all first semester of anatomy
1/390
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
391 Terms
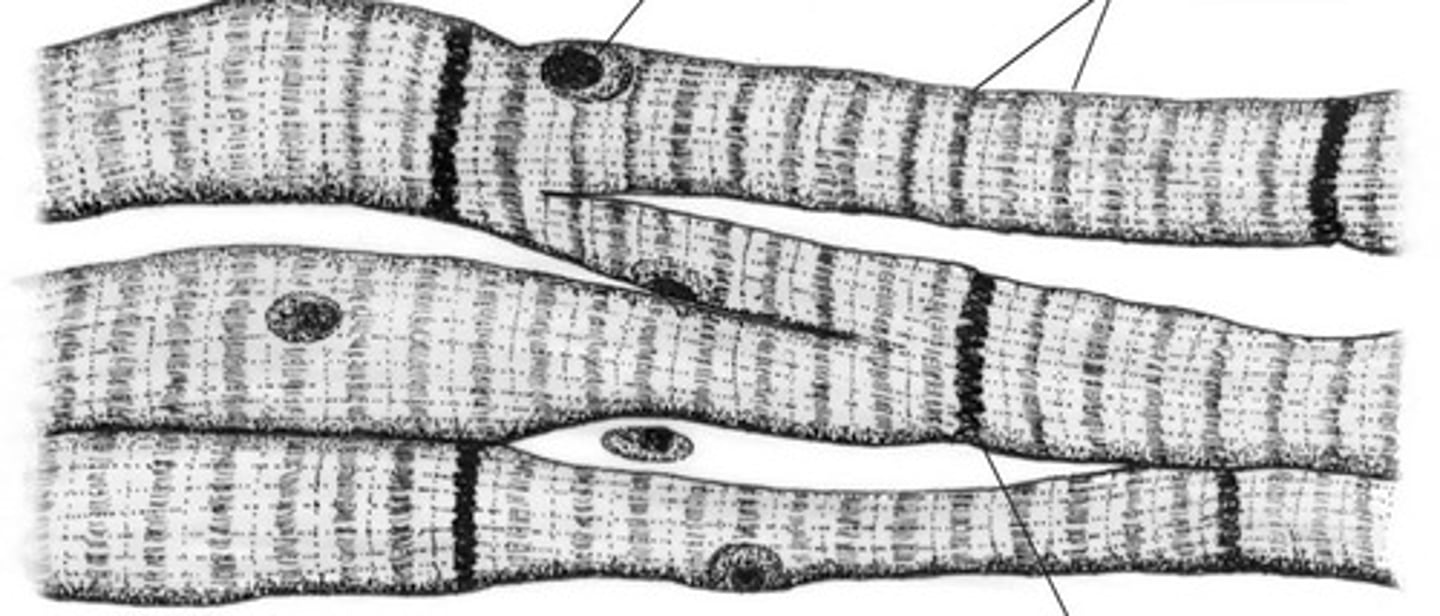
skeletal muscle
voluntary, multi-nucleated striated muscle that allows movement, maintains posture, stabilizes joints and generates body heat

myo
prefix meaning 'muscle'
sarco
prefix meaning 'flesh', indicates the word is related to muscle
basic jobs of all muscles
contract and relax
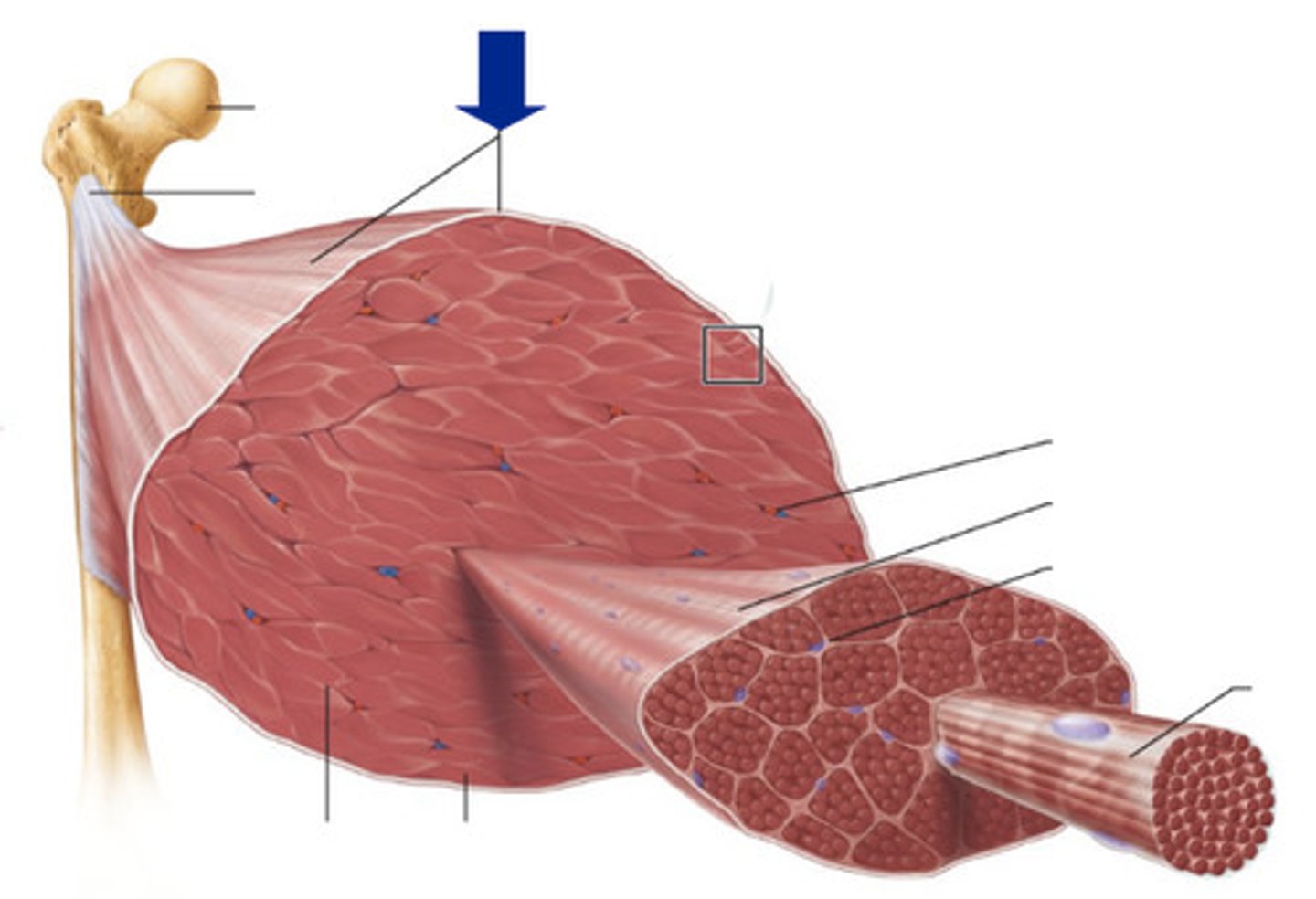
tendon
cord-like extension of the epimysium made of dense connective tissue that attaches to bone, cartilage or other connective tissue
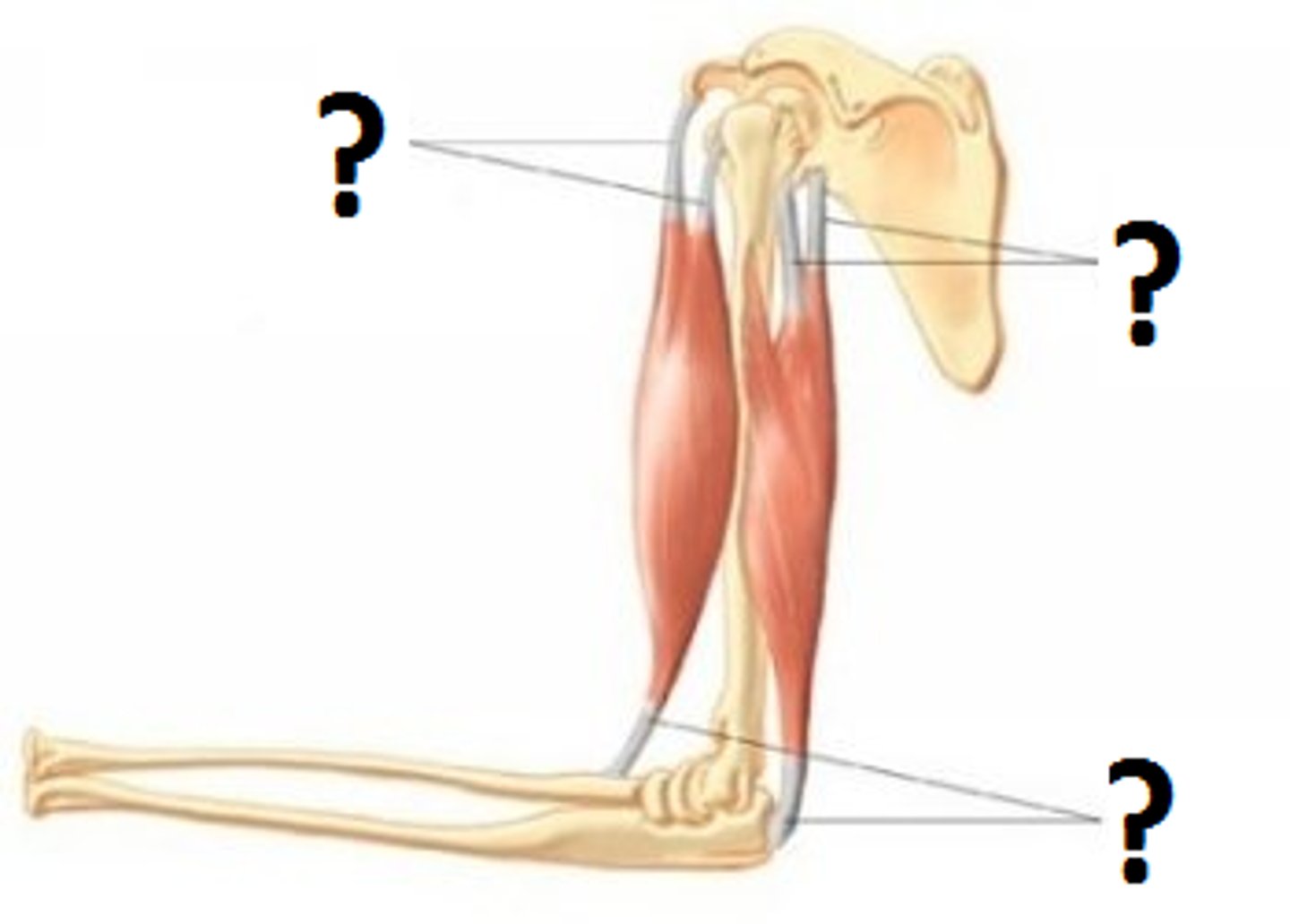
aponeurosis
sheet-like extension of the epimysium made of dense connective tissue that attaches to bone, cartilage or other connective tissue
endomysium
connective tissue surrounding muscle fiber (cell)
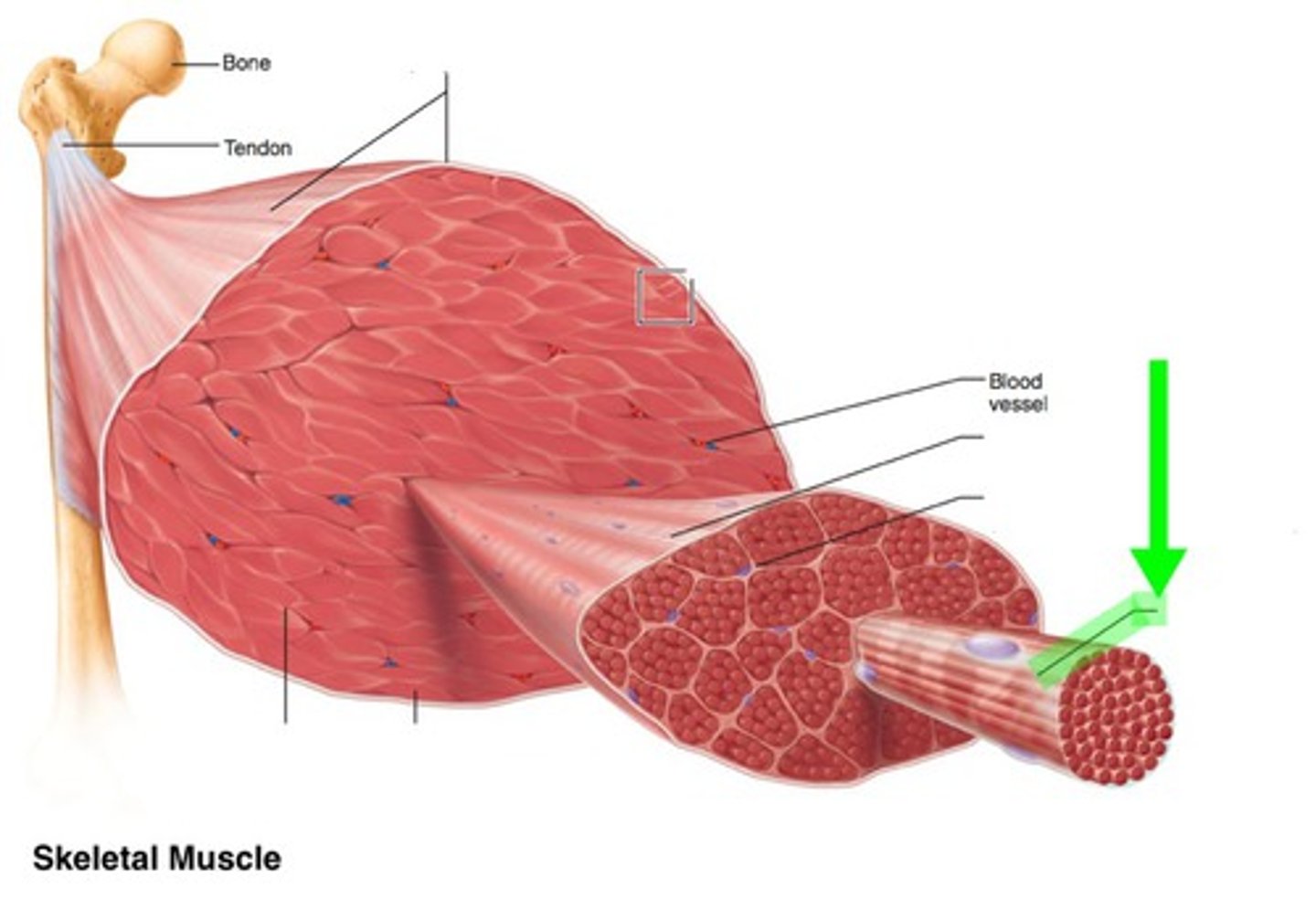
perimysium
connective tissue enclosing several muscle fibers to form a fasicle
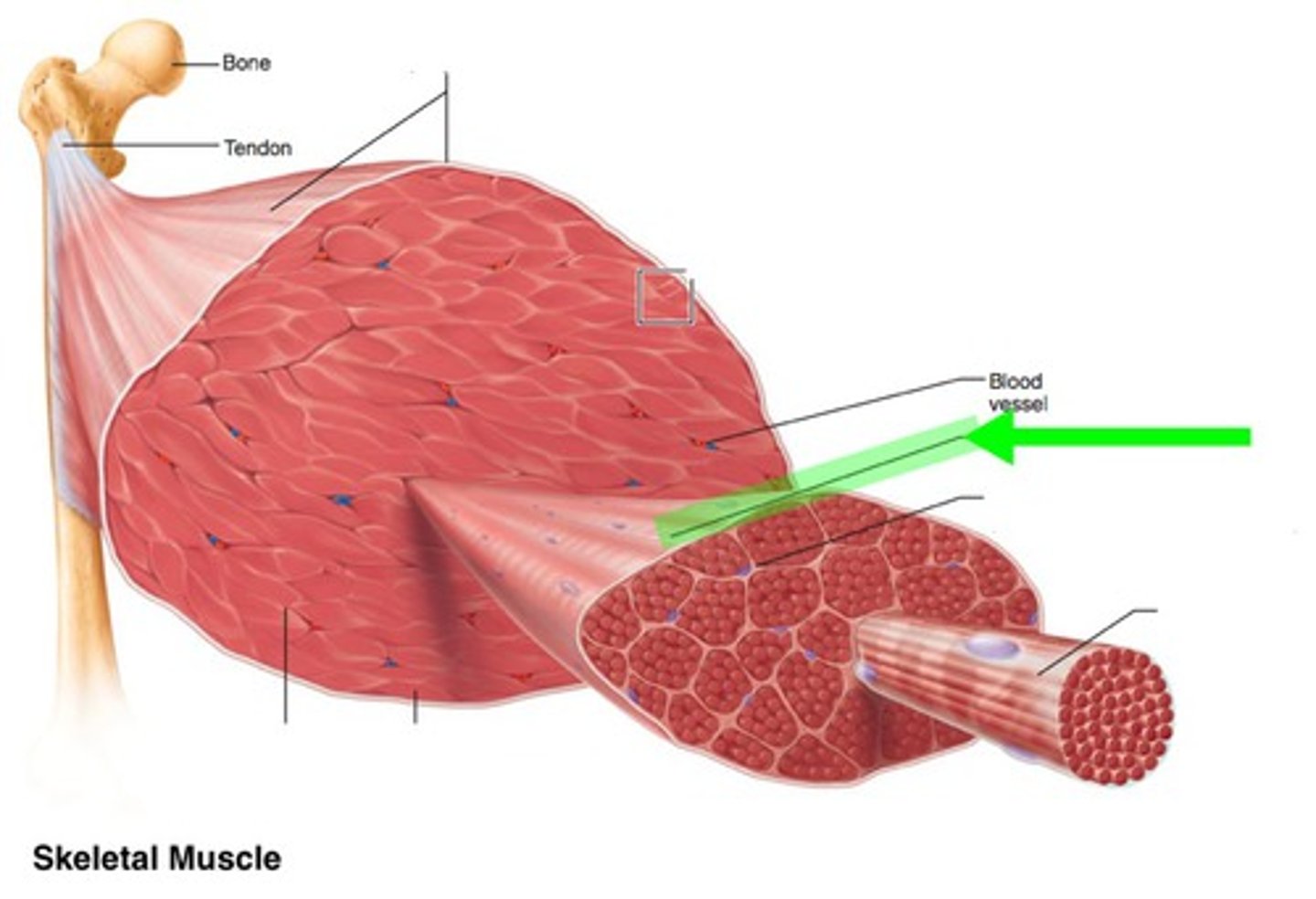
epimysium
connective tissue wrapping around the many fasciles of an entire muscle
smooth muscle
non-striated muscle that lines the walls of hollow organs such as the digestive tract, lungs, blood vessels and bladder, involuntary
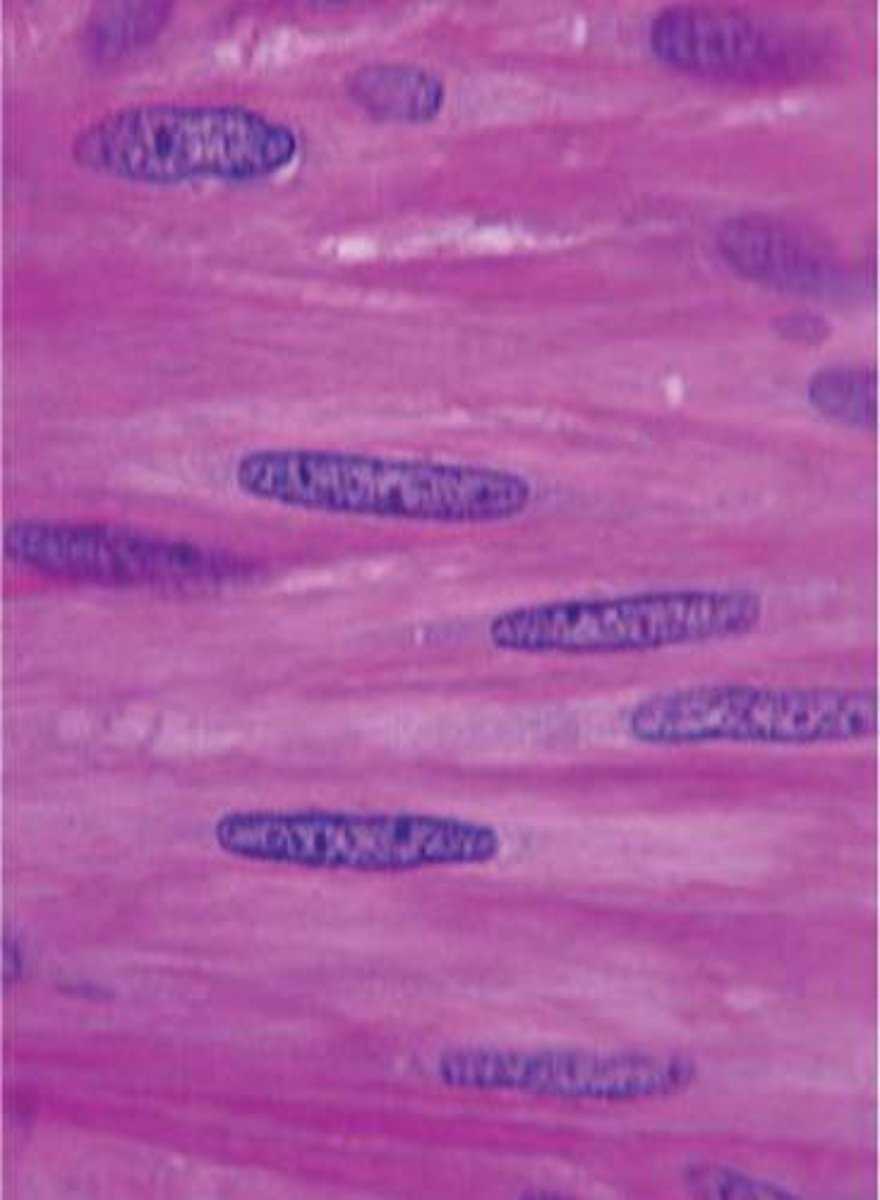
cardiac muscle
striated, involuntary, uninucleate, branching muscle fibers arranged in figure 8 shape which compose the bulk of the walls of the heart
sarcoplasmic reticulum
Organelle of the muscle fiber that stores calcium.
