Osteology - Skull and Spine
1/260
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
261 Terms
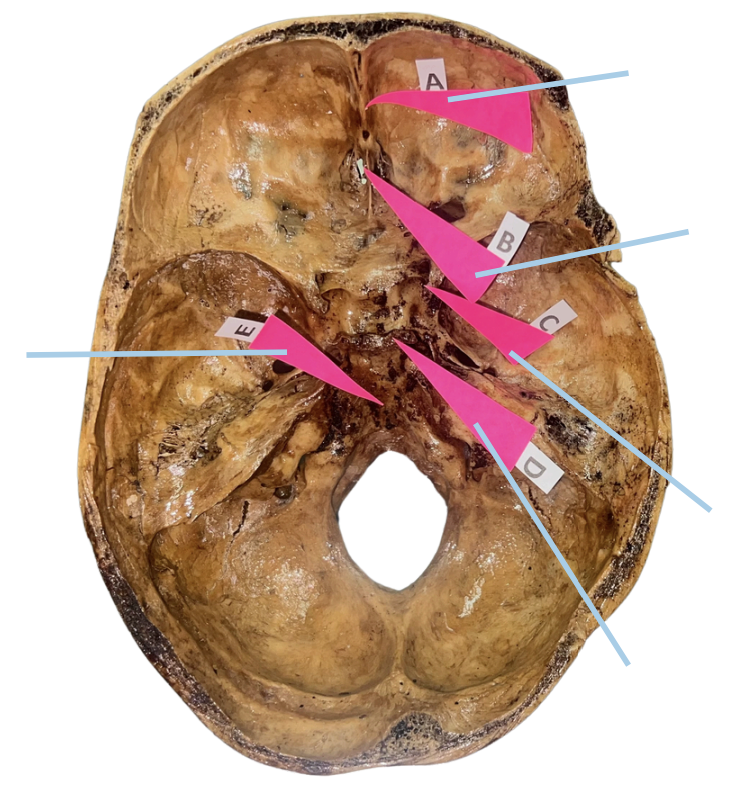
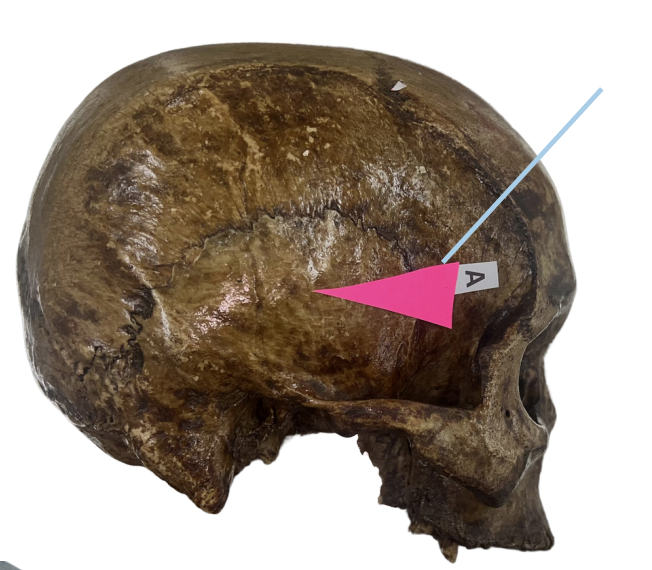
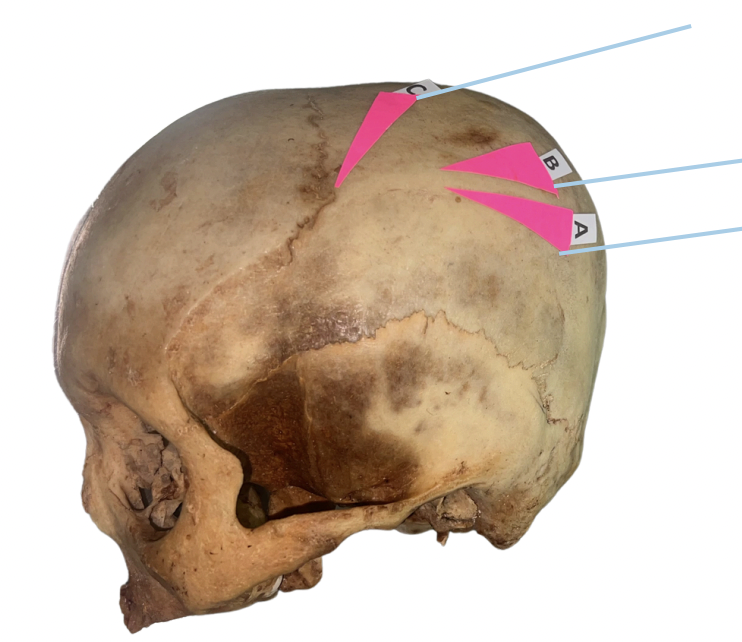
Temporal Bone
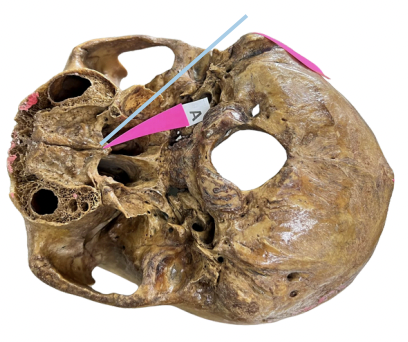
Identify the bone structure labeled as A.
A. Temporal Bone
B. Occipital Bone
C. Parietal Bone
D. Frontal Bone
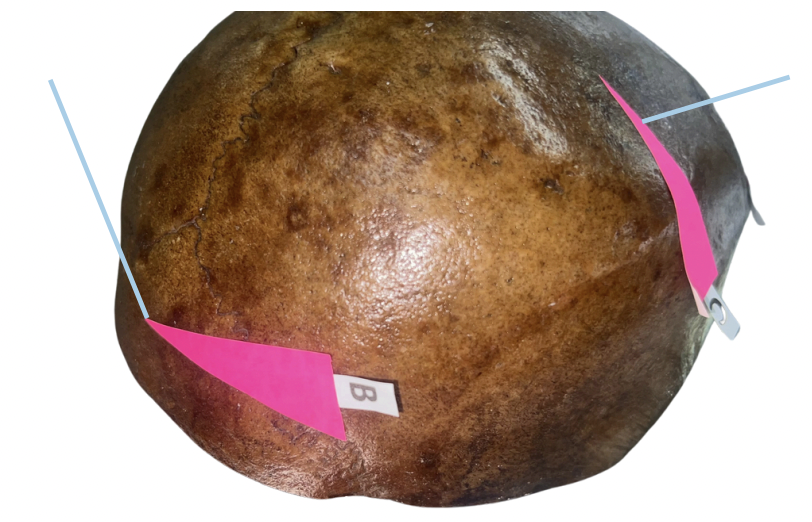
Occipital Bone
Identify the bone structure labeled as B.

