Need To Know Terms for AP Comp Gov Exam
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
129 Terms
Anarchism
A political ideology which believes in eliminating the state as a whole
Citizenship
An individuals relationship to the state where they swear allegiance to the state and the state in return is obligated to provide rights to said citizens
Communism
A political-economic system in where all wealth and property are shared to eliminate exploitation
Conservatives
A political attitude that supports the current order and is resistant to change
Culture
Basic institutions that define a society
Ethnic Conflict
A conflict where different ethnic groups struggle to achieve certain political or economic goals at each other's defense
Ethnic Identity
Specific attributes and societal ideals that make one group of people culturally different from another
Fascism
A political ideology that supports superiority of one group of people and inferiority of another ex: Hitler
Fundamentalism
A view of religion as absolute that should be legally enforced by making faith the sovereign authority
Liberal Democracy
A political system that supports participation, competition and liberty where emphasizes humans equality and freedom ex: American gov
Liberals
Those with a political attitude that favors evolutionary change and that existing governments can be instruments of positive change
Nation
A group that desires self-government through an independent state
National Conflict
A conflict in where one or more groups within a country develop clear aspirations for political independence, clashing with others as a result
Political Attitude
Description of one's views regarding the speed and methods with which political changes should take place
Political Culture
A population’s values and beliefs about the role of government, the rights of the individual, and the extent and role of citizens in controlling government policymaking
Political Ideology
The basic values held by an individual on the fundamental goals of politics or the balance between freedom and equality
International Relations
How countries interact with one another ex: foreign policy, war, trade
Institutions
Organizations or activities put in place that serve value to exist
Politics
The struggle in any group for power that will give person(s) power over a larger majority
Power
The ability to influence or impose upon other's free will
Comparative Method
The means by which socialists make comparisons across countries
Inductive Reasoning
Uses cases(countries) to generate hypotheses about political history
Deductive Reasoning
Tests hypotheses on cases
Correlation
An apparent association between certain factors or variables
Casual Relationship (Causation)
This happens because this did that (cause + effect) ex: You hit him in the nose so it bled
Selection Bias
An issue comparative researchers face in which the sample is not representative of the population being studied, so that some opinions are over- or underrepresented
Qualitative Method
Study type that uses few meaningful cases over numerous cases
Quantitative Method
Study type that uses numerous numbers from many cases
Formal Institution
An institution based on officially sanctioned and written rules ex: electoral systems
Informal Institution
An institution based on unwritten, unofficial rules ex: morals
Equality
A material standard of living shared by individuals within a population
State
A monopoly of force and a set of political institutions that secure the population and generate policy
Sovereignty
Ability of a state to govern its territory free from control of its internal rivals or external actors
Regime
The fundamental political system and norms of a country, defining how power is exercised and how the government interacts with society.
Government
The leadership that runs the state
Country
The combined political entities: state, regime, government, population
Legitimacy
A value of someone or something is recognized as right and proper
3 types of legitimacy
Rational-legal legitimacy, traditional legitimacy, charismatic legitimacy
Traditional Legitimacy
Built by habit + custom over time, stressing history and being strongly institutionalized ex: monarchies
Rational-legal legitimacy
Built on rules and procedures and the offices that create and enforce those rules, strongly institutionalized
Charismatic Legitimacy
Built on the force of ideas and the presence of the leader, weakly institutionalized ex: Hitler
Federalism
Powers such as taxation, lawmaking and security are devolved down to smaller regional legislatures which are protected in the constitution ex: US, providences in Canada
Asymmetric Federalism
Power is divided unevenly amongst regional bodies ex: Canada's providences
Unitary
Power concentrated at the national level and local authority is limited
Devolution
Separating power farther from the bstate and closer to the people
Failed State
States that are not able to fulfill basic tasks: defend their territory, manage economy usually have corruption or war
Capacity
The ability of the state to wield power in order to carry out the basic tasks of providing security + reconciling freedom and equality.
Autonomy
The ability of a state to wield its power independently of the public or international actors
Symmetric federalism
All regions have the same powers ex: US states
Political Economy
The study of interaction between states and markets
Markets
The interaction between the forces of supply and demand that allocates resources. The medium through which buyers and sellers exchange goods.