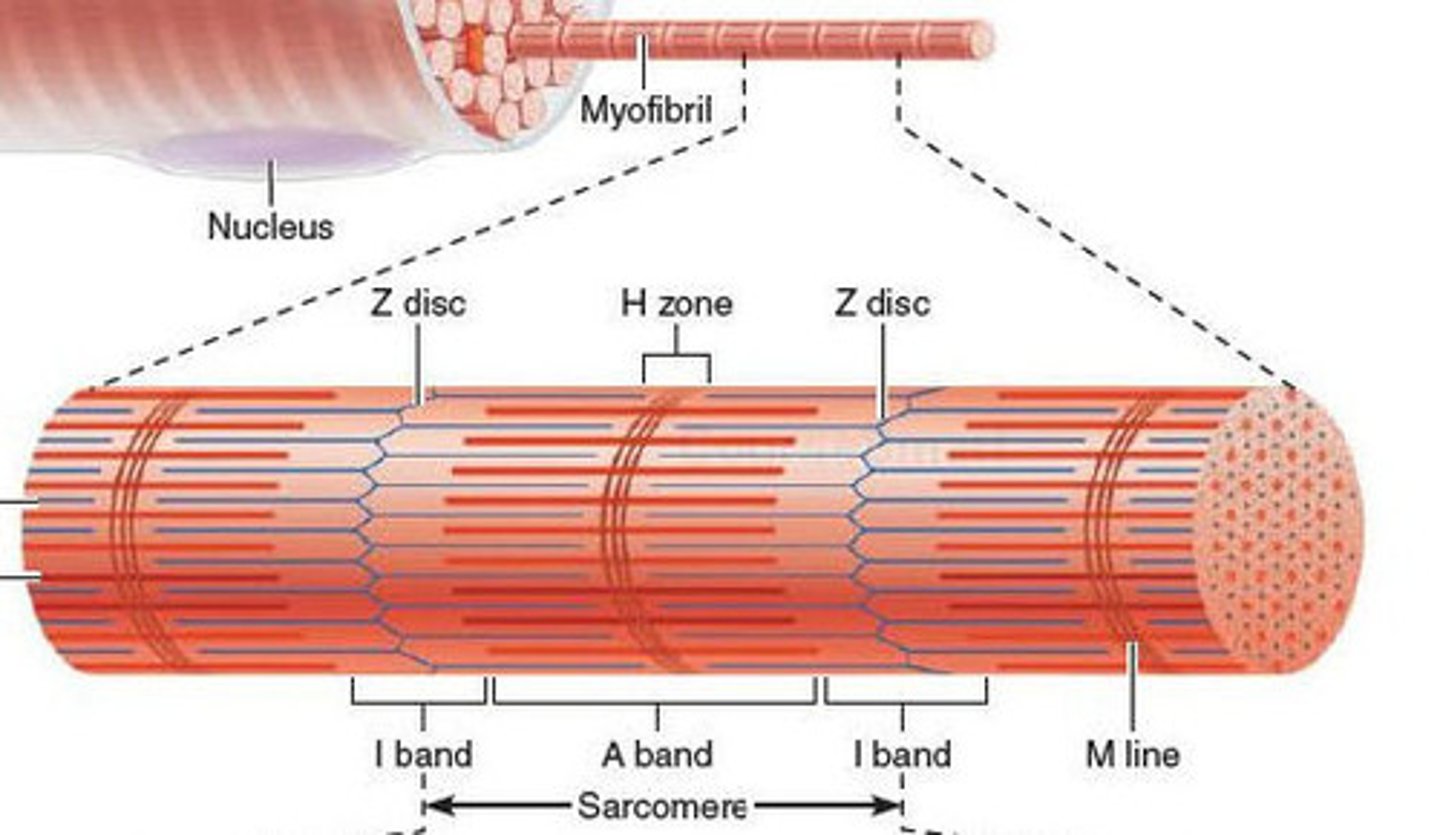
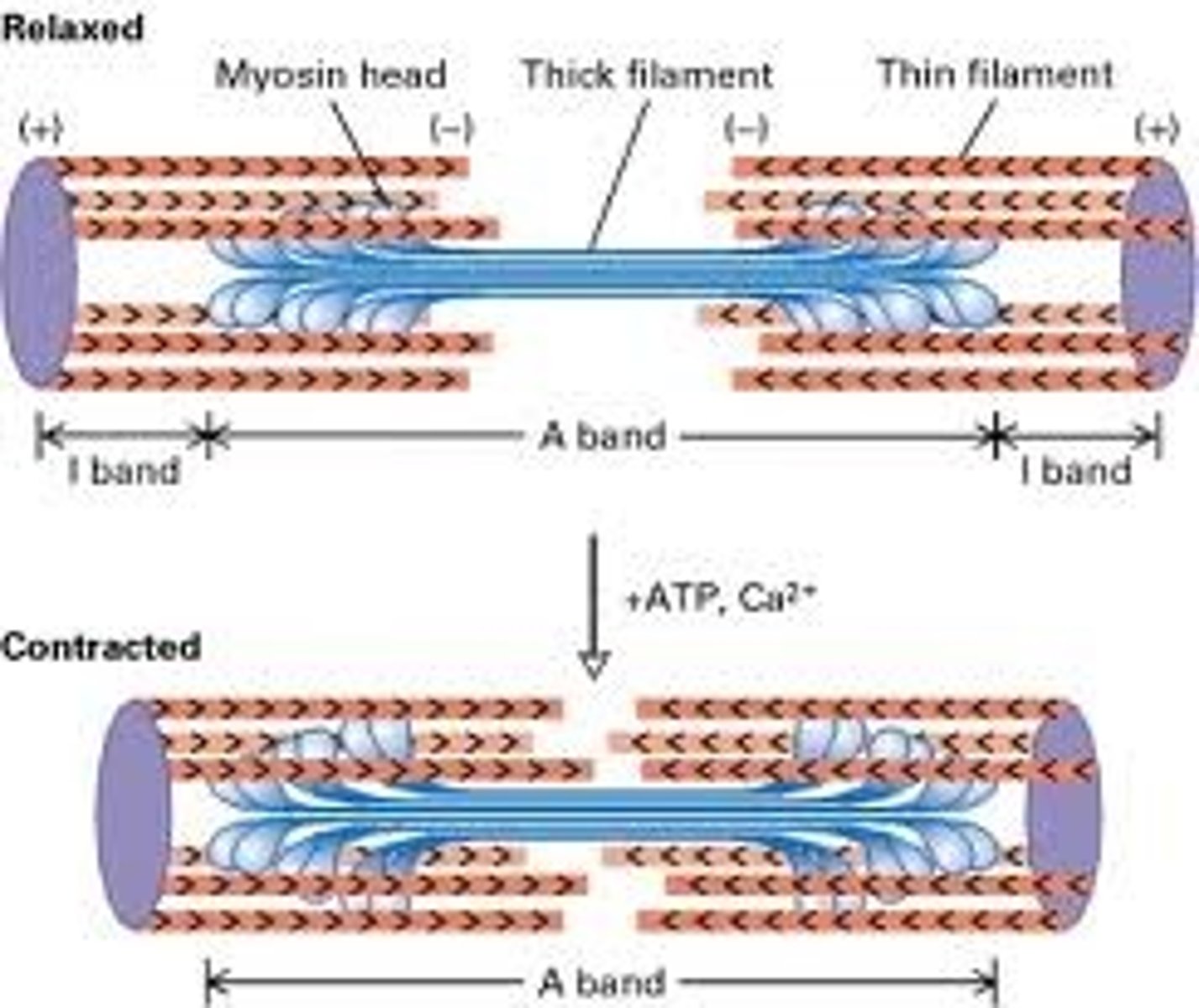
sarcomere
functional and structural unit of muscle contraction
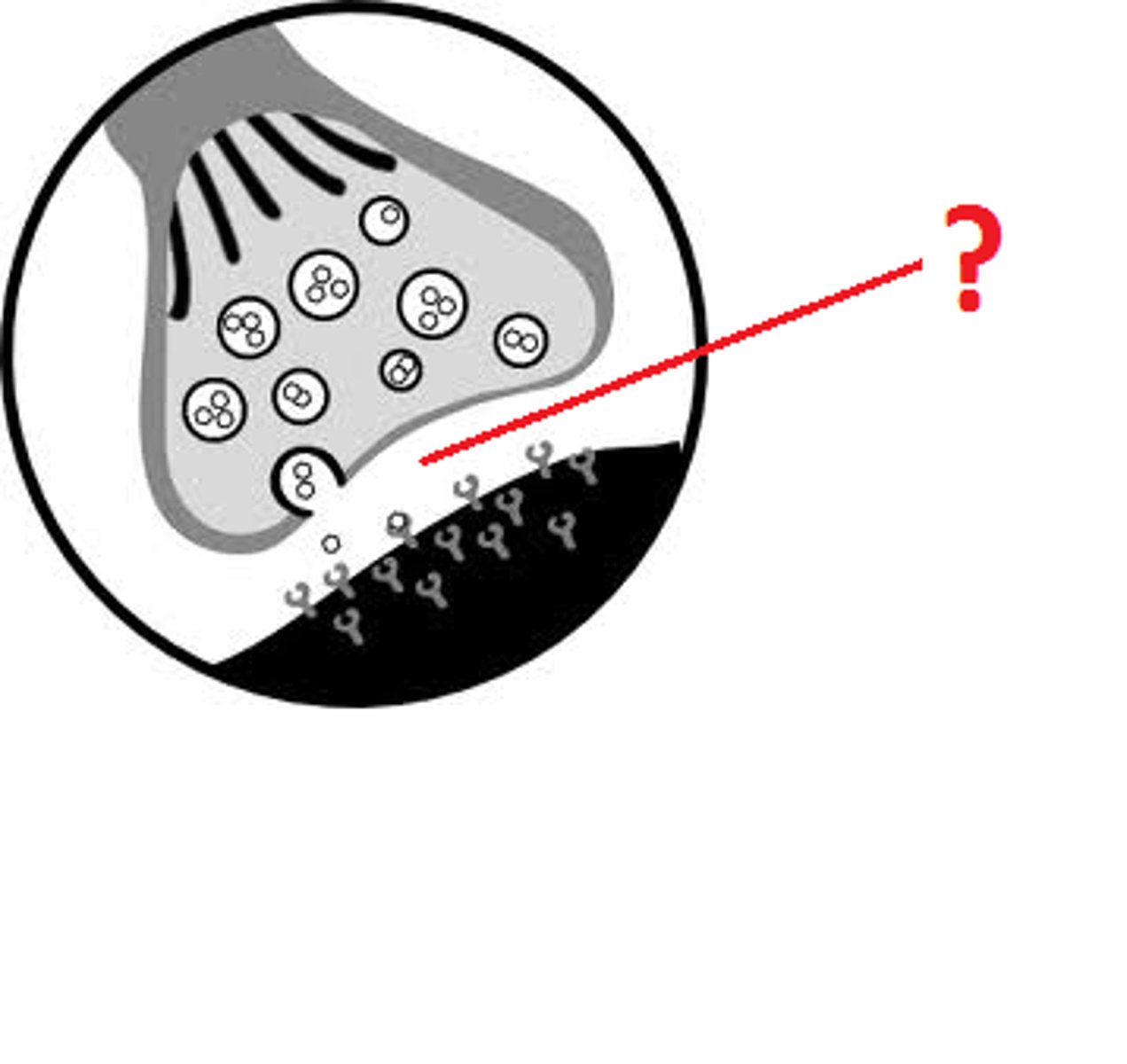
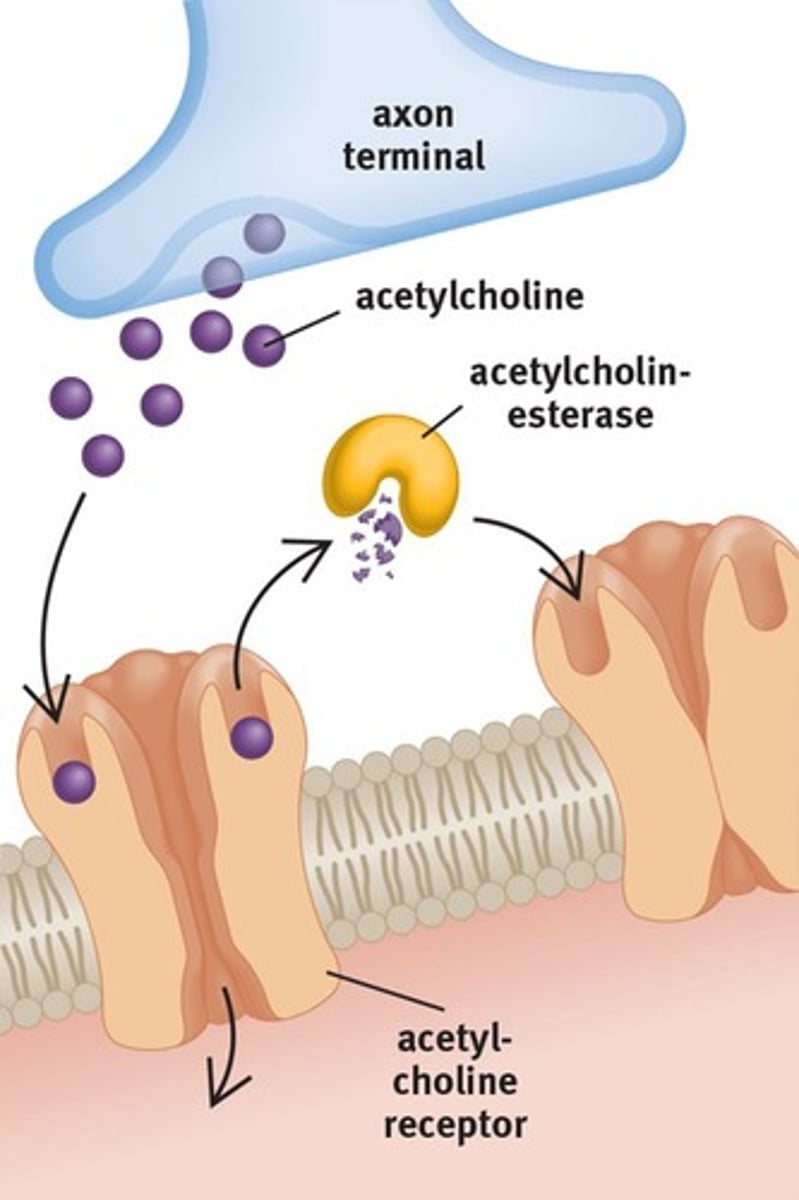
synaptic cleft
a gap between the axon terminal and the muscle cell into which neurotransmitters are released from the axon terminal
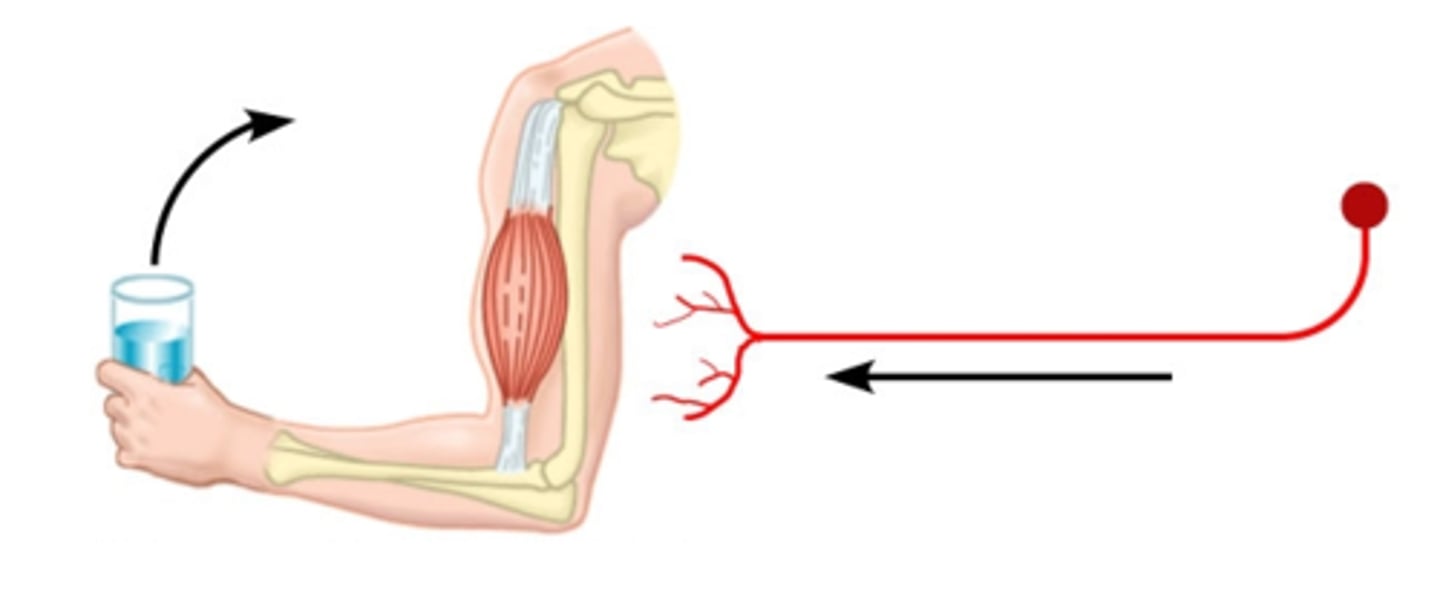
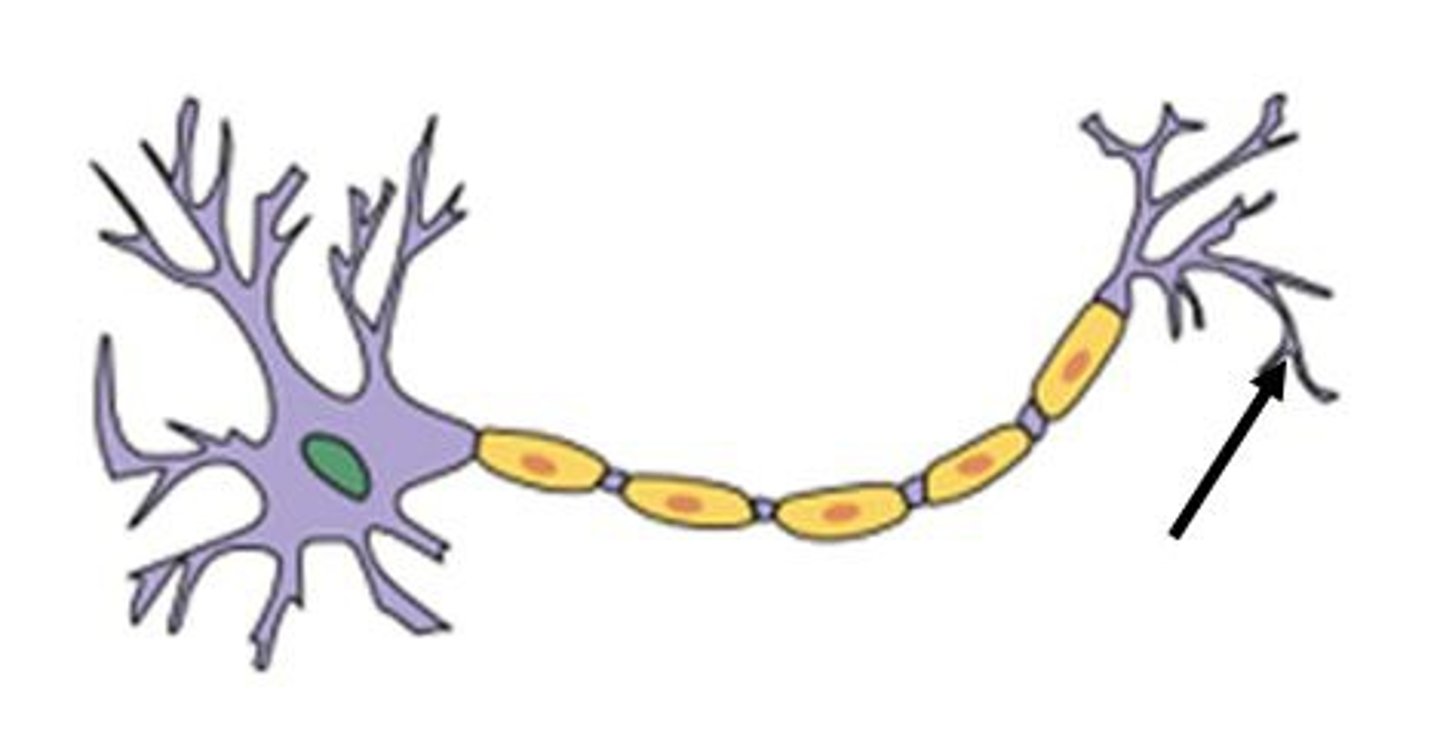
motor neuron
one nerve cell and all the skeletal muscles it stimulates
axon terminal
The endpoint of a neuron where neurotransmitters are stored
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon (and into a muscle cell)
actin
thin contractile protein filaments
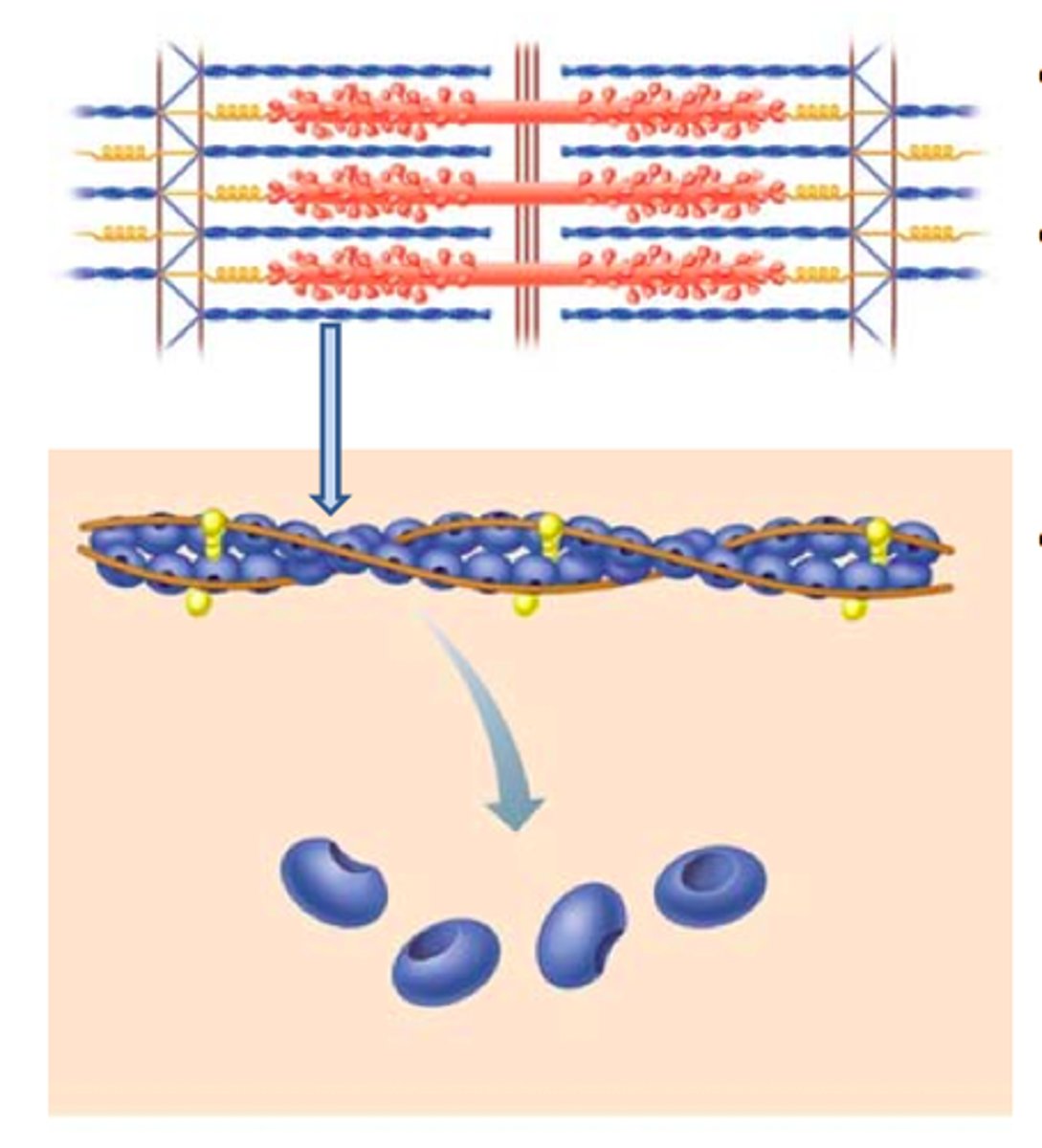
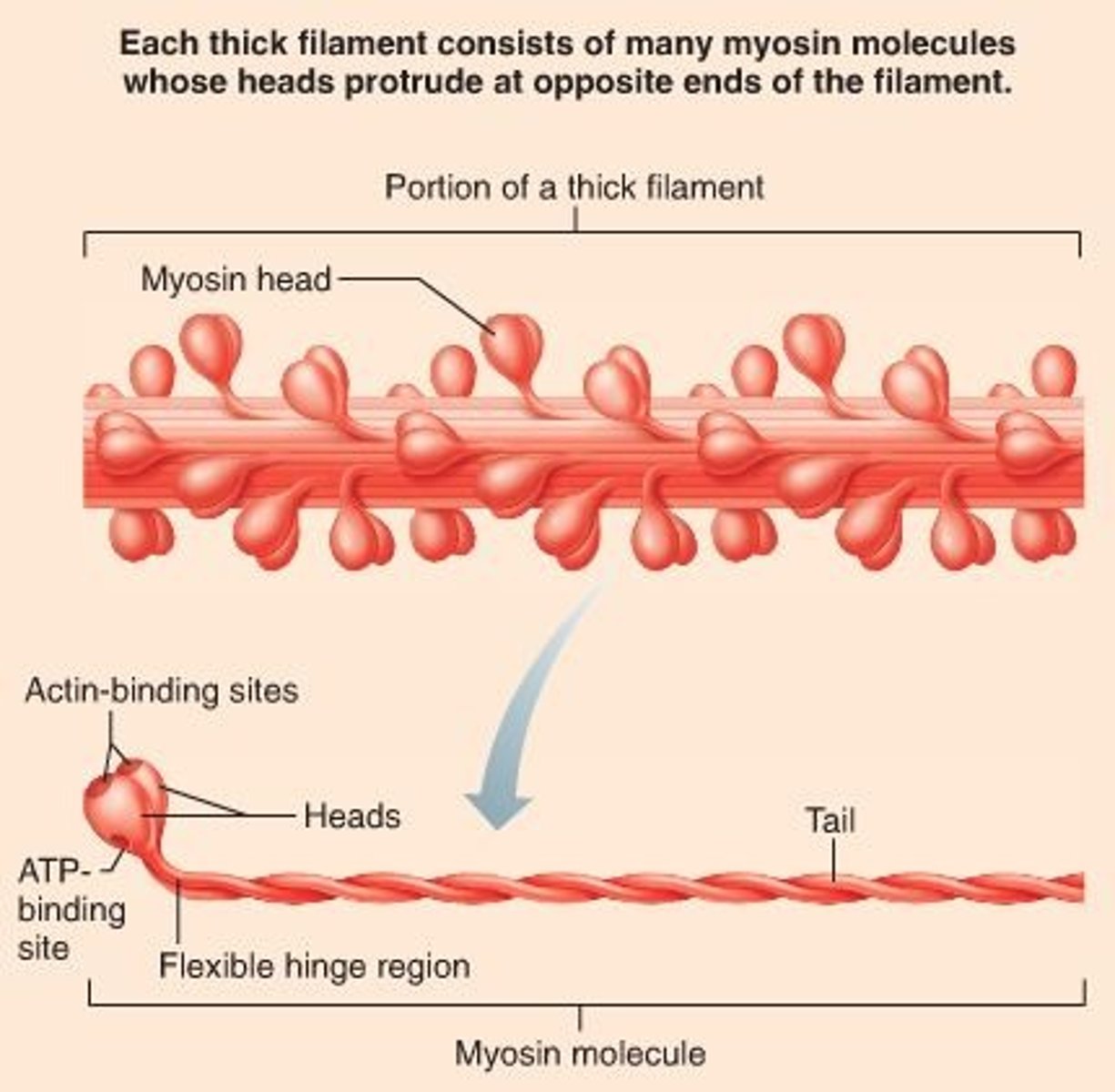
myosin
thick contractile protein filaments
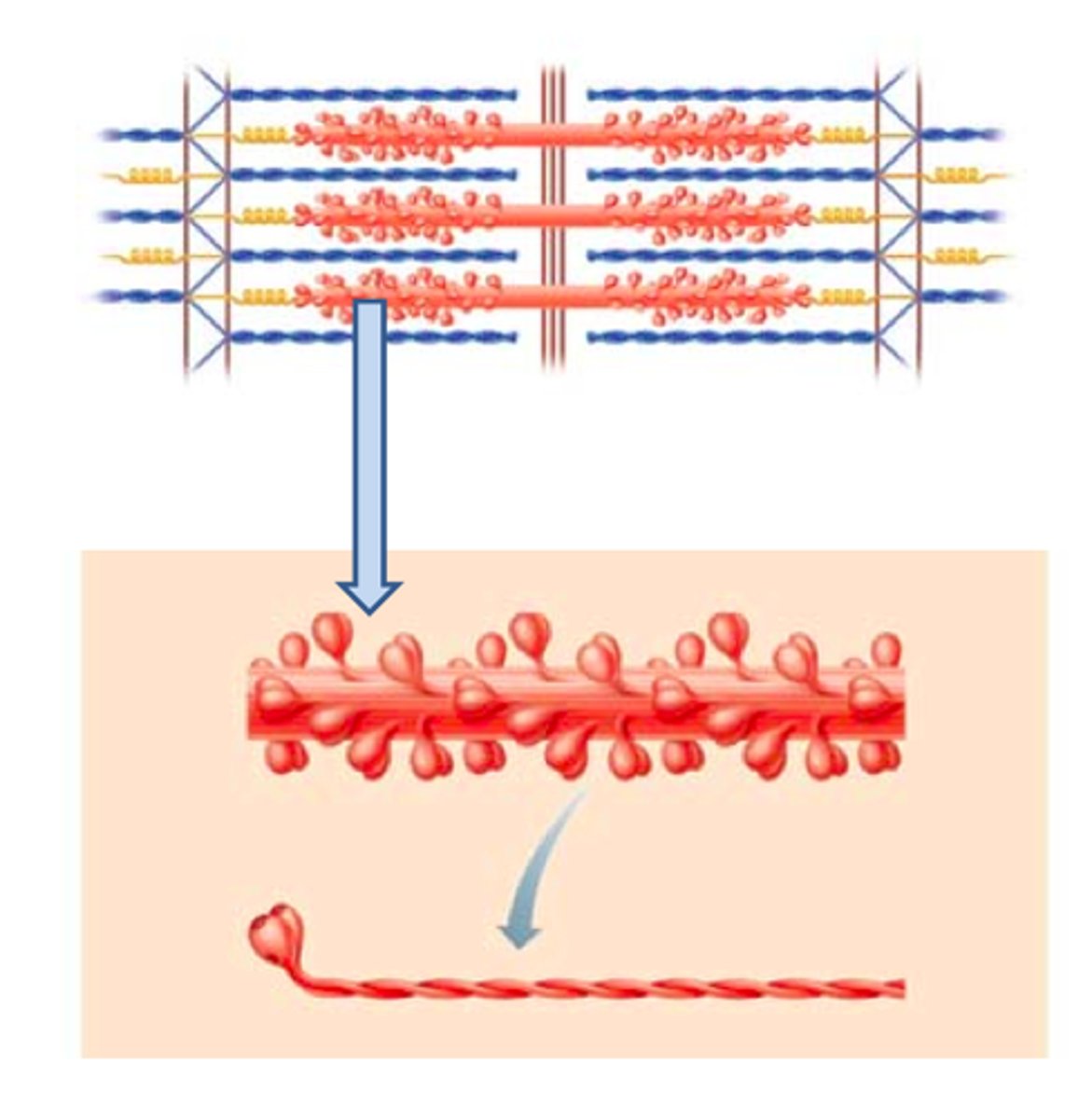
myosin heads
extensions of myosin filament that bind to specific sites on actin molecules to form cross bridges
Acetylcholine
A neurotransmitter that triggers muscle contraction (and also enables learning and memory)
sliding filament theory
theory of muscle contraction;
sarcomeres shorten when thick filaments pull on thin filaments
Z disc
