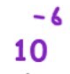eosc 114 - impacts ❗️❗️❗️❗️ + fragile systems 2
1/109
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
110 Terms
1 ma
1 mega annum : 1 million years 1 000 000
10^6 years
understanding of earth’s geological history is built:
understanding that earth is a system
steno’s laws of stratigraphy (layering of earth)
bio stratigraphy (fossils)
correlation
radiometric dating
five major extinction events NEWEST TO OLDEST
extinction occurs in PERIODS that are WITHIN ERAS, multiple epochs can occur in a period
(newest) end of cretaceous period (66ma)
end of triassic period (200 ma)
end permian period (250 ma)
// end of Paleozoic era, entering Mesozoic era
end late devonian period(360 ma)
(oldest) end late ordovician period (450 ma)
CTP DO
what defines a mass extinction
30% species are extinct
broad range of ecosystems affected
extinction happens QUICKLY in relation to the geological timescale
taxonomy
species are a must be capable of interbreeding
extinct species - we use their physical characteristics to identify them
KPCOFGS
kingdom
phylum
class
order
family
genus
species
most recent mass extinction : CRETACIOUS
cretaceous period: 66ma
asteroid impact
75% species extinction globally
triassic mass extinction
200 ma
MAYBE massive volcanic eruptions, asteroids
70-80% of species extinct globally
permian mass extinction
250 ma
asteroid impacts
intense volcanic activity
95% of species extinct globally
THE GREAT DYING ❗
devonian mass extinction
375-360 ma
drastic drop in oxygen levels
75% of species extinct globally
ordovician mass extinction
445 ma
PROBABLE CAUSE: intense ice age
60%-70% of species extinct globally
causes of mass extinctions
biological causes
plate tectonics
climate change
extraterrestrial events
biological causes of extinction
generally leads to extinctions but not mass extinctions
COMPETITION, PREDATION, PATHOGENS
effects on earth system : ex first soils washed into oceans caused anoxia
plate tectonics as a cause of extinction
can lead to changes in climate and sea level
ex. late Ordovician glaciation was likely promoted by movement of gondwana to south pole
supercontinents: pangea, gondwana, nuna
DECREASE OF BIODIVERSITY
climate change as a cause of extinction
in geological past, sudden climate changes were typically caused by volcanism + FLOOD BASALTS
long term shifts of icehouse/greenhouse were influenced by volcanism
icehouse→ ice at poles
greenhouse → no ice at poles
extraterrestrial events as a cause of extinction
asteroid impacts (cretaceous mass extinction)
gamma radiation bursts ( possibly end of ordovician mass extinction)
galactic cycles
overall causes of mass extinctions
tends to be caused by a combination of factors
causes that disrupt the earth’s system, therefore the BIOSPHERE
it is never really one specific cause
end permian mass extinction
251 ma - THE GREAT DYING; 90-96% species extinct
permian world
supercontinent pangea
huge and dry → collapse of carboniferous rainforest 300ma
by 290ma, forests were vast deserts and an ice cap in the southern hemisphere → ARID WASTELANDS
fewer ecological niches on the land + fewer continental shelves in the oceans
OCEAN STAGNATION
polar waters couldn’t sink, bad ocean circulation, anoxia
SEA LEVEL FALL
mid-ocean ridge activity (spreading center) slowing in the Permian
AT THIS TIME, an impact breccia (shockwave + massive shattering/melting and solidification) might’ve occurred
SIBERIAN TRAP - 3million km³ of basalt lava eruption that released lots of CO2 and methane + ERUPTION SET FIRE TO LARGEST COAL+OIL deposit on earth at the time
massive amounts of greenhouse gas, soars in global temperature, climate change (MAJOR INCREASE OF GHG)
METHANE CLATHRATE MELTING - added to climate change, bottom of ocean decay of organic material it is a deep sea sediment
warm ocean → melting of clathrates → methane release METHANE IS STRONGER OF A GHG THAN CO2
in the ocean: 40C on average, reef collapse, anoxia
on the land: 50-60C on average, no trees, acidic rain to live you’d need to be able to burrow, eat little, and not breathe
what effected the permian extinction
pangea is dry
already ocean stagnation and sea level fall
IMPACT BRECCIA
SIBERIAN TRAP
METHANE CLATHRATE MELTING
triassic
251ma (permian) it took until 230 ma ( 20ma) for earth to recover pre extinction levels of coal
