Week Biological 8-agents of terrorism and warfare (focus on Anthrax infection)
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Bioterrorism
the malevolent use of bacteria, viruses or toxins against humans and animals in an attempt to cause harm and fear.
deal bioterrorism agent include:
Accessibility
Durability
Infectiousness
Agents ranked A-C by Centre for Disease Control based on perceived threat. Anthrax and Smallpox are category A agents.
used throughout history
-black plague; catapult dead ppl body over walls
-smallpox; colonizers with indigenous people
-anthrax; used to by germans to kill ally cattle, Russian bioweapons leakage caused anthrax to kill village
Biological weapons
-cheap and easy to make compared to nuclear and chemical weapons
-point of release is typically unknown = “silent” (escape easy)
-very contagious = spreads very effectively
-causes significant and widespread panic
High-priority agent
include organisms that pose a risk to national security because they:
• can be easily disseminated or transmitted from person to person;
• result in high mortality rates and have the potential for major public health impact
• might cause public panic and social disruption
• require special action for public health preparedness.
Bacillus anthracis
-gram-positive bacterium
-forms stable endospores when nutrients are limited
the spore is the infectious particle
-long-lived
-resistant to destruction/environment -
ability to cause lethal infections
3 main clinical forms of disease caused by anthrax:
Cutaneous anthrax (common-contact with spores or infected animals – entry through cuts in hands)
Gastrointestinal anthrax (ingestion of spore-contaminated meat)
Inhalational anthrax (rare-aerosolized spores are inhaled
Cutaneous anthrax
-most common
-contact with spores or infected animals – entry through cuts in hands
-ulceration of skin that clears without scarring – antibiotics recommended
Gastrointestinal anthrax
-ingestion of spore-contaminated meat
-bloody stools, massive edema and abdominal pain -
mortality is very high = shock and blood/fluid los
Inhalational anthrax
-rare -aerosolized spores are inhaled
-spores reaching the alveoli are engulfed by macrophages and transported to lymph nodes where replication occurs
-flu-like symptoms, extensive internal hemorrhage, meningitis
-very high mortality = fatal unless treated very early (wiithin 48 hours need intravenous antibiotics)
Anthrax
is on Category A of the list of Priority Biological Agents of the CDC = highest priority research
weaponization” of anthrax: drying and milling the spores to a size that reaches deep into the lungs and remains airborne longer
-anthrax does not spread from person to person
-rapid progression to death means that antibiotics and vaccine supplies critical
– top choice for germ warfare!
Ease of manufacture and dissemination
Dissemination could be as high tech as missiles, aerial bombs or as low tech as the mail! à 2001 in the USA
were used in 2001 mail attack; traced the letter spores back to the stocks that Ivins handled, as Anthrax spores have sub-populations bearing some mutations
Bacillus anthracis virulence
depends on the presence of its 2 large plasmids:
Plasmid pXO2 → genes for the capsule (needed for infection to spread, and spore durability
Plasmid pXO1 → toxins (toxins below)
Edema toxin –contains edema factor (EF), which is a calmodulin-dependent adenylate cyclase à increases cAMP levels à upsets cellular water balance
Lethal toxin –contains lethal factor (LF), a zinc metalloprotease which inactivates many cytosolic enzymes including MAPK.
Protective antigen (PA) – mediates cell entry of LF & EF
Anthrax treatment
-Antibiotics = penicillin, tetracycline, erythromycin, and ciprofloxacin.
Inhalational anthrax requires infusion of antibiotics continuously
Military Vaccine Agency of the US has an FDA approved effective vaccine
-only available to the military and “at risk” individuals (until now)
-still used in conjunction with antibiotics if an “attack” were to occur
-has been linked to “Gulf war syndrome”
-multi-symptom rheumatic disorder in veterans of the 1990-1991 war
-The August 2002 article is entitled "Antibodies to Squalene in Recipients of Anthrax Vaccine" (Exp. Mol. Pathol. 73,19-27 (2002))
Plague
–Caused by a bacterium: Yersinia pestis - gram negative bacterium (Coccobacillus)
- many virulence factors that are anti-phagocytic and anti-inflammatory -also a lipopolysaccharide endotoxin
Multiple plague pandemics in history -The Black Death; in ~1346; killed 30 million in Europe!