Property
Goods or services that are owned by a individual or group, privately or publicly
Public Goods
Goods, provided or secured by the state, available to society, and which no private person or organization can own
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The total market value of all goods and services produced by a country over a period of one year
Central Bank
The state institution that determines how much money is flowing through the economy, as well as how much it costs to borrow money
Inflation
An outstripping of supply by demand, resulting in an increase in the general price level of goods & services and the resulting loss of value in a country's currency
Deflation
A period of falling prices and value goods, services, investments and wages due to less money circulating
Monopoly
A single producer that is able to dominate the market for a good or service without competition
Tariffs
A tax on imported foreign goods
Quotas
A nontariff barrier that limits the quantity of a good that may be imported into a country
Liberalism
Political system that favors a limited state role in society and economy and laces a high priority on individual political and economic freedom
ex. United Arab Emirates, United States, United Kingdom
Capitalism
A system of production based on private property and free markets
Social Democracy
Political-economic system in which freedom and equality are balanced through state control of the economy and social expenditures
ex. Sweden, has free trade but but government owned and affiliated businesses. Lots of public goods are provided to the public through high taxation
Communism
Political-economic system in which all wealth & property are shared to prevent exploitation
ex. China, gov owns everything
Purchasing Power Parity (PPP)
A statistical tool that attempts to estimate the buying power of income across different countries by using prices in the USA as a benchmark
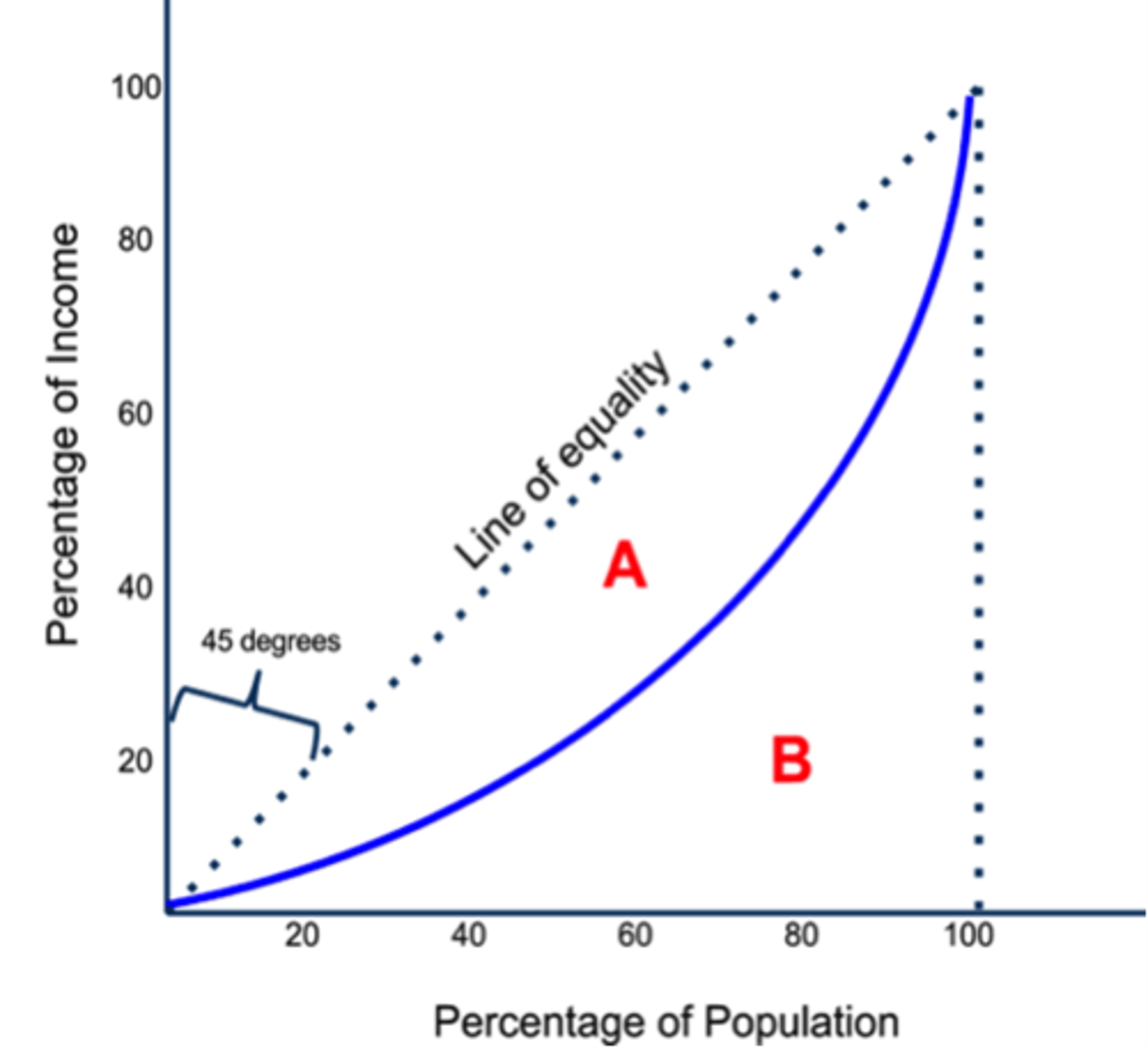
Gini Index
A statistical formula that measures the amount of inequality in a society; its scale ranges from 0-100, where 0 corresponds to perfect equality and 100 to perfect inequality
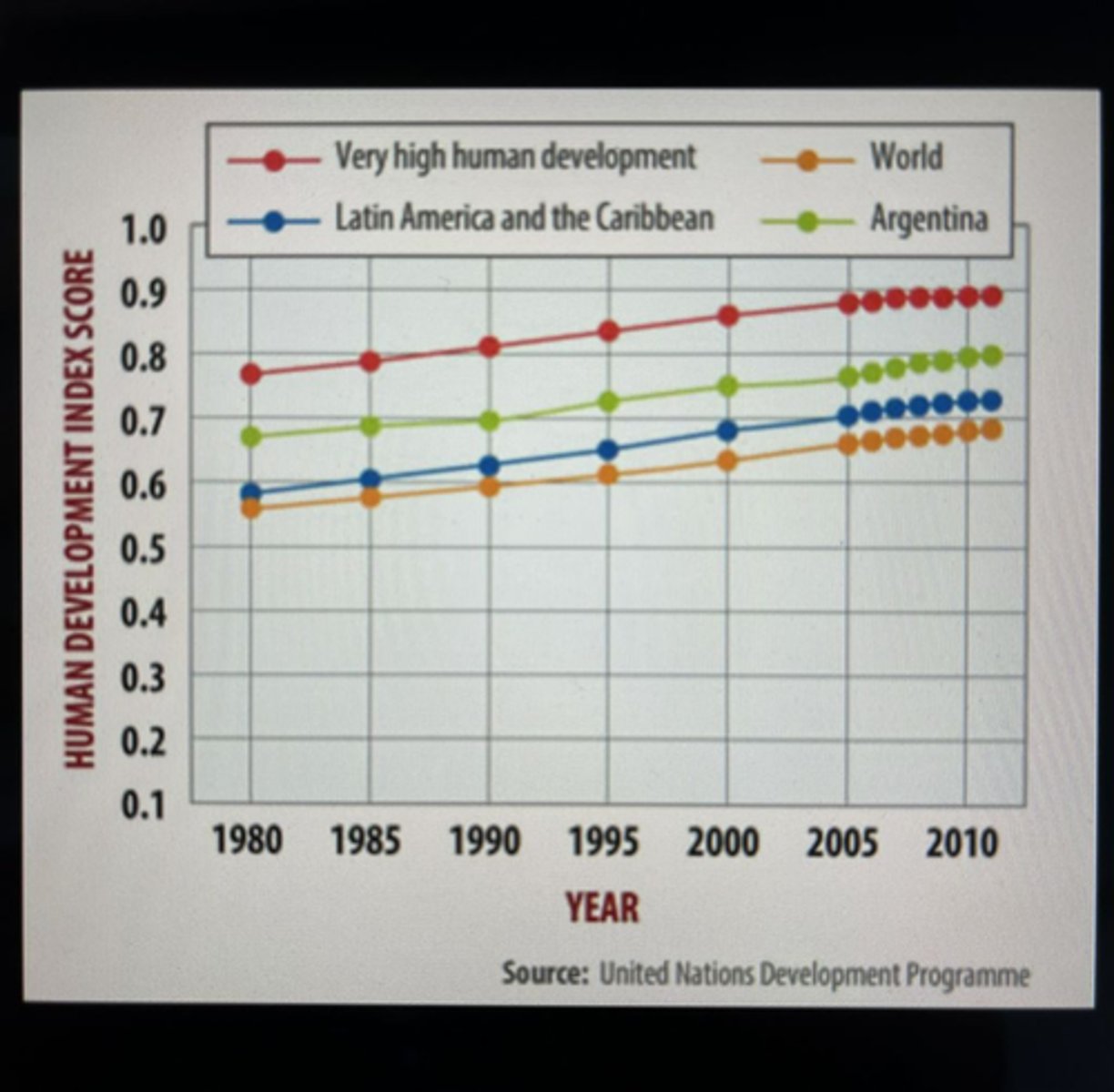
Human Development Index (HDI)
A statistical tool that attempts to evaluate the overall wealth, health, acknowledgement of a country's people
Economic Liberalization
Changes consistent with liberalism that aim to limit the power of the state & increase the power of the market and private property