Parietal Bone
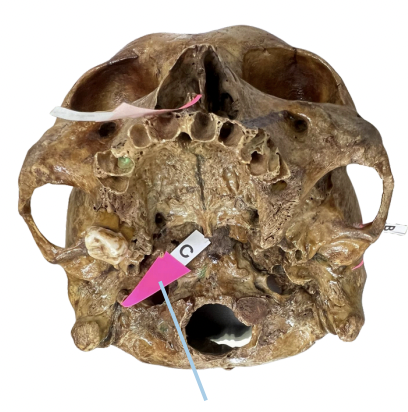
Identify the bone structure labeled as C.
Frontal Bone
Identify the bone structure labeled as D.
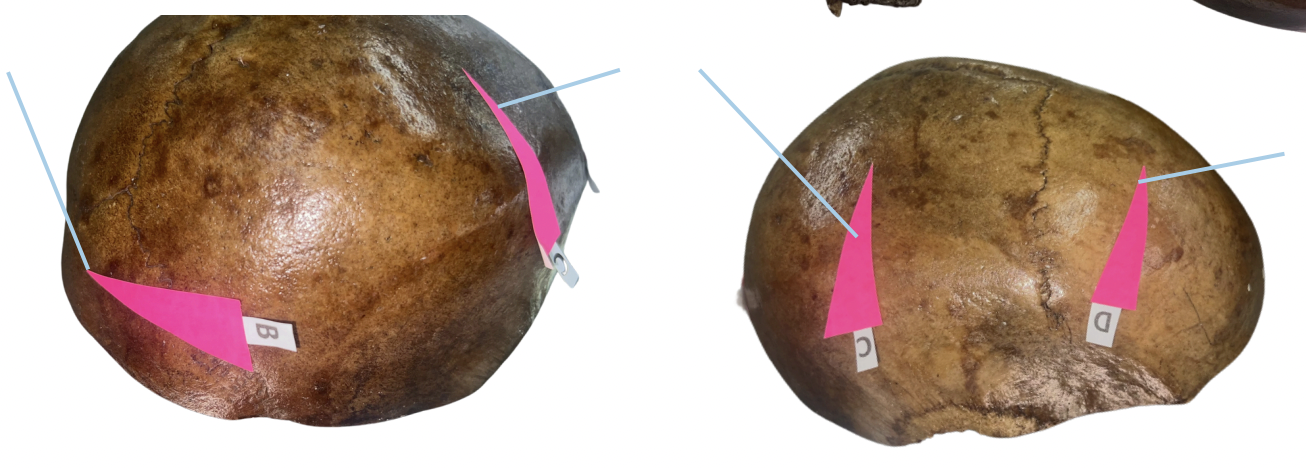
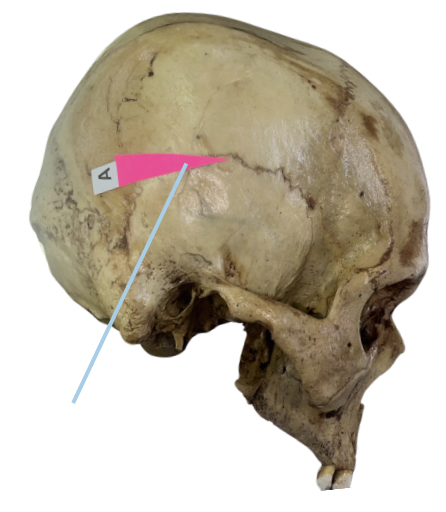
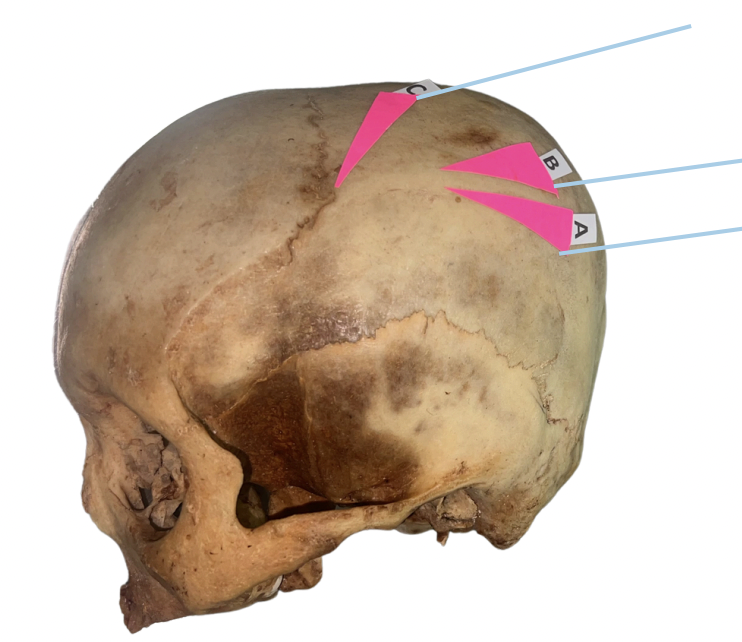
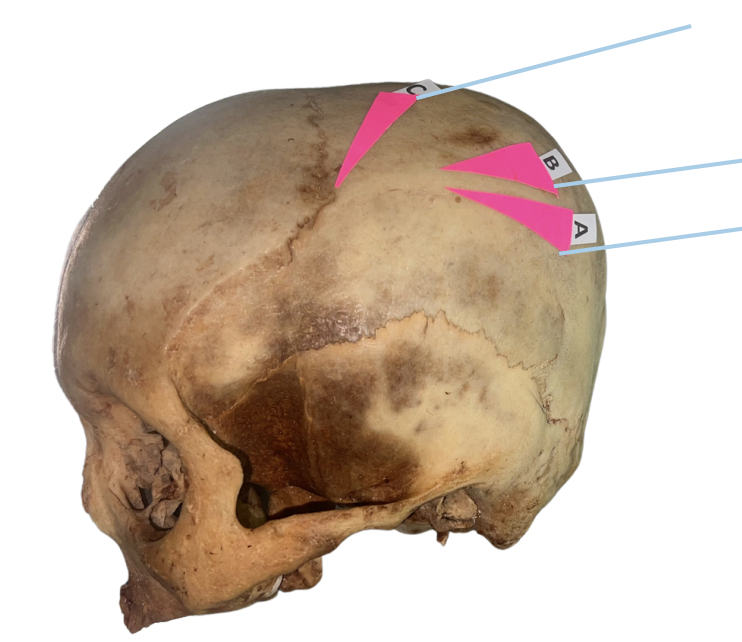
Squamosal Suture
Identify the suture labeled as A.
