ORGO Exam 2
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
what does it mean to draw an enantiomer?
change all wedge/dashes from the original to be opposite (have opposite R/S configuration at every asymmetric center)
is axial or equatorial more stable?
equatorial is always more stable (lower energy)
what does it mean to draw a diastereomer?
only some of the wedge/dashes change from the original compound not ALL (have oppositie R/S configuration at some asymmetric centers, but not all)
what is a conjugate acid?
when a base accepts a proton (H+)
what is a conjugate base?
remains after an acid loses a proton (H+)
nucleophile
negative (-) or partially negative (δ-) charge, but loves protons (+)
electrophile
positive (+) or partially positive (δ+), but loves electrons (-)
what does it mean when there is a low pka?
the acid is strong
what does it mean when there is a high pka?
the acid is weak
Keq <1
equilibrium favors the reactants (more reactants than products)
Keq >1
equilibrium favors products (more products than reactants)
Keq =1
roughly equal amounts of products & reactants
What must a chiral compound or asymmetrical center need to be considered?
4 different groups attached to it
what can never be apart of an asymmetric center?
double and triple bonded carbons
how do you assign priorities in the R/S system?
based on atomic # (from high to low)
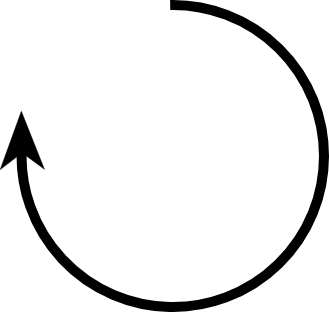
what is clockwise configuration?
R
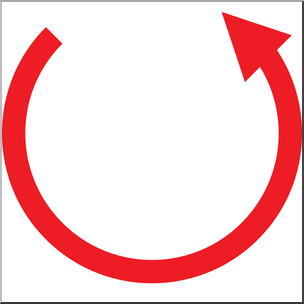
what is counterclockwise configuration?
S
what tells us how many possible stereoisomers there are?
2n (24=16)
dextrorotatory
positive (+) twists to the right
levorotatory
negative (-) twists to the left
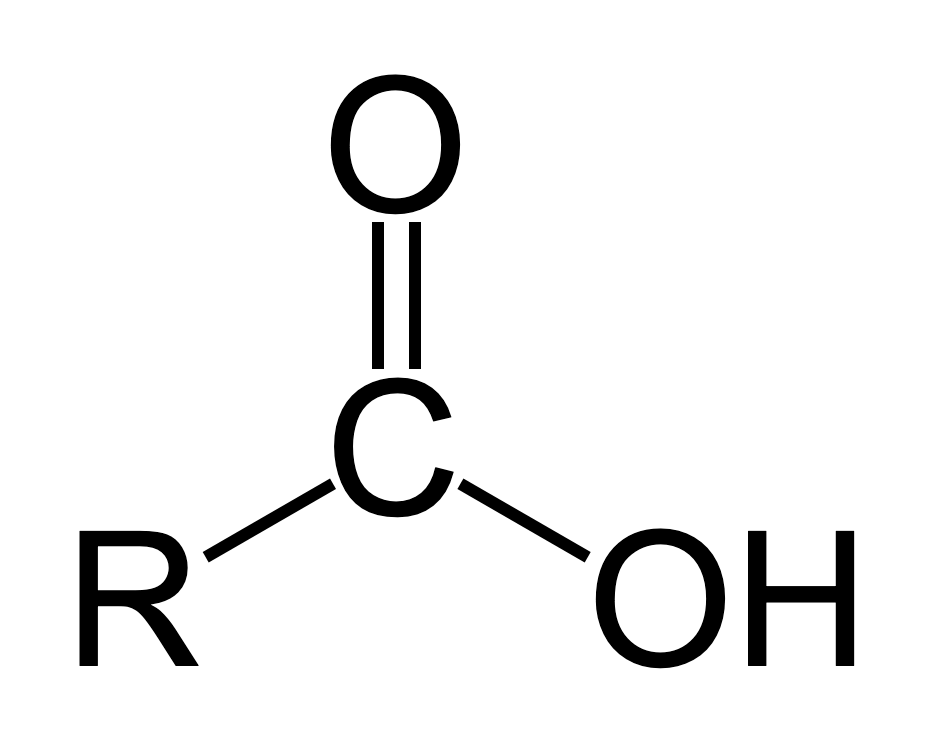
what is the pka for carboxylic acid (COOH)?