provides anchorage for thin filaments and elastic filaments
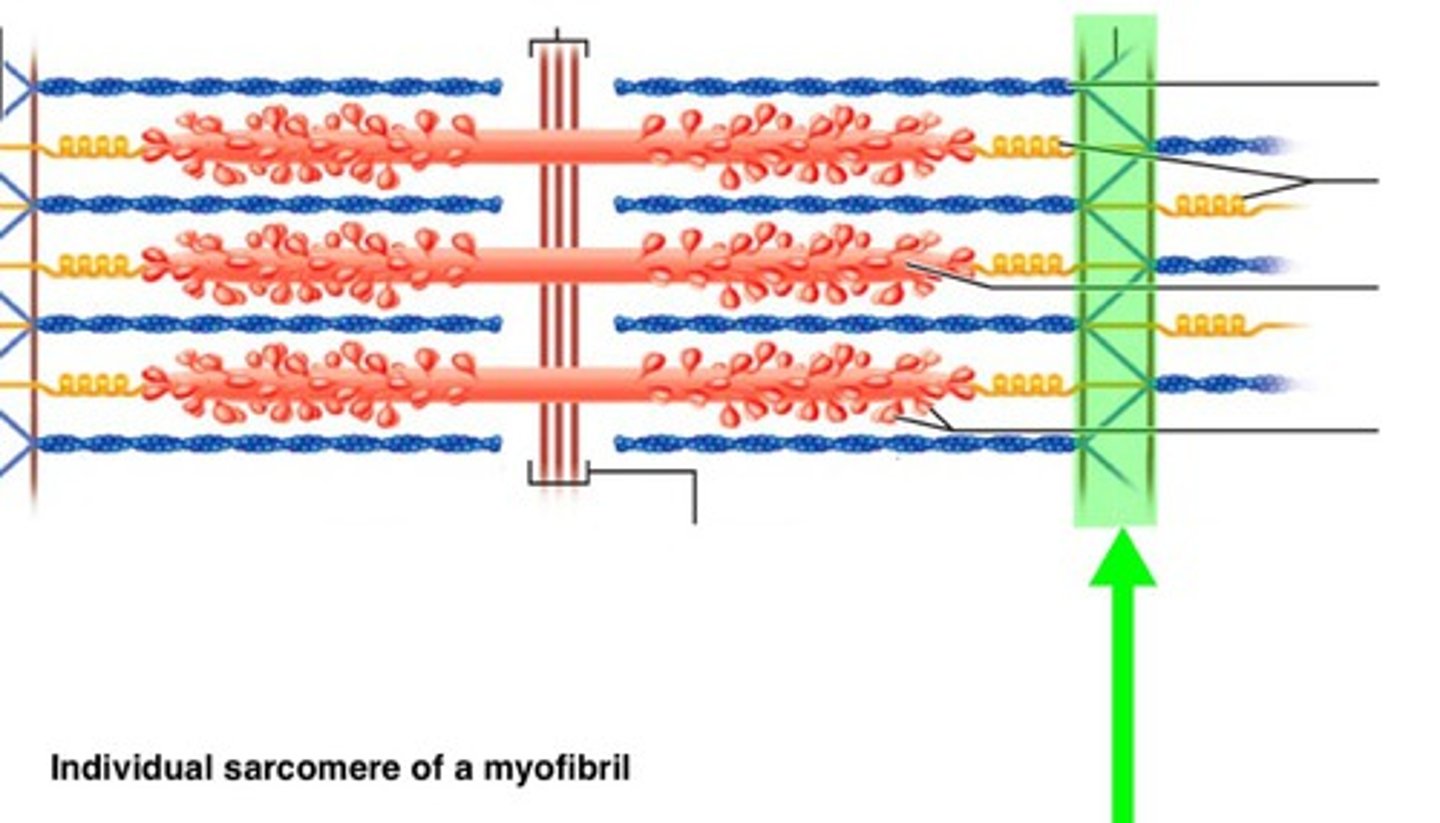
fasicle
bundle of muscle fibers, encased in perimysium
A band
dark band
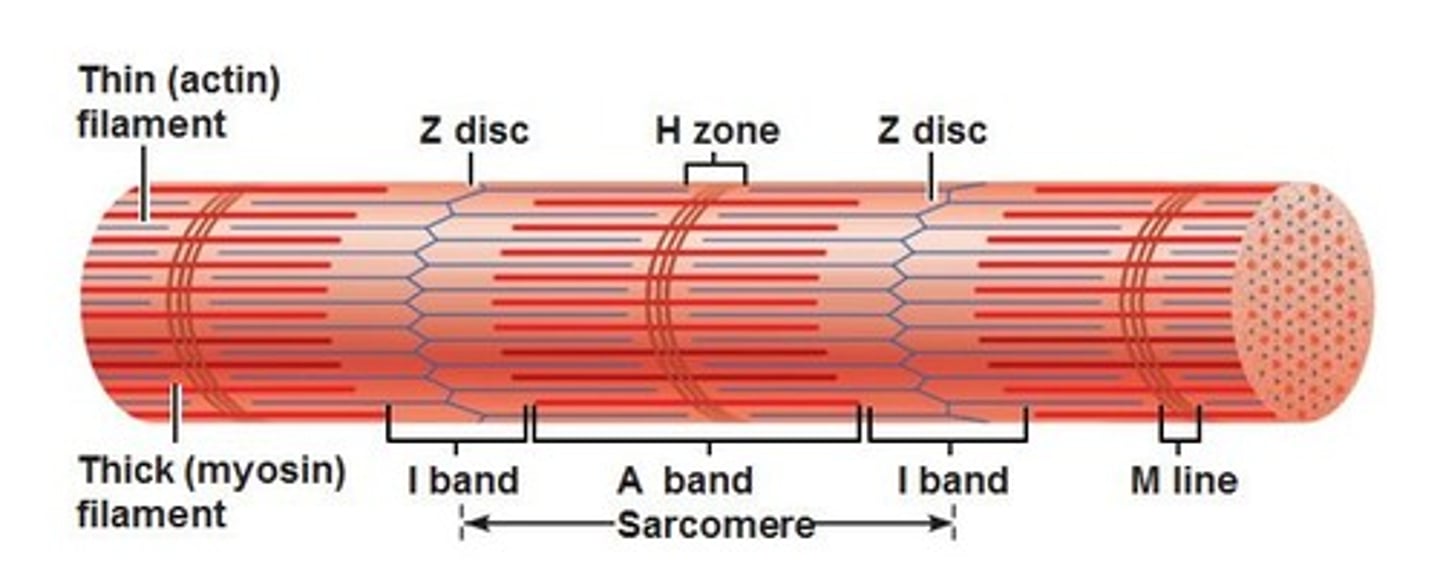
I band
light band, thin filaments only
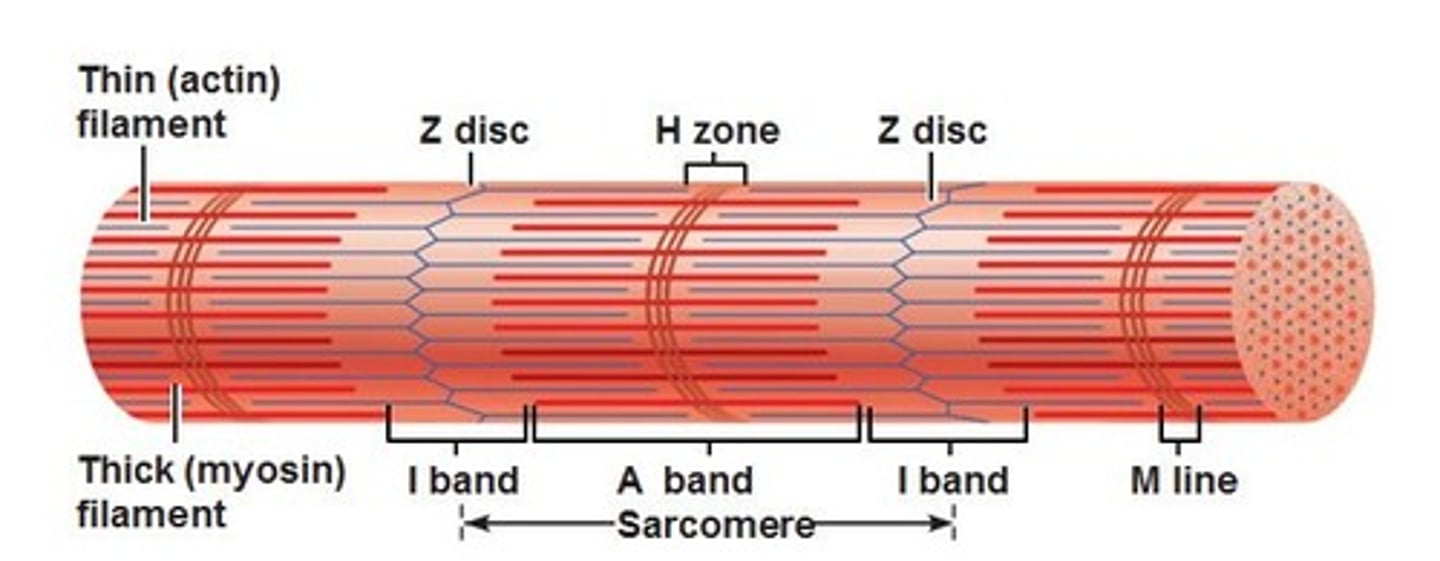
H zone
center part of A band where no thin filaments occur, disappears in full contraction

fused tetanus
when stimulus frequency is so high that no muscle relaxation takes place between stimuli
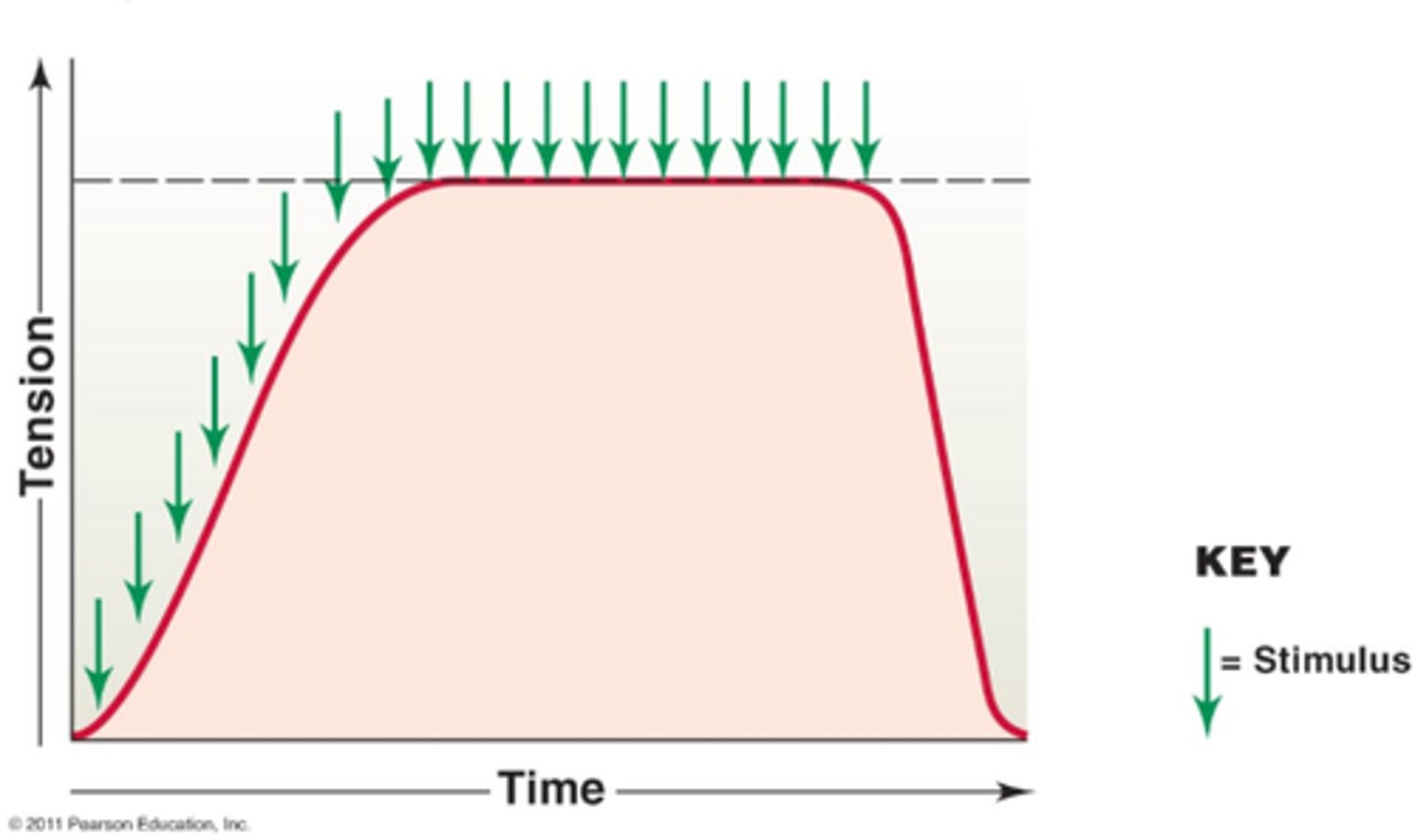
unfused tetanus
some relaxation occurs between contractions

ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
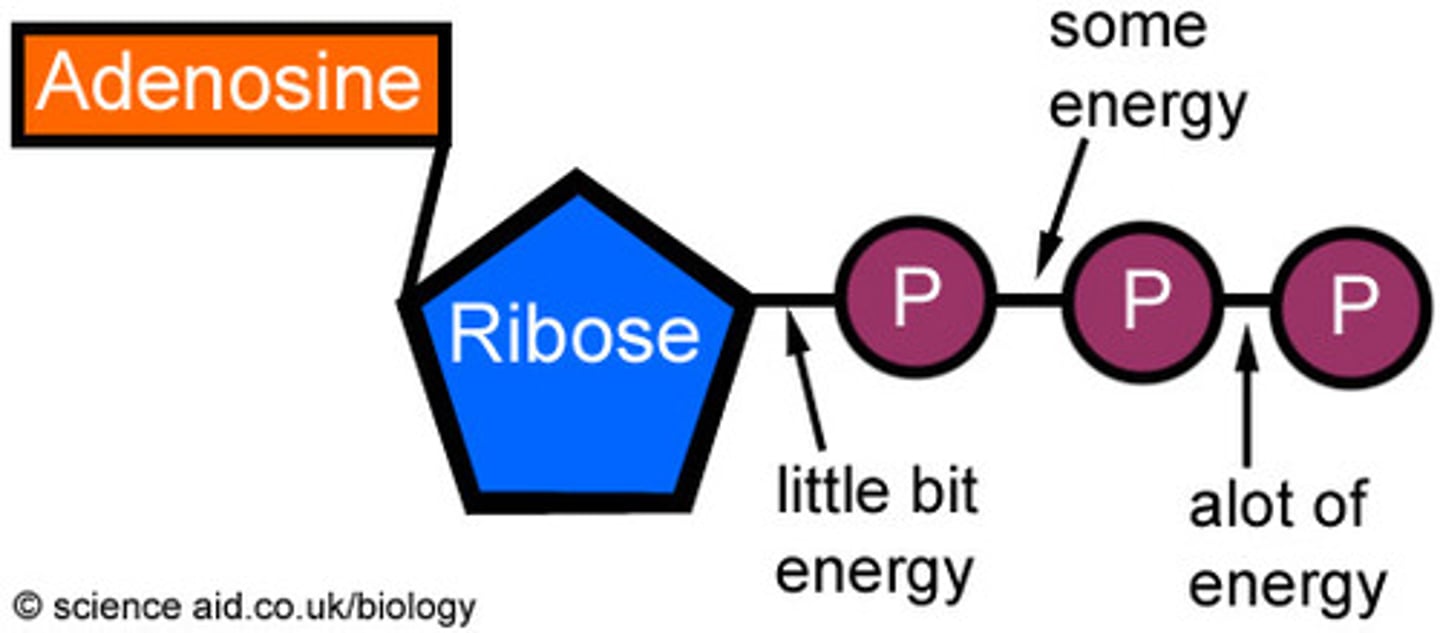
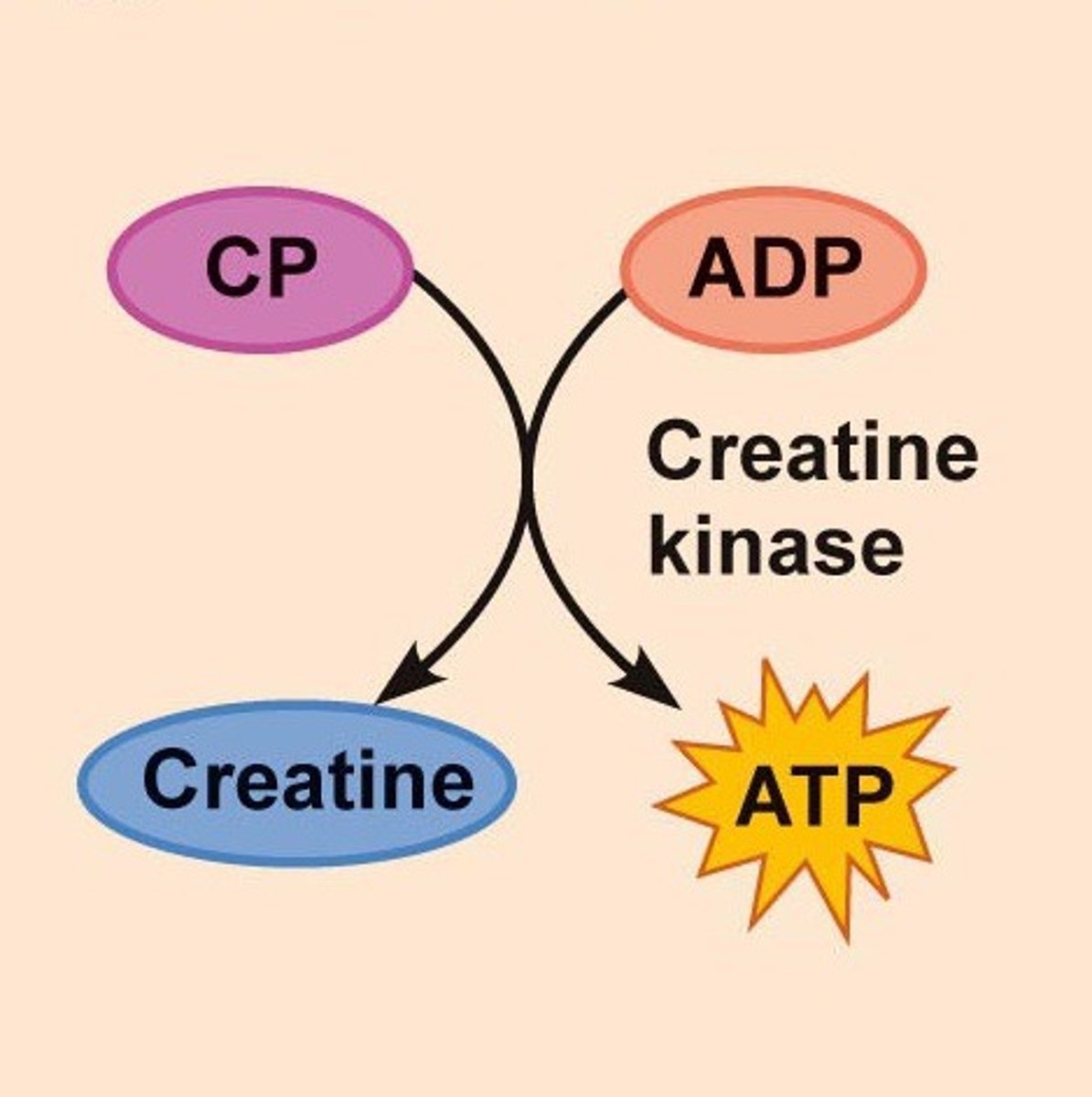
creatine phosphate
biochemical molecule that stores energy and can directly phosphorylate ADP
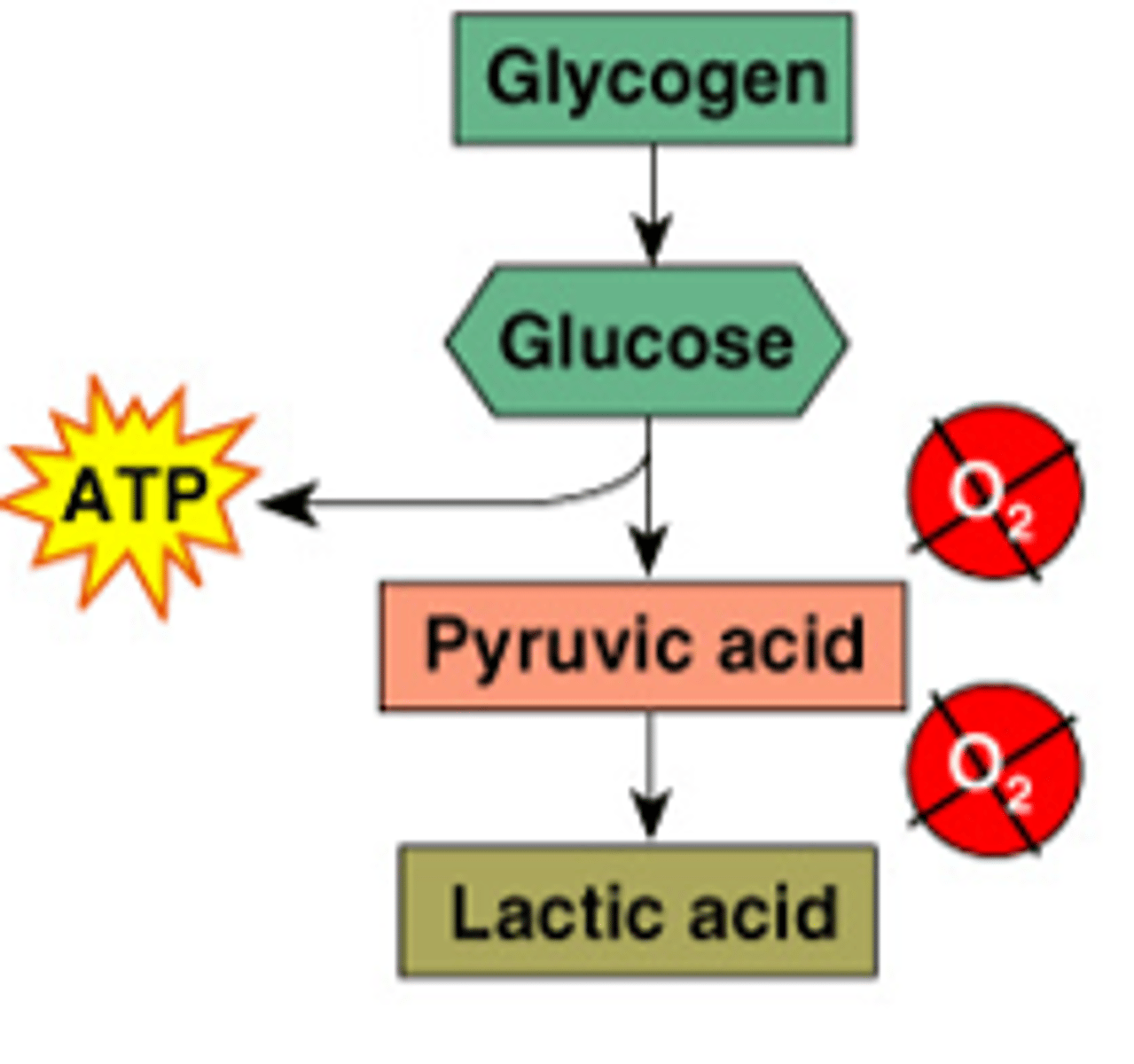
anaerobic glycolysis
the overall process where sugar is split into pyruvic acid to generate 2 ATP and lactic acid (byproduct)
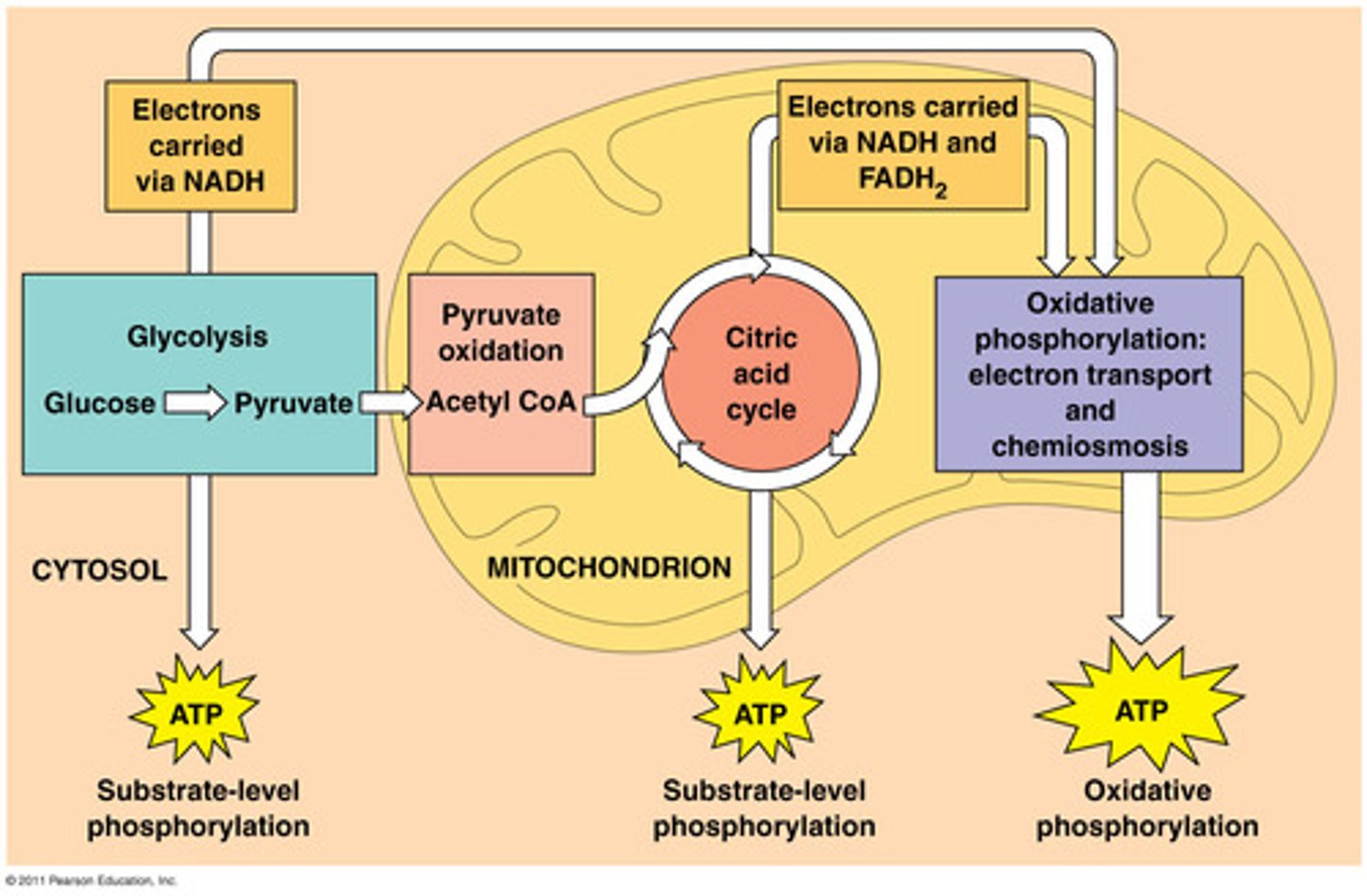
aerobic respiration
cellular respiration that uses oxygen, sequentially releasing energy and storing it in ATP (~32 ATP per glucose)
isotonic contraction
A muscle contraction that pulls on the bones and produces movement of body parts.