due to the ecological room for evolution, DINOSAURS CAME TO BE after the end triassic mass extinction
dinosaurs lived until the next mass extinction — triassic (200ma)
triassic coal gap
there was no coal on earth after permian period for 20 million years
what did the permian period extinction leave behind
absence of coal for 20 million years
lots of ecological space — opportunity for survivors to evolve and dominate available ecological niches
end triassic mass extinction
70-80% of species extinct
more than half of animals and around 60% of plants
decline in ammonites
extinction of conodocts
STILL UNCLEAR WHAT CAUSED IT - lots of impacts but they were either too small or too young/old
attributed to CAMP - central atlantic magmatic province
volcanism and climate change played a role
CAMP - central atlantic magmatic province
during the triassic period
3 million km³ of basalt erupted at 201 ma → LARGE AMOUNTS OF CO2 + sulphur dioxide
oceans were acidifed, carbon deposition stopped (no more absorption of co2)
atmospheric co2 doubled, sulphur dioxide cools but NOT ENOUGH
climate change
what did john spray notice about impacts
there is a change in the geological time scale and impacts DO NOT overlap in time.
triassic jurassic boundary
triassic jurassic boundary
visual evidence of the growth of dinosaurs in evolution in the triassic period (when they existed but weren’t dominant) and in the jurassic period (when they were dominant)
dinosaurs adapted to their ecological niches by ADAPTIVE RADIATION
what mass extinctions led to the rise of dinosaurs
end triassic and end permian
uniformitarianism
“the present is the key to the past”
used by earliest geologists to measure modern geological processes and estimate how long it would take to build the crust
the natural laws and processes that operate in the past world today have always operated in the past and apply everywhere
physics
lord kevin : rate at which a molten body of rock the size of earth would cool
20-40 million years
radiometric dating of how old earth is
4.6 billion years
based off radioactive decay of isotopes of meteorite material
oldest rock 4.03 billion years
oldest meteor 4.54
geological timescale
earth’s 4.5 billion year old history is organized into this
eons, eras, period, epoch
clowns only shoot ducks carrying people that just cant play quietly
(oldest → newest)
cambrian
ordovician
silurian
devonian
carboniferous
permian
triassic
jurassic
cretaceous
paleogene
quaternary
precambian eon
over 4 billion years in which earth had no plants or animals
makes up 87% of earth’s history
earth system science
study of earth as a system with interconnected parts
lithosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, biosphere
biosphere is likely easiest thanks to fossils
ecosystem
community of organisms and their environment
primary producers
marine terrestrial flying animals
water, ice, air
HAVE CHANGED OVER TIME
ordovician oceans
~450 ma
nautiloids declined after ordovician period
graptolites, brachiopods (major decline), trilobites (extinction) affected by end permian
end triassic: conodocts mass extinction
cretaceous oceans
~130 ma
turtles
marine reptiles, plesiosaurs
mosasaurs
diving birds
ammonites + ray finned fish
bolded: extinct in end cretaceous
stratigraphy and its varieties
chronostratigraphy
in time
lithostratigraphy
rock type
biostratigraphy
fossils
chemostratigraphy
chemistry
history of stratigraphy
1669 - steno suggested that deeper layers of rock must be older
1760s - ardunio started naming layers of rock in the alps based on depth and composition
1780s - button “uniformitarianism”
deeper : first
then layer establishment
uniformitarianism
stratigraphy
BUILT ON THE ORGANISATION OF LAYERS OF ROCK (STRATA)
f 2 rocks contain similar fossil species, they are likely to have been deposited from the same/similar time
can define biozones, which correlate rocks of similar age
ONLY WORKS BECAUSE SPECIES HAVE EVOLVED
huge amount of geological time was organised using fossils and still is today
extinction
was understood before evolution
there was a conclusion that elephants and mammoths are distinct species
there was also a conclusion that mammoths were once a living species but became extinct
tells us that fossils were once living before they became extinct
how was the chronostratigraphic chart accomplished
identifying rocks which are on top of others (biostratigraphy) and radiometric dating
