DPT 642: The Hip
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
both
is the hip built for stability or mobility?
supports organs and muscles of the bowel, bladder and reproductive system
what is the function of the pelvis?
fovea
only portion of femoral head that is not protected/covered with hyaline cartilage
superior-anterior
region of the femoral head & acetabulum has the most developed cartilage
weight bearing demands
why does the superior-anterior region of the femoral head & acetabulum have the most developed cartilage?
superior-medial anterior
What is the orientation of the femoral neck?
inferior-lateral anterior
what is the orientation of the acetabulum?
anterior bowing
this feature of the femur is important for weight bearing, allowing it to dissipate forces
posterior
compression forces on the femur are dissipated in what direction
anterior
tensile forces on the femur are dissipated in what direction
external rotators
the greater trochanter serves as an attachment point for mainly these kind of muscles
frontal plane stability
muscles that attach to the greater trochanter have a major role in...?
helps maintain negative pressure
what effect does the suction effect between the acetabular labrum and femoral head have on the intraarticular space?
may help develop hip torque to help them flex their hip and help propel them. Keeps them stable and upright
how can a patiet with paraplegia use the iliofemoral ligament to their advantage?
pubofemoral ligament
Limits abduction and extension. Limits some external rotation
iliofemoral ligament or Y ligament
Limits external rotation and extension; consists of 2 bands
ischiofemoral ligament
Limits internal rotation and extension, some adduction
ligamentum teres
Connects femoral head to acetabulum
it is a conduit for blood supply to the femoral head
why is ligamentum teres critical to the pediatric population?
lumbar plexus (L2-L4)
innervation of the anterior compartment muscles
sacral plexus
innervation of the deep muscles
greater sciatic foramem
where the sacral plexus exits out of
sciatic nerve
largest nerve of the sacral plexus
piriformis
sciatic nerve occasionally passes through this muscle, causing compression of the muscle
anterior
primary hip flexors are located on this side
Iliopsoas complex, rectus femoris, tensor fascia latae, sartorius, pectineus, and adductors (depends on leg position)
name the primary hip flexors
slightly flexed
rectus femoris contributes to hip flexion most often when the knee is...?
Adductor brevis, gracilis, anterior fibers of gluteus minimus
name the secondary hip flexors
glutes and hamstrings
what are the primary hip extensors?
extension
the most effective way to target the hamstrings is to place the knee into....?
puts them into active insufficiency
when targeting the hamstrings, if the knee is flexed, what does this do to the hamstrings?
gluteus medius and some adductor magnus
secondary hip flexors
lateral
hip abductors are located on this side
gluteus medius and minimus and tensor fasciae latae
primary hip abductors
side lying leg raise
How would we assess the function of the hip abductors in a non-weight bearing position?
trendelenburg sign
hip drops towards side of weakness during gait; weight-bearing indication of weak abductors
medial
what side are the hip adductors located on?
adductor brevis/longus/magnus
primary hip adductors
gluteus maximus
hip external rotation is mainly controlled by which muscle?
piriformis, obturator internus/externus, superior/inferior gemelli and quadratus femoris
muscles that stabilize & contribute to hip external rotation
No
is any muscles primary action external and/or internal rotation?
tensor fasciae latae, adductor longus/brevis, pectineus and anterior fibers of gluteus medius and minimus
internal rotators of the hip are....?
Full extension, full internal rotation and slight abduction
describe closed-packed position for the hip
30 degrees flexion, 30 degrees abduction and slight external rotation
describe open-packed position for the hip
hamstrings
structures taut in hip flexion- knee extended
posterior and inferior capsule; gluteus maximus
structures taut in hip flexion- knee flexed
primarily iliofemoral ligament, anterior capsule, some fibers of the pubofemoral and ischiofemoral ligaments and iliopsoas
structures taut in hip extension- knee extended
rectus femoris
structures taut in hip extension- knee flexed
pubofemoral ligament, adductor muscles
structures taut in hip abduction
IT band, abductor muscles (TFL & gluteus medius)
structures taut in hip adduction
isciofemoral ligament, external rotator muscles (piriformis and gluteus maximus)
structures taut in hip internal rotation
iliofemoral and pubofemoral ligaments; internal rotator muscles (TFL and gluteus minimus)
structures taut in hip external rotation
angle of inclination
angle between shaft of femur through femoral neck
125 degrees
normal angle of inclination
hip stability
what does angle of inclination affect?
