Chapter 6: Digestion
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
What are the five main functions of the digestive system?
Ingest food
Mechanical breakdown
Chemical breakdown
Absorption of nutrients
Elimination of waste
What is the purpose of enzymes in the digestive system?
Enzymes increase the rate of chemical reactions, aiding in digestion.
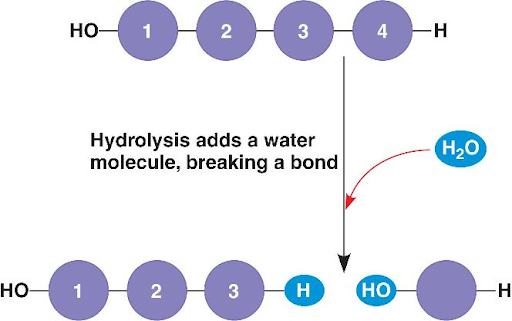
What is hydrolysis in relation to macromolecules?
Hydrolysis is the process where water is added to break bonds in larger molecules, resulting in smaller molecules.
What are the main types of macromolecules?
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
How are ulcers formed? What causes ulcers in the digestive system?
Ulcers are formed when the mucus lining in the stomach is damaged and erodes by the acidic environment of the stomach, often caused by Helicobacter pylori bacteria.
What role does the liver play in digestion?
The liver produces bile for emulsifying fats and detoxifies the blood.
What is the structure and function of villi in the small intestine?
Villi are finger-like projections that increase surface area for nutrient absorption.
Describe the process of dehydration synthesis.
Dehydration synthesis is the process of forming a bond between molecules by removing a water molecule.
What happens in the stomach during digestion?
Mechanical digestion occurs through churning, while chemical digestion takes place with gastric juice secretion.
What is the function of lipase in the digestive system?
Lipase digests lipids by breaking down triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol.
What is the significance of the epiglottis during swallowing?
The epiglottis prevents food from entering the windpipe during swallowing.
How do competitive inhibitors affect enzyme activity?
Competitive inhibitors bind to the active site of an enzyme, preventing the substrate from binding.
What is the role of the pancreas in digestion?
Secretes pancreatic fluid into the duodenum of the small intestine that mixes with the chyme that comes from the stomach.
What is the main site of nutrient absorption in the digestive system?
The small intestine is the main site for nutrient absorption.
What is the function of carbohydrates in the body?
Carbohydrates serve as an energy source and help regulate blood glucose levels.
What is the importance of maintaining homeostasis in digestion?
Homeostasis maintains consistent internal conditions, crucial for optimal enzyme function and digestion.
What are the main factors affecting enzyme activity?
The main factors affecting enzyme activity include temperature, pH, substrate concentration, enzyme concentration, and inhibitors.
How does temperature affect enzyme activity?
Each enzyme has an optimal temperature range where its activity is maximized; too high can denature the enzyme or slow its activity. Too low temperatures cause them to be too cold to function.
How does pH affect enzyme activity?
Each enzyme has an optimal pH level; deviations from this pH can reduce enzyme activity or lead to denaturation.
What role does substrate concentration play in enzyme activity?
Increasing substrate concentration generally increases the rate of reaction up to a certain point where the enzyme becomes saturated.
What happens to enzyme activity when enzyme concentration changes?
Increasing enzyme concentration generally increases the rate of reaction, assuming substrate is available; however, after a certain point, the rate will level off due to substrate limitation.
What are enzyme inhibitors?
Enzyme inhibitors are substances that reduce or block enzyme activity, preventing substrate from binding or reducing the effectiveness of the enzyme.
What are the two types of enzyme inhibitors?
The two types of enzyme inhibitors are competitive inhibitors, which compete with the substrate for binding to the active site, and non-competitive inhibitors, which bind to an allosteric site, altering the enzyme's activity.
Does more enzyme always mean and increased rate of reaction?
Not necessarily, as increased enzyme concentration will only enhance reaction rates until the substrate becomes limiting and the reaction reaches its maximum reaction rate.
Hydrochloric Acid jobs
activates pepsin, denatures proteins, kills microbes
Pepsin
is a digestive enzyme produced in the stomach that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides.
Why doesn’t our stomach digest itself?
The stomach mainly secretes gastric juice when food is present (secretory cells)
The stomach secretes mucus, which protects the stomach lining
The protein digesting enzyme PEPSIN, is inactive until hydrochloric acid is present
What is the final site of mechanical and chemical digestion in the digestive system?
The small intestine.
What structural features in the small intestine increase the surface area for nutrient absorption?
Villi and microvilli.
What are the three parts of the small intestine?
Duodenum, jejunum, and ileum.
Which accessory organs are important for digestion but not part of the gastrointestinal tract?
Pancreas, liver, and gallbladder.
What is the role of the pancreas in digestion?
It secretes pancreatic fluid into the duodenum and hormones to regulate blood glucose levels.
What does bile do in the digestive process?
Emulsifies fats for better digestion.
What is cirrhosis?
A condition where scar tissue replaces healthy liver tissue, impairing liver function.
What is hepatitis?
Inflammation of the liver that can prevent bile production.
What is the function of the gallbladder?
Stores and releases bile into the small intestine.
What are gallstones?
Small, hard masses that form in the gallbladder from cholesterol.
How are carbohydrates digested in the small intestine?
By enzymes called carbohydrases, including pancreatic amylase and disaccharidases.
What happens to amino acids after being absorbed into the bloodstream?
They travel to the liver for various processes, including conversion into sugars or new proteins.
What is the role of lipases in lipid digestion?
They hydrolyze triglycerides into fatty acids and glycerol.
How are nucleic acids digested in the small intestine?
Hydrolyzed into nucleotides by nucleases and further broken down by nucleosidases.
What is the main function of the large intestine?
To concentrate and eliminate waste materials while absorbing water, salts, and vitamins.
What is Crohn’s disease?
An inflammatory bowel disease that can cause frequent intestinal emptying and diarrhea.
What is celiac disease?
A genetic autoimmune disorder where the body reacts to gluten, damaging the villi of the small intestine.
What occurs during lactose intolerance?
Individuals lack lactase, causing undigested lactose to lead to stomach pain, bloating, and diarrhea.
What are chylomicrons?
Triglycerides coated in proteins, which makes them soluble for transport in the lymph vessels.
What does a Iodine Solution test for?
The presence of starch in a sample, turning blue-black when starch is present.
What does a Benedict’s Solution test for?
The presence of simple sugars in a sample, resulting in a color change from blue to green, yellow, or brick red depending on the amount of sugar.
What does a Biuret’s Reagent solution test for?
The presence of proteins in a sample, resulting in a color change to pink or purple when proteins are present.
Trypsin and chymotrypsin
are enzymes that hydrolyze proteins into polypeptides and peptides into individual amino acids.
Where does digestion of carbs? Broken down by which enzyme?
The digestion of carbohydrates begins in the mouth and is broken down by salivary amylase.
Where does digestion of protiens? Broken down by which enzyme?
The digestion of proteins begins in the stomach and is broken down by pepsin.
Where does digestion of lipids? Broken down by which enzyme?
The digestion of lipids occurs in the small intestine and is primarily broken down by pancreatic lipase.