Exercise and Sport Psychology EOT Exam Flashcards
1/531
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
532 Terms
Exercise Psychology
Study of psychological factors in exercise behavior.
Sport Psychology
Focus on mental aspects of competitive sports.
Lifespan Considerations
Impact of age on exercise participation.
Functional Capacity
Ability to perform physical activities effectively.
Perception of Competence
Belief in one's ability to succeed.
Motivation
Driving force behind participation in activities.
Anxiety in Children
Nervousness affecting performance and enjoyment.
Burnout
Emotional exhaustion from excessive demands.
Task Orientation
Focus on personal performance improvement.
Outcome Orientation
Comparison of performance against others.
Social Competence
Ability to fit in and connect socially.
Self-efficacy
Belief in one's ability to achieve goals.
Sociocultural Influences
Impact of society on children's participation.
Participation Statistics
Data on rates of involvement in sports.
General Dropout
Withdrawal from all sports or activities.
Specific Dropout
Withdrawal from a particular sport.
Psychological Factors
Mental aspects influencing participation decisions.
Physical Factors
Physical limitations affecting exercise participation.
Stress Response
Reaction to perceived demands exceeding capabilities.
Perfectionist Tendencies
High standards leading to anxiety about failure.
Parental Pressure
Influence of parents on children's sports involvement.
Impairment Types
Categories of physical or cognitive limitations.
Congenital Impairments
Disabilities present from birth.
Acquired Impairments
Disabilities resulting from injury or illness.
Neuromuscular Diseases
Disorders affecting muscle control and movement.
Traumatic Impairments
Injuries causing significant physical limitations.
Age-related Impairments
Declines in function associated with aging.
Coping Mechanisms
Strategies to manage stress and anxiety.
Connectedness
Sense of belonging and support from others.
Holistic Approach
Considering all aspects of an individual's well-being.
Psychological Well-being
Individual's perception of life satisfaction and happiness.
Positive affect
Experience of positive emotions and feelings.
Negative affect
Experience of negative emotions like sadness or anxiety.
Subjective Well-being
Self-rated assessment of life satisfaction and emotions.
Self-acceptance
Having positive views of oneself and self-worth.
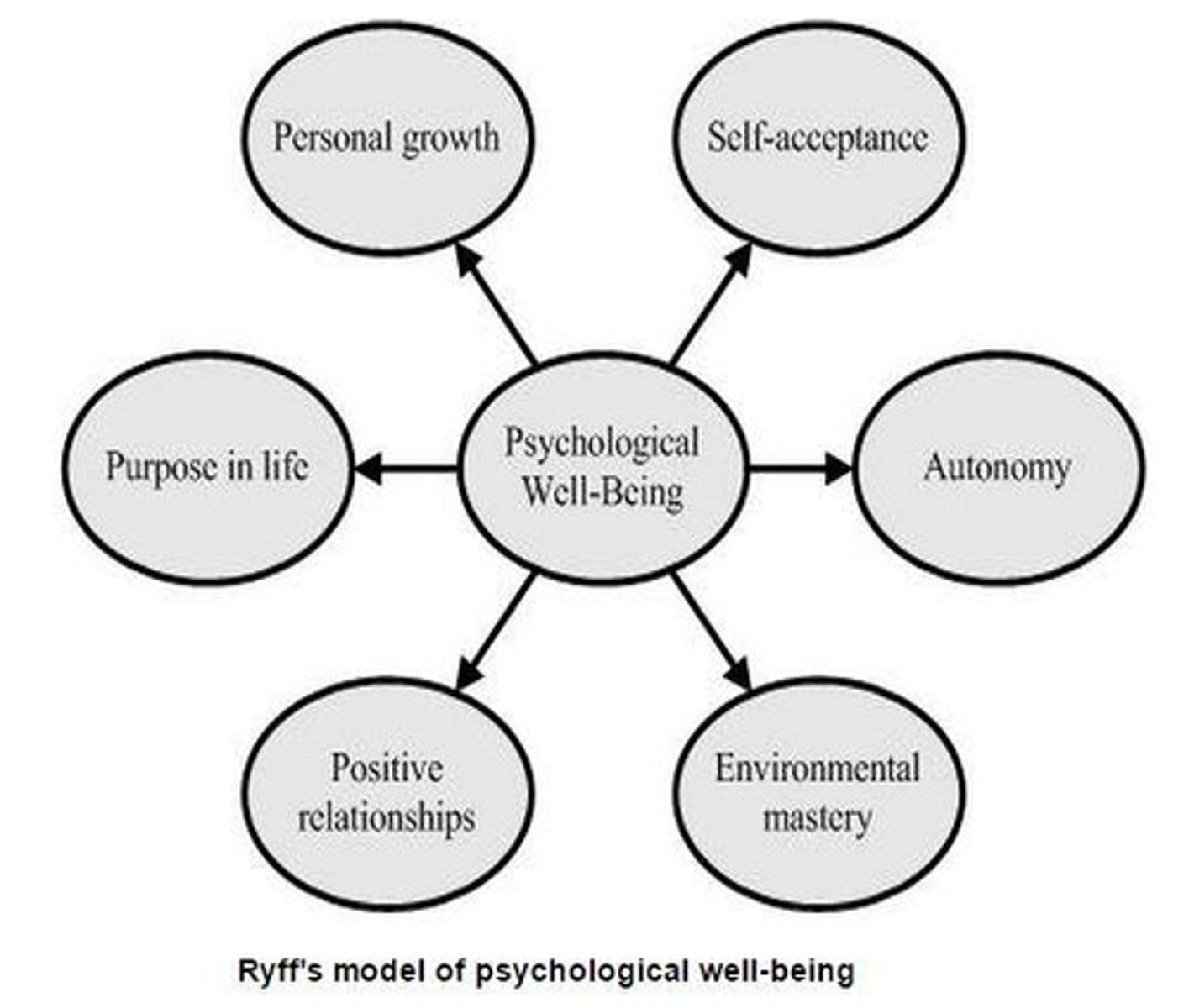
Positive relations to others
Trust, care, and empathy in relationships.
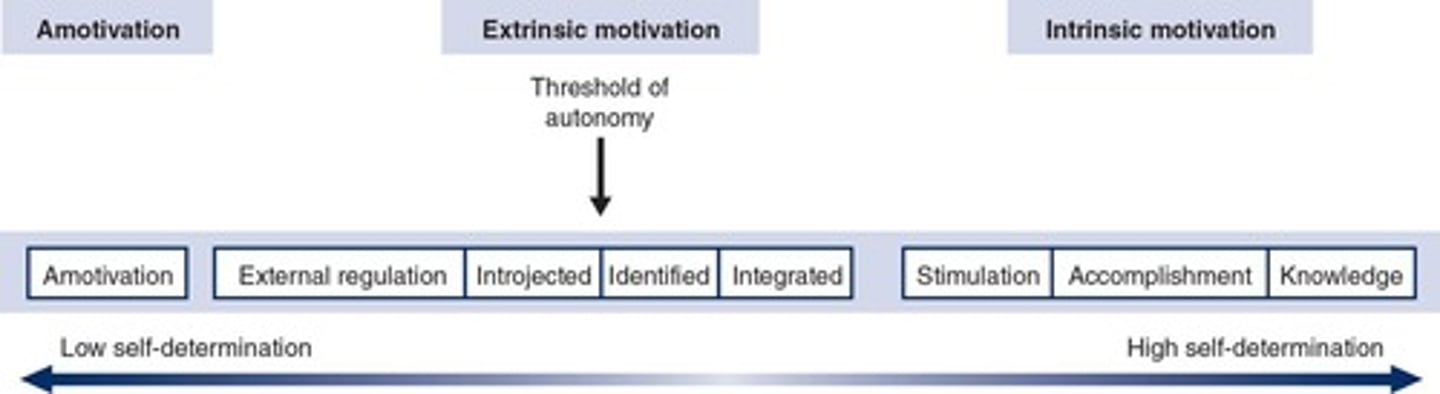
Autonomy
Self-determined behavior driven by intrinsic motivation.