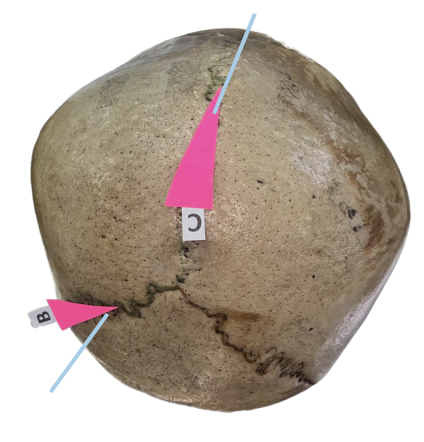
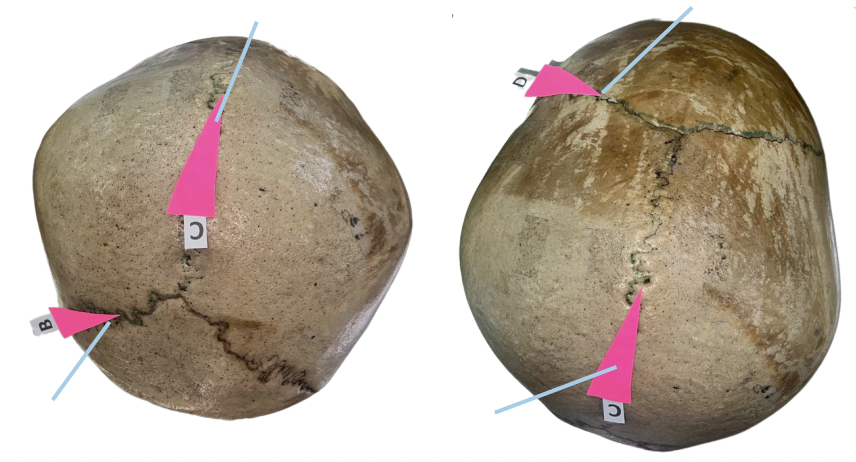
Occipital Suture
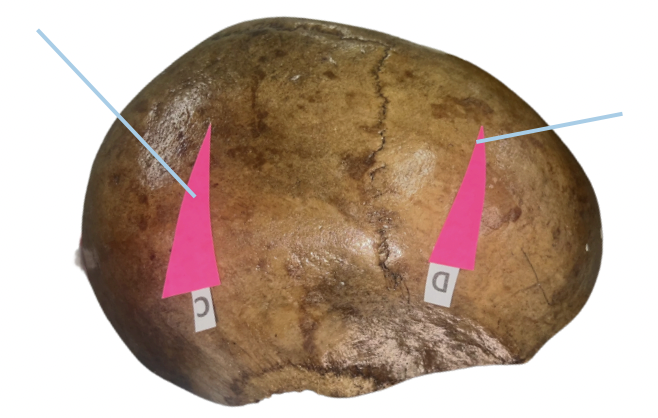
Identify the suture labeled as B.

Sagittal Suture
Identify the suture labeled as C.
F. Occipital Bone
Probable site of Mendosal Suture if present
E. Frontal Bone
F. Occipital Bone
E. Frontal Bone
Probable site of Metopic Suture if present
E. Frontal Bone
F. Occipital Bone
Asterion
Identify the suture labeled as A.
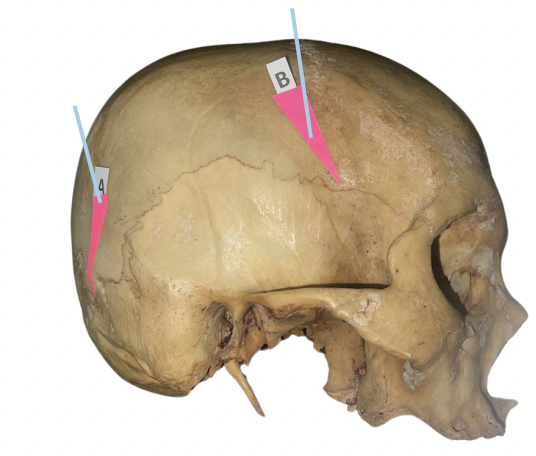
Pterion
Identify the suture labeled as B.