5
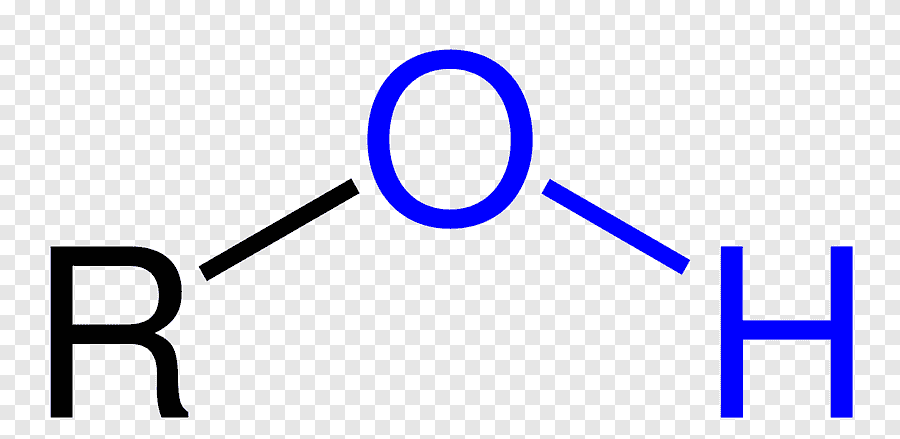
what is the pka of Alcohol (OH)?
15
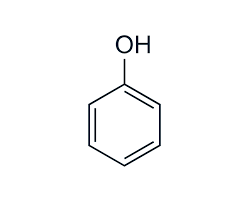
what is the pka of phenol?
10
does having a positive charge make a compound more acidic or basic?
acidic
acid base equilibrium favors the side with the…
weaker acid (higher pka)
for an endergonic reaction ΔG is….
positive
for an exergonic reaction ΔG is…
negative
what is the equilibrium constant (Keq)?
products/reactants
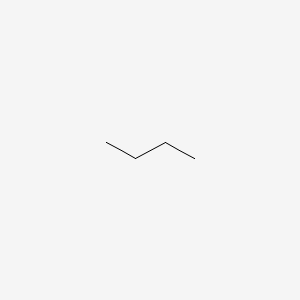
T or F: butane is a chiral molecule
False
is ethane saturated or unsaturated?
saturated
is ethene saturated or unsaturated?
unsaturated
the lowest priority group (likely H) when determining R/S has to be on a ________.
dash
if the lowest priority group is NOT on a dash and it is on a wedge the R/S configuration…
switches to whatever is opposite (R changes to S - S changes to R)
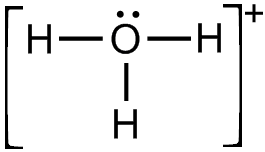
what is the pka of H3O+?
0 (strongest acid)
what is an acid?
proton donor (usually the attacked H)
what is a base?
proton acceptor (lone pair that is attacking the H)
what is the pka of NH3+?
10
what is the order of carbocation stability (least stable to most stable)?
methyl → primary (1°) → secondary (2°) → teritary (3°)
when comparing the pka’s of acids to determine which is stronger/weaker, what do you look at when the molecule is identical?
inductive effects, whichever one is closer to the functional group is the stronger acid
when comparing pka’s and the functional groups are the same but the element is different, what do you do?