Environmental mastery
Ability to effectively manage and adapt to surroundings.
Personal growth
Sense of self-development and fulfillment over time.
Purpose in life
Having directed goals and meaning in existence.
Cerebral blood flow
Increased blood circulation to the brain during exercise.
Neurotransmitter regulation
Balance of chemicals like serotonin and endorphins.
CNS plasticity
Structural changes in the central nervous system.
Maximum oxygen consumption
Peak rate of oxygen usage during intense exercise.
Muscle tension reduction
Decreased tension in muscles post-exercise.
Self-efficacy
Belief in one's ability to succeed in tasks.
State anxiety
Temporary feelings of nervousness and apprehension.
Acute effects of exercise
Short-term psychological benefits from immediate physical activity.
Chronic effects of exercise
Long-term mental health benefits from regular activity.
Moderate-intensity exercise
Exercise level that optimally enhances positive feelings.
Physical fitness
Overall health and capability of the body to perform.
Anxiety reduction
Decrease in feelings of nervousness through exercise.
Depression reduction
Lowered symptoms of depression associated with regular exercise.
Exercise
Physical activity reducing stress and negative emotions.
Anxiety
Negative emotional state of nervousness and worry.
Depression
Mood state of inadequacy and despondency.
Neuroticism
Tendency towards anxiety and emotional instability.
Stress Indicators
Measures like heart rate and tension levels.
Long-term Exercise Adherence
Consistent exercise linked to reduced anxiety traits.

Aerobic Exercise
Cardiovascular workouts reducing depression symptoms.
Anaerobic Exercise
Strength training associated with lower depression levels.
Mood State
Emotional condition lasting hours to months.
Inadequacy
Feeling unable to cope with situations.
Despondency
Loss of hope and dejection.
Pessimism
Expectation of negative outcomes in situations.
Exercise and Depression Correlation
Moderate link between physical activity and mood improvement.
Psychotherapy
Therapeutic intervention for mental health issues.
Exercise Duration
Training programs over 9 weeks enhance antidepressant effects.
Reasons for Exercising
Motivations like weight control and enjoyment.
Barriers to Physical Activity
Challenges like health issues and lack of motivation.
Exercise Prescription
Guidelines often neglect psychological readiness.
Behavior Change
Process of modifying habits for better health.
Self-responsibility in Exercise
Empowerment for long-term behavior change.
Factors Influencing Exercise
Elements affecting initiation and maintenance of activity.
Socializing
Engaging with others as a reason to exercise.
Competition
Desire to compete motivating physical activity.
Health Belief Model
Predicts exercise based on perceived health risks.
Theory of Planned Behaviour
Intentions predict behaviour, influenced by attitudes.