law of superposition STENO
guiding principle of stratigraphy which states that rocks on top are younger than the rocks beneath
principle of original horizontality STENO
even if strata and rocks are tilted or folded today, they were originally flat
principle of lateral continuity STENO
OFTEN (but not always) layers of rock can be traced out laterally
they are continuous until they encounter other solid bodies that block their deposition ex. water
principle of cross cutting relationships STENO
IF ONE ROCK CUTS THROUGH ANOTHER, it must be younger
(crack in old rock is filled with new rock, new rock is younger")
unconformities
period of non deposition / erosion that disrupts stratigraphy
faulting
layers of rock can be offset by faults → disrupting stratigraphic sequence
push up “ reverse fault”, hanging down “normal fault”
faunal succession
fossils must change over time for biostratigraphy, reason for this: evolution
there are species that are ideal for biostratigraphy : INDEX FOSSILS
index fossils
common
white geographical distribution
short range: greater resolution of age (distinctive start and end) + SHORTER TIME A SPECIES EXISTED FOR
died in an environment with good fossilization and preservation
AMMONITES extinct from cretaceous end
adaptive radiation
Rapid diversification after a mass extinction into new forms and species
open new ecological niches, new resources and new selection pressures
background extinction
not all extinctions are mass extinctions
background extinctions wipe out 5-10% of the species per million years while mass extinctions wipe out 30% or more in one go
dodo birds
sixth major extinction?
the appearance and migration of modern humans may be associated with greater numbers of extinctions
for mammals, the current extinction rate is about 30 000 times faster than the background rate
the cretaceous palaeogene extinction ( K/PG EXTINCTION EVENT)
dinosaurs first appeared 240ma (in the triassic period) on pangaea; went extinct at the end of the Cretaceous period at 66 ma
at least 50% of all species went extinct including dinosaurs
on land no animals larger than a dog survived minus alligators and crocodiles
80-90% of marine species went extinct
half of plants went extinct
all non avian dinosaurs went extinct. birds survived and are now considered part of the dinosauria clade
what is a hypothesis that explains the cretaceous palaeogene extinction
ALVAREZ HYPOTHESIS
the impact of a large asteroid
led to the discovery of the iridium anomaly
1cm clay layer at the top of the cretaceous layer that is RICH IN IRIDIUM
iridium is rare on earth’s surface
MORE COMMON IN ASTEROIDS !!!!!!
suggested impact of a 10km + asteroid
ALVAREZ hypothesis / k-pg impact
iridium anomaly layer at the top of the cretaceous
found all over the world
NASA deep impact : confirms high amounts of iridium in comets and asteroids
soot concentration in iridium anomaly: FORM OF BLACK CARBON produced by burning organic matter
suggests that there were massive forest fires on a global scale
fern spores: first plants to colonize burned landscapes : excess of ferns = FERN SPIKE
tektites: natural glass particles produced by melting rocks during an impact
shocked quartz : lots of internal fracturing, which form when extraterrestrial impacts produce intense seismic waves that shatter rock : Magnitude 16 earthquake (omg)
shock lamellae : cross hatched lines in grain of quartz
chicxulub impact crater: crater that was formed in Mexico 66 ma ago by a 10 km wide asteroid
tanis fossil site 2022: broken remains of dinosaurs, broken fish fossils with tektites in gills (implying that tektites would have rained down across north America as they tried to breathe)
what made it worse:
limestone platform
dust
evaporites → sulphuric acid rain
deccan traps
chicxulub impact crater
mexico 66ma perfectly in time to serve as strong evidence of being the asteroid event on the boundary of the cretaceous period
10 km wide
layers of shocked quartz and tektites
concentric ringed structure
central peak
ROCK CALLED SUEVITE IN THE CRATER, suevite is a breccia (fractured) rock formed during impacts
contained evaporites : high rates of evaporation → precipitation of salts. evaporite minerals are rich in sulphates leading to sulphuric acid rain
devastated primary producers like phytoplankton
after the kpg impact