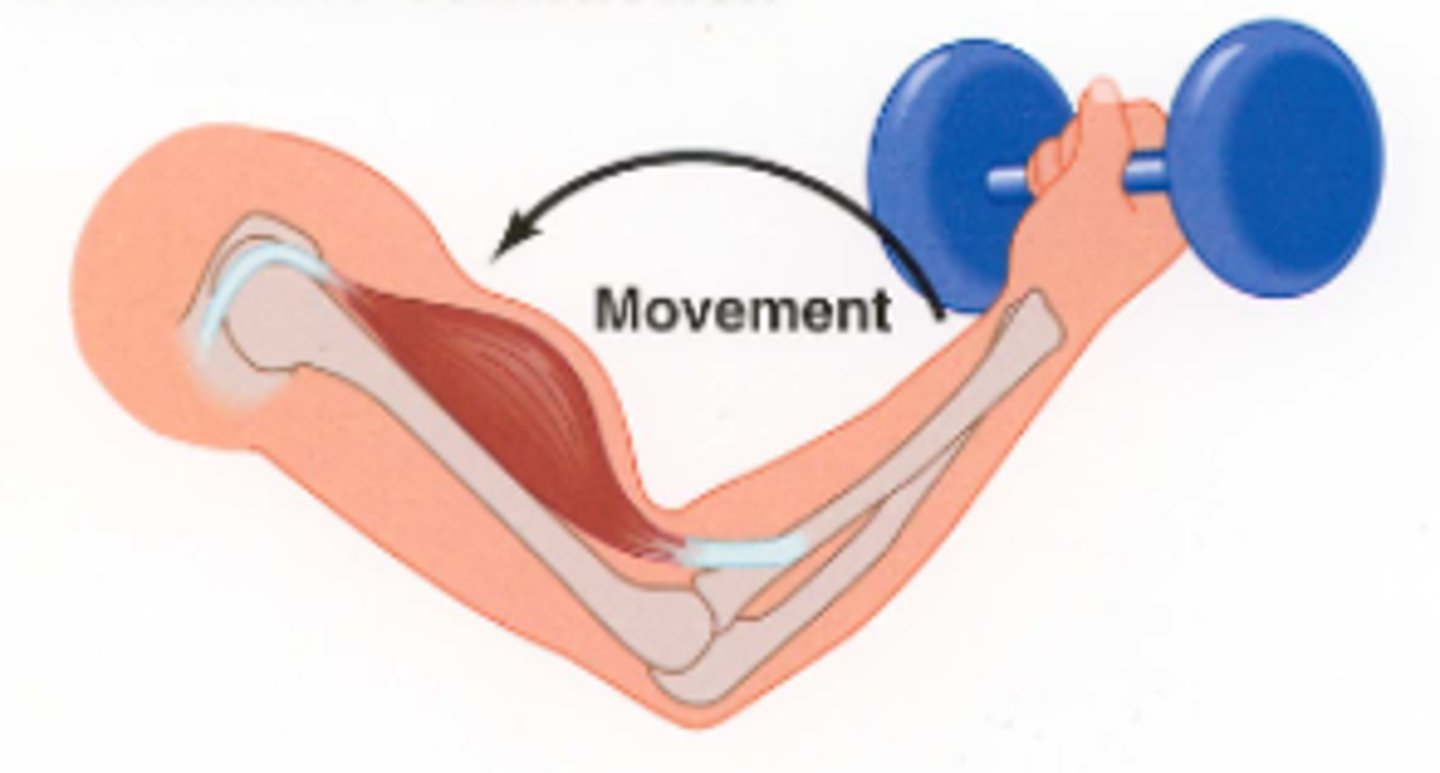
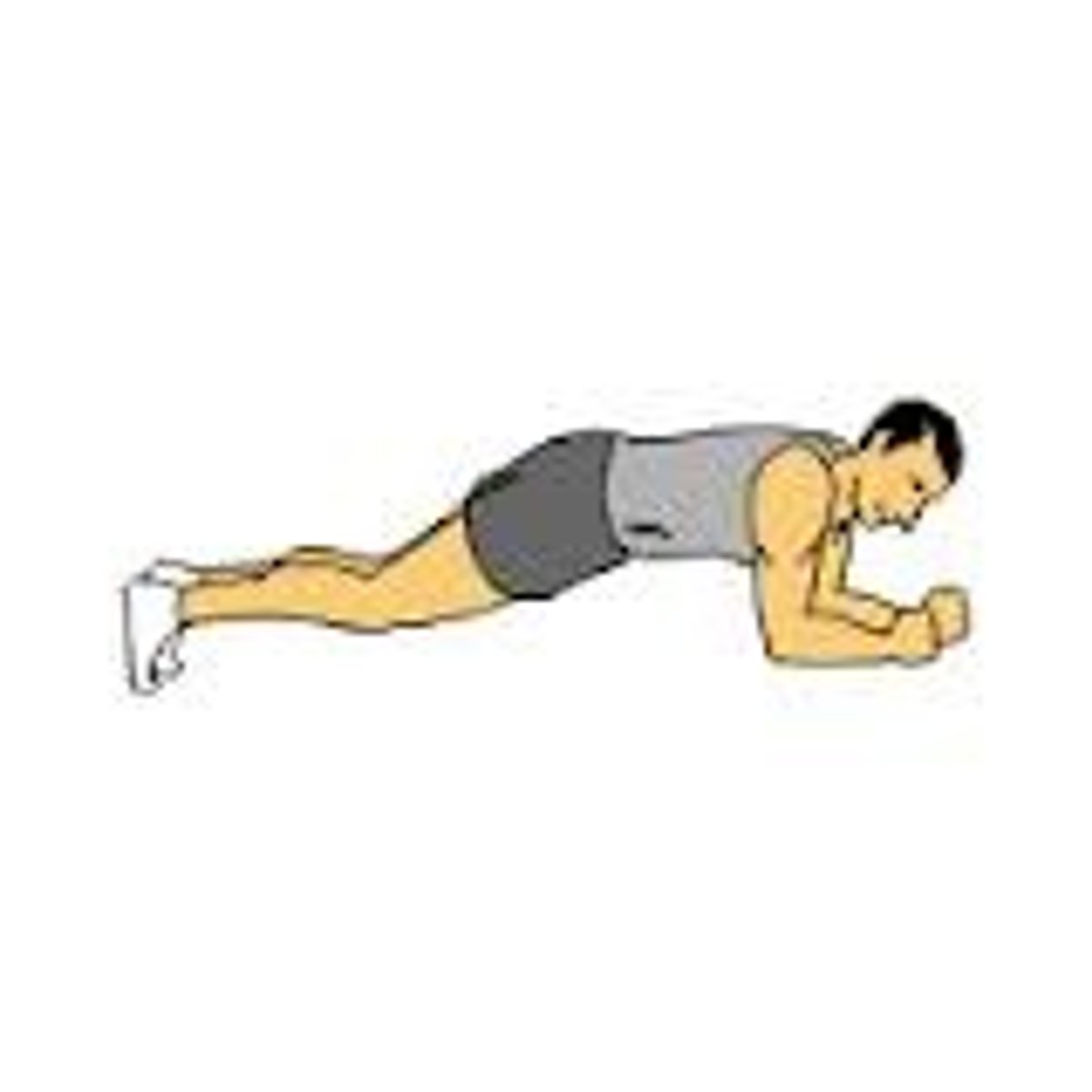
isometric contraction
Muscle contracts but there is no movement, muscle stays the same length

extension
Straightening of a joint
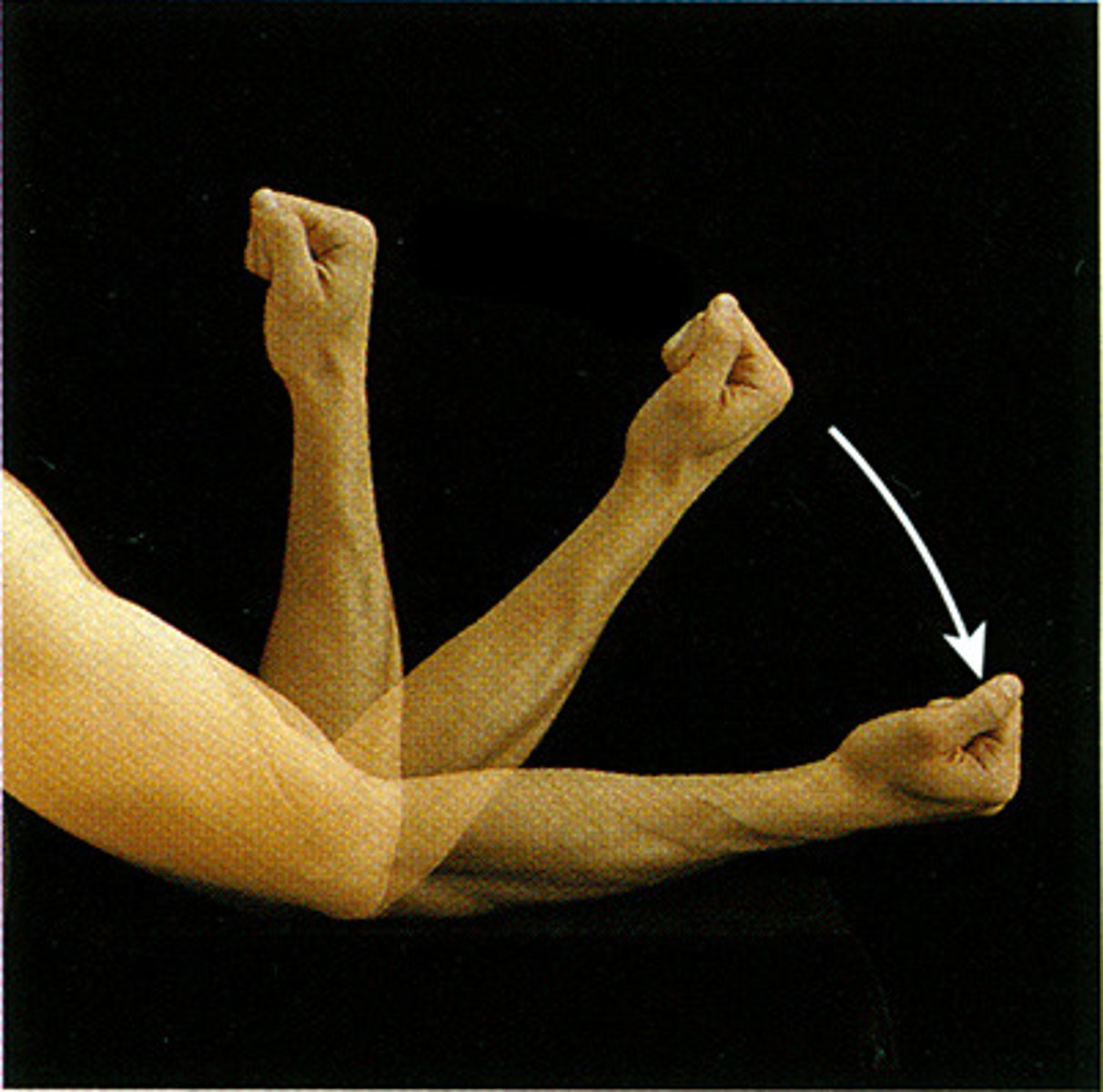
flexion
Decreases the angle of a joint
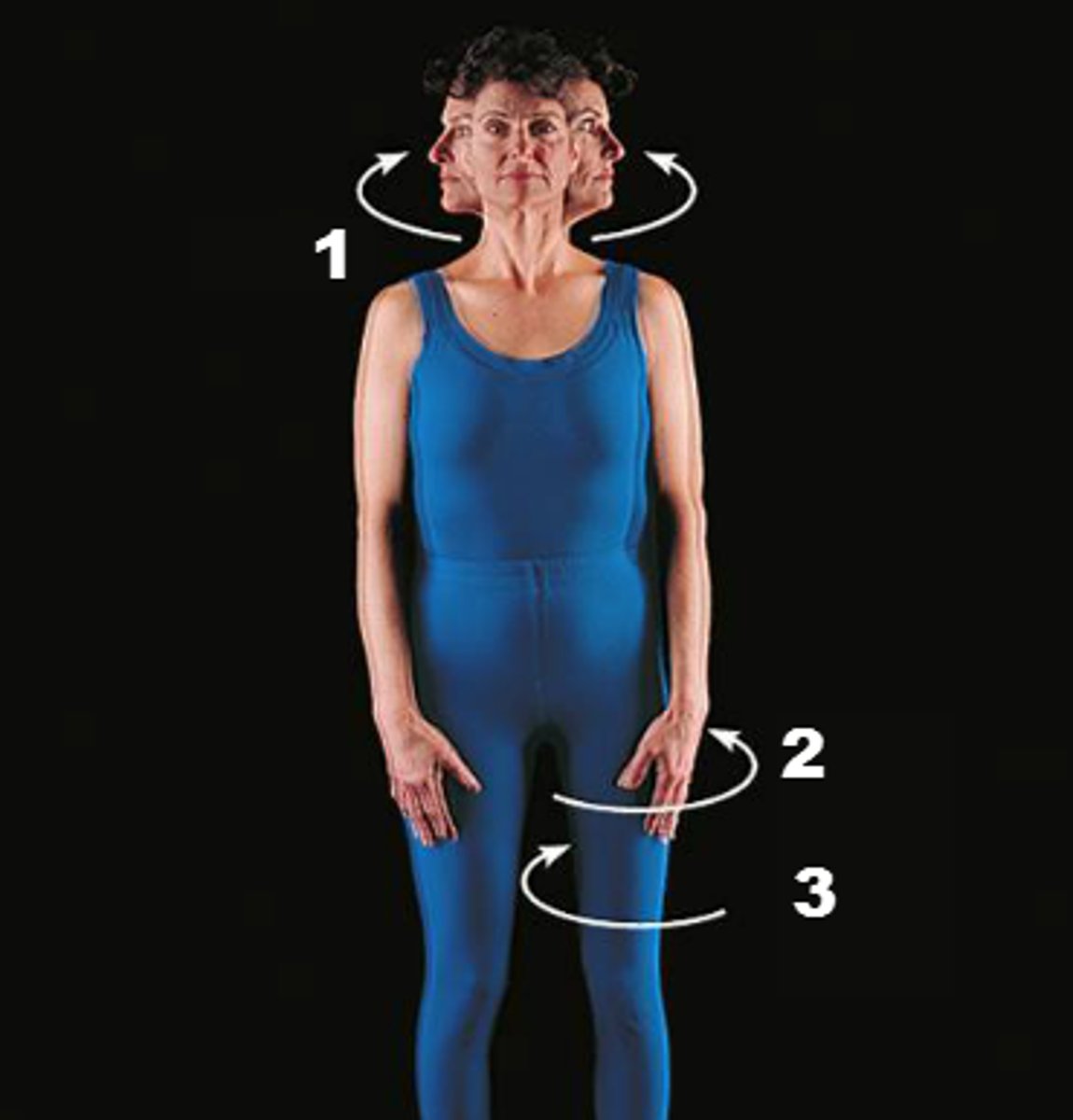
rotation
movement of a bone around its longitudinal axis
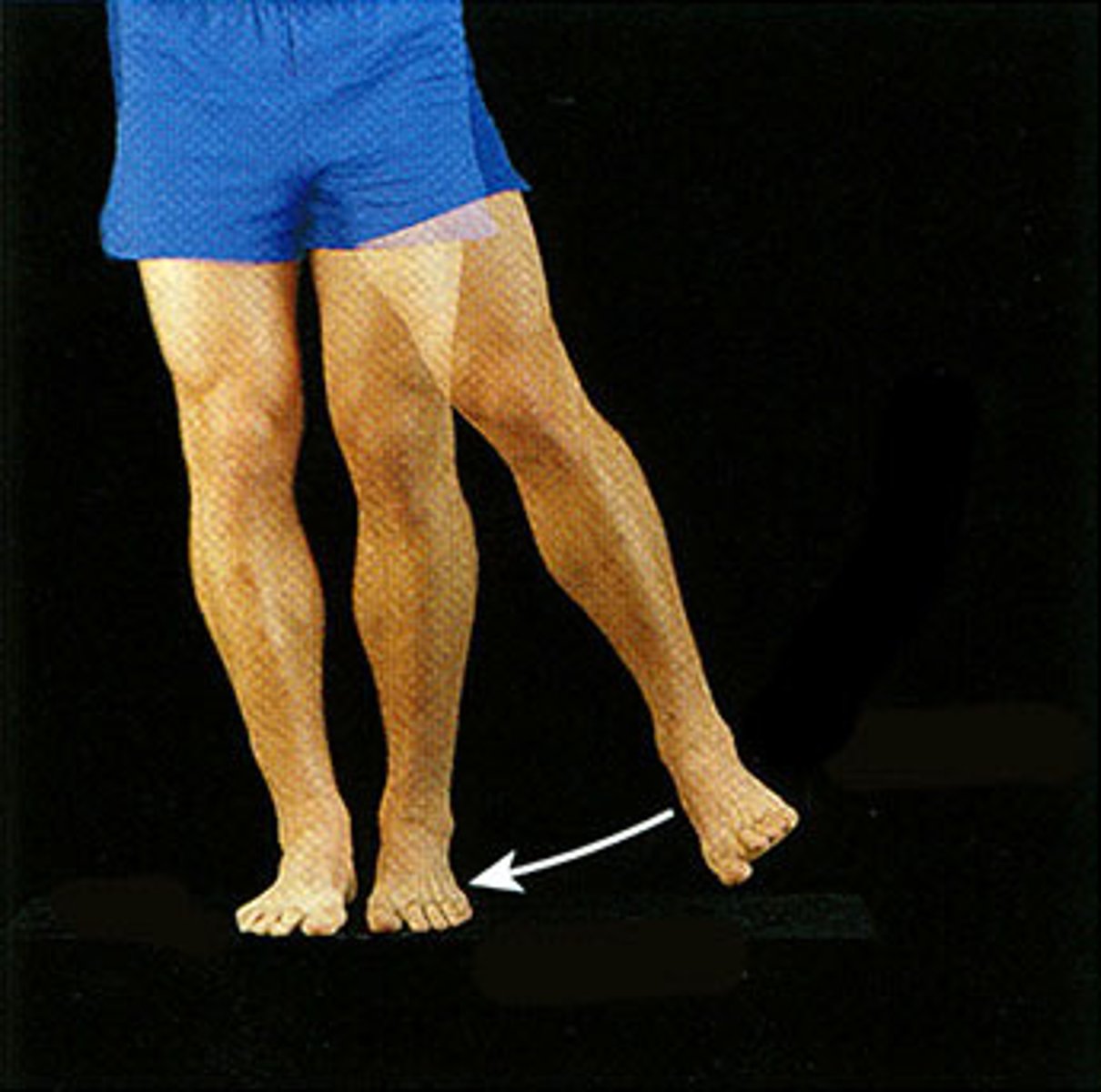
abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body
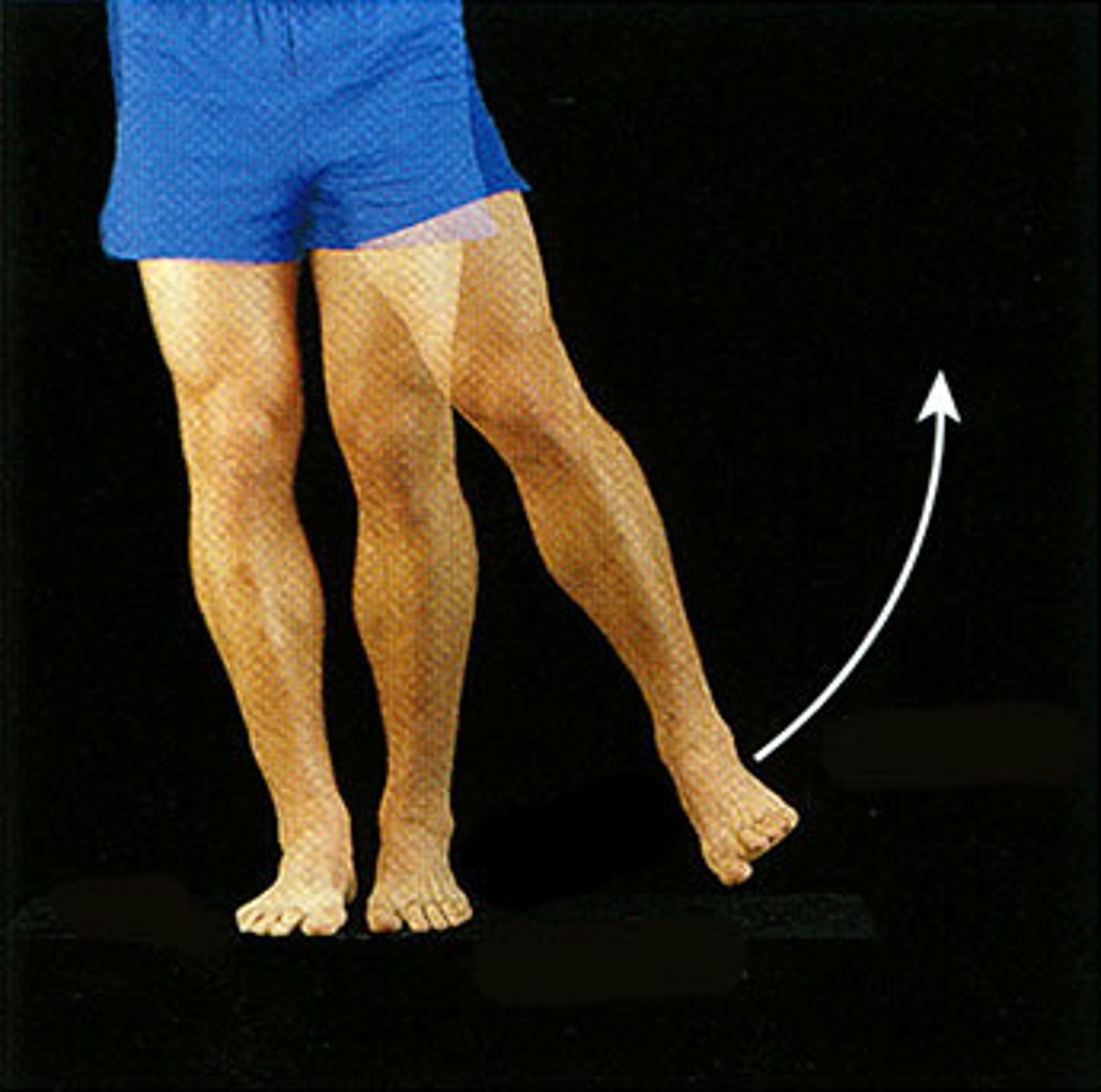
adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body
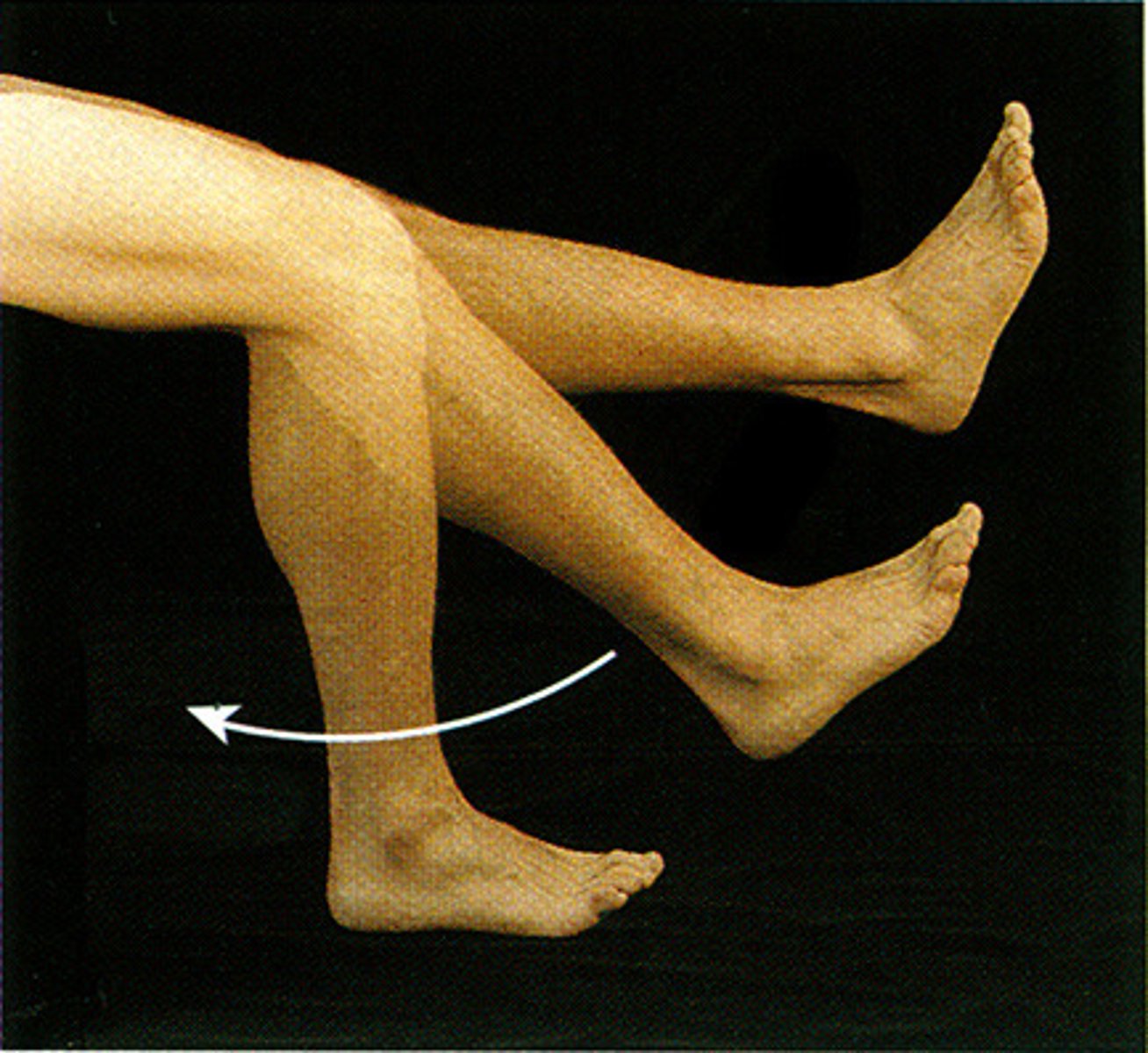
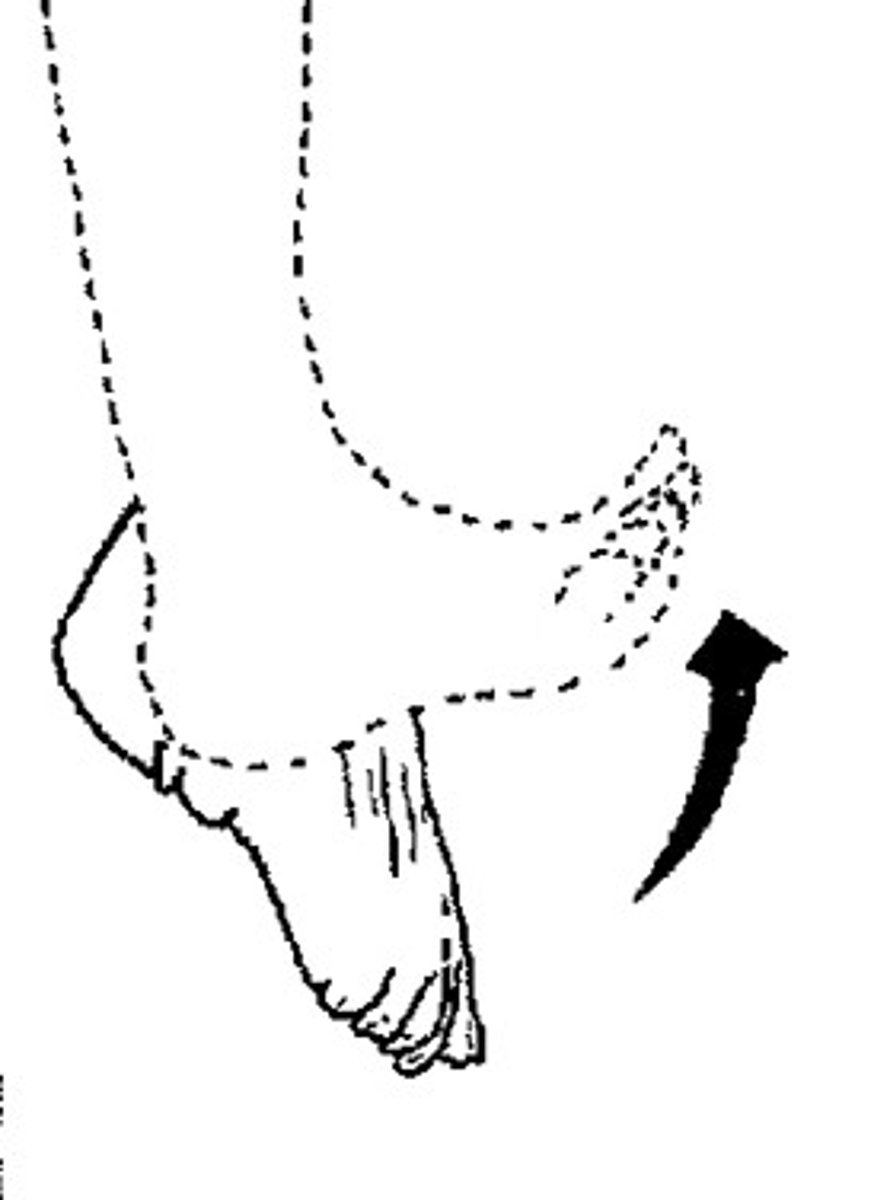
Dorsiflexion
bending of the foot or the toes upward
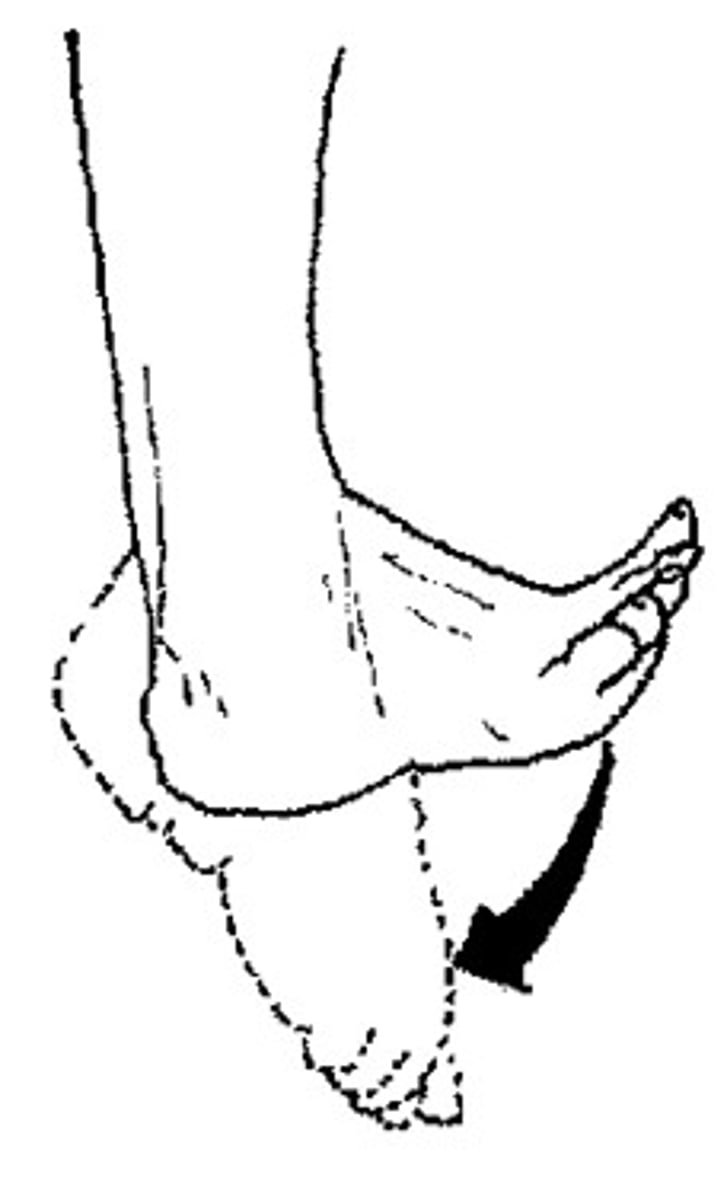
plantar flexion
pointing toes
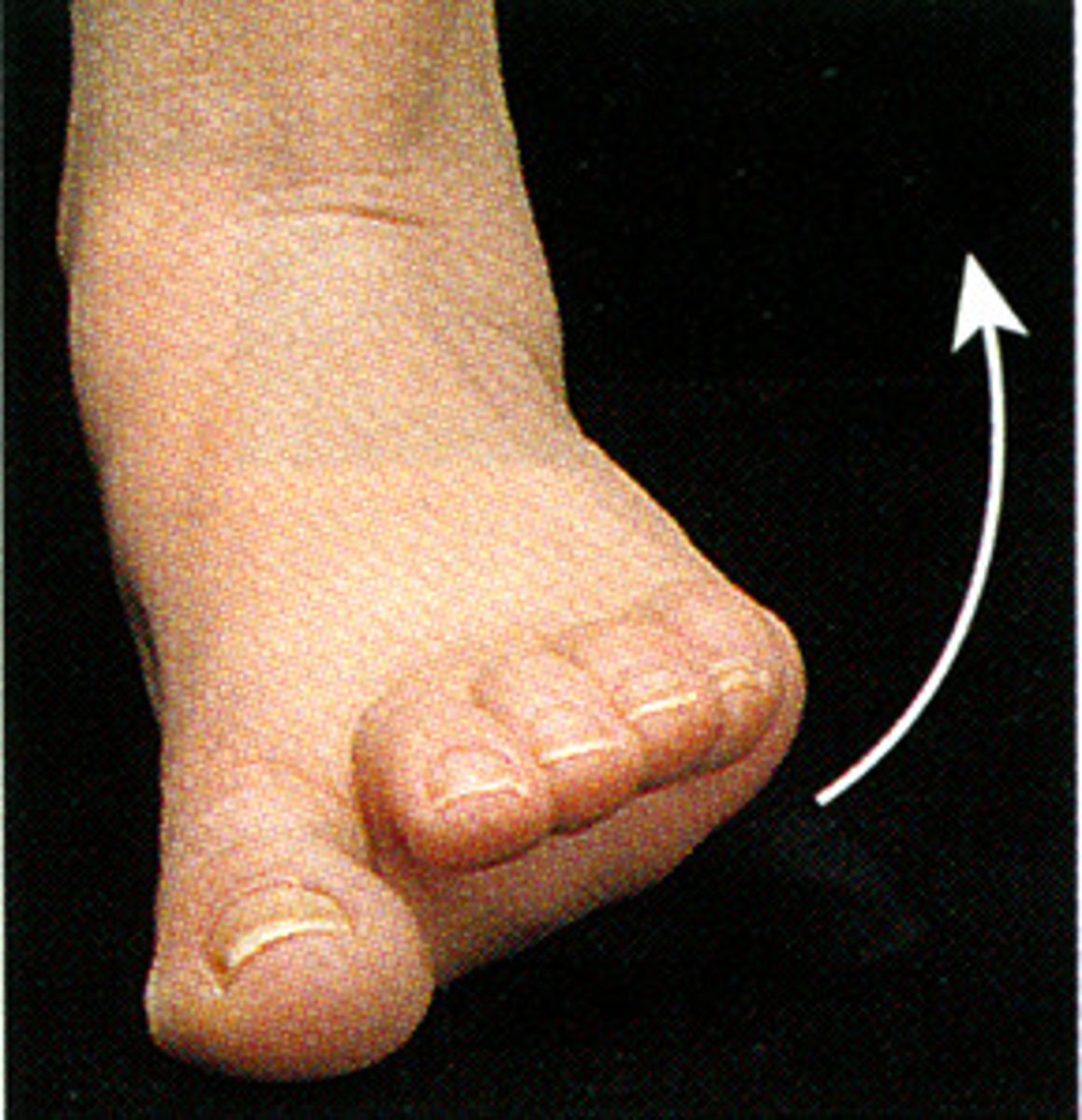
Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot inward
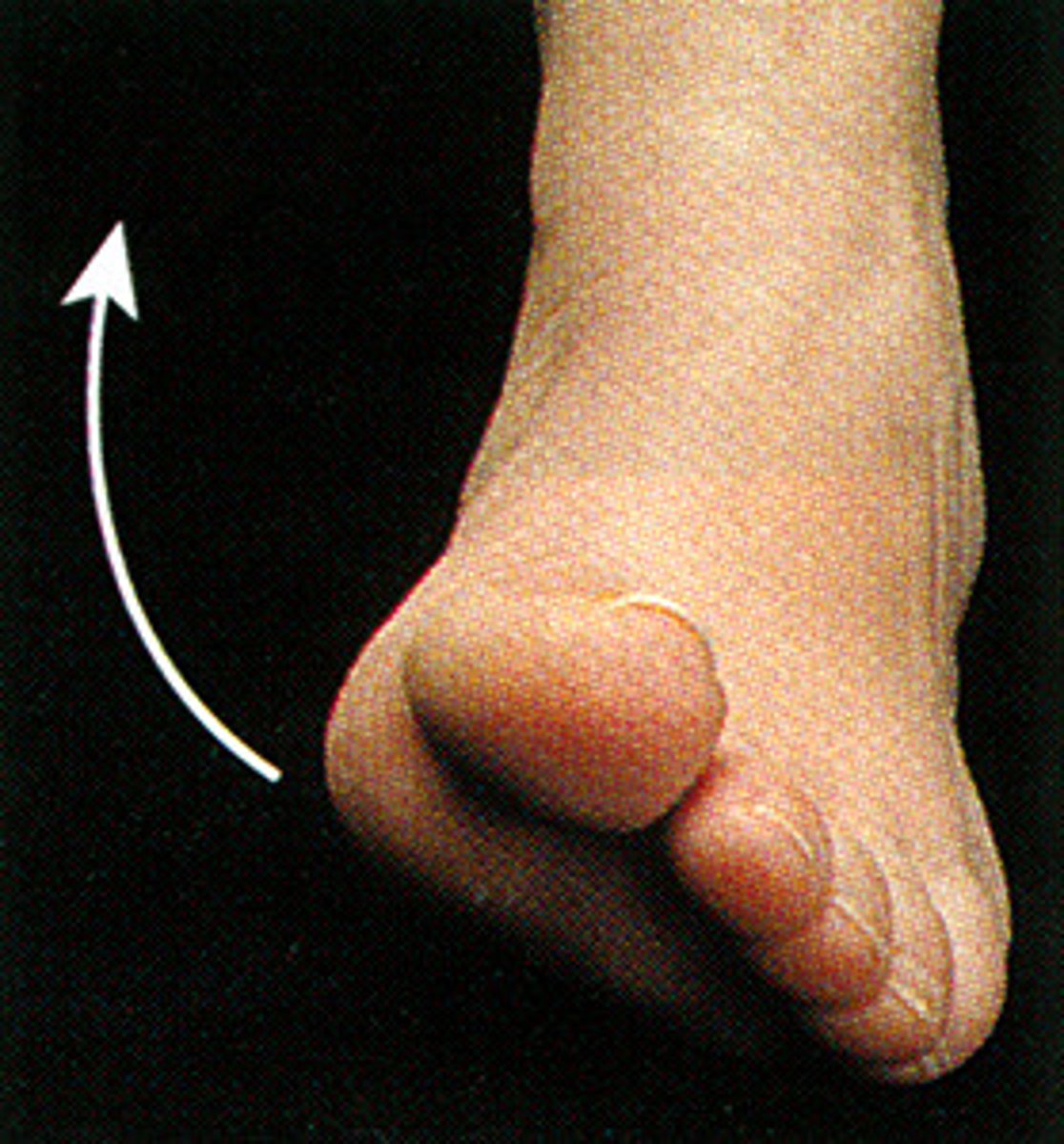
