Ultimate AP Human Geo Vocab Review
1/293
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All the Vocab from every unit 1-7 (Not finished yet)
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
294 Terms
Absolute Direction
Corresponds to the direction on a compass: north, south, east, west, and combinations such as northeast and southwest
Absolute Distance
The distance that can be measured with a standard unit length, such as a foot, yard, mile, or kilometer.
Absolute Location
A precise position on Earth's surface
Census Data
an official count or survey of a population, typically recording various details of individuals such as age, sex, and race.
Cultural Landscape
The built forms that cultural groups create inhabiting Earth and the meaning, values, representations, and experiences associated with those forms
A natural land that has been modified by humans, reflecting their cultural beliefs and values
Elevation
distance above or below sea level
Environmental Determinism
The belief that the physical environment is the dominant force shaping cultures and that humanity is a passive product of its physical surroundings
Formal Region
A geographical area inhabited by people who have one or more traits in common
Functional Region
A geographic area that has been organized to function politically, socially, culturally, or economically as one unit
Geographic Information System (GIS)
A software application for capturing, storing, checking, and displaying data related to positions on Earth's surface; allows the rapid manipulation of geospatial data for problem-solving and research
Global Positioning System (GPS)
A system of 24 satellites that orbit Earth twice daily and transmit radio signals Earthward; the basis for many map-based apps that provide directions on how to get from one place to another
Natural Resources
Materials or substances that occur in nature and can be used for economic gain
Perceptual/Vernacular region
A geographic area that is perceived to exist by its inhabitants, based on the widespread acceptance and use of a unique regional name
Place
A location on Earth that is distinguished by its physical and human characteristics
Possibilism
The belief that any physical environment offers a number of possible ways for a society to develop and that humans can find ways to overcome environmental challenges
Reference map
A map that shows geographic locations on Earth's surface, such as the locations of cities or oceans
Region
A geographical unit based on one or more common characteristics or functions
Relative Direction
A direction that can be described as position, such as in front of or behind, to the left or to the right
Relative Distance
A measurement of the level of social, cultural, or economic similarity between places despite their absolute distance from each other
Relative Location
The position of one place (or person) in relation to the position of another place (or person)
Remote Sensing
the scanning of the earth by satellite or high-flying aircraft in order to obtain information about it.
Satellite Imagery
Images of Earth's surface gathered from sensors mounted on orbiting satellites; these sensors record in both the visible and non-visible portions of the electromagnetic spectrum, allowing humans to view patterns and processes that are both visible and invisible to the naked eye
