Ecology 2022
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:17 PM on 11/15/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
1
New cards
Ecology
Scientific study of interactions among organisms and between organisms and their environment
2
New cards
Habitat
the natural home or environment of an animal, plant, or other organism.
3
New cards
Biome
A group of ecosystems that share similar climates and typical organisms
4
New cards
Community
All the different populations that live together in an area
5
New cards
Ecosystem
A biological community of interacting organisms and their physical environment.
6
New cards
Abiotic Factors
Nonliving components of environment.
7
New cards
Biotic Factors
All the living organisms that inhabit an environment
8
New cards
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
9
New cards
Limiting Factors
Conditions in the environment that put limits on where an organism can live
10
New cards
climax community
A stable, mature community that undergoes little or no change in species over time
11
New cards
Pioneer Species
First species to populate an area during primary succession
12
New cards
primary succession
An ecological succession that begins in an area where no biotic community previously existed
13
New cards
secondary succession
Succession following a disturbance that destroys a community without destroying the soil
14
New cards
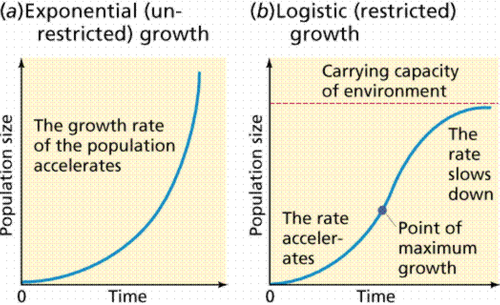
logistic growth
Growth pattern in which a population's growth rate slows or stops following a period of exponential growth
15
New cards
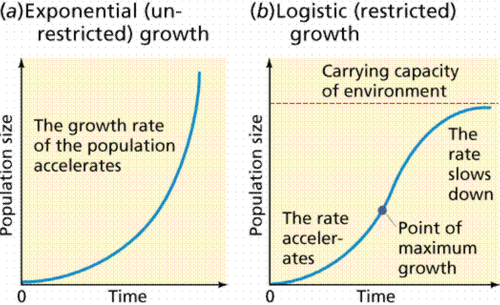
exponential growth
Growth pattern in which the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate
16
New cards
predator
An animal that hunts other animals for food
17
New cards
density dependent factors
A limiting factor of a population wherein large, dense populations are more strongly affected than small, less crowded ones.
18
New cards
density-independent factors
limiting factor that affects all populations in similar ways, regardless of population size
19
New cards
mutualistic
both organisms benefit
20
New cards
Commensalism
Relationship where one organisms benefits, the other isn't effected
21
New cards
Parasitism
A relationship between two organisms of different species where one benefits and the other is harmed
22
New cards
symbiotic relationship
close interaction between species in which one species lives in or on the other
23
New cards
niche
Full range of physical and biological conditions in which an organism lives and the way in which the organism uses those conditions
24
New cards
population density
A measurement of the number of people per given unit of land
25
New cards
prey
An organism that is killed and eaten by another organism
26
New cards
competition
the struggle between organisms to survive in a habitat with limited resources
27
New cards
host
an animal or plant that nourishes and supports a parasite
28
New cards
Autotroph
An organism that makes its own food
29
New cards
Heterotroph
organism that obtains energy from the foods it consumes; also called a consumer
30
New cards
food chain
A series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten
31
New cards
food web
a system of interlocking and interdependent food chains.
32
New cards
Decomposer
An organism that breaks down wastes and dead organisms
33
New cards
trophic level
Each step in a food chain or food web
34
New cards
Biomass
total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level
35
New cards
carbon cycle
The organic circulation of carbon from the atmosphere into organisms and back again
36
New cards
water cycle
The continuous process by which water moves from Earth's surface to the atmosphere and back
37
New cards
nitrogen cycle
The transfer of nitrogen from the atmosphere to the soil, to living organisms, and back to the atmosphere