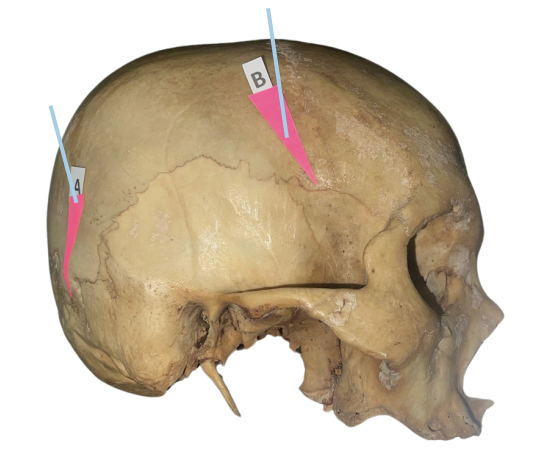
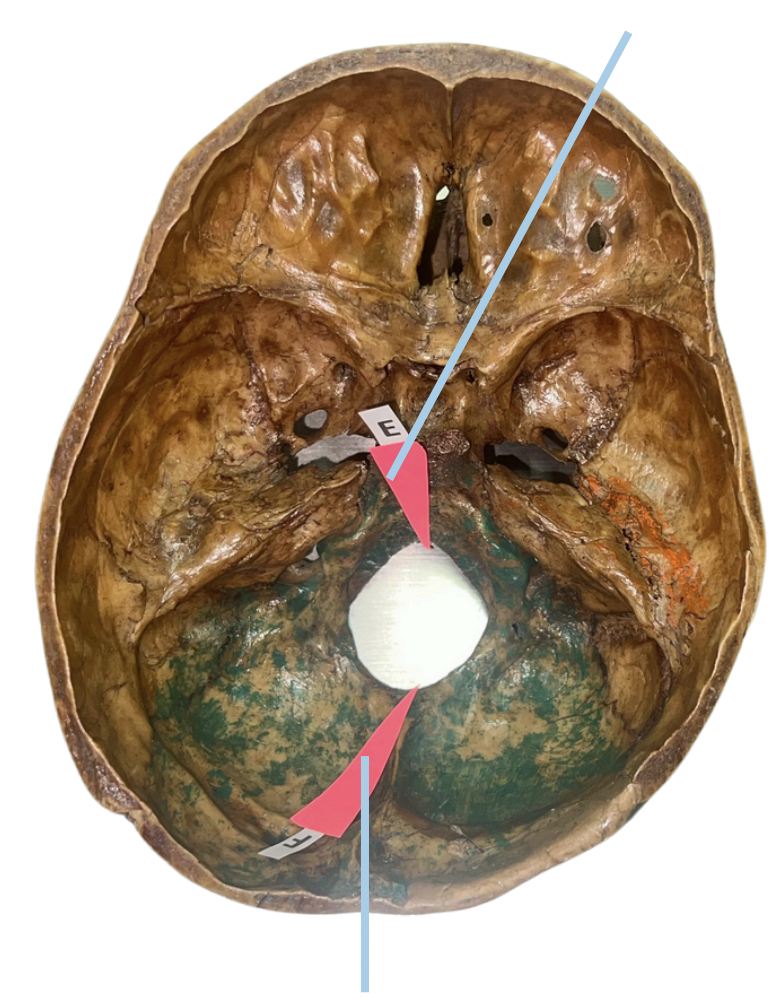
Basion
Identify the suture labeled as E.
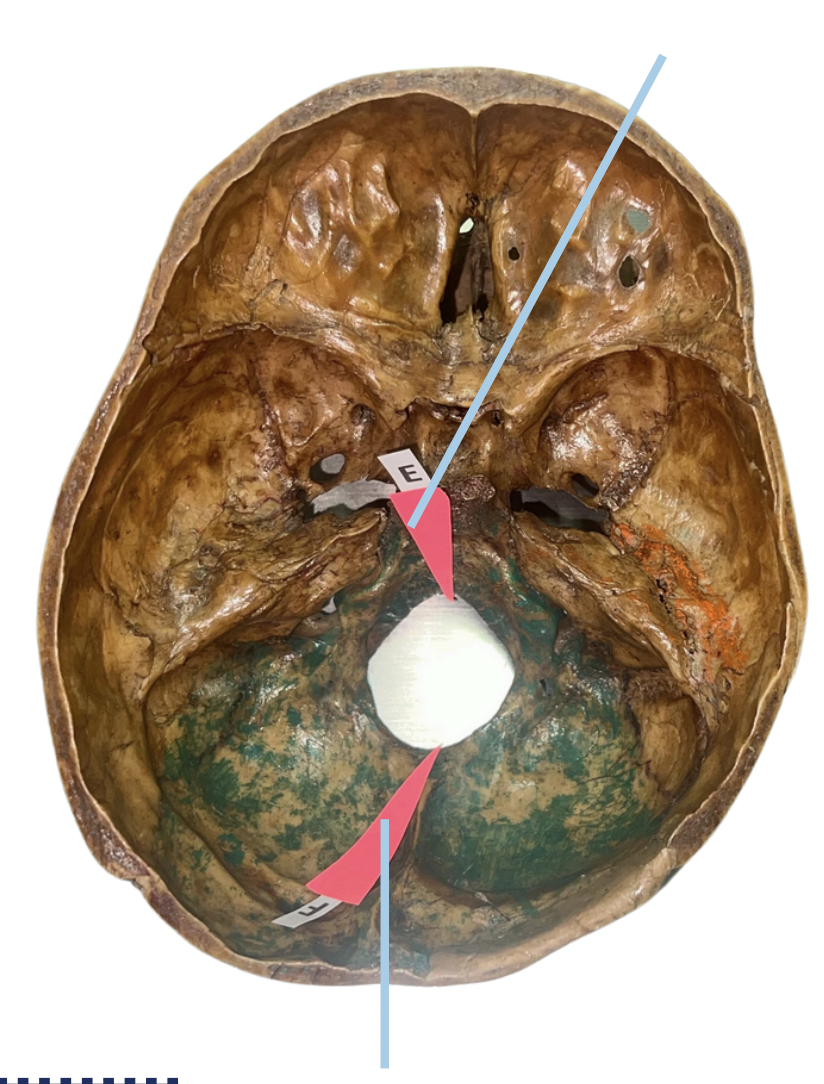
Opisthion
Identify the suture labeled as F.