Scale
The territorial extent of an idea or object
Sense of Place
How a person feels about a particular place and why it's important to him or her
Thematic Map
A map that emphasizes the spatial patterns of geographic statistics or attributes, and sometimes the relationships between them
Distance Decay
Idea that near things are more related than distant things, and interaction between two places decreases the farther apart they are until ultimately the interaction ends or does not exist
Time-Space Compression
The decreasing distance between places, as measured by travel time or cost; often summarized by the phrase "the world is shrinking”
Flow
Movement of people, goods, or information that has economic, social, political, or cultural effects on societies.
Globalization
Increasing interconnection of all parts of the world as the full range of social, cultural, political, and economic processes becomes international in scale and effect. One result of space-time compression: Expansion of economic, cultural, and political processes on a worldwide scale
Human Geography
The study of the processes that have shaped how humans understand, use, and alter Earth
Pattern
The way in which things are arranged in a particular space
Sustainability
The use of Earth's land and natural resources in ways that ensure they will continue to be available in the future; Development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs
Scale of Analysis
Observation of data at the global, regional, national, or local scale
Clustering
Spatial pattern where people or objects are closely grouped together in specific areas of a population. This suggests that the concentrated regions have a higher density than the surrounding areas
Dispersal
Spatial pattern where objects are spread out from one another
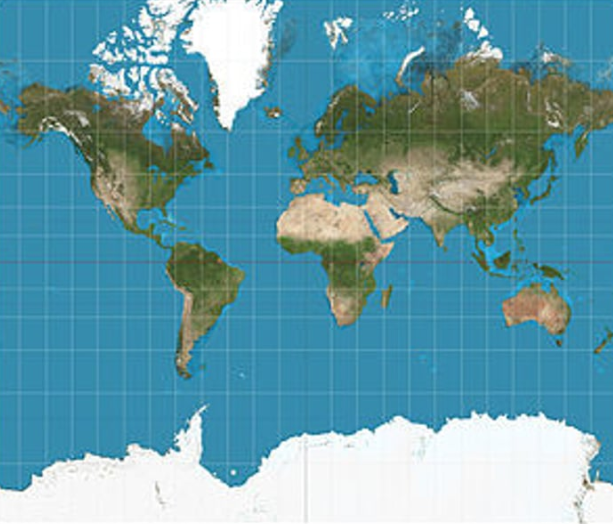
Mercator Projection
- Preserves accurate compass direction, distorts land masses relative to each other
- Landmasses most distorted near the poles (high latitudes)
Peters Projection
An equal-area projection purposely centered on Africa in an attempt to treat all regions of Earth equally
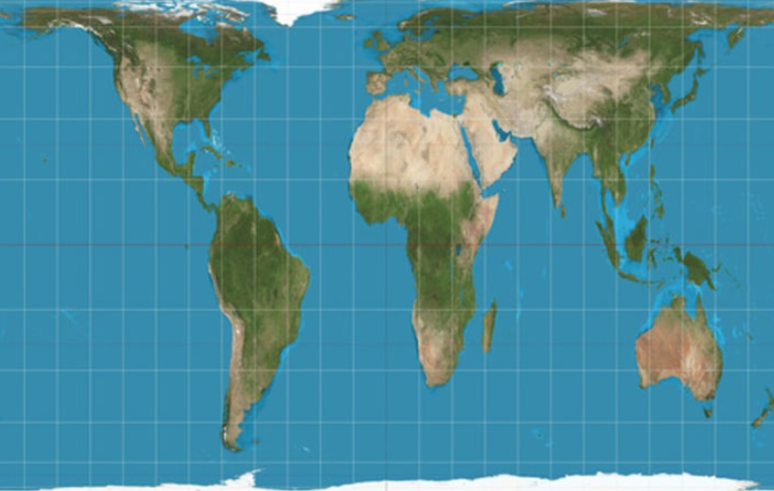
Robinson Projection
- Minimizes the errors in area, shape, distance, and direction - land areas smaller
- Aesthetically pleasing balance - good for displaying information across oceans
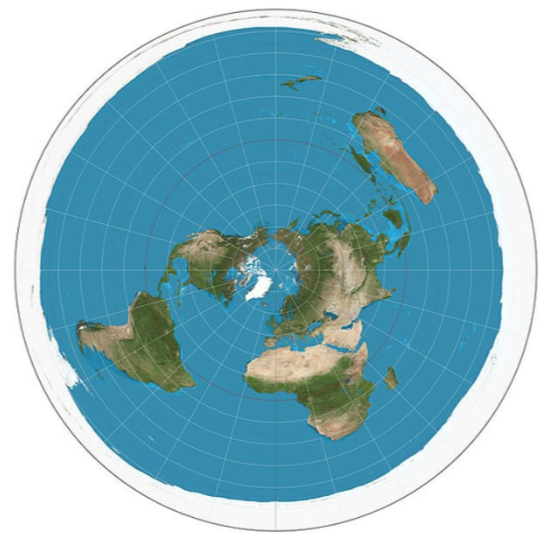
Azimuthal Projection
A map projection in which the plane is the most developable surface
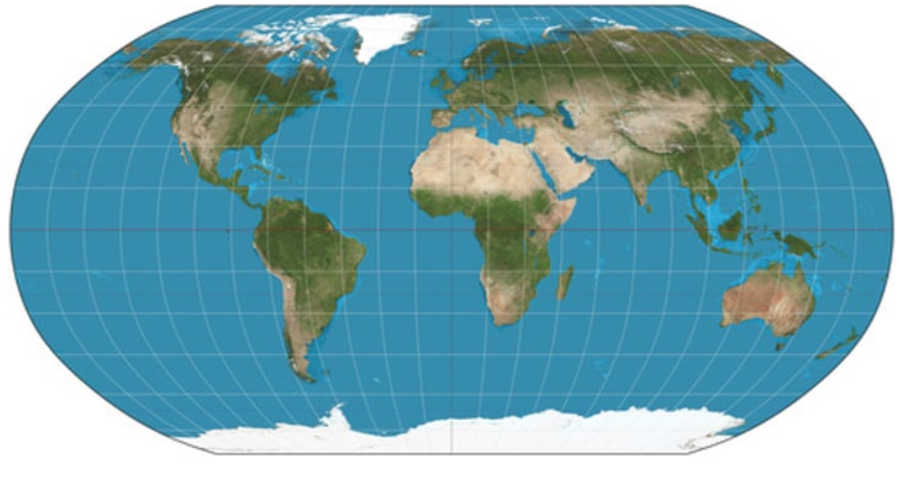
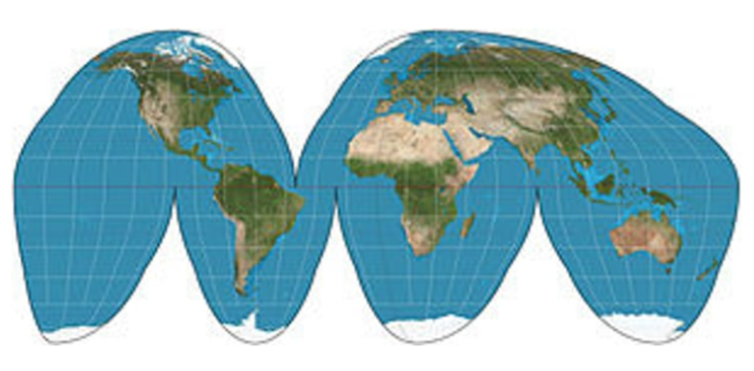
Goodes-Homosline Projection
area is fairly accurate but oceans are divided, causing distance to be distorted
Choropleth Map
Use of different colors or tonal shadings to represent categories of data
Cartogram Map
Map that distorts the geographic shape of an area in order to show the size of a specific variable
Graduated Symbol Map
A map with symbols that change in size according to the value of the attribute they represent
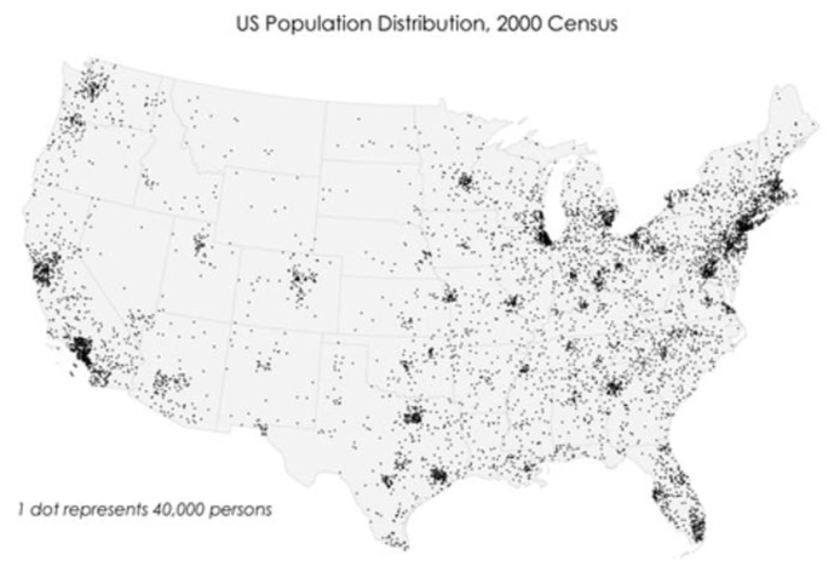
Dot Density Map
Use points to show precise locations of specific observations or occurrences
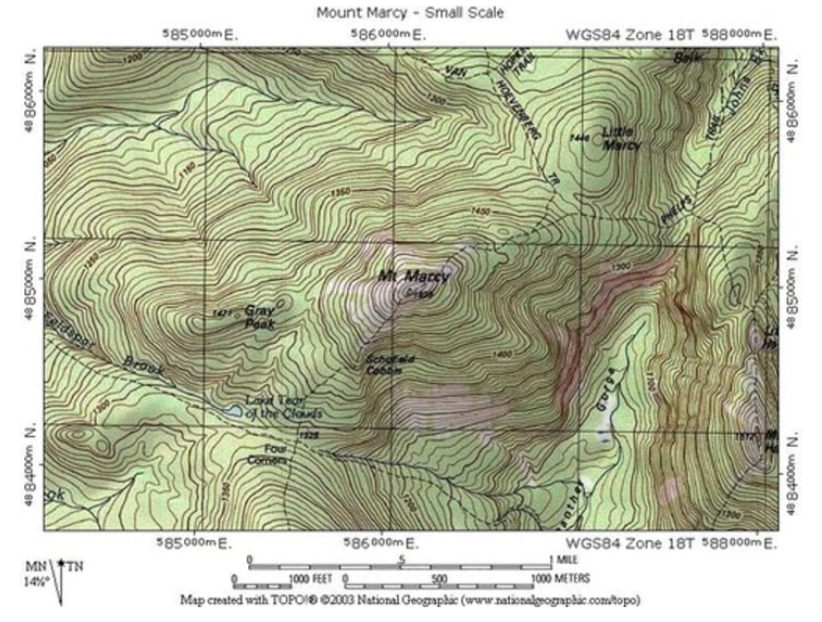
Topographic Map
Include contour (isoline) lines to show the shape and elevation of an area