coxa vara
angle of inclination less than 125 degrees
improves joint stability, increases moment arm for hip abductor force
"positive" clinical implications of coxa vara
decreased function length of hip abductor muscles, decreased bending moment
"negative" clinical implications of coxa vara
sheer force across femoral neck, which puts them more at risk for injury
decreased bending moment in coxa vara increases...?
coxa valga
angle of inclination significantly more than 125
less sheer force across femoral neck, increases functional length of femoral muscles
"positive" clinical implications of coxa valga
decreases moment arm for hip abduction, favors joint dislocation and instability
"negative" clinical implications of coxa valga
version (torsion) angle
Angle formed between femoral neck and line distally bisecting femoral condyles in transverse plane
the amount of internal/external rotation ROM of hip
what does version/torsion angle significantly affect?
anteversion
excessive anterior placement of femoral neck in transverse plane.
inward toe pattern to increase hip stability
how would someone with anteversion appear to walk? why?
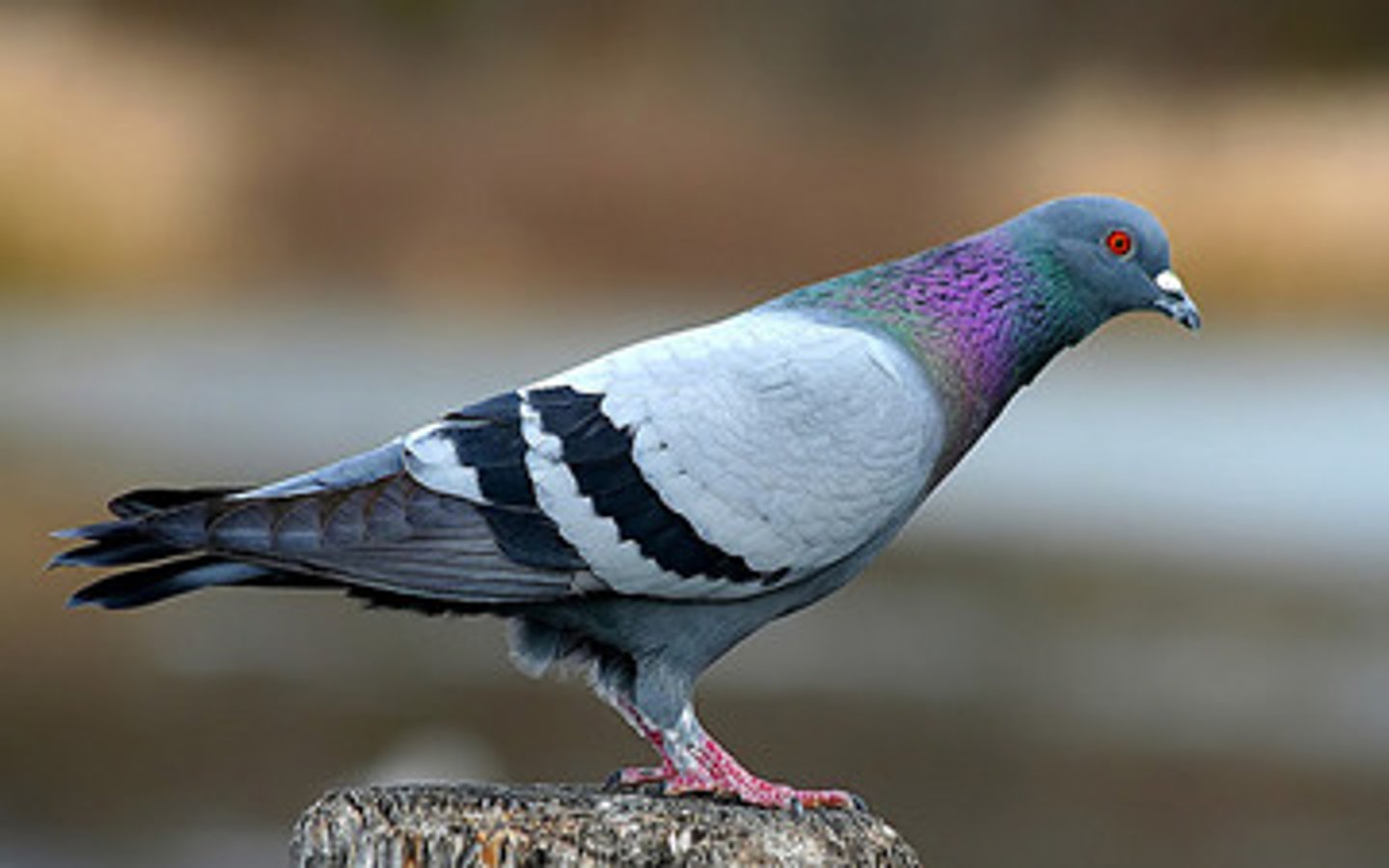

external rotation
in anteversion there is less...?
retroversion
excessive posterior placement of femoral neck in transverse plane.
decrease