tonnes of dust would have COOLED THE PLANET and caused impact winter for years (freezing temperatures)
dust blocked sunlight and no more photosynthesis would occur
biological production and food chains collapsed in lands and oceans
the asteroid hit a carbonate platform full of limestones which increased atmospheric co2; vaporization during the impact : global temperatures rose 2-8 degrees which lasted for decades
deccan trap
erupted in indea in 66 ma as well : large igneous province with lots of flood basalt lava
this eruption may have contributed to the cretaceous palaeogene KPG mass extinction through the release of co2 and so2
iridium layers in basalts told us the year in which this happened
AFTER THE IMPACT, GLOBAL VOLCANIC ACTIVITY DOUBLED, which added to the stress on the biosphere
KPG extinction conditions
cretaceous biosphere was already stressed
deccan traps influence climate
breakup of pangea also meant changes in environments
asteroid was the main cause of extinction for dinosaurs
MAMMALS WERE BEST ABLE TO BURROW, HIDE, AND HIBERNATE, hence they were able to survive the conditions best
what animal today is the only surviving group of dinosaurs
modern birds
meteoroids
rocks smaller than 1m
meteors: as they enter earth’s atmosphere
meterorite: if it survives entry to earth’s atmosphere as an in tact rock
bolides: fireballs that explode in the atmosphere
SOURCE: ASTEROID BELT BETWEEN MARS AND JUPITER
asteroids
larger rocks (1m >); smaller than a planet
rocky and metallic
can be dwarf planets
SOURCE: ASTEROID BELT BETWEEN MARS AND JUPITER
comets
rock mixed with ice that are leftovers from planet formation
near the sun it has a tail of gas and dust particles
SOURCE:
kuiper belt
oort cloud
asteroid belt
meteoroids and asteroids come from the asteroid belt located in orbit of mars and jupiter
kuiper belt
similar to asteroid belt but larger
composed of frozen volatiles like water, methane, ammonia (ices)
more dwarf planets like pluto are here
some of the solar systems moons are believed to have originated here (neptune and saturns moons)
oort cloud
1000x farther from sun, halfway to alpha centauri
“edge of solar system”
composed of mostly ices
source of halley’s comet and hale boop
meteor influx
100 billion meteroids hit earth’s atmosphere every day
log graph
it is expected that a 10km sized object hits earth every 100 million years on average
shoemakers hypothesis
geological changes can arise from asteroid strikes, asteroid strikes are common, and impact craters form large circular structures associated with impact ejecta, shocked quartz, etc
shoemakers studied ries crater and noticed the building stone was suevite → 14 ma impact crater
we found more than 200 other examples on earth now, one of the oldest being in quebec : 214 ma
raup and sepkoski’s hypothesis
“there is believed to be a 25 myr cycle in impacts and extinctions”
possibly due to the gravitational distribution of the oort cloud. possibilities?
nemesis, the companion star
planet 9
movement through galactic plane
could just be a coincidence
theory of oort cloud that could be responsible for the 25 myr extinction: NEMISIS
the sun has a companian star far beyond the oort cloud whose orbit comes every 25 myr
gravitational effects kick comets more into inner solar system
if it were a brown dwarf or a black hole, it would be hard to detect
no evidence so far
theory of oort cloud that could be responsible for the 25 myr extinction: planet 9
existence of a distant planet far beyong neptune could shift oort cloud orbit
possibily came from viewing orbits of distant solar system bodies
no evidence so far and it is believed that it is unlikely
theory of oort cloud that could be responsible for the 25 myr extinction: moving through the galactic plane
solar system orbits through center of galaxy
galaxy isnt flat but has thickness of stars and material
as we move (sin graph shape kinda) through the denser parts of the galaxy, oort cloud could be disturbed
theory of oort cloud that could be responsible for the 25 myr extinction: chance, it isn’t actually a thing
there could be no cycle
dating and spacing is not always consistent
there have surely been more impacts that we arent sure of (deep sea ocean, etc)
we know that meteorites hitting isn’t the only cause of extinction
as such: NASA things the raup sepkoski hypothesis is not needed
our concern?