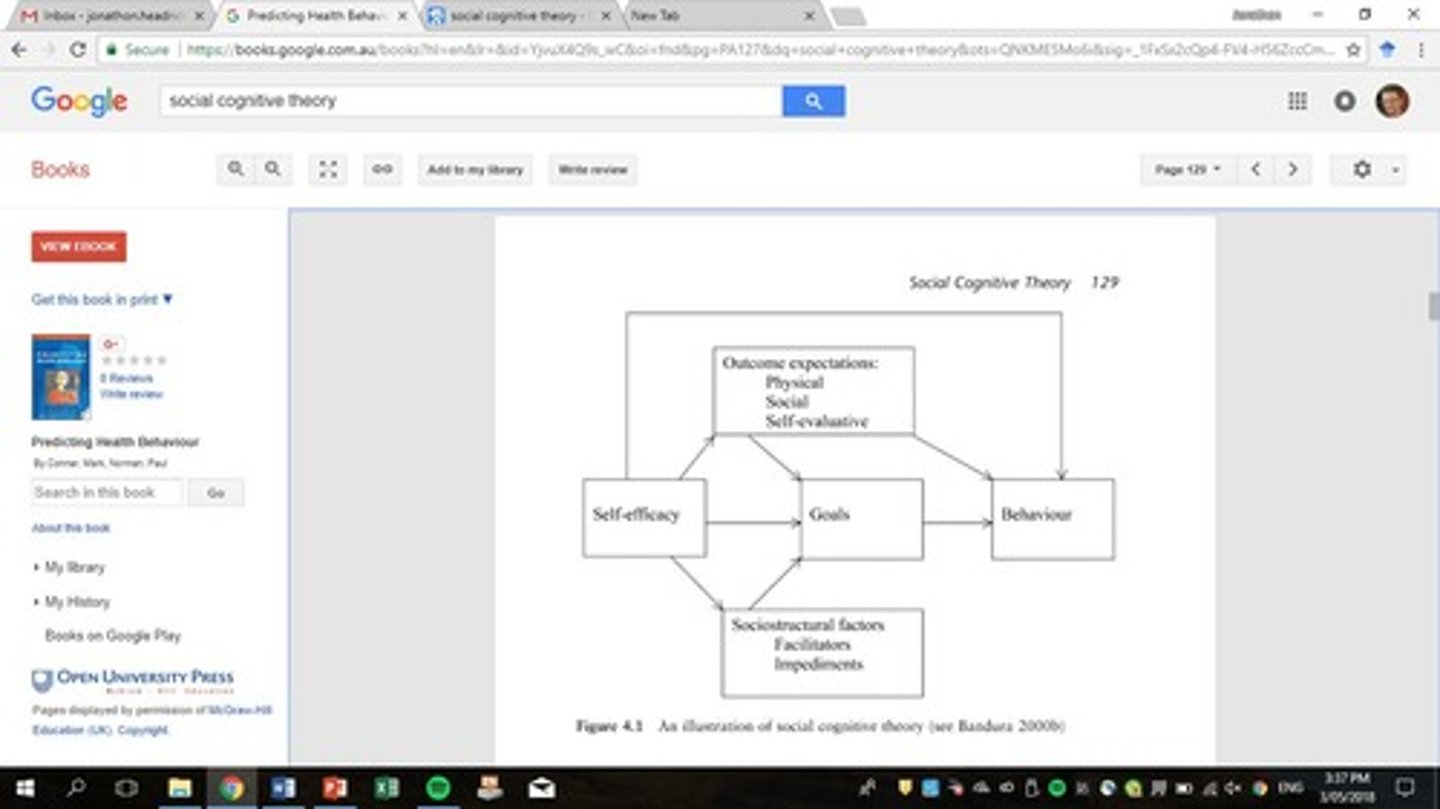
Social Cognitive Theory
Behaviour influenced by personal and environmental factors.
Self-Determination Theory
Motivation driven by connection and personal initiative.
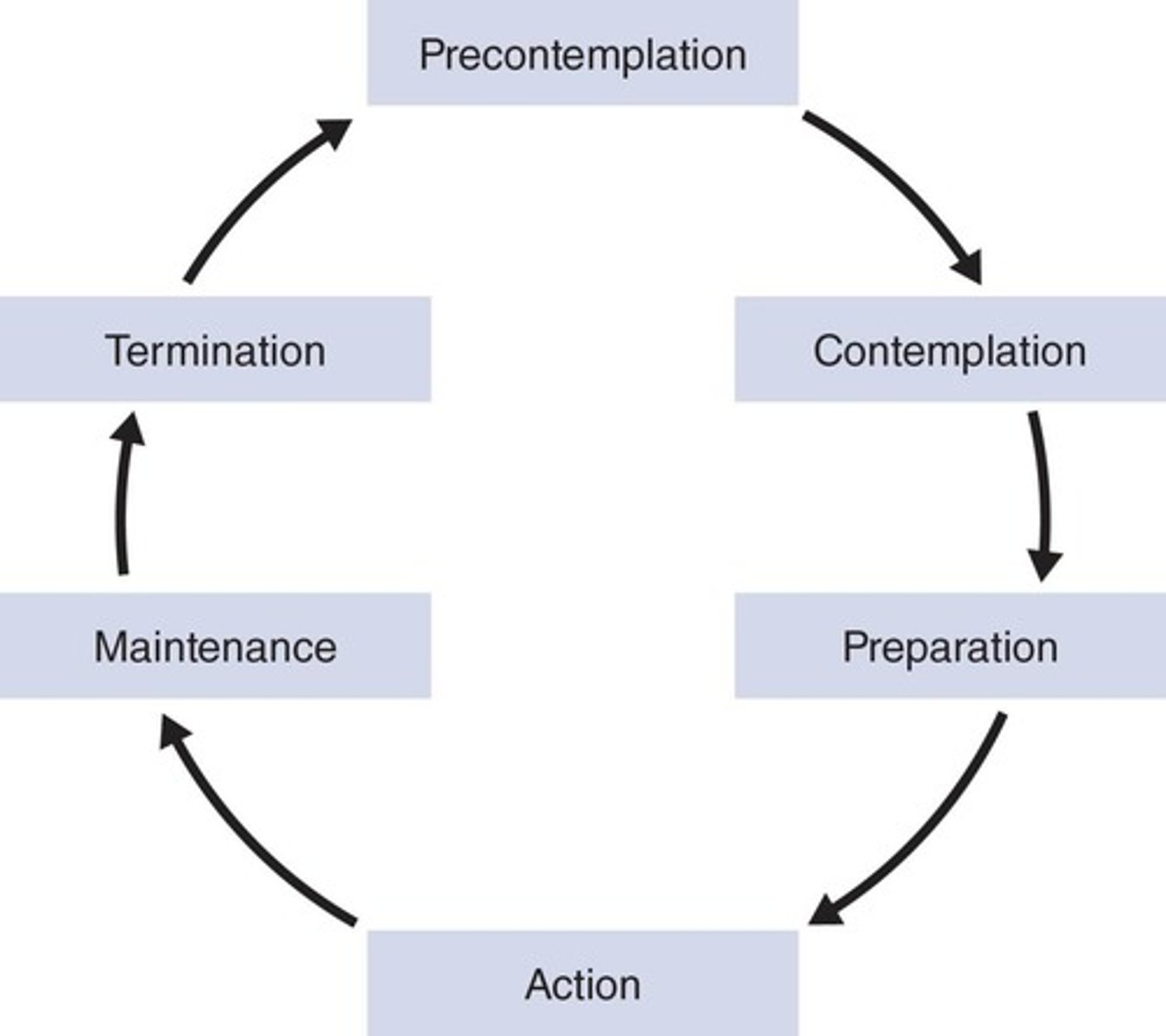
Transtheoretical Model
Stages of change in behaviour modification.
Physical Activity Maintenance Model
Focuses on sustaining physical activity over time.
Ecological Models
Considers multiple environments affecting exercise behaviour.
Subjective Norms
Social pressure influencing behaviour intention.
Perceived Behavioural Control
Individual's perceived control over performing behaviour.
Attitude Towards Behaviour
Personal evaluation of the behaviour's outcomes.
Sociocultural Influences
Cultural and social factors affecting exercise participation.
Preventative Health Behaviours
Actions taken to prevent health issues.
Cost-Benefit Appraisal
Evaluation of exercise benefits versus costs.
Inconsistent Support
Mixed evidence for model predictions in exercise.
Behaviour Initiation
Starting a behaviour based on strong intentions.
Behaviour Maintenance
Continuing a behaviour over time.
Exercise Participation
Engagement in physical activity regularly.
Environmental Factors
External conditions affecting exercise behaviour.
Personal Factors
Individual characteristics influencing exercise decisions.
Health Risks
Potential negative health outcomes from inactivity.
Social Support
Assistance from others that enhances motivation.
Intrinsic Goals
Personal satisfaction derived from exercise.
Extrinsic Goals
External rewards or recognition for exercising.
Self-Determined Behavior
Actions driven by personal choice and motivation.