Flow Line Map
Shows movement with arrows of different size
Mental Map
A map which represents the perceptions and knowledge a person has of an area

Age Structure
Refers to the breakdown of a population into different age groups or cohorts
Aging Population
A population of a country or place that ages as the number or proportion of its elderly people increases
Agricultural Density
The number of farmers per unit of land
Antinatilist Policies
Designed to curtail population growth by reducing fertility rates
Arable Land
land suitable for cultivation
Arithmetic (Crude) density
The average number of people per unit of land area (usually per square mile or kilometer)
Carrying Capacity
The number of people a particular environment or Earth as a whole can support on a sustainable basis
Crude Birth Rate (CBR)
The average number of births per 1000 people; the traditional way of measuring birth rates
Crude Death Rate (CDR)
Also known as mortality rate. The number of deaths per 1000 people in a society in a given year
Demographic Transition Model (DTM)
How crude birth rate (CBR) and crude death rate (CDR) as well as the resulting rate of natural increase (RNI) change over time as countries go through industrialization and urbanization
Dependency Ratio
The number of dependents in a population that each 100 working-age people (15-64 y.o.) must support
Doubling Time
The number of years it takes for a population to double in size (Formula is 70 divided by RNI)
Epidemiological Transition Theory
Seeks to explain how changes in health services and living standards affect patterns of disease; A model that describes changes in fertility, mortality, life expectancy, and population age distribution, largely as the result of changes in causes of death
Life Expectancy
the number of years a person can expect to live
Physiological Density
The average number of people per unit area (square mile or kilometer) of arable land
Population Pyramid
A very useful graphic device for comparing age ad sex structure
Pronatalist policies
Designed to boost fertility rates and ultimately population growth (Ex: do it for Denmark)
Rate of Natural Increase (RNI)
The difference between the number of births and deaths in a given year, when expressed as a percentage of total population
Sex Ratio
The number of men to the number of women in a population
Total Fertility Rate (TFR)
The average number of children born per women during her reproductive lifetime, considered to be from 15 to 49 years of age (Usually 2.1)
Human Factors - Population Distribution
Culture, economics, history, and politics influence where population settle
Physical Factors - Population Distribution
Climate, landforms, and water bodies influence where population settle
Immigration Policy
Government policies that can promote or discourage population growth by increasing or decreasing migration
Mortality Rate
Number of deaths per 1000 people in a society in a given year
Population Distribution
Pattern where people live (clustered/dispersed, density, and pattern)
Scale of Analysis
Observation of data at the global, regional, national, or local scale
Chain Migration
The process by which some people's migration to a new place leads their family members, friends, and others to move to same place.