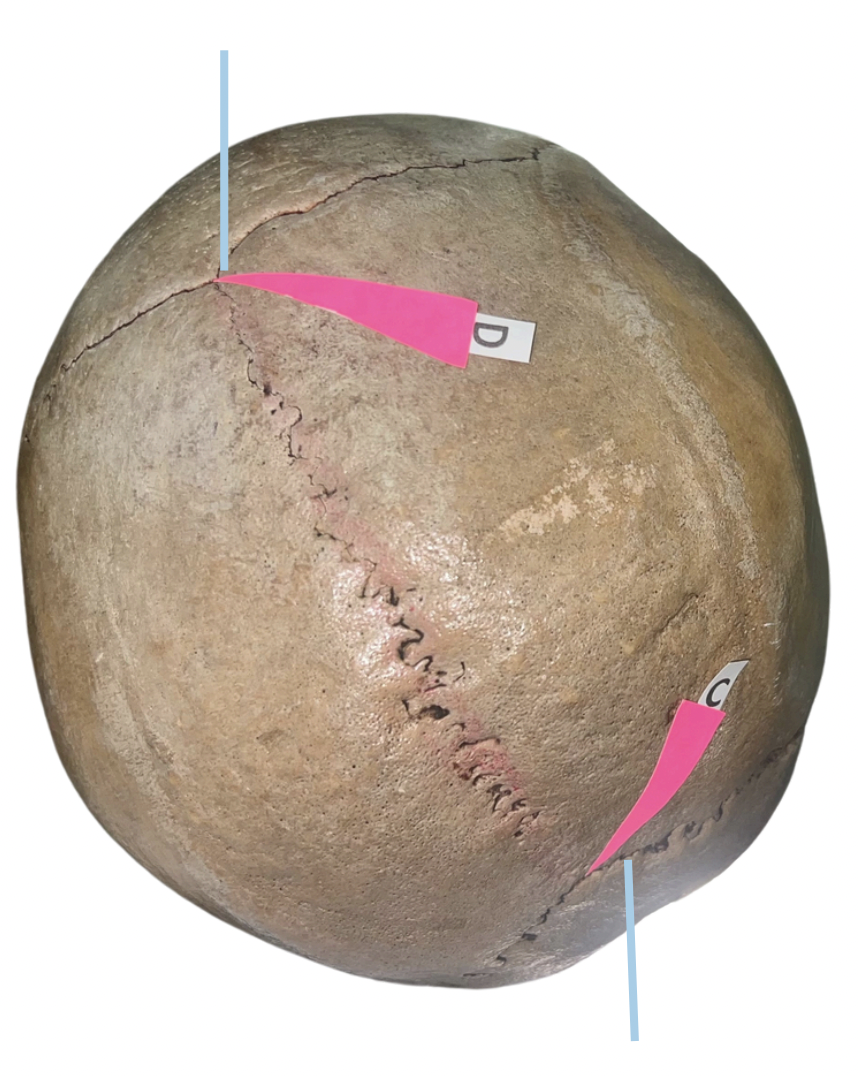
Lambda
Identify the suture labeled as C.
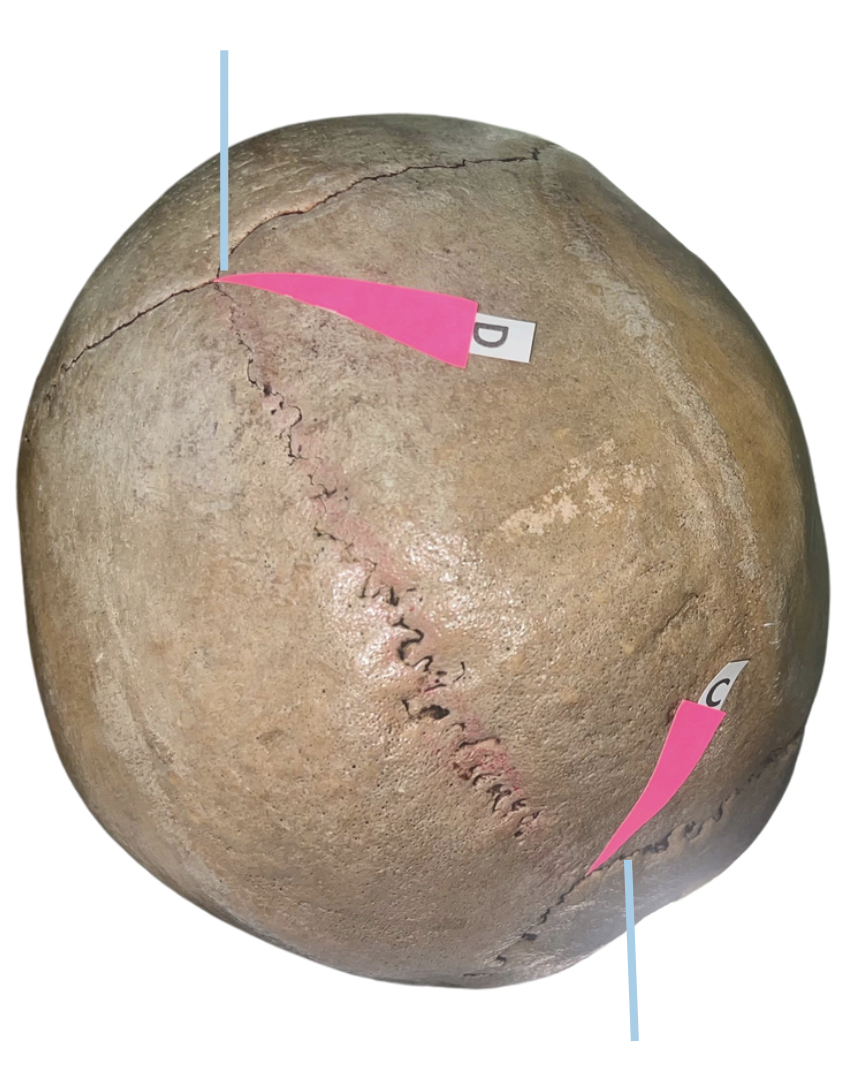

Bregma
Identify the suture labeled as D.

Pterion
Suture known as “God’s Little Joke”
A. Anterior division of middle meningeal artery
Pterion protects:
A. Anterior division of middle meningeal artery
B. Posterior division of middle meningeal artery
Lambda
Suture that closes first
Bregma
Suture that closes last
McRae Line
Eponym name for the line that connects basion and opisthion
Lambda
This suture time of closure is 2-3 months after birth.
Pterion
This suture time of closure is 4-6 months after birth.
Asterion
This suture time of closure is 6-18 months after birth.
Bregma
This suture time of closure is 18-24 months after birth.
Bregma
Which of the sutures (as a fontanelle) is commonly used by pediatricians in checking signs of dehydration, increase in intracranial pressure, and progress of ossification?
Stephanion
Cephalometric landmark where it marks the point of contact between: superior temporal line and coronal suture
Inferior Temporal Line
Identify the structure of the skull labelled A.
Superior Temporal Line
Identify the structure of the skull labelled B.
Stephanion
Identify the structure of the skull labelled C.
Zygomatic Arch
Identify the structure lined with the pink strip.