look at which element is more electronegative to determine which acid is stronger/weaker
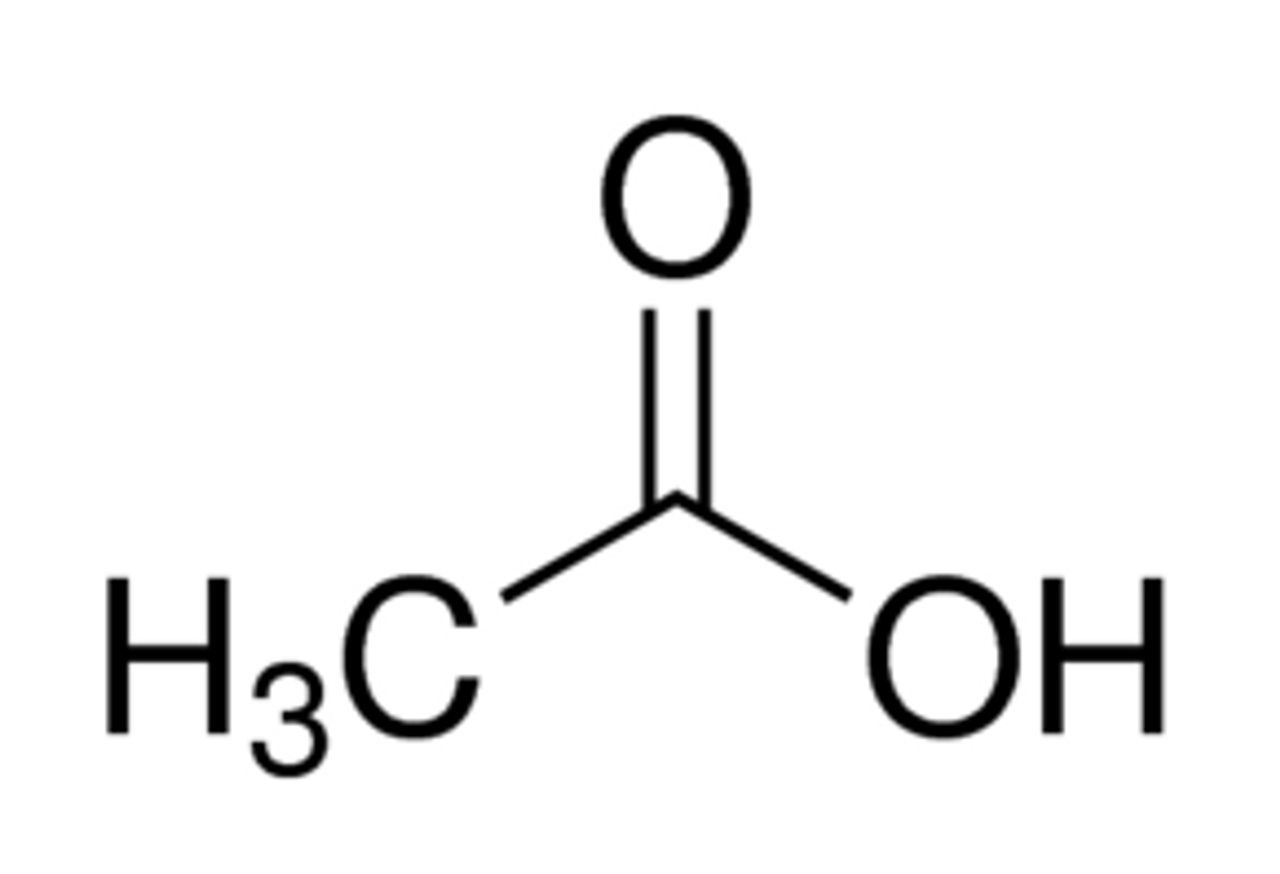
what is the pka of acetic acid?
5
how many arrows are in an Sn2 reaction?
2 arrows
how many arrows are in an E2 reaction?
3 arrows
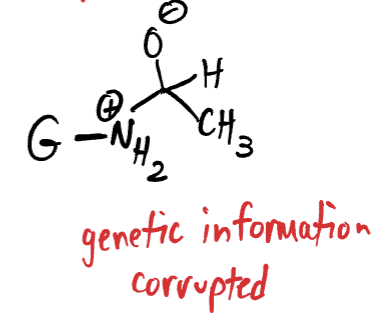
how does chronic drinking cause cancer?