Forced Migration
Migration caused by forces out of ones control, such as disasters, social conflicts, or developed states.
Internal Migration (Interregional Migration)
When people move within the borders of a country
Internally Displaced Person (IDP)
Someone who remains within his or her country's borders despite being persecuted by their home country
International (Transnational) Migration
When moves are made across national borders
Intervening Obstacles
A complication that potential migrants will need to overcome to reach their destination.
Intervening Opportunity
A nearby attractive locale where migrants may decide to settle instead of going to the intended destination farther away.
Pull Factors
The attributes of other places that make than appealing to potential migrants
Push Factors
Factors that cause people to be dissatisfied with their present locales and want to move somewhere else.
Refugee
A person who leaves their country because of persecution based on race, ethnicity, religion, nationality, or political opinion.
Step Migration
Migration carried out in a series of stages, usually from nearby to bigger and more distant places; The series of smaller moves to get to the ultimate destination
Transhumance
A phenomenon where herders and their livestock move seasonally between their summer and winter pastures.
Transnational Migration
When migrants move back and forth between their home countries and those to which they have migrated
Voluntary Migration
Migration that is done willingly
Asylum-Seeker
A person who seeks political refuge (asylum) in a country other than their own due to fear harassment, imprisonment, or even death caused by the government.
Guest Worker
A migrant permitted to work in a country other than their homeland due to a temporary labor shortage; Migrants who travel to a new country as temporary laborers
Fertility Rate
Number of babies born per 1000 people in a society in a year
Malthusian Theory
Population grows faster (exponentially-geometrically) than food supply (arithmetically-linear) leading to starvation
Malthusian Crisis
Point in which total population exceeds food supply leading to negative events to reduce population
Mortality Rate
Number of deaths per 1000 people in a society in a year
Ravenstein’s Laws of Migration
Set of rules proposed to explain and predict migration patterns
Rural-To-Urban Migration
People moving from rural (agricultural) areas to urban (cities) areas. Occurs at higher rates during industrialization and development
Centrifugal Force
A force that threatens the cohesion of a neighborhood, society, or country
Pull people apart or drive a wedge between different segments of society
Centripetal Force
A force that brings people together and unifies a neighborhood, society, or country
Contagious Diffusion
The wavelike spread of ideas in the manner of a contagious disease or viral internet idea, moving throughout space without regard for hierarchy
Creole
A combined language that has a fuller vocabulary than a pidgin language and becomes a native language
Language that results from mixing of colonizer’s language with the indigenous language
Cultural Relativism
An approach to understanding other cultures that seeks to understand individuals and cultures from a wider perspective of cultural logic