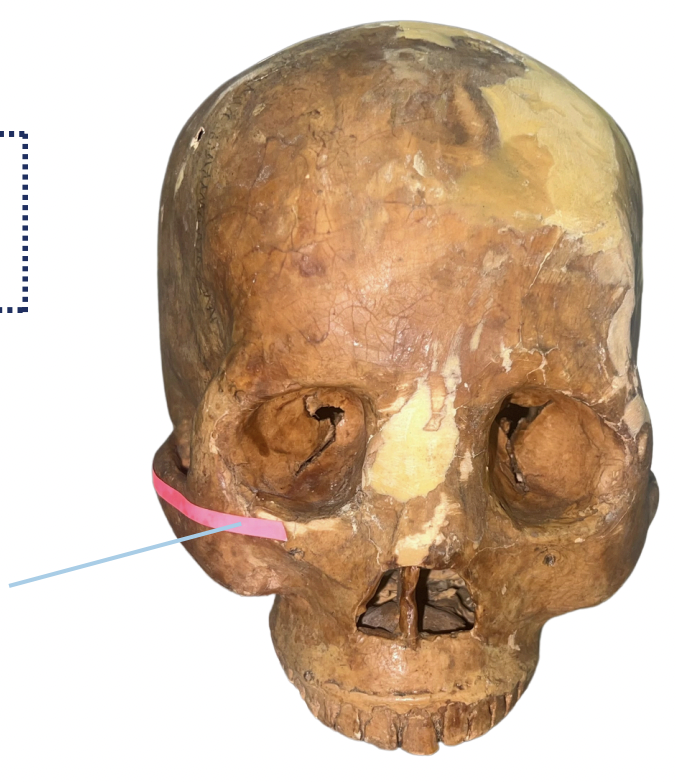
Zygomatic arch
Provides structural support and security for the face. It serves as an attachment for the masseter muscle, a major muscle for mastication. It is also used as a landmark in facial surgeries and trauma evaluation.
Diploe
Identify the structure of the skull labelled A.
Paranasal Sinus
Identify the structure of the skull labelled B.
Palatine Process of Maxillary Bone
Identify the structure of the skull labelled A.
Palatine Bone
Identify the structure of the skull labelled B.
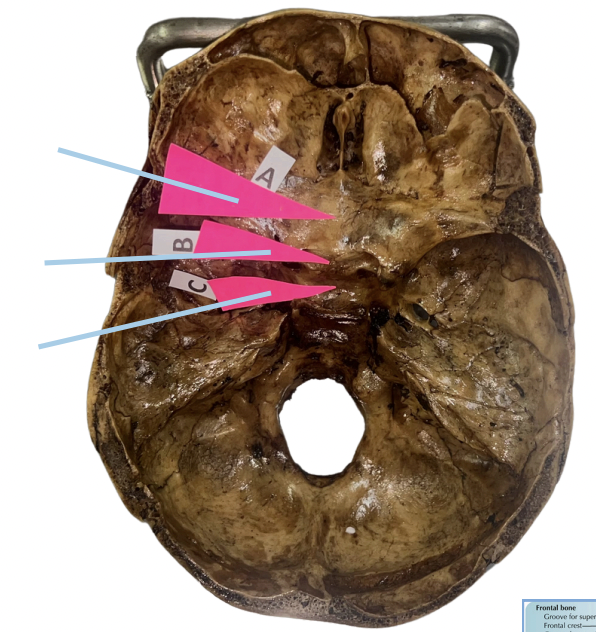
Jugum
Identify the structure of the skull labelled A.
Pre-chiasmatic Groove
Identify the structure of the skull labelled B.
Sella Turcica
Identify the structure of the skull labelled C.
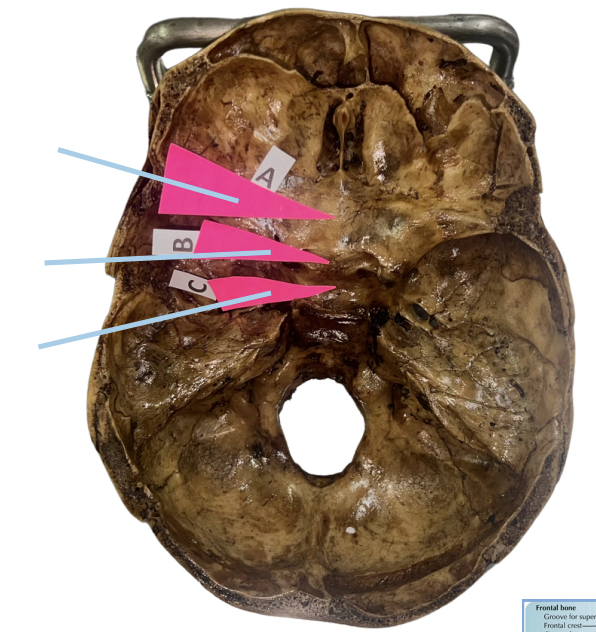
C (Sella Turcica)
This affords lodgment of the pituitary gland
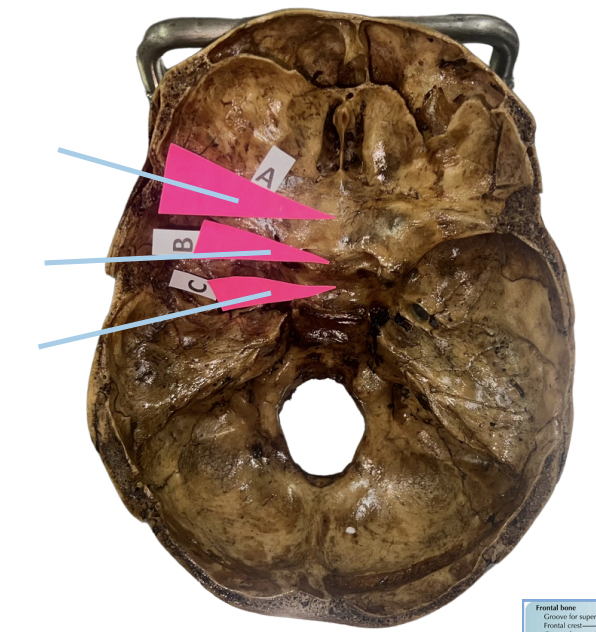
B (Pre-chiasmatic Groove)
This affords lodgment of the optic chiasm
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve I?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
B. Optic canal
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve II?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve III?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve IV?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve V1 (Ophthalmic)?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
D. Foramen Rotundum
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve V2 (Maxillary)?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
E. Foramen Ovale
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve V3 (Mandibular)?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve VI?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve VII?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve VIII?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
G. Jugular Foramen
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve IX?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
G. Jugular Foramen
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve X?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
G. Jugular Foramen
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve XI?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
H. Hypoglossal Canal
What is the point of exit of Cranial Nerve XII?
