oxidative phosphorylation & electron transport chain
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
mitochondria
major site for aerobic respiration and the production of energy
where is the demand for energy high?
liver and muscle
cells like ______________ don't have mitochondria and rely on _______________ for energy.
erythrocytes; glycolysis
what are the structural parts of the mitochondria?
- outer membrane
- intermembrane space
- inner membrane space
- matrix
outer membrane of mitochondria
relatively permeable to small molecules and ions due to porin
- allows anionic (-) molecules to pass through
- transport occurs through porins
porin
is a voltage gated anion channel and forms pores across the membrane
inner membrane of mitochondria
impermeable to most small molecules and ions
what can pass through the inner membrane of mitochondria?
- water, gases such as CO2 and O2
- metabolites, phosphate, protons
- transport of other molecules requires specific transporters
what are the multiple folds which increase the surface area called in the inner membrane?
cristae
what does the matrix contain?
- pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
- citric acid cycle enzymes
- fatty acid b-oxidation enzymes
- amino acid oxidation enzymes
what is bound to the inner membrane?
electron transport chain
NADH and FADH2 transfer their electrons to molecular O2 through a series of redox reactions in a process called _____________.
respiration
what are redox reactions catalyzed by?
membrane-embedded enzymes
respiratory complexes and auxiliary proteins together comprise the __________________ _____________.
respiratory chain
- aka electron transport chain
____________ _______________ - linked dehydrogenases catalyze reversible reactions between the oxidized and reduced forms of NAD(P)+
nicotinamide nucleotide
what contain a very tightly, sometimes covalently bound flavin nucleotide (FMN or FAD)
flavoproteins
what is another name for coenzyme Q?
ubiquinone or just q
- ubiquitous in cells
what is coenzyme Q?
a lipid-soluble benzoquinone with a long isoprenoid side chain
quinone structure
QH2 is the reduced dihydro form
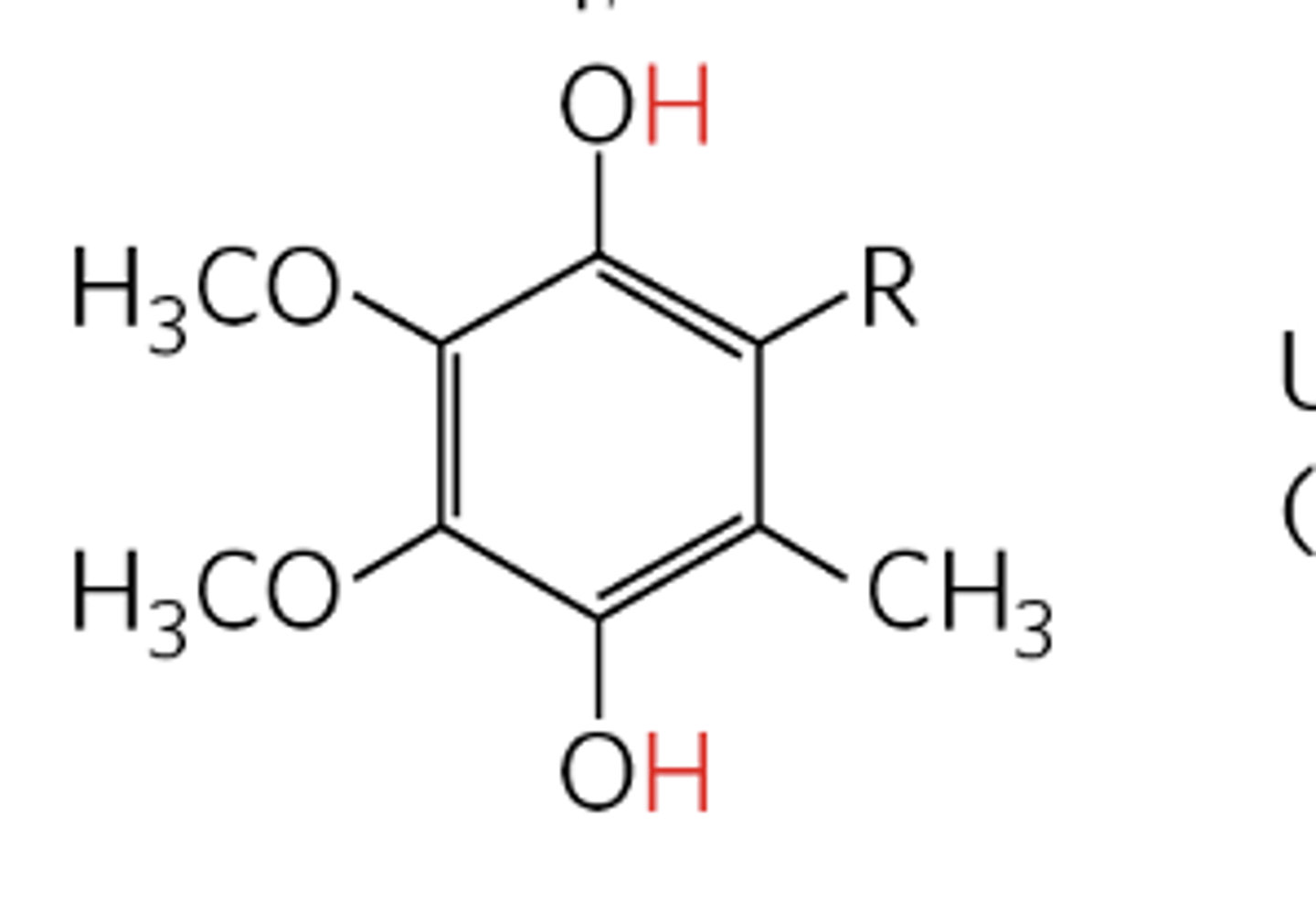
what are the functions of coenzyme Q?