Eversion
turning the sole of the foot outward
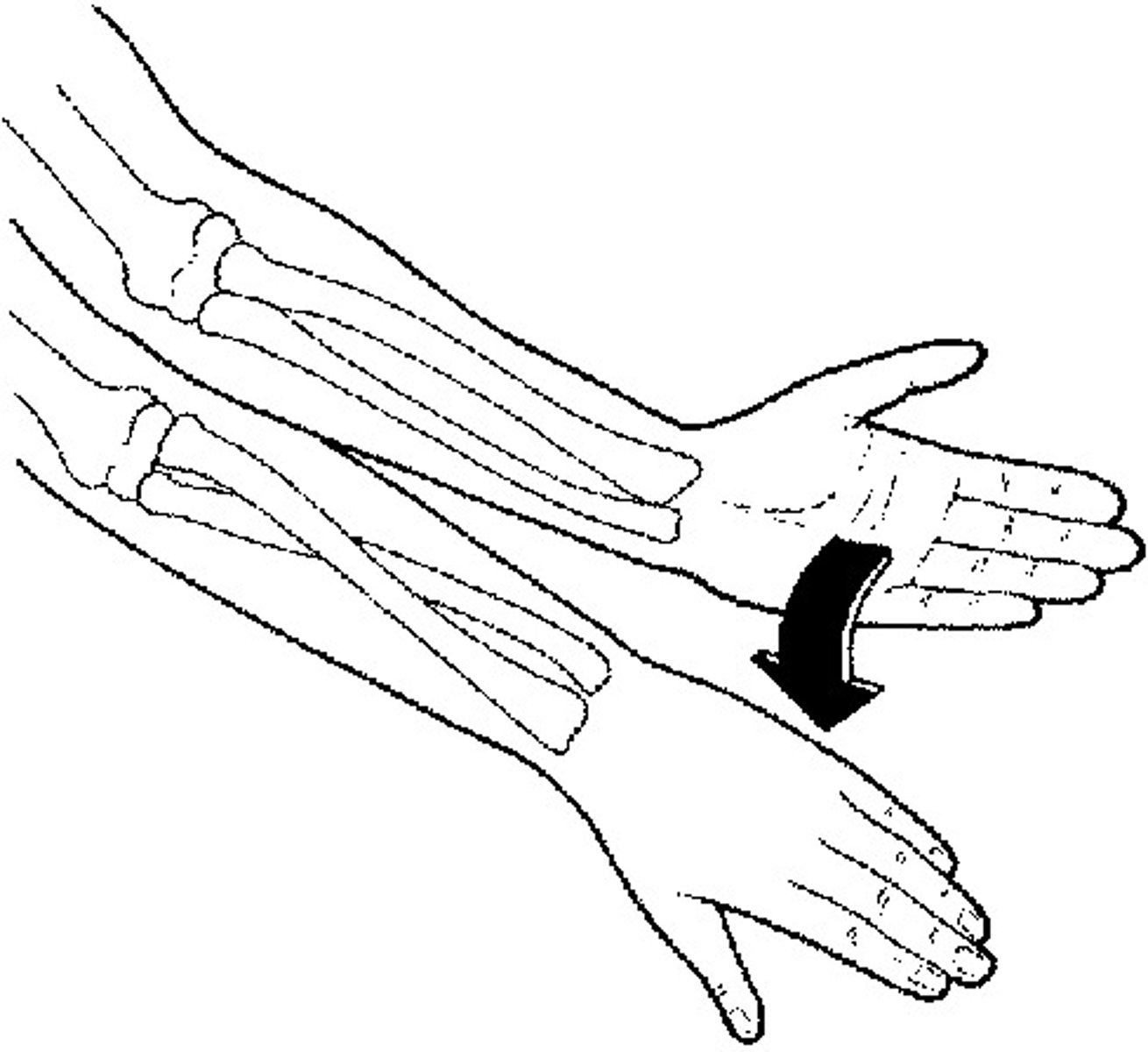
Pronation
turning the palm downward
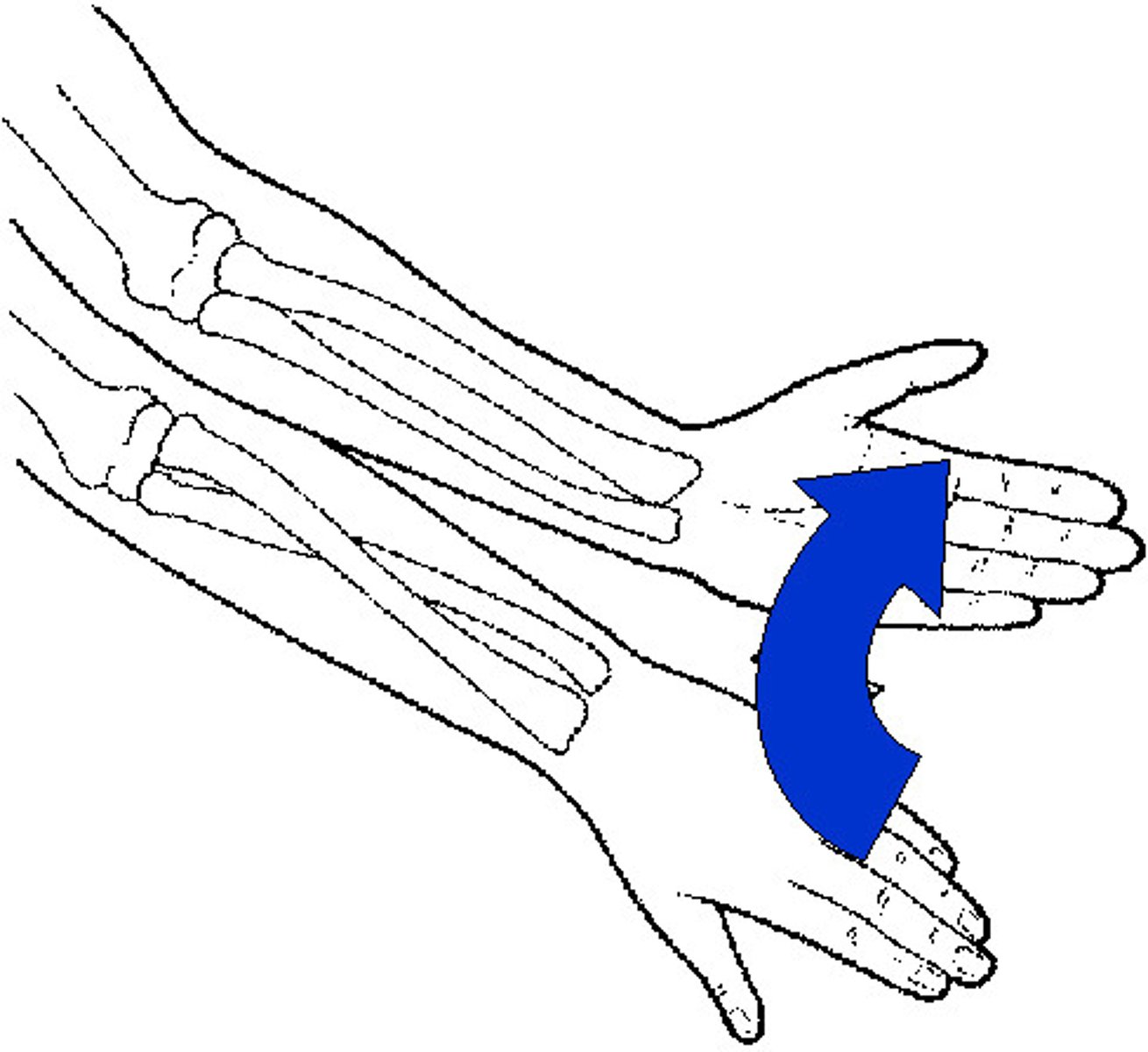
Supination
movement that turns the palm up
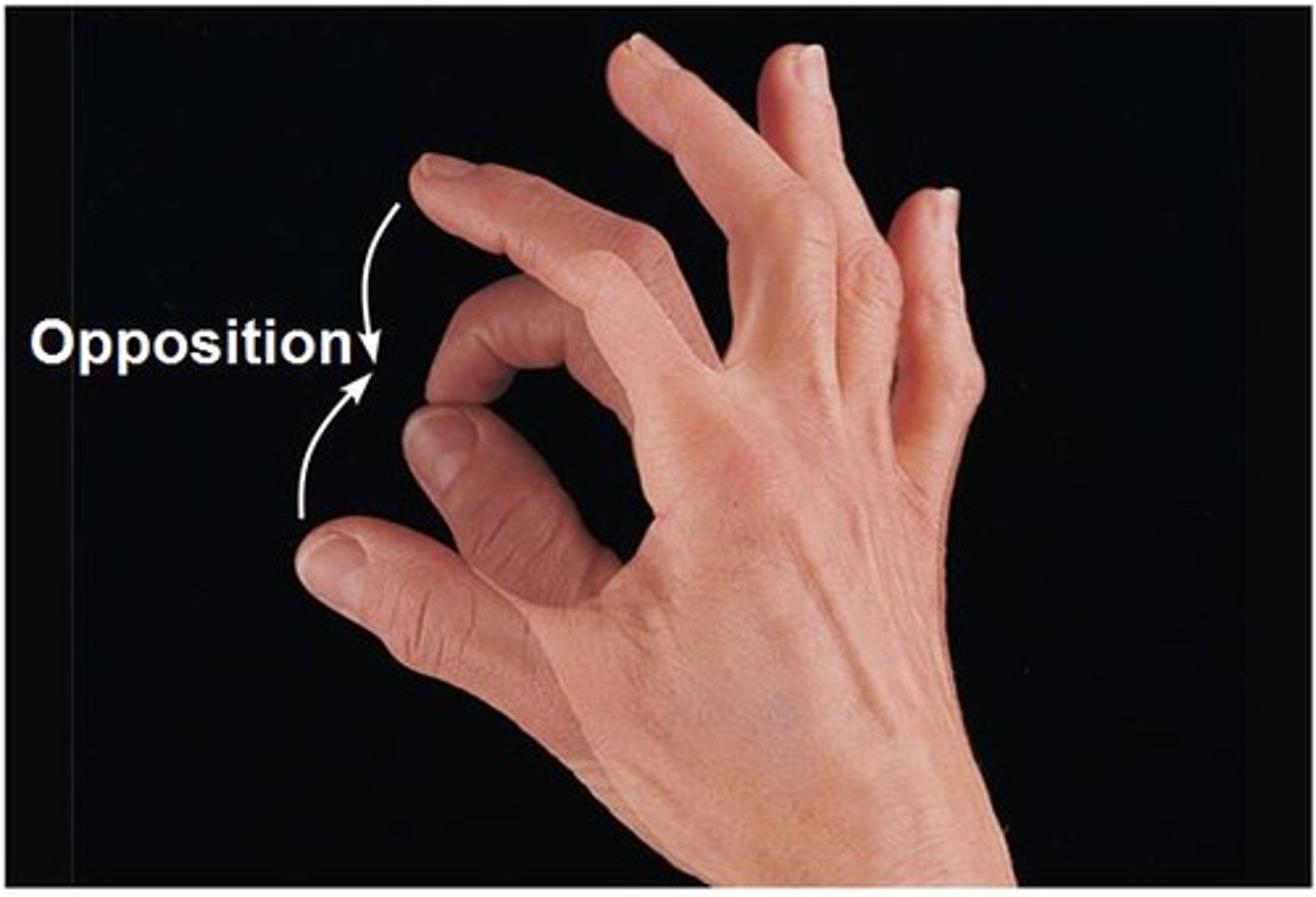
opposition
Movement of the thumb to touch the fingertips
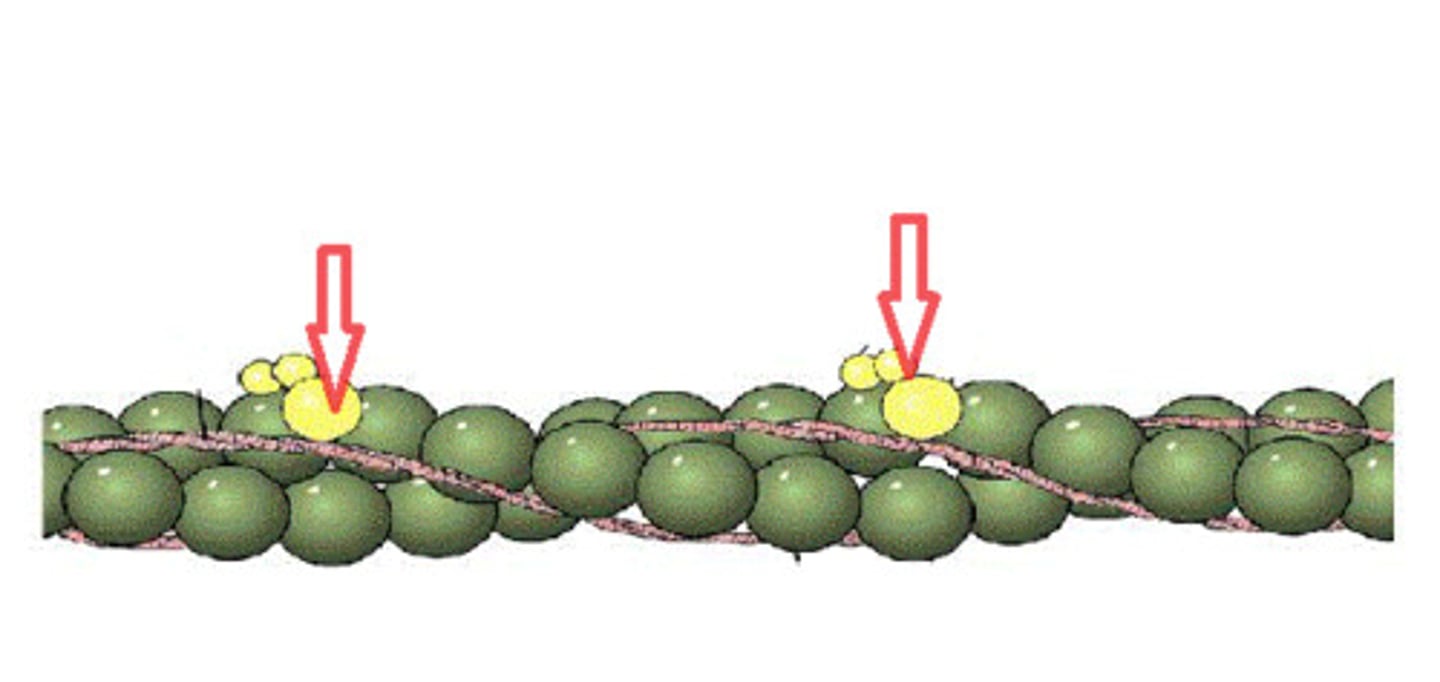
troponin
regulatory protein that binds to actin, tropomyosin, and calcium (when contraction is happening). When not contracting troponin is blocked.
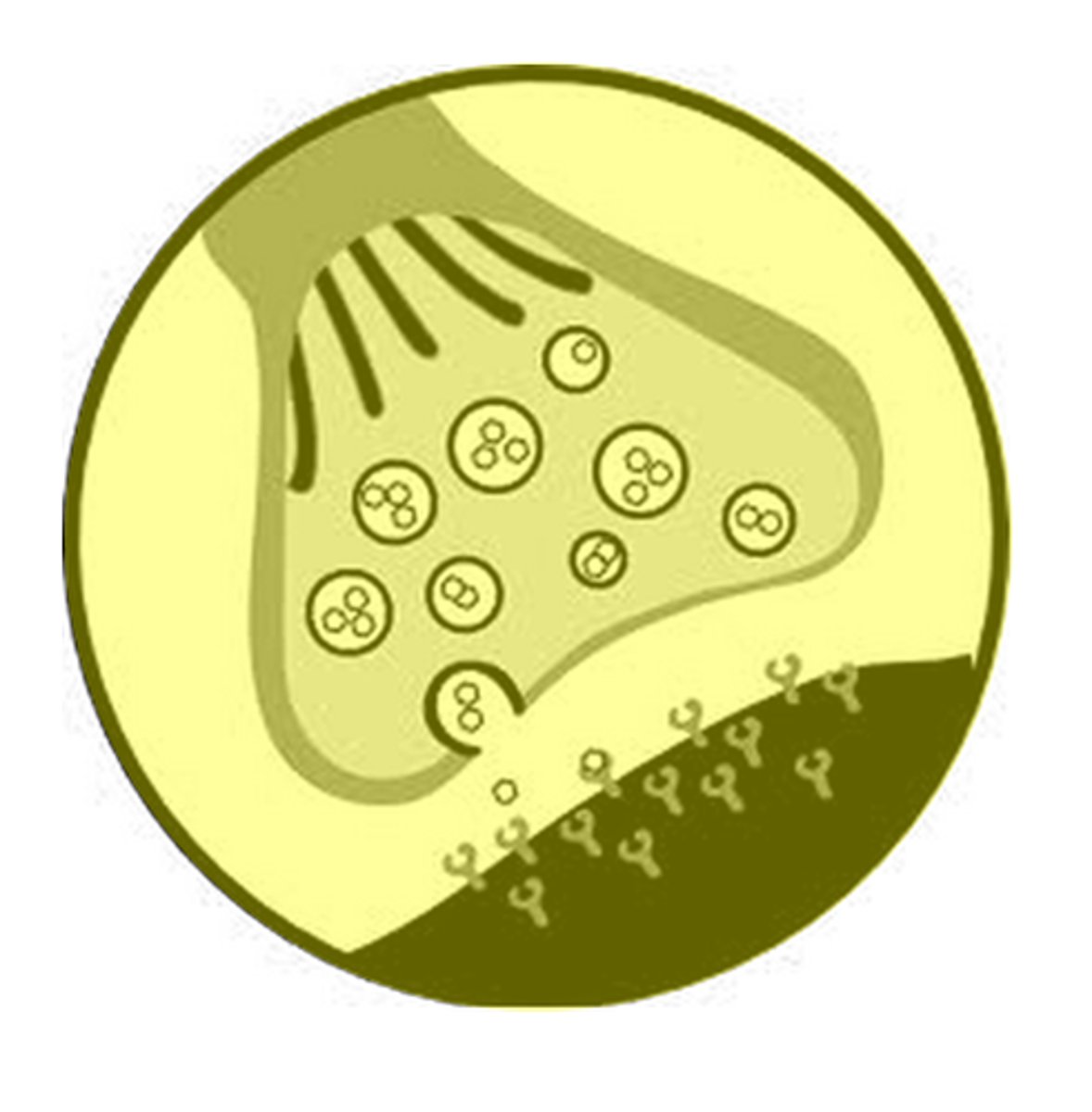
Synapse
the junction between the axon terminal of the sending neuron and the muscle, organ or neuron that is receiving the signal
acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
the enzyme that breaks down acetylcholine in the synaptic cleft
Testes
male gonads, produce sperm & hormones (mostly testosterone)
Gonads
Sex organs: ovaries in females, testes in males.