A. Cribriform Plate of Ethmoid Bone
B. Optic canal
C. Superior Ophthalmic/Orbital Fissure
D. Foramen Rotundum
E. Foramen Ovale
F. Internal Acoustic Meatus
G. Jugular Foramen
H. Hypoglossal Canal
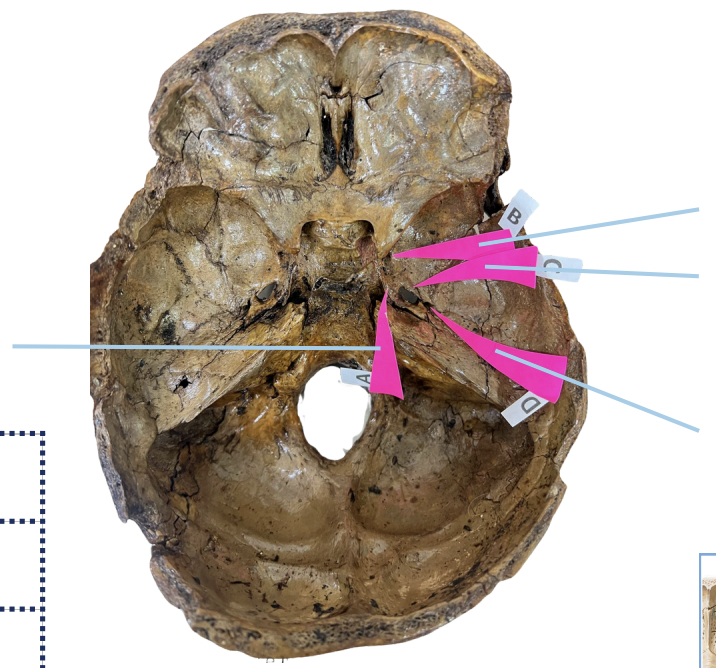
Foramen Lacerum
Identify the foramen of the skull labelled as A.
Foramen Rotundum
Identify the foramen of the skull labelled as B.
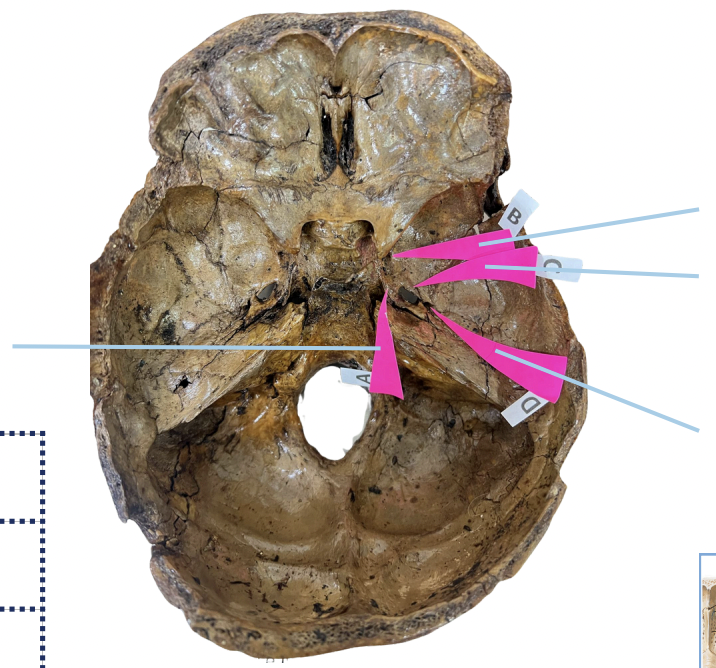
Foramen Ovale
Identify the foramen of the skull labelled as C.
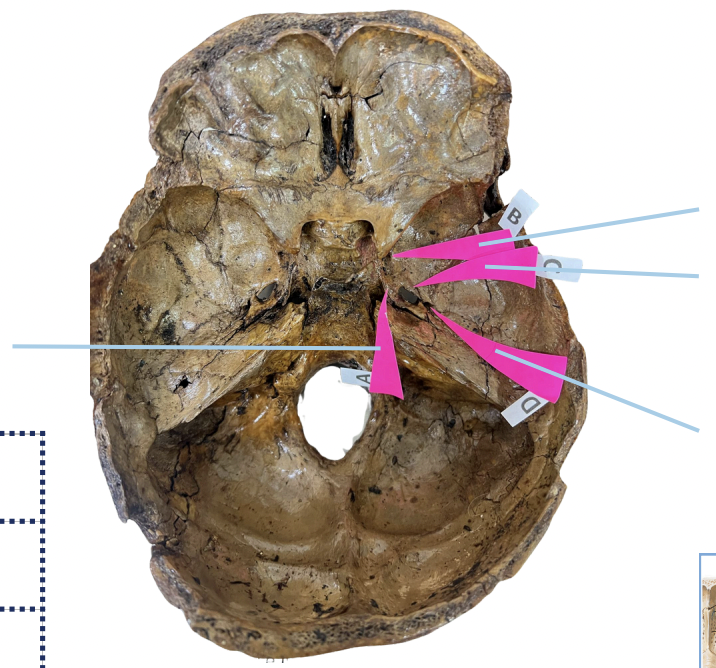
Foramen Spinosum
Identify the foramen of the skull labelled as D.