- a redox participant in the electron transport chain
- freely diffusible within the inner mitochondrial membrane
- plays a central role in coupling electron flow to proton movement
heme groups
tightly bound prosthetic groups
- involves fe(II) and fe(III)
cytochromes
proteins with characteristic strong absorption of visible light due to their iron-containing heme prosthetic groups
what are the 3 classes in mitochondria
a, b, c
which hemes of cytochromes are not covalently bound to associated proteins?
a and b
c is covalently attached through ________ residues
cys
iron-sulfur proteins
proteins that contain iron in association with inorganic sulfur atoms and/or with the sulfur atoms of Cys residues in the protein
what do iron sulfur proteins contain?
1, 2 or 4 Fe atoms linked sulfides
where is iron-sulfur proteins found?
membrane-bound enzymes and soluble enzymes
____________ ___________ help stabilize the enzyme structure and protect it against proteoytic attack
Fe-S clusters
how many muti-subunit enzyme complexes does the electron transport chain contain?
4
what is the name of complex I (ETC)?
NADH-Q reductase
what is the name of complex II (ETC)?
succinate-Q reductase
what is the name of complex III (ETC)?
QH2-cytochrome c reductase
what is the name of complex IV (ETC)?
cytochrome c oxidase
complex I: NADH-Q reductase
- from NADH to ubiquinone
- flavoprotein that uses FMN
- contains non-heme iron centers (Fe-S complexes)
- proton pump
in complex I (ETC) how many electron are being transferred?
2 electrons from NADH are transferred via FMN to conenzyme Q
for every 2 electrons of NADH transferred, what is being pushed out and where?
4 H+ are pushed out of the matrix into the inter-membrane space
complex II: succinate-Q reductase
- couple the oxidation of succinate with the reduction of ubiquinone
- functions to convert succinate to fumarate in the citric acid cycle
- transfers electrons but NOT a proton pump
- from succinate to ubiquinone
what does complex II contain?
- FAD
- heme molecules
- Fe-S centers
- cyt b
in complex II succinate is _______________ to fumarate.
oxidized
- FAD is reduced to FADH2
- FADH2 re-oxidized to FAD and re-enters Krebs cycle
in complex II coenzyme Q is ____________.
reduced
complex III: QH2-cytochrome c reductase
- couples the transfer of 2 electrons from ubiquinol to cytochrome c
- acts as a proton pump
- for every molecule of QH2 converted to coenzyme Q
electrons are passed one at a time from QH2 to 2 successive molecules of cyt c
what does complex III contain?
- cyt b
- cyt c
- Fe-S centers
complex IV: cytochrome c oxidase
- carries electrons from cyt c to molecular oxygen, reducing it to H2O
what does complex IV contain?
- cyt a
- cyt a3
- 2 Cu ions
what is the final electron acceptor?
O2
what is the final product?
water
electron bounce from complex 1 ,3, 4 or complex 2, 3, 4 but they do NOT bounce from complex ____ to ____.
1 to 2
in electron flow, how does energy move?