Revolution
Public seizure of the state in order to overturn the existing government & regime
Terrorism
The use of violence by non-state actors against civilians in order to achieve a political goal, can be ideological based
Guerrilla War
A conflict where by non-state combatants who largely abide by the rules of war target the state
Mercantilism
A political-economic system with the goal to increase state power by maximizing wealth
ex. Japan 50-80's, England's colonies
Interests rates + banks
High interest: less loans, more money saved = less money circulating through economy (can cause deflation)
Low interest: more loans, less money saved = more money circulating through the economy (can cause inflation)
Nontariff regulatory barriers
Health, packaging or other regulations use to limit imports of foreign goods besides taxing and quotas
Gross Domestic Product Per capita (GDP)
This divides the GDP by total population which gives a measure of the average person's contribution to generating a country's wealth in a year.
Direct Democracy
Public participates directly in governance and policy making; historically found in small communities such as ancient Athen's
Indirect Democracy
Public participates indirectly through its elected representatives; the prevalent form of democracy in the modern age
Civil Society
Any non-governmental organization outside of the state that help people define and advance their own interests
ex. book club, girl scouts, sports team
Executive branch
The branch of government that carries out the laws and policies of a state
Head of State
The executive role that symbolizes and represents the people both nationally and internationally
ex. Monarch, Prime Minister or in some places the President
Head of Government
The executive role that deals with the everyday tasks of running the states such as formulating and executing policy
Legislature
The branch of government changed with making laws
Bicameral System
A political system in which the legislature comprises of two houses
Unicameral System
A political system in which the legislature comprises of one house
Rule of Law
A system in which all individuals and groups, including those in government, are subject to law, irrespective of their power or authority
Constitutional Court
The highest judicial body in a political system that decides whether laws and policies violate the constitution
Judicial Review
The mechanism by which courts can review the actions of government and overturn those that violate the constitution
