Comp Sci Final
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
Python Data Structures
-built in non primitive structures: list, tuple, set, dictionary
-used to store and organize collections of data
-choice dpeends on mutabilty, order, and uniqueness
Lists
-ordered, mutable, allows duplicates
-can store mixed data type and nested lists
List concepts
-indexing (positvie and negative)
-slicing creates a new list
-slice assignment modifies a list in place
-lists are passed by refernece to functions
List common methods
-append(0, extend(), insert()
-pop(), remove(), clear()
-sort(), reverse()
Aliasing
b=a both refernce the same list
-changes to one affect the other
-use slicing ( a[ :] ) to copy safely
Tuples
-ordered and immutable
-allow duplicates
-faster and more memory-efficient than lists
Tuple Rules
-single element tuple needs a comma: (5, )
-cannot add/remoce elements (immutable)
-can modify mutiable elements inside a tuple
Tuple Operatiosn
-concatenation + and repetition *
-tuple unpacking: a, b = b, a
-sorted() returns a list, NOT a tuple
Sets
-unordered
-no duplicates
-no indexing
Sets Operations
-add(), update()
-remove()
-discard()
Set math
union, interaction, difference
Set use cases
remove duplicates, membership testing, mathematical set operations
File Handling Open methods
“r” read
“w” write (overwrite)
“a” append
“r+”, “w+”, “a+”
“b” binary, “t” text (default)
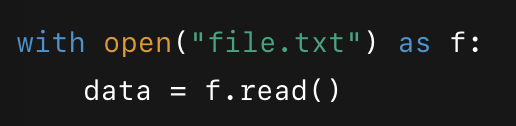
Reading & Writing
-read(), readline(), deadlines()
-write(), writelines()
-ALWAYS include \n for new lines
JSON Serialization
-convert python objects to string
-used heavily with APIs
json.dumps()
serialize
json.loads()
deserialize
Serialization
converting python object (like dictionary or list) into a JSON-formatted string
APIs
requests library

Status codes
200 OK, 400 Bad request, 401 Unauthorized, 403 Forbidden, 404 Not found, 503 Service unavailable
Returned Data
-usually dictionaries
-access via keys
Core OOP Concepts
-class: blueprint
-object: instance
-attributes: data
-methods: behavior
self.
refers to the object
instance attributes
belong to each object
class attributes
shared by all objects
encapsulation
-access data via methods (get or set)
-protect internal state
inheritance
-child class inherits from parent
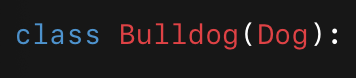
overriding
child replaces parent method/attribute
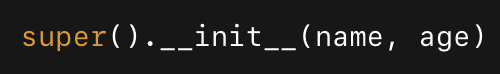
super()
reuse parent methods
Inheritance types
-single
-multilevel
-multiple inheritiance
NumPy
-fast numerical arrays
-fixed size, same data type
NumPy Array creation
-np.array()
-np.zeros(), np.ones()
-np.arange(), np.linspace()
NumPy Indexing
similar ot lists
-multi-dimensional: a[row, col]
-boolean indexing is common on exams
NumPy Operations
-element-wise math
-statisitcal functions: mean, std, max, min
Pandas Series
-one dimensional labeled data
-like a column
Pandas Data Frame
-two dimensional table
-rows and columns
Pandas Indexing
df [ col ]
df.loc [ label ]
df.iloc [ index ]
-boolean filters
Visualization
-uses NumPy + Pandas data
-typically wiht matplotlib
-often paired with statiscal analysis
False
bool ( 0 ), ( 0, 0 ), ( “ “ ), ( None )
for loop
-iterates over knwon sequence
-ex: list, range, string
while loop
-runs until a condition change
-used when number of iterates is unknown
%
finds division remainder
//
integer divsion so must be whole number output
Why is range(5, 10, 0.5) incorrect
can NOT hvae float numbers in a range ONLY integers
continue
-skips remaining code in the loop
-immediately jumps to the next iteration
comments
-python ignores
-only exist for humans
and
need both to be True to return True
or
True if at least one operand is True
Natural Languages
change and evolve
Formal Language
strict fixed rules
==
equals
!=
not equal
case_:
-matches anything not previously matched
-acts like else
interpreter
-python executes code line by line
-no full compilation step
XOR operator (ex: 1011 ^ 0111)
same = 0
diff = 1
What happens if you hvae a return statment in a Python function with no value following
implicit return value is None
AND operator (ex: 110101 & 101010)
returns 1 if both 1
returns 0 if one is 0
pass
-placeholder
-does nothing
-prevents syntax erros for empty blocks
upper()
makes the string all uppercase
[::-1]
reverses
.find()
returns the starting index of the term
spilt()
spilts on any white space
-returns a list of words
iterations are more efficient
than recursion
s.clear()
removes all items from a set
pop()
removes the last element