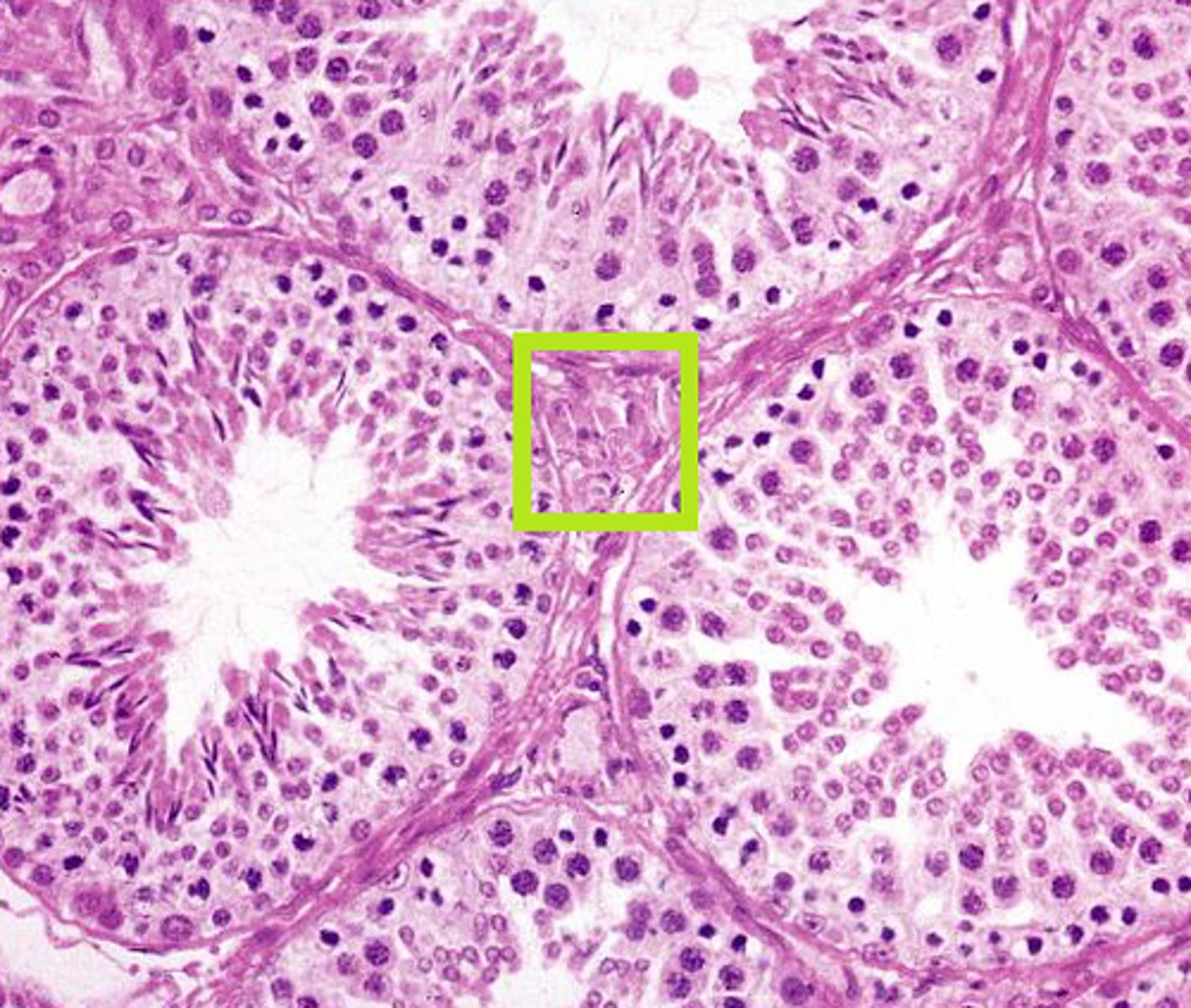
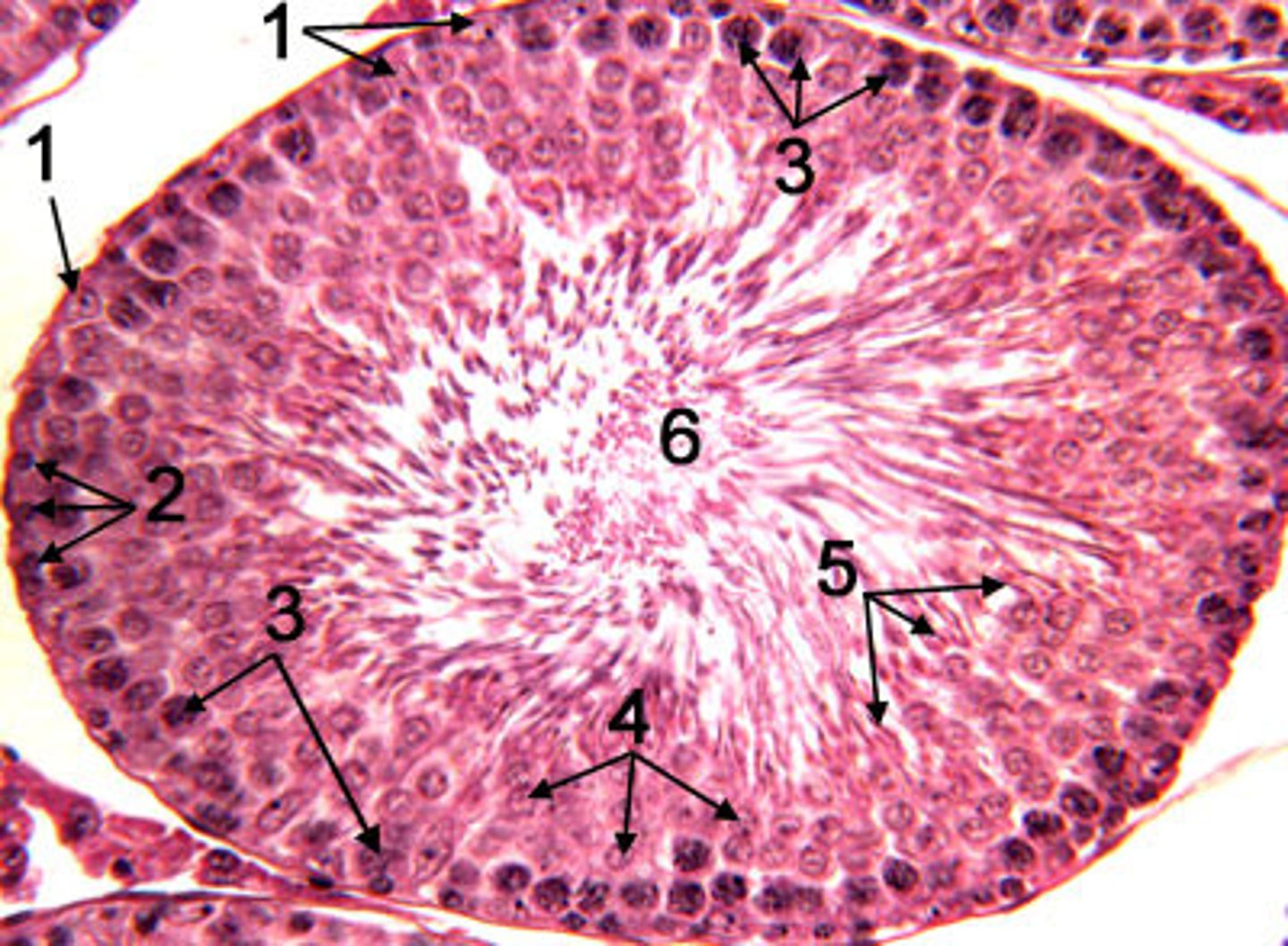
seminiferous tubules
Narrow, coiled tubules that produce sperm in the testes.
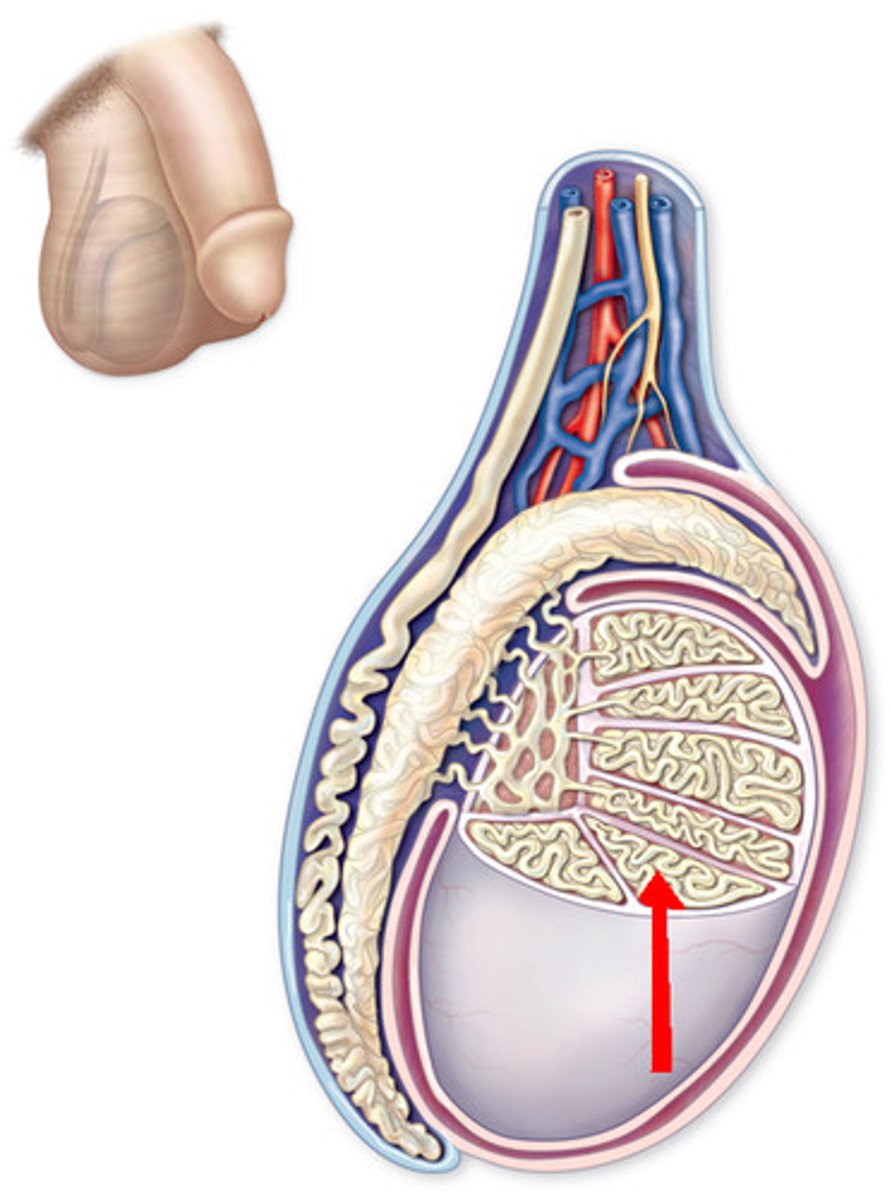
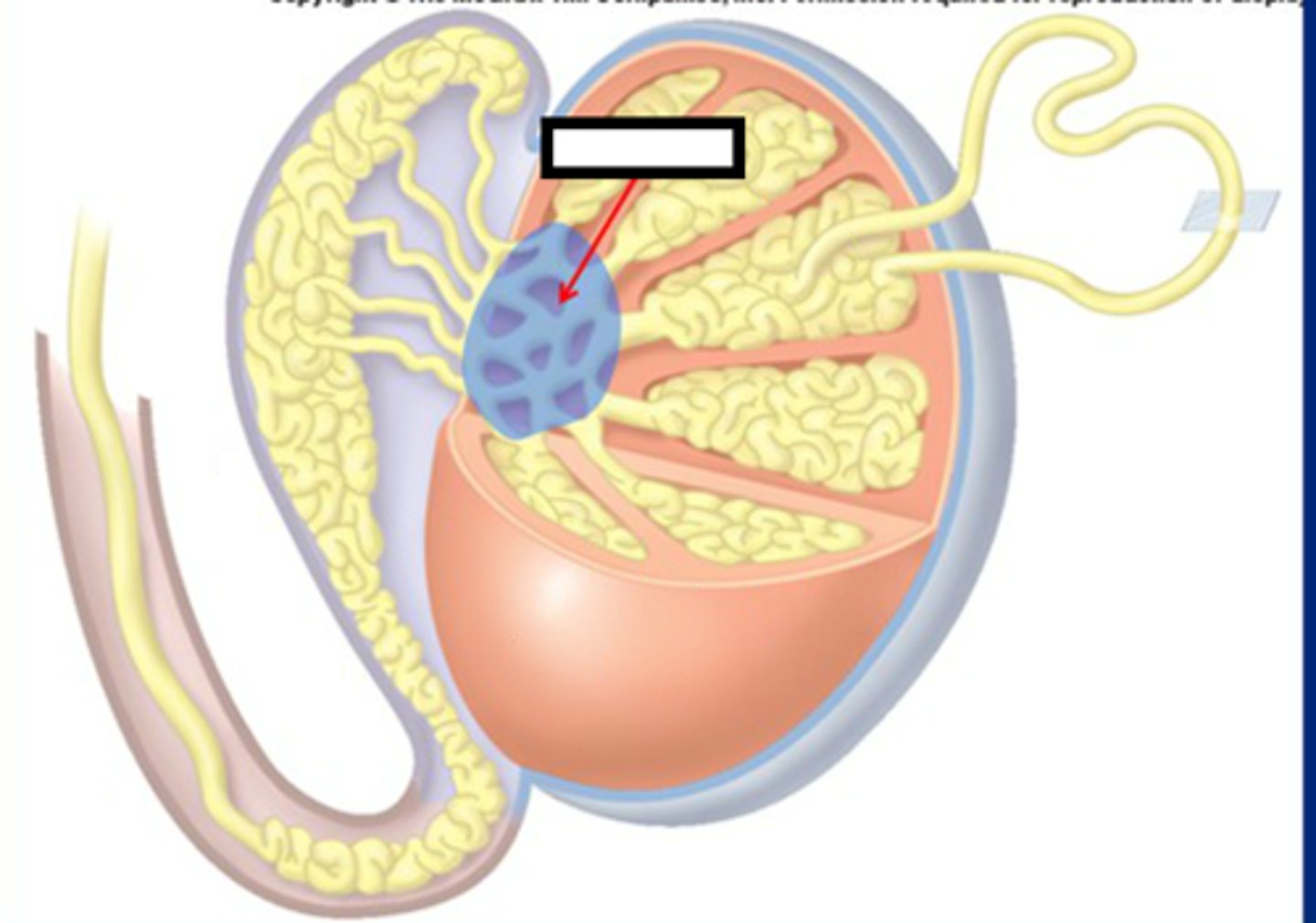
rete testis
network of tubules between the seminiferous tubules and the epididymis, concentrate & mix sperm
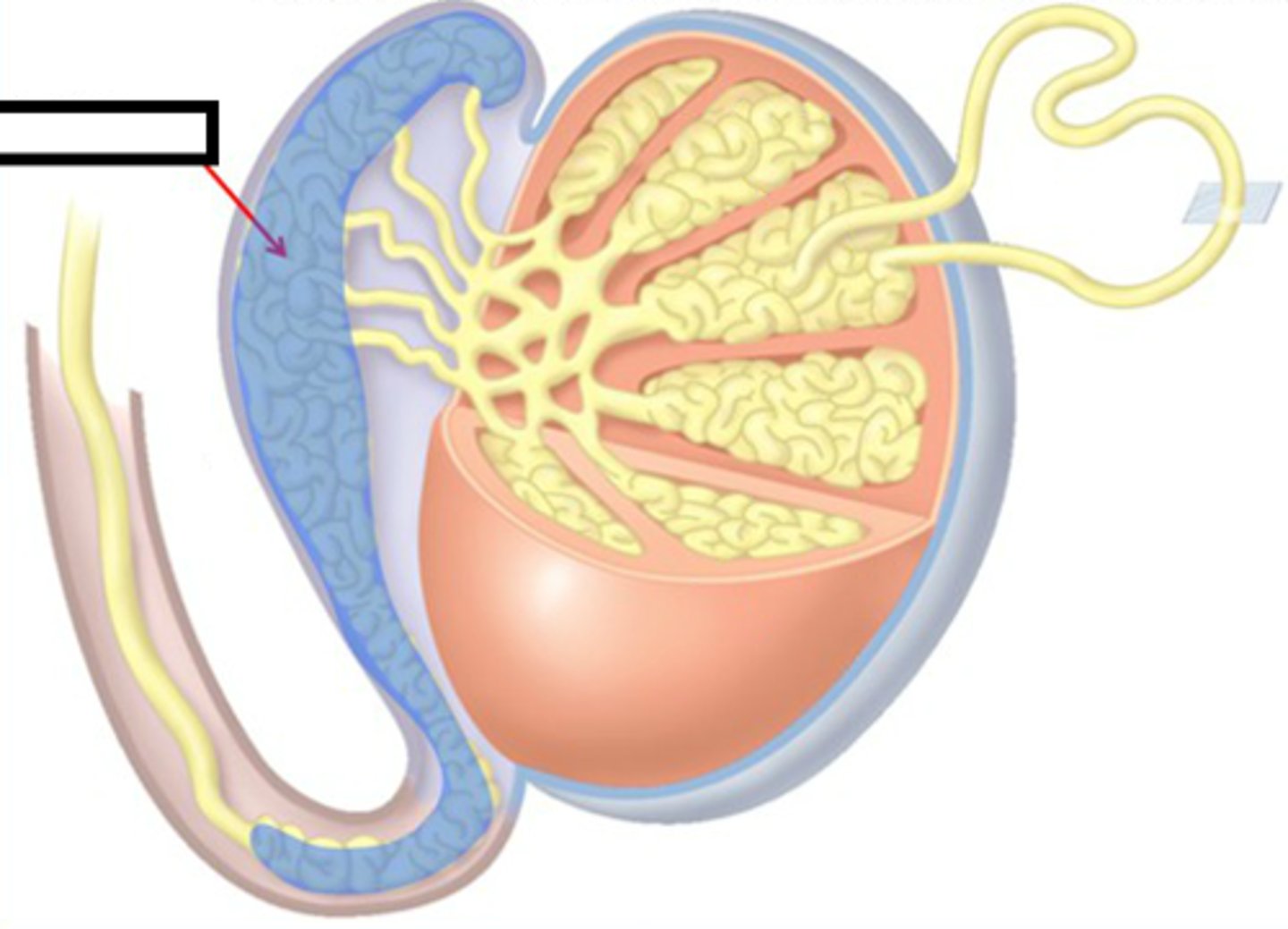
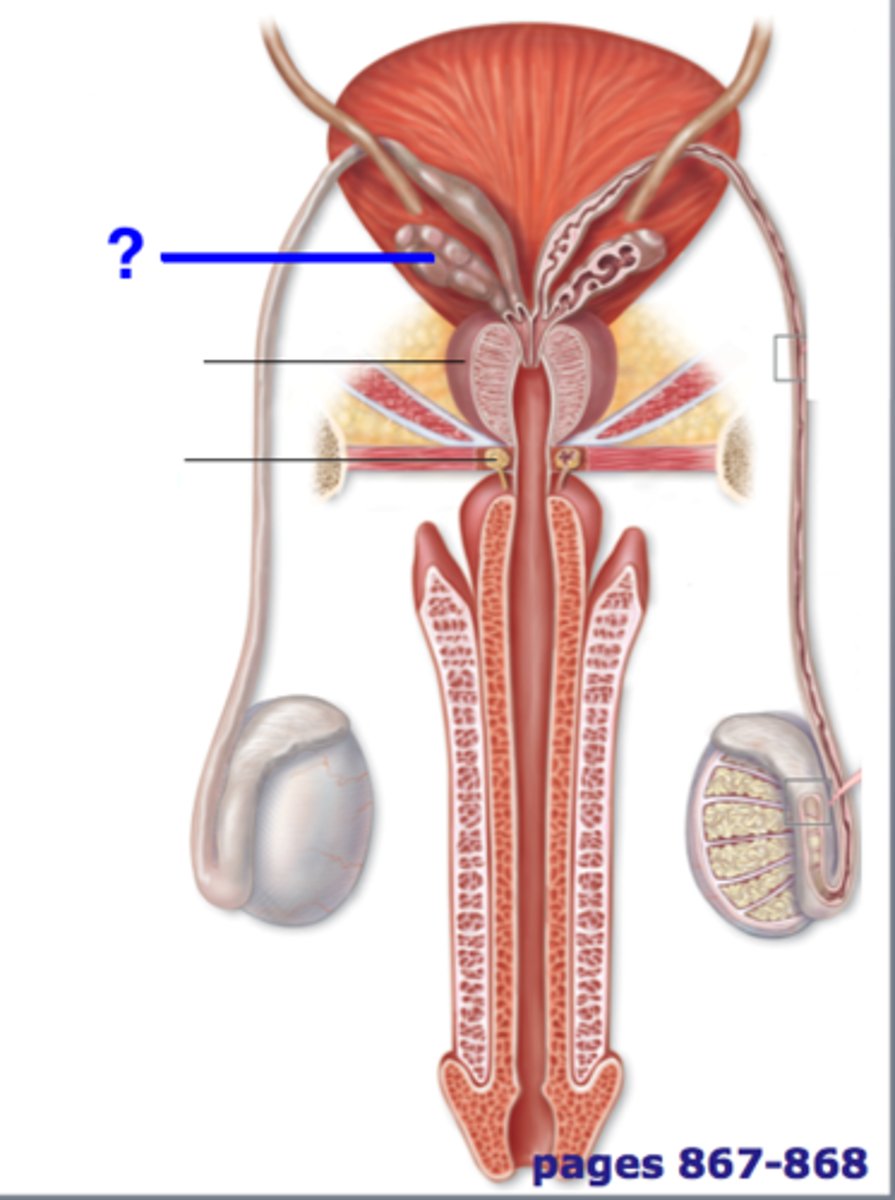
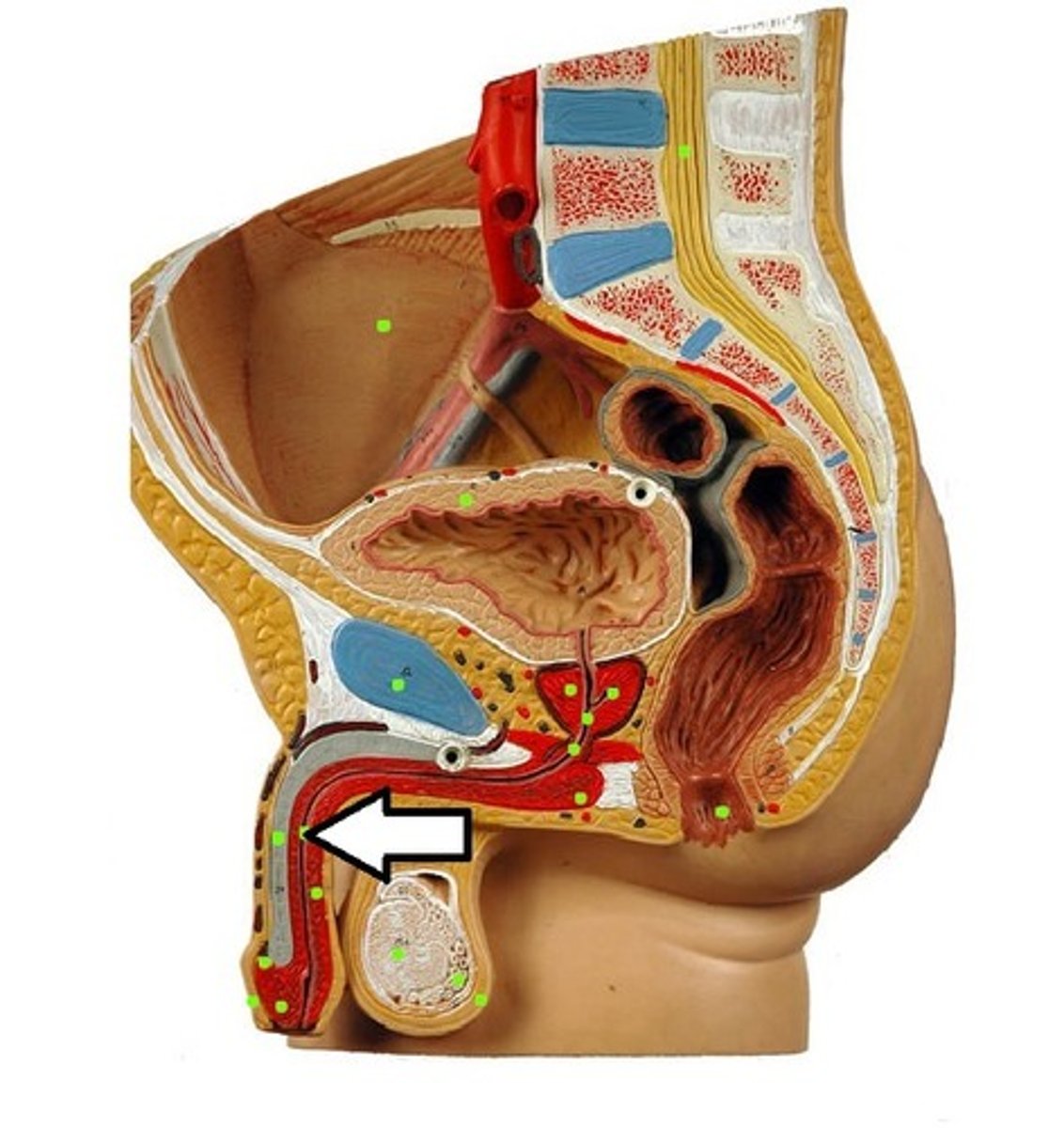
epididymus
structure in the male reproductive system in which sperm are fully matured and are stored (can be 6m long!)