Parliamentary System
A political system in which the roles of head of state and head of government are assigned to separate executive offices & the roles of the legislative branch and executive branch are fused into one branch.
"Vote of No Confidence"
A vote taken by legislature as to whether its members can continue to support the current prime minister. Depending on the country, the vote can force resignation of prime minster or lead to new parliament elections. (Legislature gives the vote and the party removal is an internal party decision)
In Parliamentary systems people vote for...
The party they want and the party that wins the majority send their head of party to be the prime minister. If no majority wins the largest minority party usually names the prime minister in a coalition government
3 types of gov. with Prime Ministers
1. Constitutional Monarchy
2. Parliamentary Republic
3. Semi-Presidential
Constitutional Monarchy
The head of state is a monarch while the head of government resides as the democratically elected prime minister
ex. UK, Denmark, Japan
Parliamentary Republic
Prime minister is head of gov. while President is the head of state
Semi-presidential
An executive sysytem that divides power between two strong executives, prime minister and president. President helps set policy while prime minister executes it.
ex. Russia, South Korea, France
2 types of semi-presidential systems of government
1. President-parliamentary system
2. Premier-presidential system
President-parliamentary system
President is head of gov. and picks their own cabinet and prime minister. Prime minister and cabinet also report to parliament which can dismiss them with a vote of no confidence. The president can also remove these officials without cooperation from parliament
Premier-presidential system
A president may intially appoint a cabinet and a prime minister. Those officials report to parliament and only parliament can remove them from office.
Presidential system
A political system in which the roles of head of state and head of government are combined in one executive office. The president directs the cabinet and formulates legislation and international and domestic policies. President serves for a fixed term and can not be easily removed.
Electoral systems
A set of rules that divides how votes are cast, counted, and translated into seats in legislature
Constituencies
A geographical area that the area's elected officials represent