by interpersonal approval.
Stage 4: Social System Morality
Morality based on authority and societal rules.
Post-Conventional Level
Moral reasoning based on internal ethical principles.
Stage 5: Social Orientation
Morality based on social contracts and group welfare.
Stage 6: Universal Ethical Principles
Morality based on abstract principles like justice.
Kohlberg's Theory Evaluation
More support than Piaget; considers gender differences.
Moral Judgment Interview (MJI)
Assessment of moral reasoning through structured interviews.
Denton & Krebs Study
Study on alcohol's effect on moral judgment.
Moral Maturity
Ability to make consistent moral judgments.
Promoting Moral Reasoning
Advancement through consistent discipline and reasoning.
Moral Behaviour in Children
Young children's judgments may not predict behavior.
Self Regulation
Ability to control behavior independently.
Control Phase
Dependent on caregivers for behavior reminders.
Self-Control Phase
Compliance with expectations without caregiver presence.
Self-Regulation Phase
Using strategies to manage behavior independently.
Delayed Gratification
Postponing immediate pleasure for future reward.
The Marshmallow Test
Experiment measuring children's ability to delay gratification.
Moral Decision Making
Process of evaluating right and wrong actions.
Social Norms
Expectations that guide behavior in society.
Interpersonal Norms
Expectations based on relationships with others.
Authority and Morality
Rules established to maintain social order.
Cultural Group Morality
Adherence to contracts benefiting group members.
Personal Moral Code
Individual principles guiding ethical decisions.
Low Self-Regulation
Inability to control behavior without external prompts.
Higher Level Moral Behavior
Modeling complex moral reasoning for children.
Marshmallow Test
Experiment measuring children's delay of gratification.
Delay of Gratification
Ability to resist immediate rewards for larger rewards.
Self-Control
Ability to regulate emotions and behaviors over time.
Warm Parenting Styles
Parenting characterized by support and open communication.
Prosocial Behaviours
Actions intended to benefit others or society.
Altruistic Behaviours
Helping others without expecting rewards or recognition.
Infant Social Evaluation
Infants assess characters based on prosocial actions.
Hamlin et al. Study
Research on infants' preferences for helpers over hinderers.
Instrumental Aggression
Aggression aimed at obtaining possessions or toys.
Hostile Aggression
Aggression intended to harm another person emotionally.
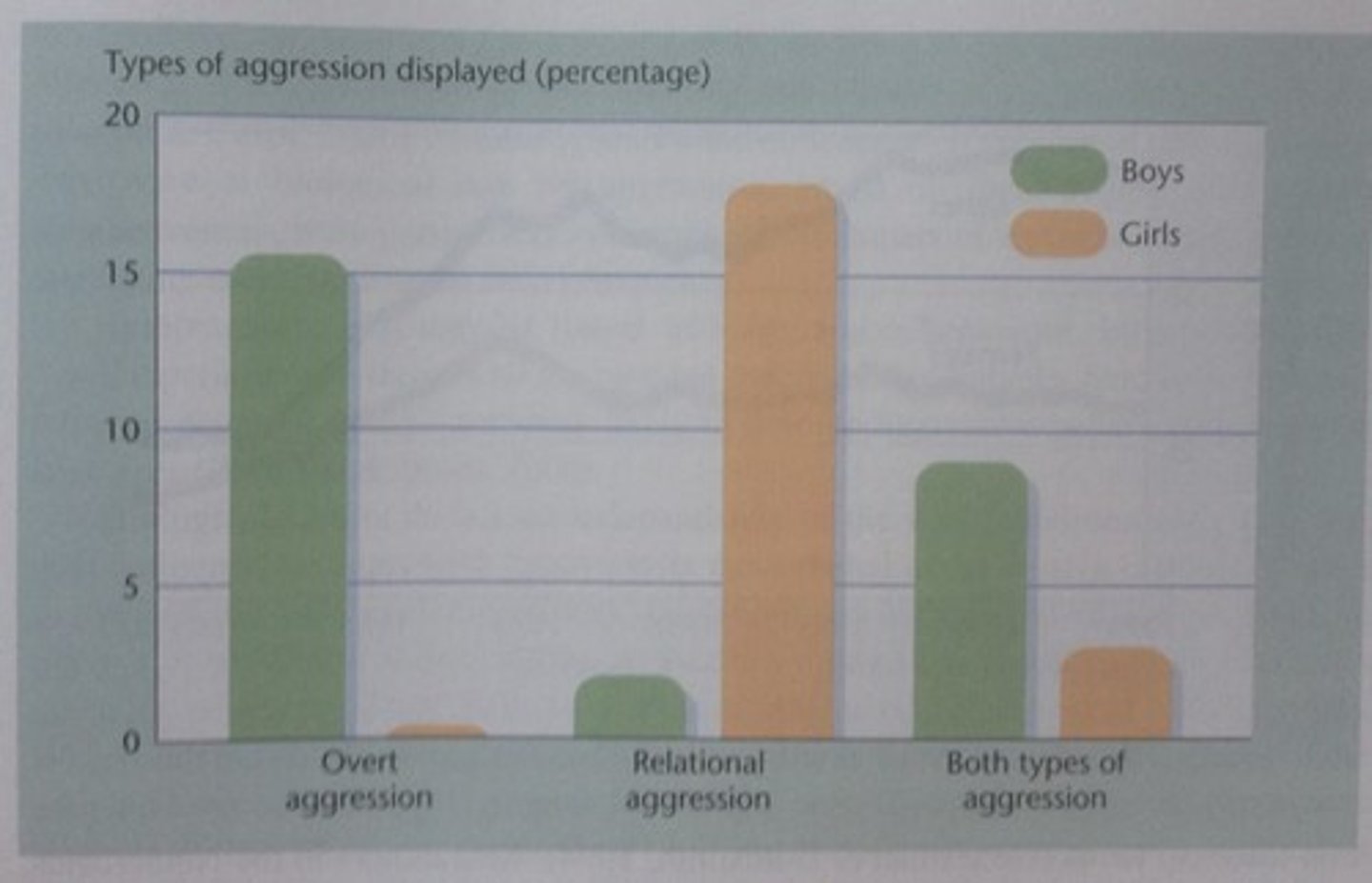
Relational Aggression
Aggression that damages social relationships or reputations.
Developmental Stability
Consistency of behaviors over time in children.
Long-Term Goals
Future objectives that require patience to achieve.
Temptation Reduction
Strategies to minimize attraction to immediate rewards.
Parent-Child Interaction
Dialogue-focused discussions about discipline and behavior.
Temperament Influence
Innate personality traits affecting self-control levels.
Coping Strategies
Methods children use to resist temptation.
Social Preferences
Tendency to favor prosocial individuals over antisocial ones.
Moral Development
Evolution of understanding right and wrong in children.
Aggression Types
Different forms of aggressive behavior exhibited by children.
Cognitive Development
Growth of thinking and reasoning abilities in children.
Emotional Regulation
Managing emotional responses to situations or stimuli.
Childhood Altruism
Early signs of helping behaviors in infants.
Reward Evaluation
Assessment of benefits versus costs in decision-making.
Social Learning
Learning behaviors through observation of others.
Behavioral Observation
Recording actions to analyze behavior patterns.
Developmental Milestones
Key behaviors expected at certain ages in children.
Peer Interaction
Social exchanges between children of similar age.