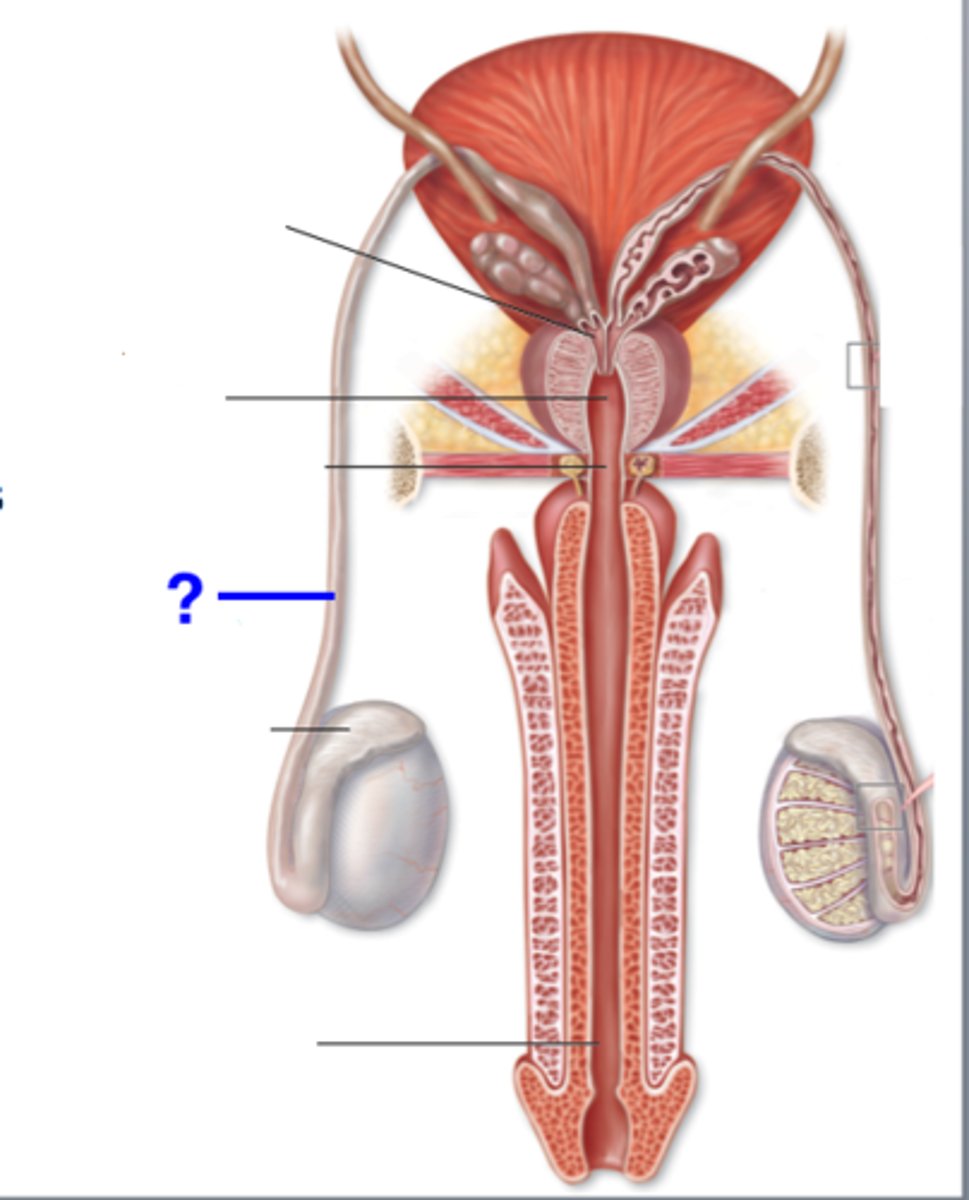
vas deferens
tube that carries sperm from the epididymis to the urethra
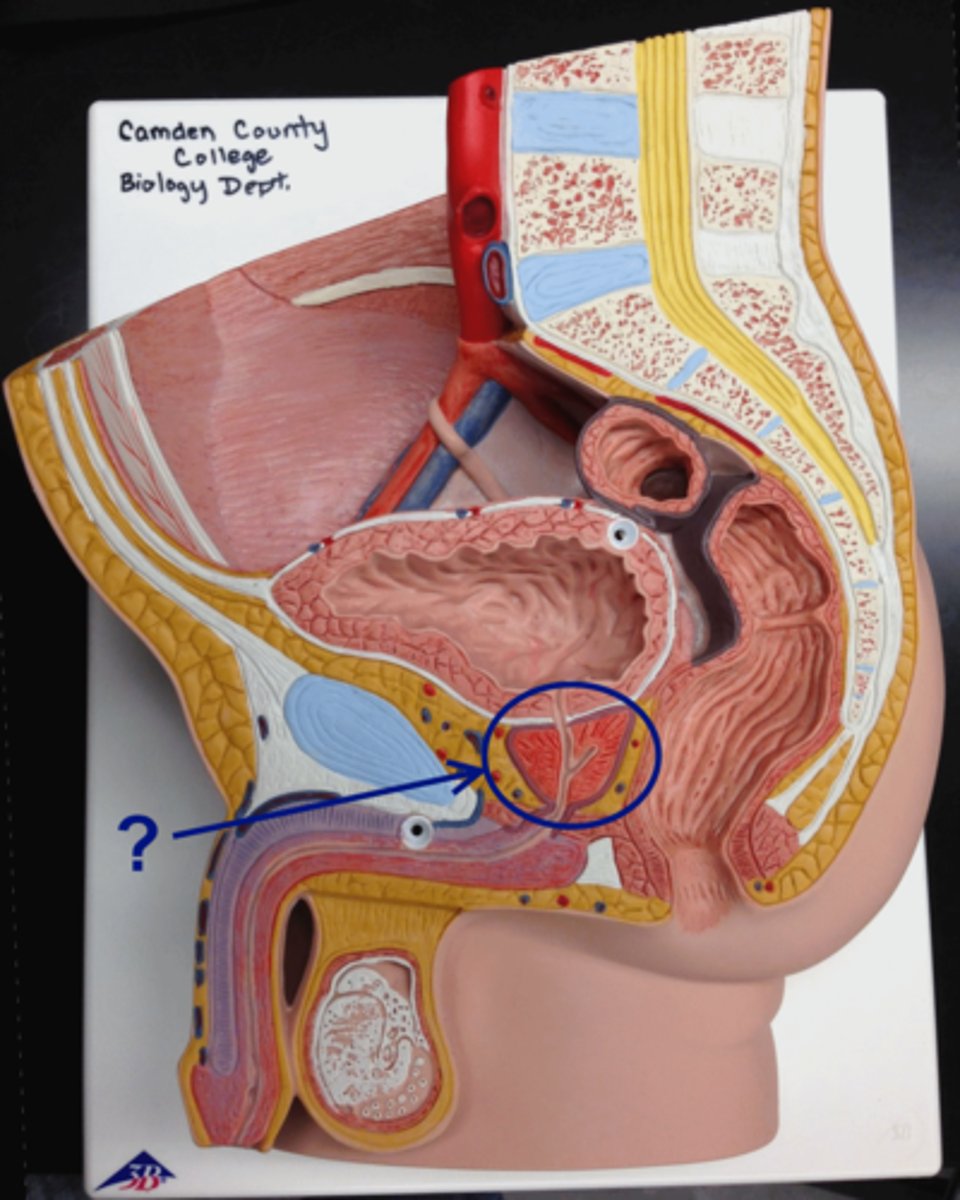
bulbourethral glands
the two glands below the prostate that secrete a sticky fluid that becomes a component of semen
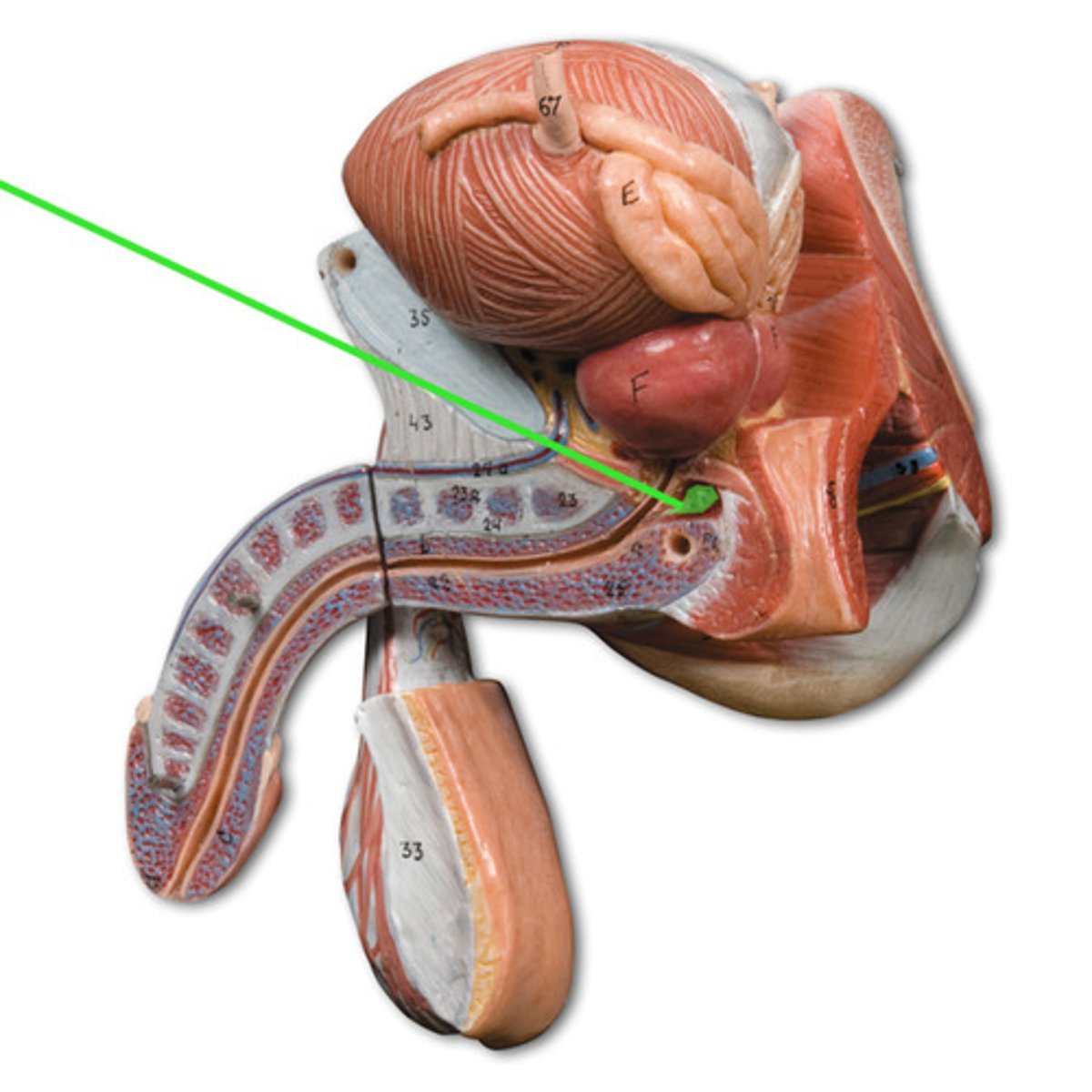
prostate
a gland surrounding the neck of the bladder in male mammals and releasing prostatic fluid.
seminal vesicles
two small glands that secrete a fluid rich in sugar that nourishes and helps sperm move
Urethra
tube leading from the urinary bladder to the outside of the body
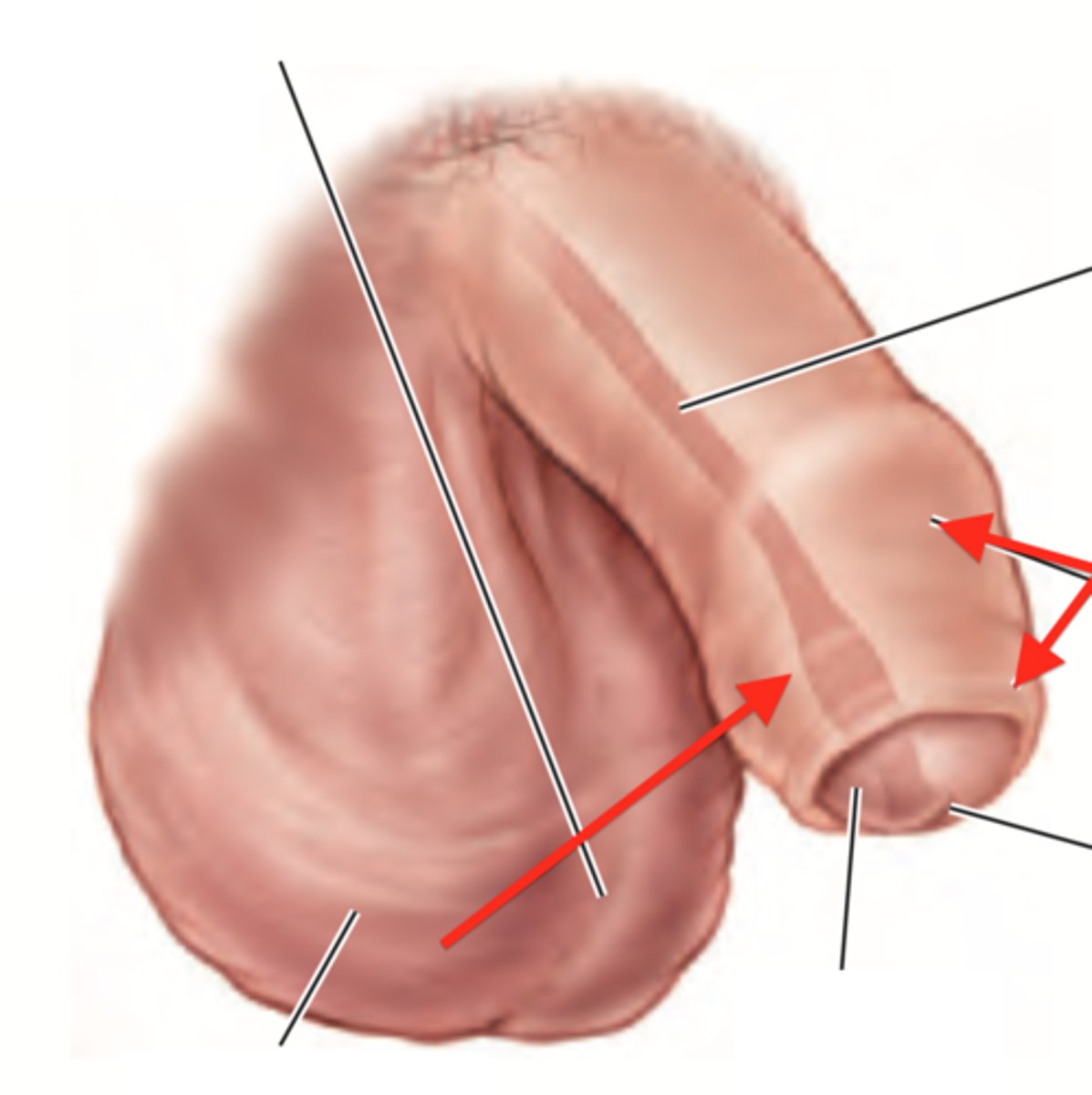
glans
head of the penis
prepuce
foreskin; loose casing that covers the glans penis; removed by circumcision
Scrotum
a pouch of skin containing the testicles.
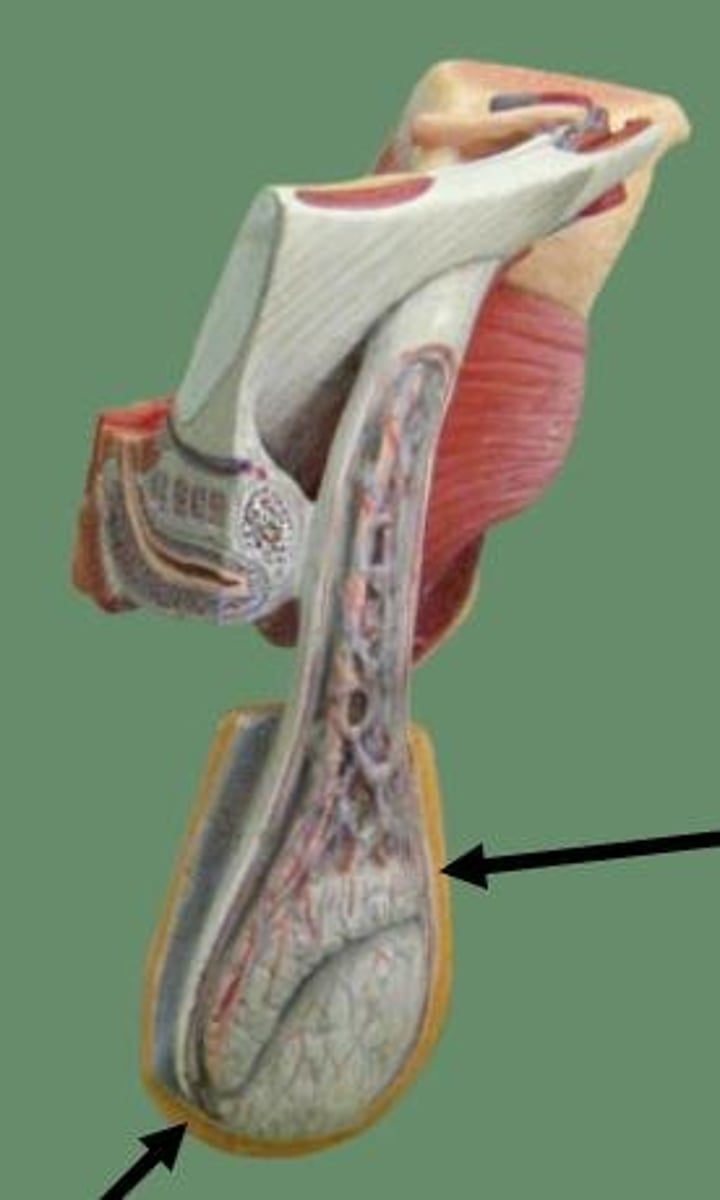
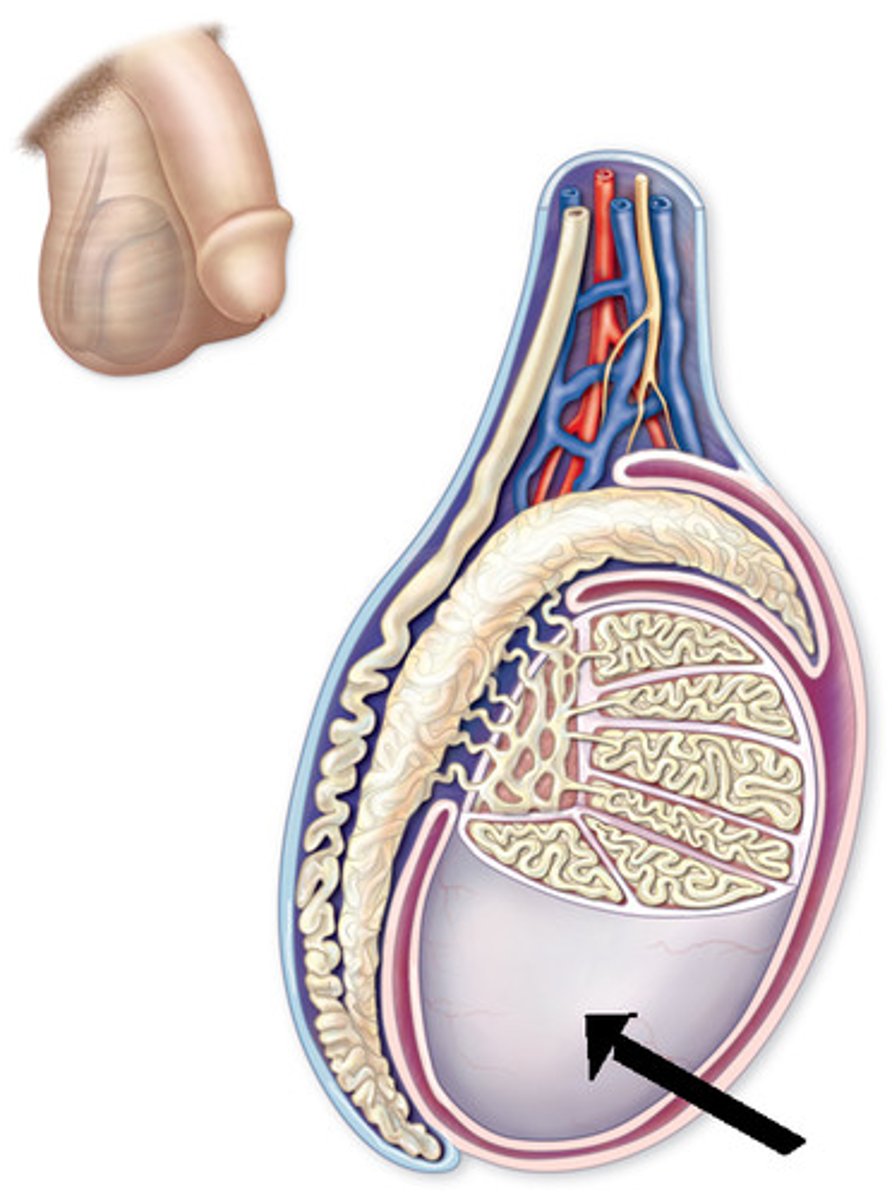
tunica albuginea
white fibrous capsule on testes
urinary bladder
muscular sac in the pelvis that stores and releases urine through the urethra
Testosterone
the most important of the male sex hormones. Both males and females have it, but the additional testosterone in males stimulates the growth of the male sex organs in the fetus and the development of the male sex characteristics during puberty
interstitial cells
small specialized cells in the testes (near the seminiferous tubules) that secrete the male sex hormone, testosterone
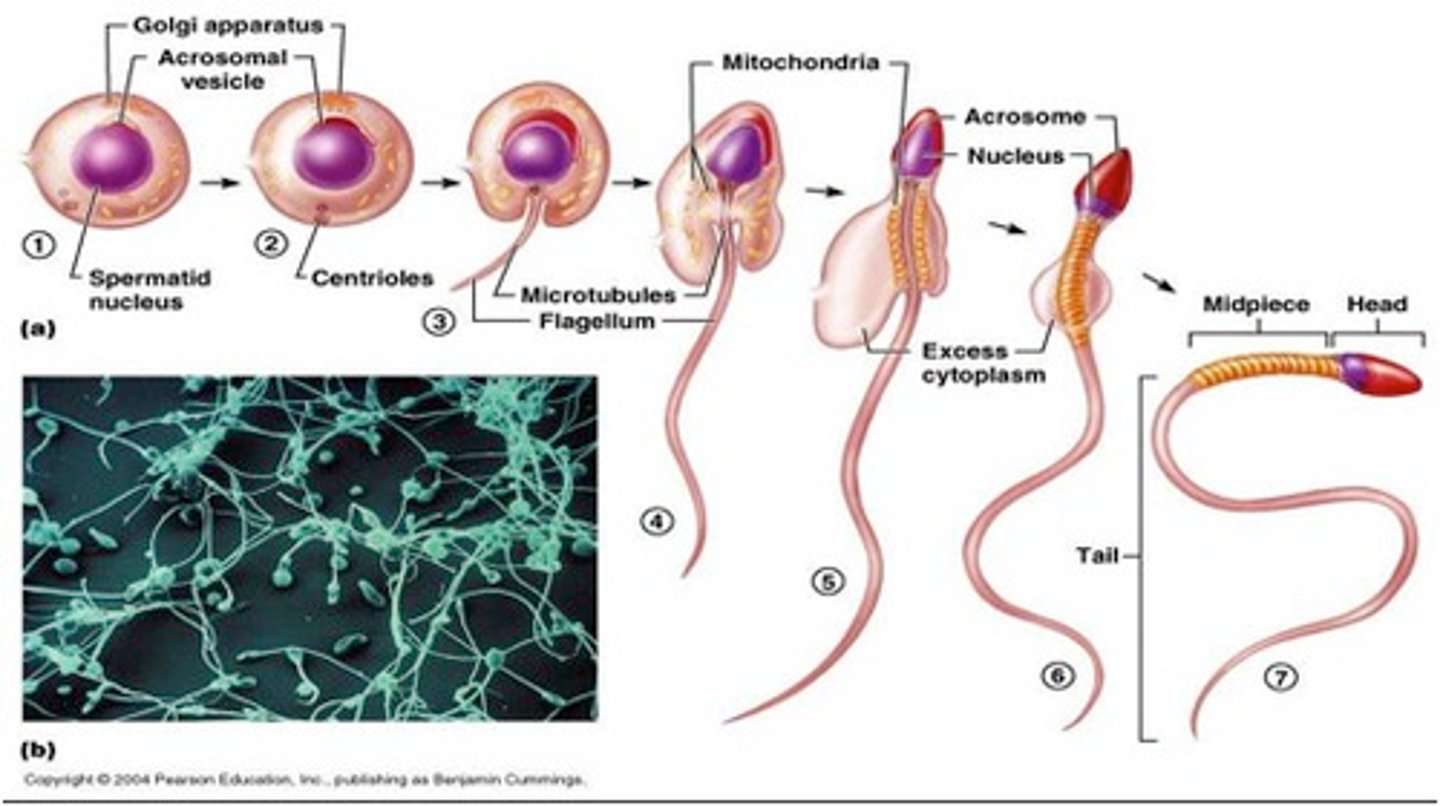
Sperm
the male gametes (reproductive cells)
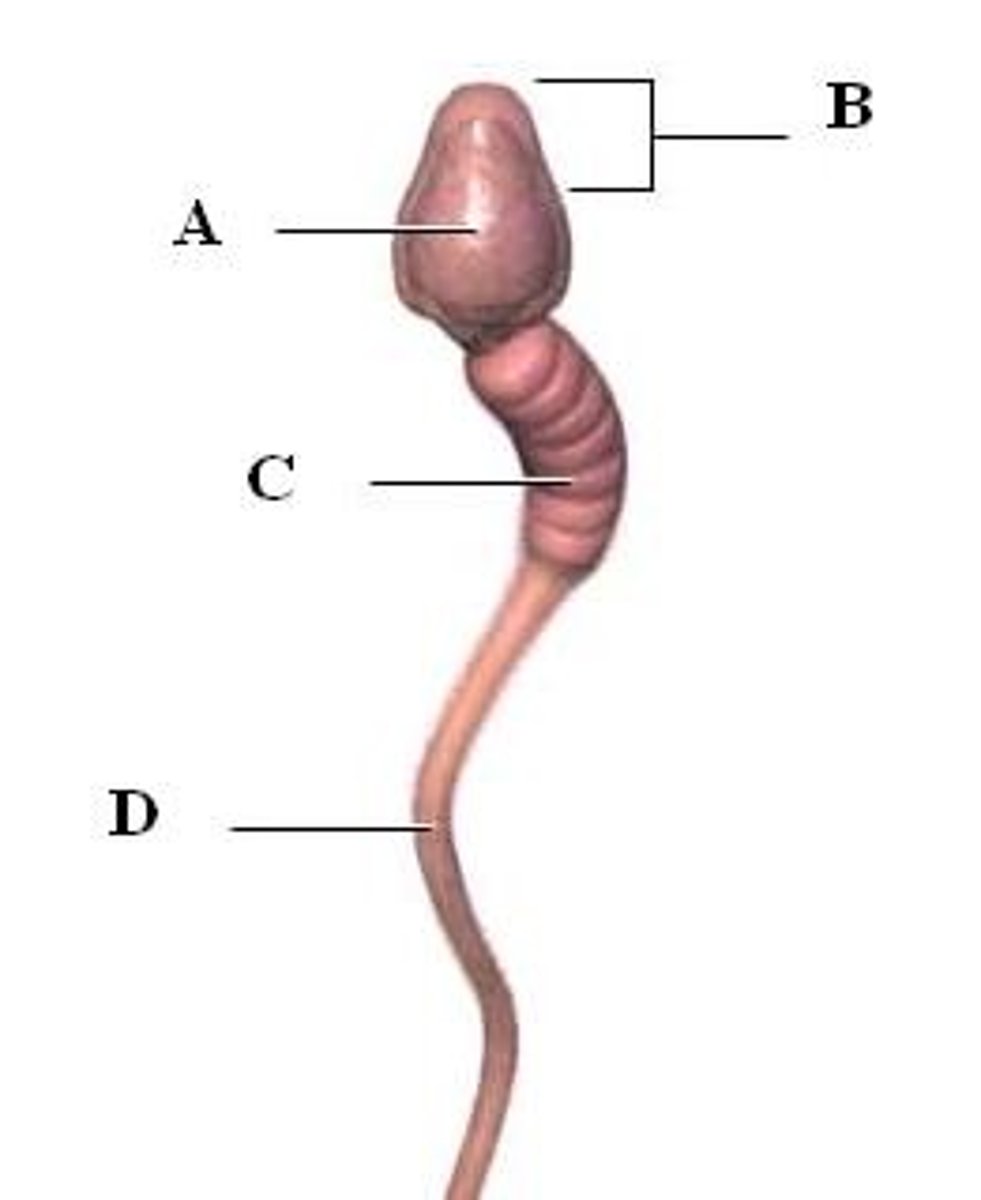
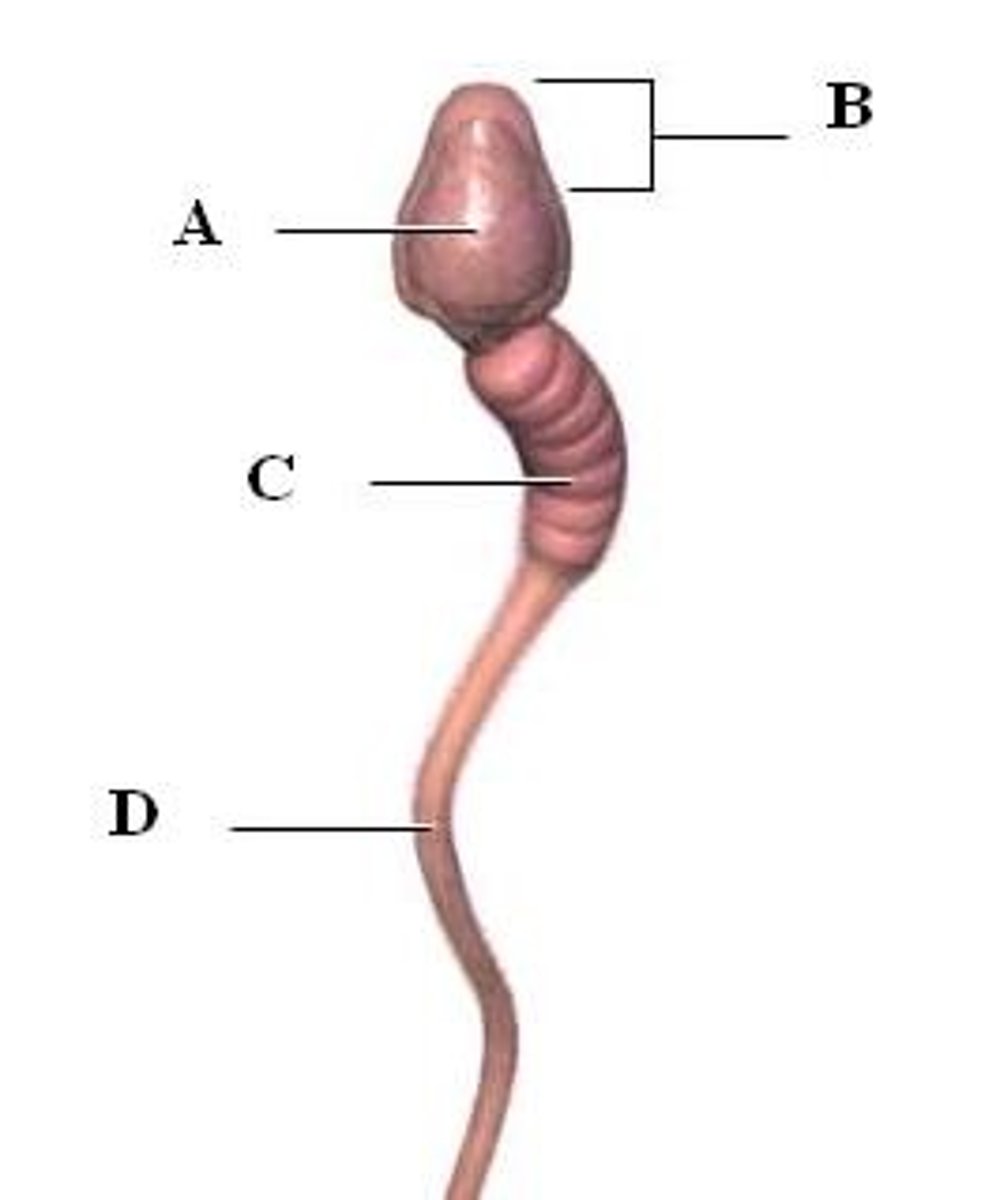
acrosome
A region at the head of a sperm cell that contains digestive enzymes to help the sperm penetrate into the oocyte (within B on the diagram)
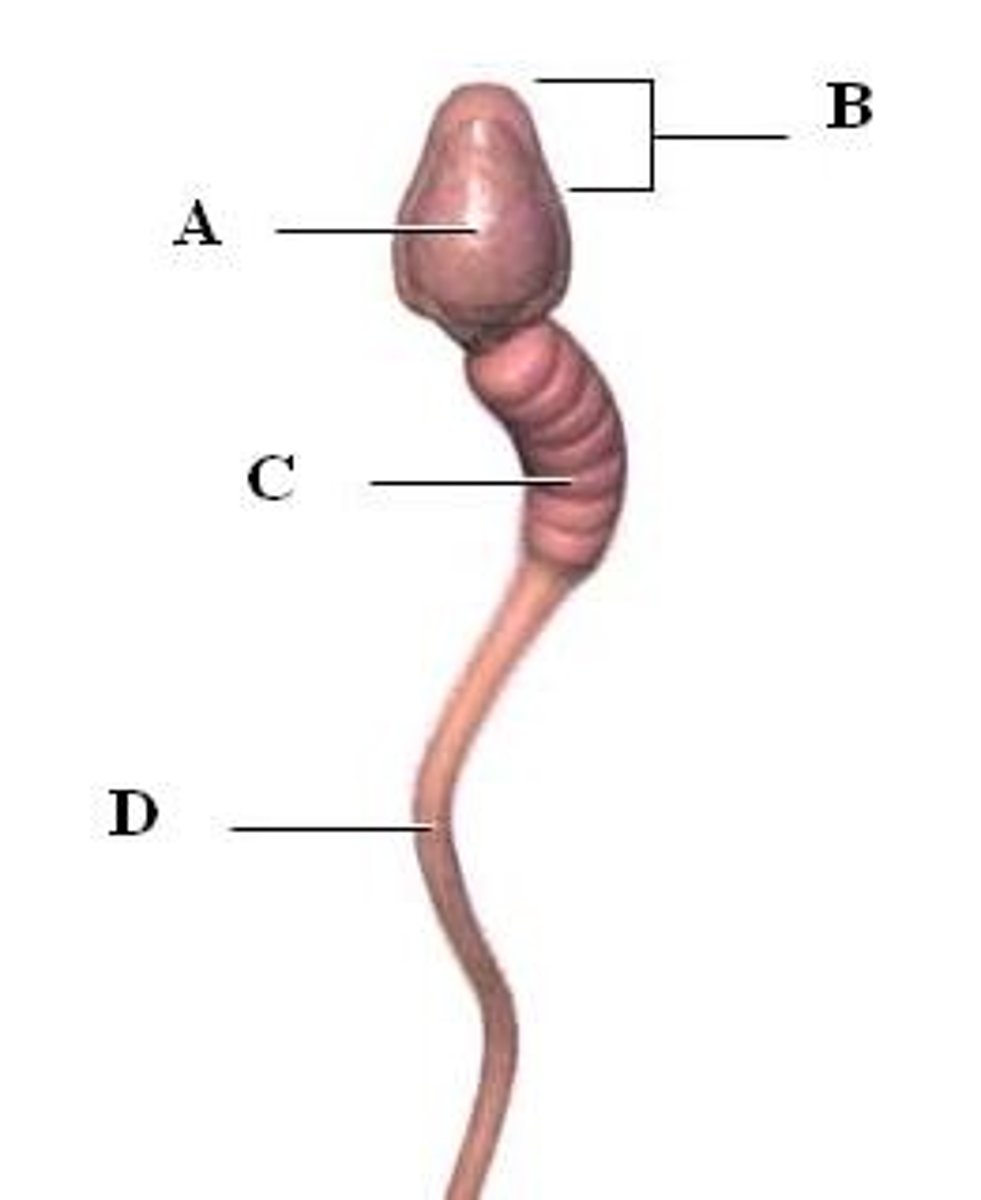
midpiece of sperm
generates ATP from fructose and contains many mitochondria (C on the diagram)
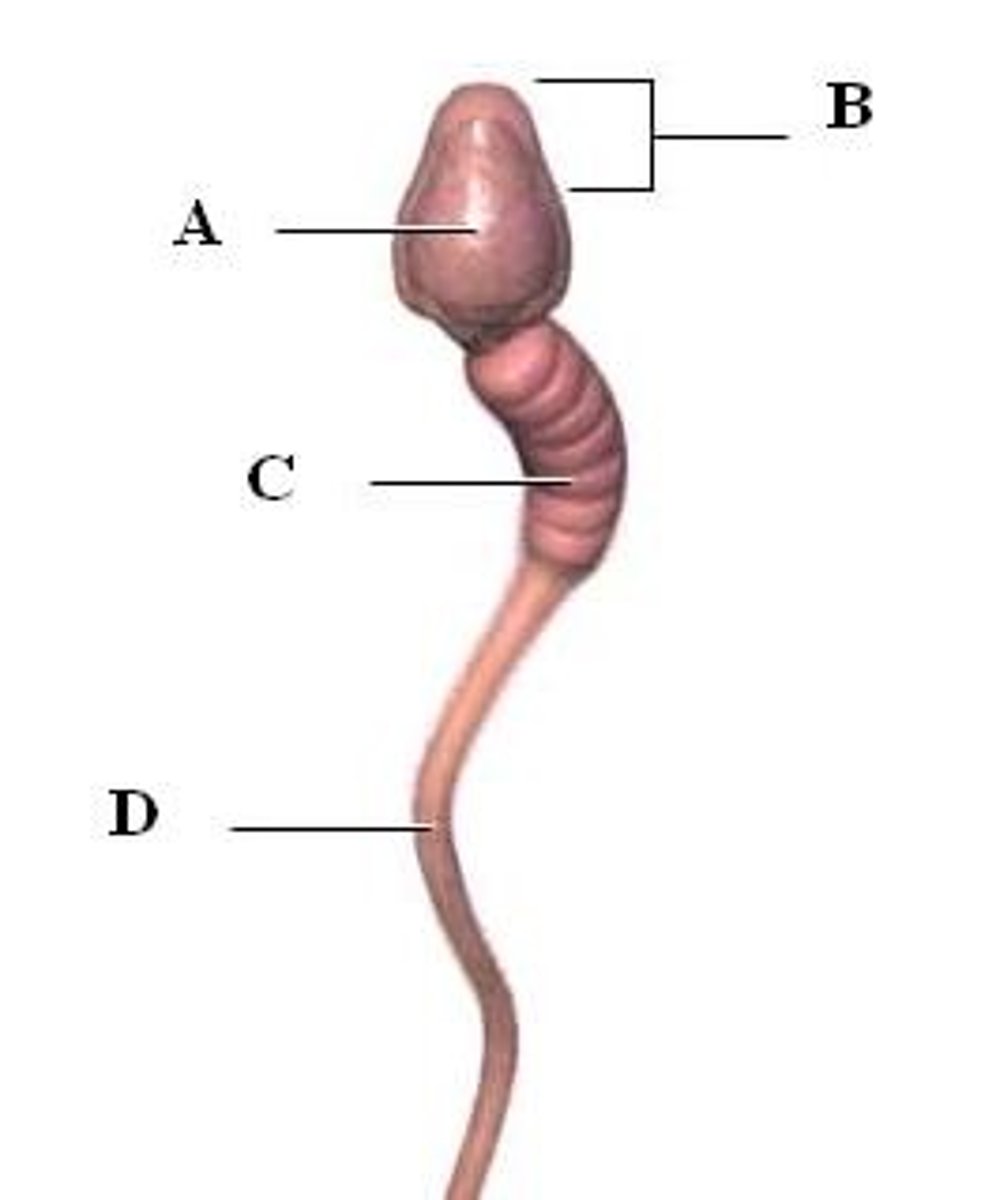
Flagellum
A long, hairlike structure that grows out of a cell and enables the cell to move. (D on the diagram)
Spermatogenesis
production of sperm
Spermiogenesis
transformation of spermatids to spermatozoa during spermatogenesis
secondary sex characteristics
male voice quality, body hair, enlargement of muscles, increased bone density
vasectomy
ligation of a segment of the vas deferens to produce sterility in the male
Hypothalamus
a neural structure lying below the thalamus; directs eating, drinking, body temperature; helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH)
A hormone released from the hypothalamus that triggers the anterior pituitary to secrete FSH and LH.
Mitosis
cell division in which the nucleus divides into nuclei containing the same number of chromosomes
