Pre-AP Biology - Semester 2 Final
1/27
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
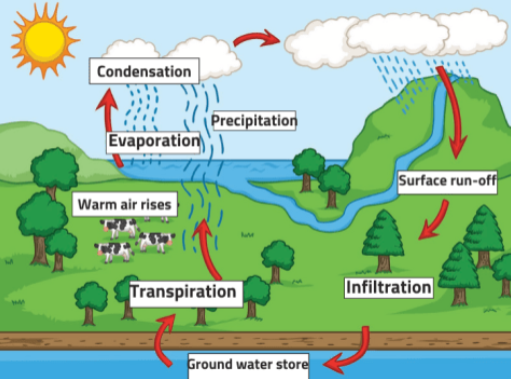
What cycle is this?
Water Cycle
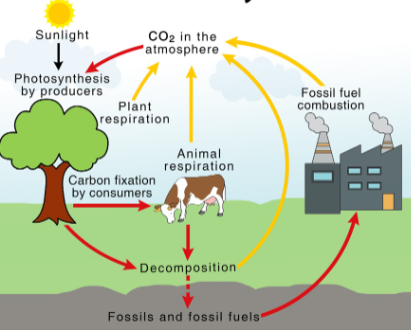
What cycle is this?
Carbon Cycle
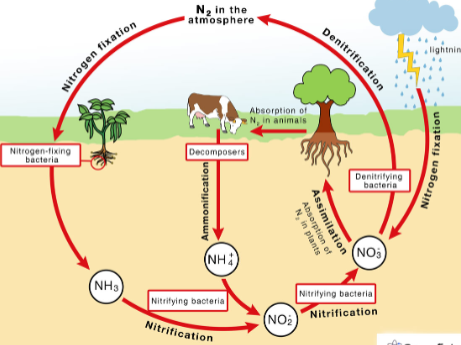
What cycle is this?
Nitrogen Cycle
Why is the Water Cycle important for life on Earth?
-It is vital for all organisms
-It’s used as a transport medium
—> moves nutrients and waste, regulates climate, and sustains life on earth
Why is the Carbon Cycle important for life on Earth?
-Major component of all organic compounds (lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, + nucleic acids)
-Key ingredient of living tissue and ecosystems
-Carbon compounds
—> regulates earth temperature, provides energy that fuels global economy, makes up the food that sustains us
What are some human activities that impact the Carbon Cycle?
-Burning Fossil Fuel
—> releases carbon stored very slowly and causes increases in global warming
-Deforestation
—> Fewer plants = less CO2 removed from atmosphere
Why is the Nitrogen Cycle important for living organisms on earth?
-Essential component of DNA, RNA, + Proteins (Building blocks of life)
-Makes up 78% of the atmosphere
What are some ways that human activities impact the Nitrogen Cycle?
Combustion - Releases toxic nitrogen compounds
Commercial Fertilizers - Releases nitrous oxide into atmosphere (introduces excess nitrogen into the environment)
-Mine for nitrogen rich mineral deposits (removes nitrogen)
-Discharge of municipal sewages releases excess nitrogen
What is a Niche?
Range of physical and biological conditions in which a species lives and the way the species obtain what it needs to survive
What is Quadrat Sampling method?
-used for estimating populations with limited/no movement
-predetermined 4-sided sampling boundary
What is Mark-Recapture method?
-capturing a # of individuals, marking them, then releasing them back into the population
What is the Formula for the Mark-Recaptured method?
R/S=M/N
R - # of recaptured individuals
S - size of 2nd sample
M - marked individuals released
N - size of the population
What are some things that affect population growth?
Birth + Death Rate
- Increase in birthrate = increase in population
- Decrease in birthrate = decrease in population
Immigration + Emigration
-Individuals move into its range from elsewhere (increase in population) (“INTO” - Immigration)
-Individuals move out of the population range (decrease in population) (“EXIT” - Emigration)
What is a Trophic Level?
Each step in a food chain/web
—> Primary producers are the first Trophic Level
What is the 10% Rule?
When energy is passed in an ecosystem from 1 Trophic Level to the next, only 10% of the energy will be passed on.
How does human activity impact the flow of energy in an ecosystem?
-Energy balance is altered
—> over exploration of resources, deforestation, pollution
-Impact the working efficiency of an ecosystem
—> makes it difficult to adapt according to new changes in the environment
Why does Competition occur?
There aren’t enough resources
Competition - when organisms attempt to use the same limited ecological resources in the same place at the same time
What are the two types of Competition (define them)?
Intraspecific - same members of the same species
Interspecific - between members of a different species
What is the Competitive Exclusion Principle?
No two species can occupy exactly the same niche in exactly the same habitat at exactly the same time
What is a Keystone Species and why is it important for the community it lives in?
Keystone species - changes in the population of a single species can cause a dramatic change in the structure of a community (important role in the food chain/web they are in)
EX: Sea Otter
What is a Symbiotic Relationship?
Any relationship in which two species live closely together
What is Mutualism?
Both species benefit from each other
EX: anemone and clownfish
What is Parasitism?
Organism lives on/inside another organism
-Host benefits
EX: fleas and tapeworms
—> Think parasites
What is Commensalism?
One organism benefits and the other (neutral) is neither harmed nor helped
EX: Barancles on whales
What is the Symbiotic Relationship between coral and microalgae? What happens when the relationship is disrupted?
Algae lives in the tissue of the coral and is a primary food source for the coral, provides color for the coral to blend in (Mutualism)
- When ocean temperatures rise, coral becomes stress and evicts the algae (coral starts bleaching)
—> lessens their chance of survival
What is Biodiversity?
Degree of variation of life measured by the variety of organisms present in different ecosystems
Why is Biodiversity important for humans and other organisms?
Protects the fresh air, clean water, and land
—> stabilizes and keeps an ecosystem functional/functioning
Important on forestry, fisheries, and agriculture
—> Depend on variety of various biological resources
Loss of it can cause serious economic and social costs
What are the effects of the loss of Artic Ice on the Biodiversity of organisms that live in that area?
Decreases the biodiversity
—walrus, polar bears, and seals are negatively affected since they needed that ice for habitat, hunting ground, or a resting spot
—> decrease in their population