Controlled through the use of antibiotics and rodent transmission - ~2000 cases/year worldwide (WHO, 2016) -in 2017 ~ 2000 cases in Madagascar alone!
A zoonotic infection of rodents
rats are the animal reservoir and is transmitted between them by the bite of their fleas
-humans become infected when fleas bite them after biting an infected rodent
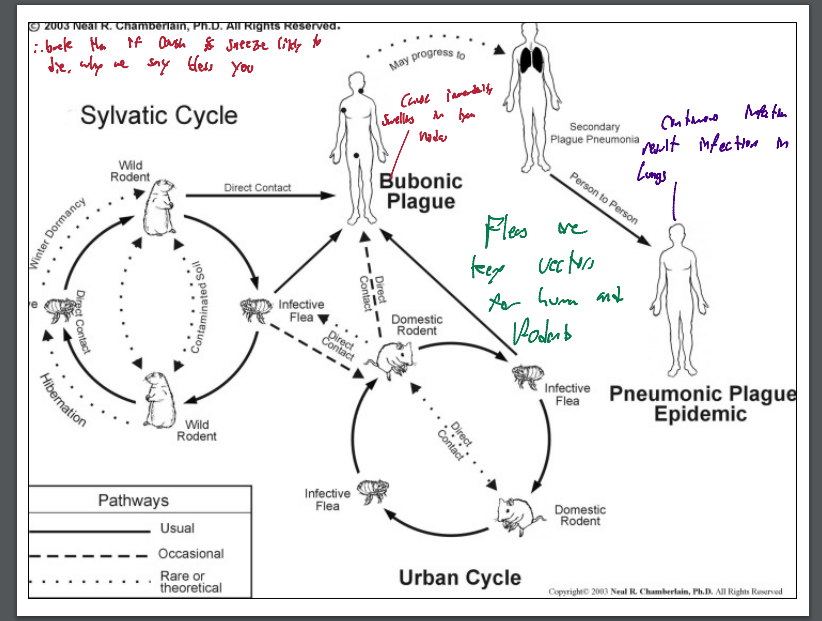
Plague various pathnogenesis
Bacteria migrate to the lymph nodes
Associate with mononuclear cells and multiply
cause
-swelling = bubo =bubonic plague
–fever, chills, bubos
migration to the lungs = pneumonic plague
Can also get primary pneumonic plague by direct inhalation of bacteria
-symptoms similar to pneumonia
disseminate to the bloodstream = septicemic plague
-black lesions on fingers and toes = Black death
Plague as a bioterror agent
–Contagious =pneumonic form; spreads easily from human to human
–Stable -up to 1 hour in aerosolized form
–Highly infective - 100-500 organisms can cause significant infection
–High mortality =100% for pneumonic form
–Public panic –Difficult to diagnose quickly; e.g. pneumomic plague would manifest as pneumonia -if treatment is not started within 24 hours of infection, mortality =100%
(Natural disasters can release bacteria to cause plague)
Smallpox
is caused by an orthopox (DNA) virus = variola virus
last naturally occurring case was in 1977 in Somalia -WHO declared the disease eradicated in 1980 -vaccination discontinued since then -original vaccine was live vaccinia (related virus) -the world is no longer immune to the viru
–Disease is characterized by disfiguring skin eruptions, fever and a high rate of mortality
-antivirals are not all that effective
-vaccination is the best protective measure
-rapid isolation would be required of infected individuals
Viral Hemorrhagic fevers
can be contracted by a bite of a mosquito, animal excrement or contact with infected animals or human
Examples are Ebola, Marburg, Lassa, Junin and Machupo
were developed as bioweapons in Russia and US until the mid-1990s (n an aerosolized attack)
Lack of humoral response in those infected -require good antivirals = seriously lacking! (need vaccinations, but are highly mutating/emerging virus thus needs to be updated)
Botulinum toxin
Made by the spore-forming microbe, Clostridium botulinnum
C. botulinnum is ubiquitous in soil and very easy to culture -easy to purify toxin -0.7 to 0.9μg inhaled is sufficient to kill a 70Kg human!
Most potent toxin known to man!
Acts at neuromuscular junctions to prevent release of acetylcholine
-a neurotransmitter that stimulates muscle contraction
-leads to paralysis, eventually respiratory paralysis
Can be aerosolized or contaminate the food supply
-BoTox only contains about 0.3% of the lethal inhalational dose!