Meiosis
Cell division that produces reproductive cells in sexually reproducing organisms
spermatogonia
Stem cells in a testis that can give rise to primary spermatocytes.
lumen
space within a tubular part or organ, such as the space within the seminiferous tubules (6 on this diagram)
spermatid
an immature male sex cell formed from a spermatocyte that can develop into a spermatozoan without further division.
erectile tissue
Specialized tissue with a lot of space that can fill with blood upon proper stimulation, causing the tissue to become firm. Found in the penis, the clitoris, the labia, and the nipples.
pregnancy
events that occur in a woman's body from the time of fertilization (conception) until delivery (birth)
gestation
the first day of the last menstrual period until birth (~280 days), time during which development occurs
fertilization
the moment the genetic material of the sperm and ovum combine
zygote
fertilized egg, 1 cell, 46 chromosomes
cleavage
the process when a single cell (zygote) rapidly divides into smaller cells as it travels to uterus
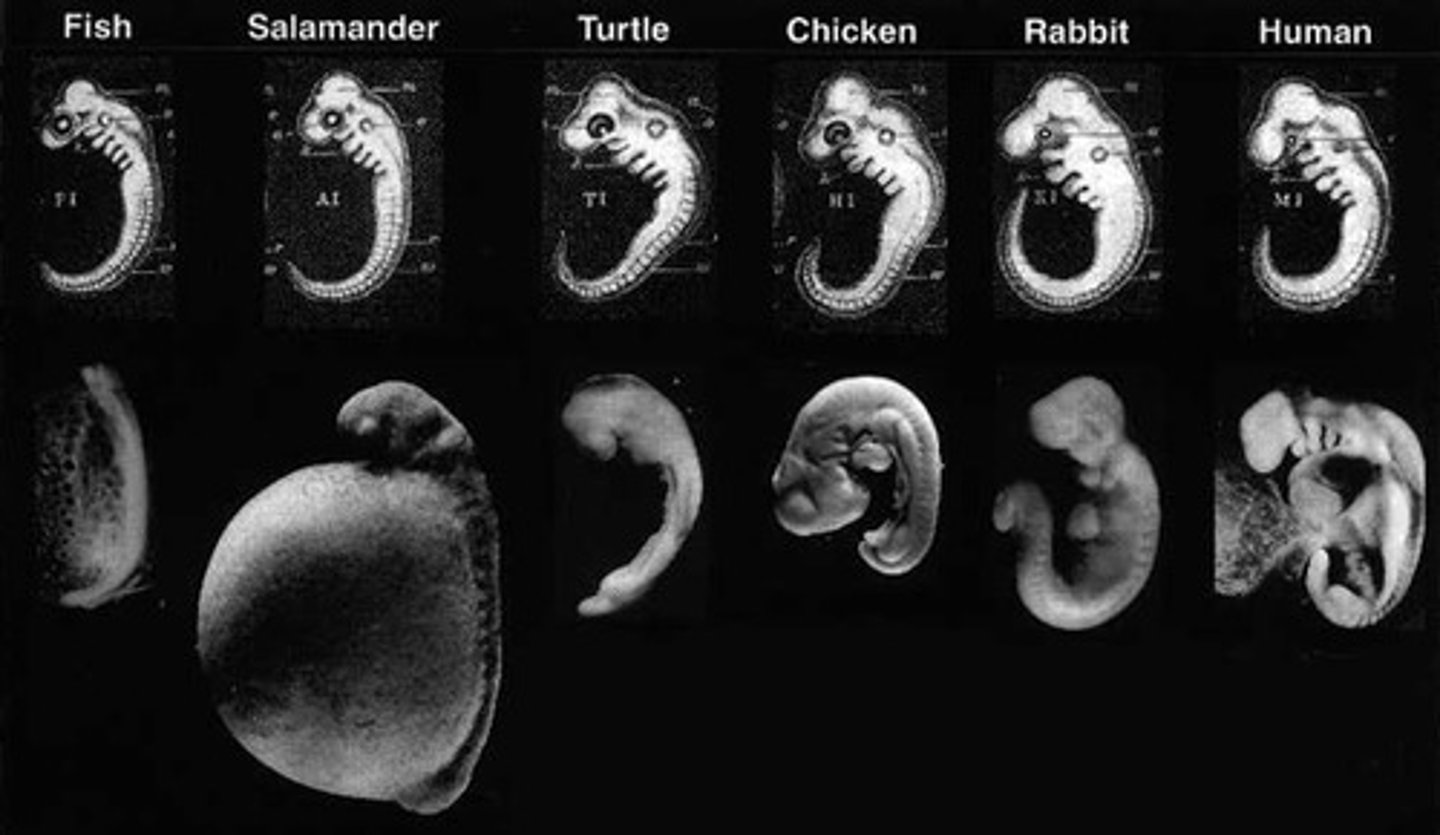
embryo
stage of development from fertilization —> 8 weeks
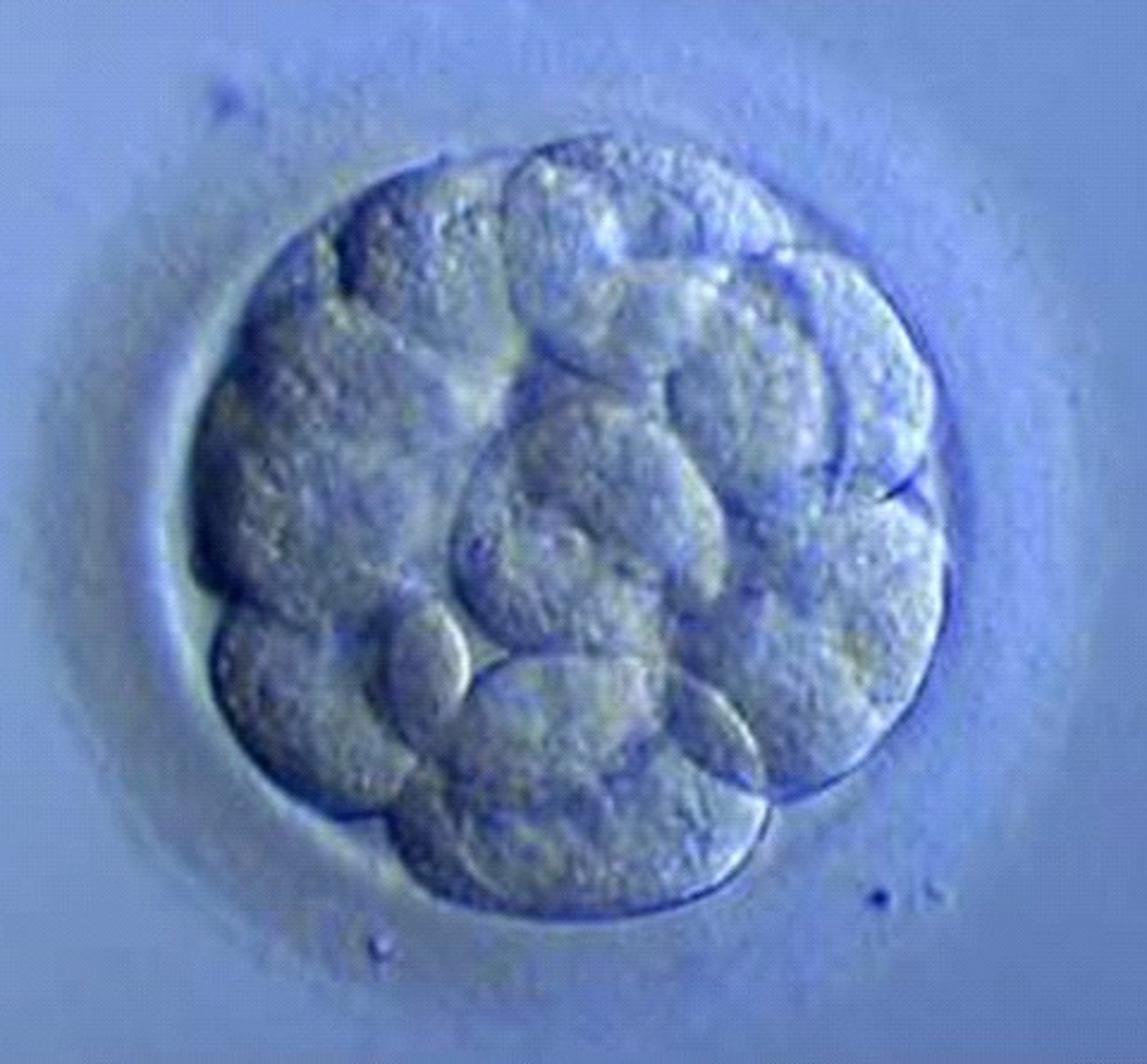
morula
a cluster of 16 cells that arrive in uterus, float free, and use uterine secretion for nutrition
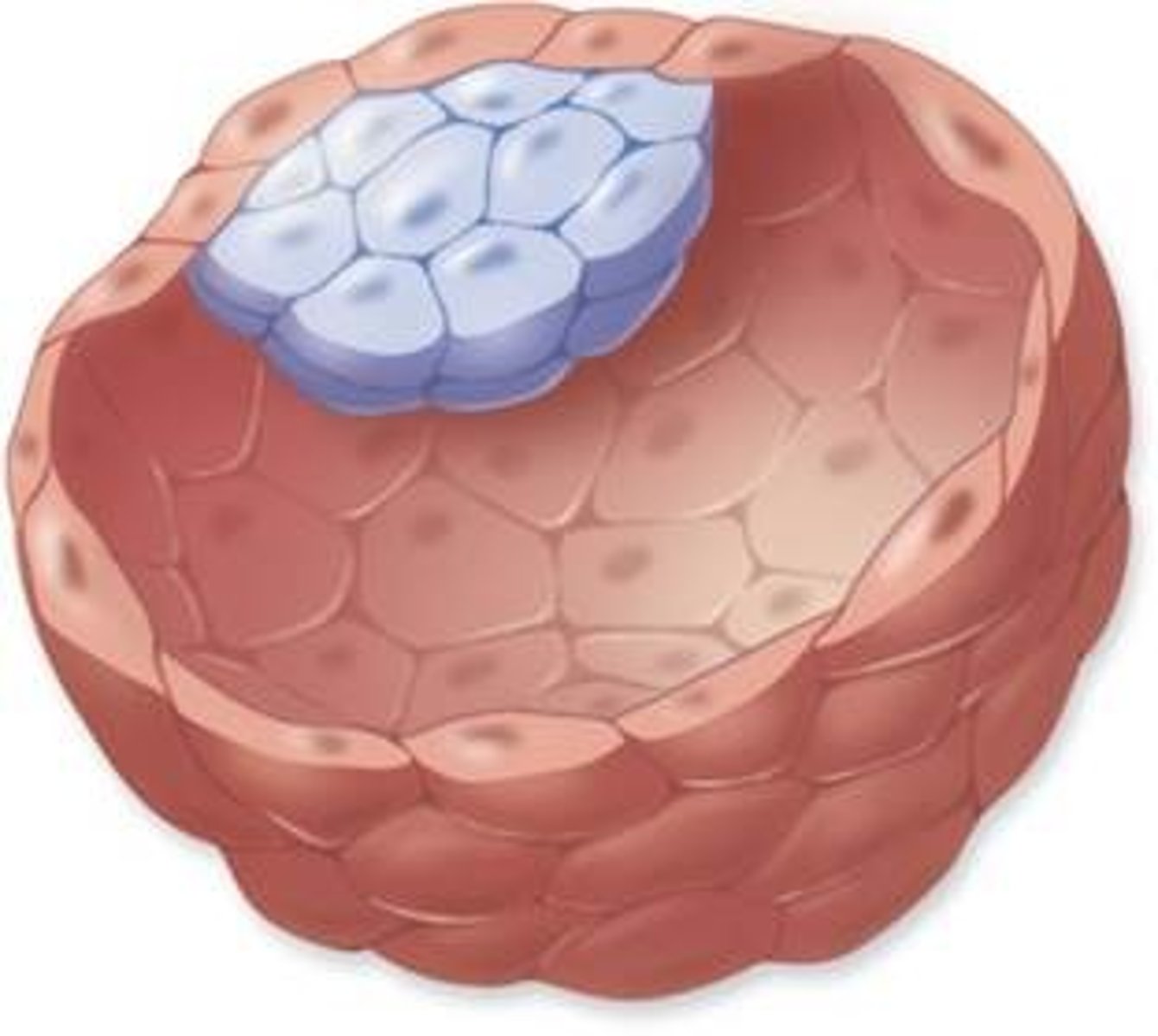
blastocyst
~100 cells, hollow, ball like, secretes human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) to signal corpus luteum to continue making hormones (to prevent sloughing off endometrium)
human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)
hormone secreted by a blastocyst that signals the corpus luteum to continue making hormones so the endometrium will not be shed
placenta
temporary endocrine organ that makes estrogens, progesterone, relaxin and other hormones for pregnancy, provides nutrients and oxygen to the developing fetus, and carries away waste
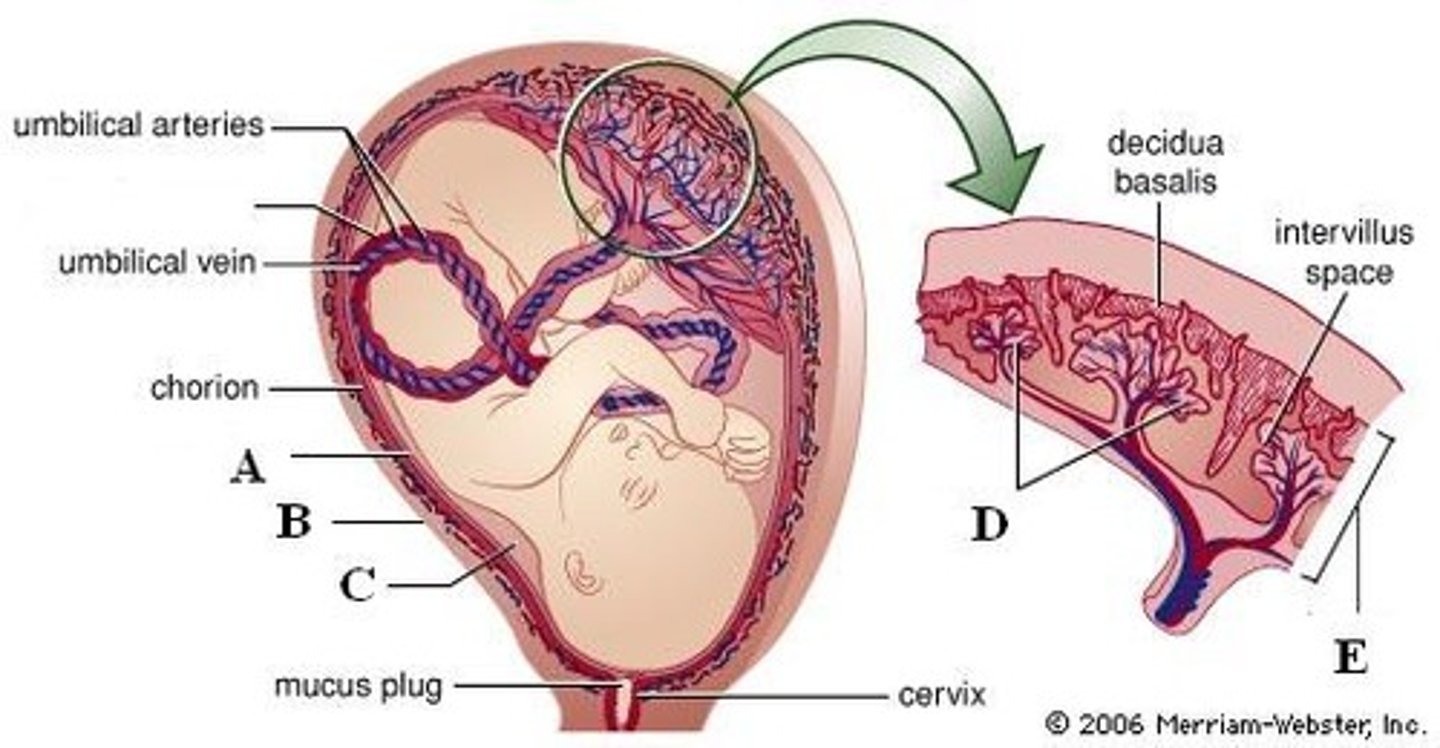
amnion
fluid sac that surrounds the embryonic body, attaches to placenta via umbilical cord
umbilical cord
a structure containing arteries and veins connecting the fetus and the placenta
fetus
stage of development from 9 weeks to infant
relaxin
hormone secreted by the placenta that causes ligaments and pubic symphysis to relax and widen (helps with birth, may cause waddle)
abortion
medical termination of a pregnancy
labor
series of events that expel the infant from the uterus
oxytocin
a hormone released by the posterior pituitary gland that causes increased contraction of the uterus during labor and stimulates the ejection of milk into the ducts of the breasts