does retroversion increase or decrease version angle?
increase
does anteversion increase or decrease version angle?
externally rotated to increase stability
how would someone with retroversion appear to walk? why?
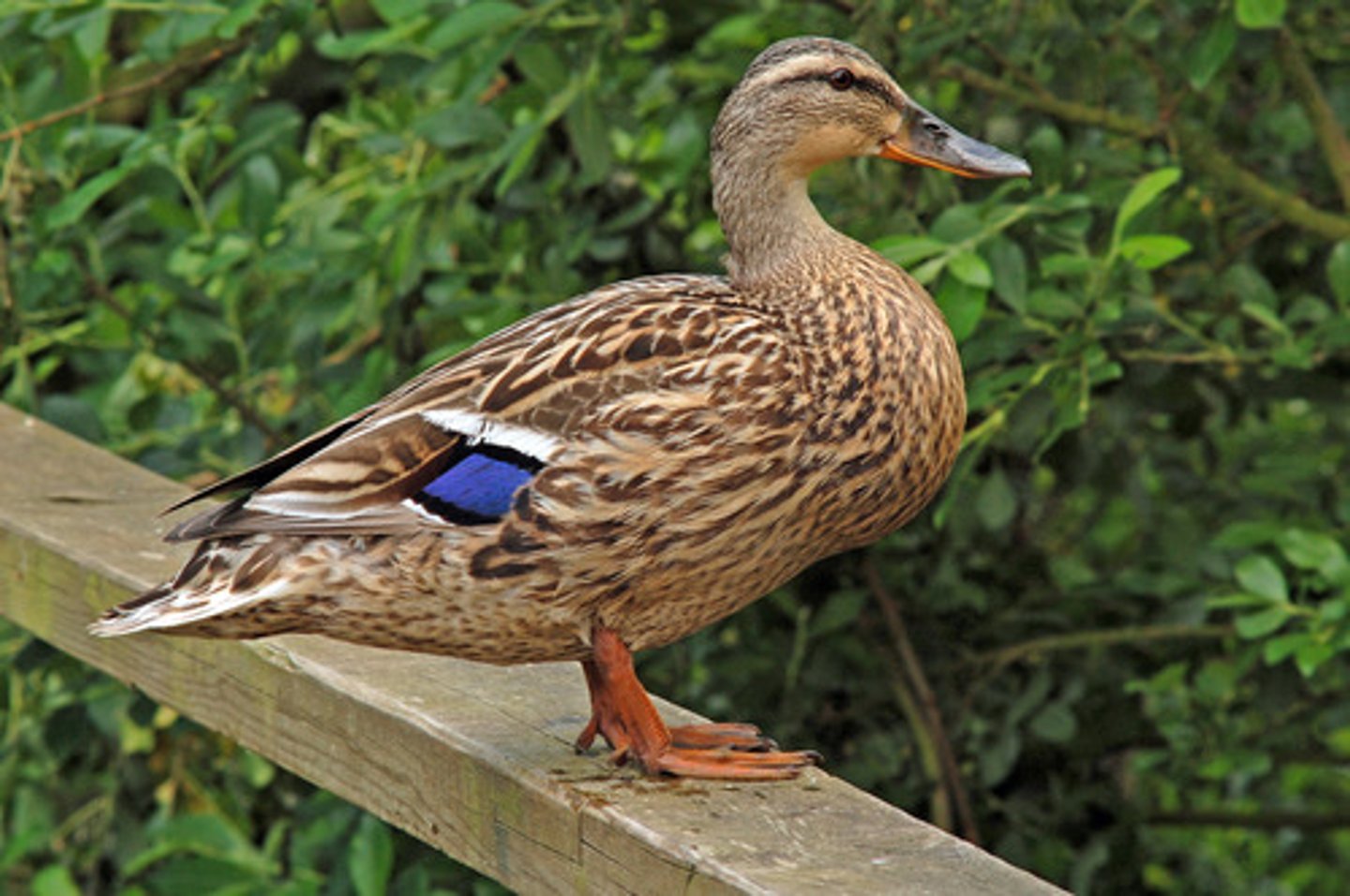

internal rotation
retroversion may limit....?
acetabular coverage
take center edge angle (center of femoral head through center of acetabulum)
pincer acetabular impingement
Abnormal shape of acetabulum; More excessive coverage of acetabulum on femoral head and neck
Cam Acetabular Impingement
Abnormal shape of the femoral head; Femoral head is abnormally shaped and cannot rotate smoothly in the acetabular labrum
compact bone
dense; located along cortex of lower femoral shaft and entire shaft. Allows for larger shear and torsion forces
cancellous bone
porous, spongy/trabeculae structure. Elasticity allows for repetitive external forces
Wolff's Law
Bone will adapt to the repetitive mechanical stresses it experiences
Plays big role in patients who have bone density issues
spins
during hip flexion and extension, the femoral head ____ on the acetabulum
lateral, medial
during hip abduction, there is a ____ roll and _____ slide
medial, lateral
during hip adduction, there is a ____ roll and _____ slide
posterior, anterior
during hip external rotation, there is a ____ roll and _____ slide
anterior, posterior
during hip internal rotation, there is a ____ roll and _____ slide
hip hike
pelvic on femoral abduction
drop down from hip hike
pelvic on femoral adduction
planted pivot
pelvic on femoral internal/external rotation
anterior pelvic tilt
pelvic on femoral flexion
posterior pelvic tilt
pelvic on femoral extension
clinical applications of a straight leg raise
Psoas and rectus used
Rectus abdominis needs to engage to prevent anterior pelvic tilt
Weak abs increase lumbar lordosis
clinical implications of kicking a ball with the right foot
Right is more of femoral on pelvic adduction
Left is pelvic on femoral adduction
figure 4 stretch
how to stretch piriformis
don't have them round the spine- puts pelvis into posterior tilt
how to maximize the strecth in hamstrings?
Want to engage rectus abdominis and glutes on side stretched to prevent pelvic tilting
when streching quadsm what do you want to engage and why?
to distribute forces to other side and stabilize other side
why are canes used on the opposite side?
for center of gravity purposes to keep them upright
When carrying groceries, why should we have them carry bag on same side?
skip
STUDY CHECKPOINT!
I am sure you are doing wonderful. Don't forget to take a break to refuel and recharge your body and brain. It's probably time to touch some grass. 💚
answer is 'skip'