Guanine (apart of our DNA) contains an NH2 (amine) group sticking off of it.
In the event of chronic drinking, the body’s ability to convert acetaldehyde into harmless vinegar can become overwhelmed.
Acetaldehyde becomes highly reactive and acts as an electrophile.
The NH2 Group on Guanine acts as the nucleophile.
The Nitrogen in NH2 attacks the partially positive carbon on acetaldehyde.
this forms a corruption to the Guanine and damage to the DNA blueprint leading to genetic mutations, and ultimately cancer.
You now have this connection between the acetaldehyde and guanine for the rest of your life.
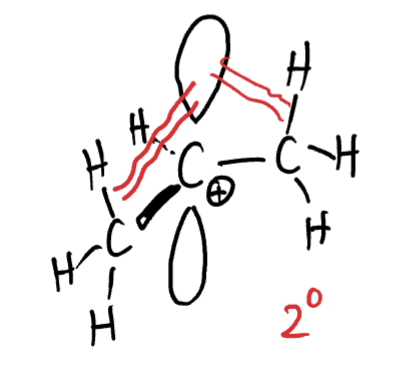
carbocations have an empty p orbital, what happens to allow for hyper-conjugaton?
Nearby C-H bonds can line up with the orbital allowing for hyper-conjugation
the strength of an acid is determined by the stability of its…
conjugate base
inductive effects are…
distance depended
ex: as electronegative Br moves away from where the (-) will be, the pka increases (becomes weaker)
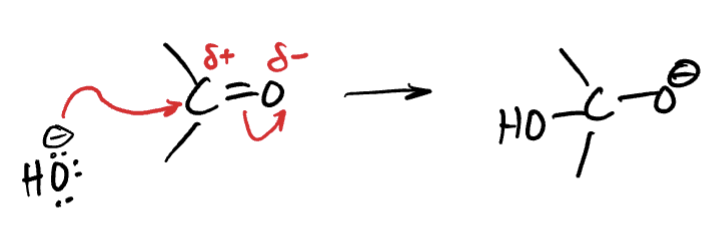
what occurs in a nucleophilic addition?
all atoms in the reactants appear in the products, there is no leaving group!
when does electrophilic addition occur?
when an electrophile (H+, NO2+, Cl+) and a non-polar pi bond approach
when performing an Sn2 reaction, what does the attacking?
draw arrow from whatever has a negative charge
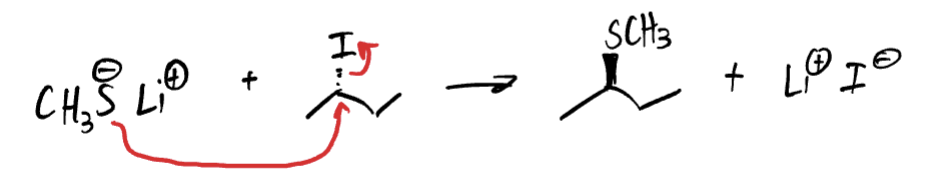
how do you identify alpha carbons?
attached to the leaving group (often Br, F, Cl, I)
how do you identify beta carbons?
carbon atom bonded to the alpha carbon (beta carbons must also have hydrogens attached to them to be considered an E2 reaction)
______ are responsible for color.
alkenes
what slows Sn2 reactions down?
steric hinderance
when an Sn2 reaction occurs, what will happen to the dash/wedge configuration?
they will flip to whatever is opposite of the reactant (dash turns to wedge, wedge turns to dash)
ex: wedge in reactant becomes dash in product
whenever you are drawing resonance, what goes away?
Hydrogen must be removed
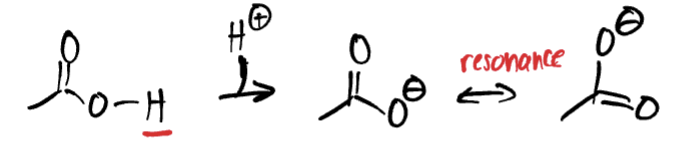
BPA
base proton acid
APD
acid proton donor