possibility of global catastrophe is a concern
civilisation ending impacts occur randomly and every 1 million years
tunguska russia, chelyabinks russia, near misses
tunguska russia
air blast; no impact crater levelled 3100 km² of forest and sent a shockwave around earth 2 times
no clue what it was as it was not on the ground, could have been or comit or an asteroid that bounced back and could still be orbiting the sun
it happened in a foresty area, if that happened in mainland, it would flatten from west vancouver to langley
chelybinsk russia
20 m asteroid that exploded 30km off ground (bolide)
entered atmosphere without warning and approached from the direction of the sun
asteroid 2019ok
july of 2019
100m diameter asteroid that passed within 73000 km of earth (1/5 distance to the moon), confirmation of existence was just 3 hours before it passed
asteroid 2005yu55
november 2011
360m diameter asteroid that is 4/5 of moon’s orbit; discovered 6 years before it passed earth
will come back in 2041
2075
eastern mediterranean event
june 2002
meteor air burst above mediterranean sea
unknown object and no fragment
similar to a small nuclear bomb
asteroid 99942 apophis
will approach earth 2029
370m diameter will pass 10x closer than the moon and closer than all communication satellites
believed to not hit earth, if it does, 5 km crater but no impact winter
comet shoemaker levy 9
jupiters gravity broke the comet apart, if it had hit earth, it would have wiped out life on the microbial level
jupiter: cosmic vacuum cleaner
our moon is large and it shields earth from potential impacts
torino scale
communicates threats of impacts on a scale from 0-10
risk assessment
spaceguard survey
identifies, catalogues, and studies near earth objects
asteroids larger than 1km are surveyed
large objects (esp those that can cause mass extinction) are tracked
neo surveyor spacecraft
planned space based infrared telescope that will survey the solar system for hazardous asteroids
dart (double asteroid redirection test)
testing to see if we can alter an asteroids impact by using an impactor
how are impact hazards unique
can be most devastating
are the only natural disaster that can be completely avoided
most important factor: TIME
mitigation strategies for impacts
fragmentation
rapid orbit adjustment
gradual orbit adjustment
ablation
ride the solar winds
fragmentation as a mitigation strategy
blowing asteroid up
we need to land on the asteroid and drilling into it
creates risk of multiple impacts + long preparation time
rapid orbit adjustment as a mitigation strategy
nuclear warhead or smash a projectile into the asteroid
requires warning period
gradual orbit adjustment as a mitigation strategy
using chemical, electric or nuclear propulsion
keeping an orbit the way we want it
predictable as we already use it for satellites but it requires a warning period
ablation as a mitigation strategy
focusing sunlight onto the surface of asteroids or using lasers to flash vaporize or ablate the asteroids mass/ deflect the objects path
we would have to place a satellite in orbit around an asteroid
riding the solar winds as a mitigation strategy
installation of solar sails / mirrors on the asteroid ; radiative pressures from sunlight would deflect it
requires a very long warning time
mitigation strategies
are real and there are many implementations being tested + it is being taken very seriously
however: all methods require research, warning time, and money
impacts are also very low frequency, we have cancer, climate change, hiv, pandemics, should we divert the money to impacts?
micromort
unit of risk:
1 in 1 million chance of death
micromorts a day = 23
value placed on risk: 1 micromort 50$
what goes in a preparedness kit
food for at least 3 days and water for a week
flashlight + batteries
radio / handcranked battery
meds blankey
charger pen notebook
poopoo stuff
teeth brushies
first aid
glasses and contacts
small bill cash
whistle
map
pico is?
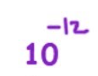
nano is?
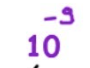
micro is ?