- downhill flow of electrons releases free energy
what form is energy released in?
heat and electricity
- some of the energy is used to pump protons out of the matrix
- much of the free energy generated is recovered and stored in the form of an electrochemical proton gradient across the mitochondrial inner membrane
chemiosmotic theory of oxidative phosphorylation
transmembrane differences in proton concentration are the reservoir for the energy extracted from biological oxidation reactions
chemiosmotic theory (h's notes)
as the proton goes from high concentration to low concentration the ATP synthase absorbs some of the potential energy from the movement and uses the energy to convert ADP and inorganic phosphate to make ATP.
what does the chemiosmotic model describe?
the coupling of ATP synthesis to an electrochemical proton gradient (the proton motive force)
as the electrons flow the respiratory complex, _________ _______ ________ _________ into the inter-membrane space.
protons are pumped out
- this pumping is an "uphill" process
overtime, the protons build up outside the matrix which drive H+ back where?
into the matrix
- doing so, they transfer their energy to ATP synthase
concH+ (outside) is greater (>) than concH+ (inside): called _______________ ________________
concentration gradient
charge e- (outside) is greater (>) than charge e- (inside): called ________________ _________________
potential gradient
______ ____________ catalyzes the formation of ATP.
ATP synthase
complex V: ATP synthase
drives the synthesis of ATP from ADP and Pi, as proton flow passively back into the matrix though its proton pore
F1 domain is located where?
on the matrix side of the inner membrane
F0 domain is locared where?
spans the inner membrane
as H+ enters the ________ portion and turns the "stalk", ADP and Pi are joined t form ATP in the ________ domain
F0 ; F1
________ H+ enter the inter-membrane space and ______ H+ re-enters the matrix
10 ; 4
- 10/4 = 2.5 ATP per NADH (rounded to 3 ATP)
- 6/4 = 1.5 ATP per FAD2 (rounded to 2 ATP) (starts at complex II)
complexes I, III, IV are ____________ ____________.
transmembrane proteins
where is complex 2 located?
on the inner surface of the inner membrane
in complex IV, 4 H+ are ejected for every molecule of O2 that accepts the electron, what is the final acceptor?
O2
ATP synthesis by the ________ _______ of ATP synthase is accompanied by H+ re-entry into the matrix.
F0-F1 domains
What is the other name of Complex I?
a. cytochrome c oxidase
b. NADH-Q reductase
c. succinate-Q reductase
d. Q-cytochrome c reductase
e. cytochrome c reductase
b. NADH-Q reductase
What type of protein makes the outer mitochondrial membrane relatively permeable?
a. voltage gated transporter
b. proton pump
c. transporters
d. ATP-powered pump
e. porin
e. porin
What is the other name of Complex II?
a. cytochrome c oxidase
b. NADH-Q reductase
c. cytochrome c
d. Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase
e. succinate-Q reductase
e. succinate-Q reductase
Coenzyme Q is also called:
a. Rieske center.
b. oxidoreductase.
c. ubiquinone.
d. NADH.
e. Complex II.
c. ubiquinone.
The subunit of ATPase embedded in the inner mitochondrial membrane is the:
a. membrane-c ring subunit.
b. F0 subunit.
c. anchor subunit.
d. Fm subunit.
e. F1 subunit.
b. F0 subunit.
What is the other name of Complex III?
a. NADH-Q reductase
b. Q-cytochrome c reductase
c. cytochrome c
d. cytochrome c oxidase
e. succinate-Q reductase
b. Q-cytochrome c reductase
What type of gradient is critical to ATP formation during oxidative phosphorylation?
a. potassium ion
b. proton
c. electron
d. sodium ion
e. chloride ion
b. proton
What is the other name of Complex IV?
a. NADH-Q reductase
b. Q-cytochrome c oxidoreductase
c. cytochrome c oxidase
d. cytochrome c
e. succinate-Q reductase
c. cytochrome c oxidase
An electron flow down the electron-transport chain leads to:
a. a dangerous imbalance of Na+ ions across the mitochondrial membrane.
b. the transport of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane from the matrix to the intermembrane space.
c. the transport of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane from the intermembrane space into the matrix.
d. a dangerous imbalance of K+ ions across the mitochondrial membrane.
e. the coupled synthesis of GTP.
b. the transport of protons across the inner mitochondrial membrane from the matrix to the intermembrane space.
What enzyme links the TCA cycle to the electron-transport chain?
a. citrate synthase
b. α-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
c. fumarase
d. malate dehydrogenase
e. succinate dehydrogenase
e. succinate dehydrogenase
what is the name of complex III (ETC)?
____________ help stabilize the enzyme structure and protect it against proteoytic attack
Fe-S clusters
what do iron sulfur proteins contain?
1, 2 or 4 Fe atoms linked sulfides
what do iron sulfur proteins contain?