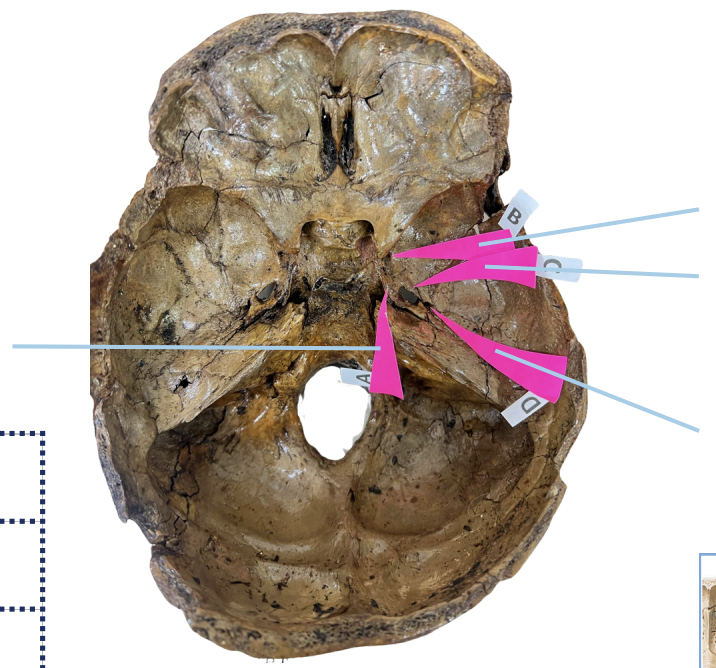
B (Foramen Rotundum)
Which permits the passage of CNV2?
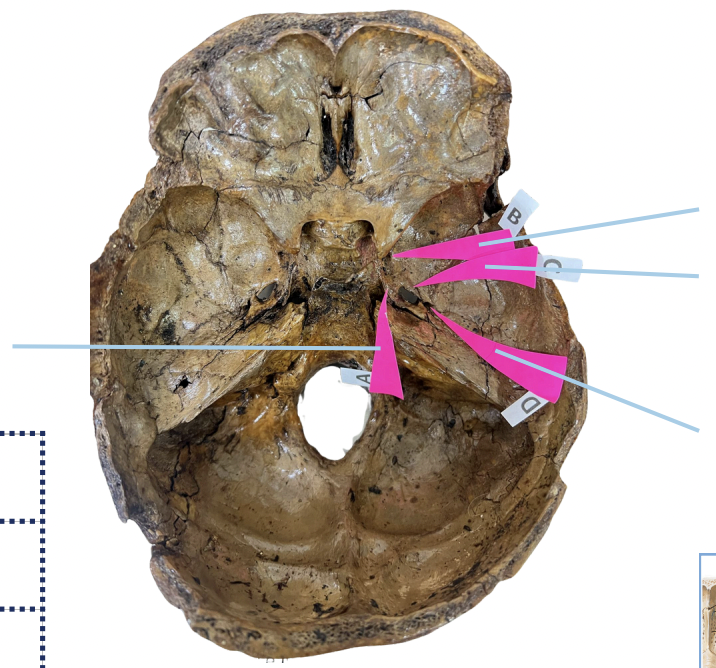
C (Foramen Ovale)
Which permits passage of CNV3 + Lesser Petrosal Nerve?
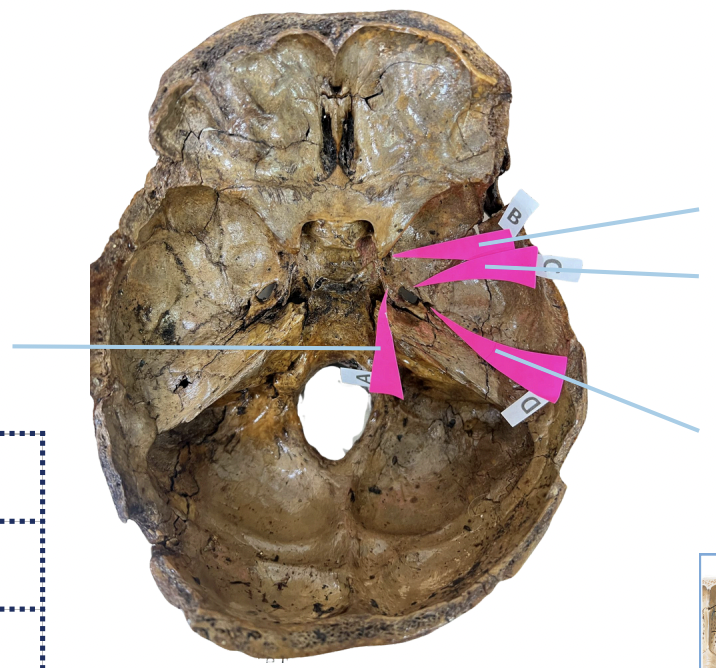
A (Foramen Lacerum)
Which permits passage of Greater Petrosal Nerve?
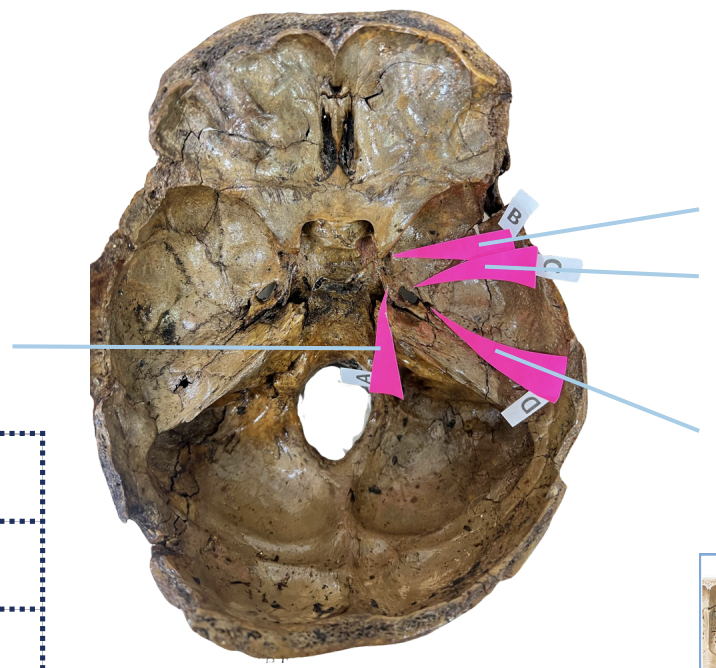
D (Foramen Spinosum)
Which permits passage of Meningeal branch of CNV3 + Middle Meningeal Blood Vessels?
Foramen Cecum
Identify the foramen of the skull labelled as A.
Foramen Magnum
Identify the foramen of the skull labelled as B.
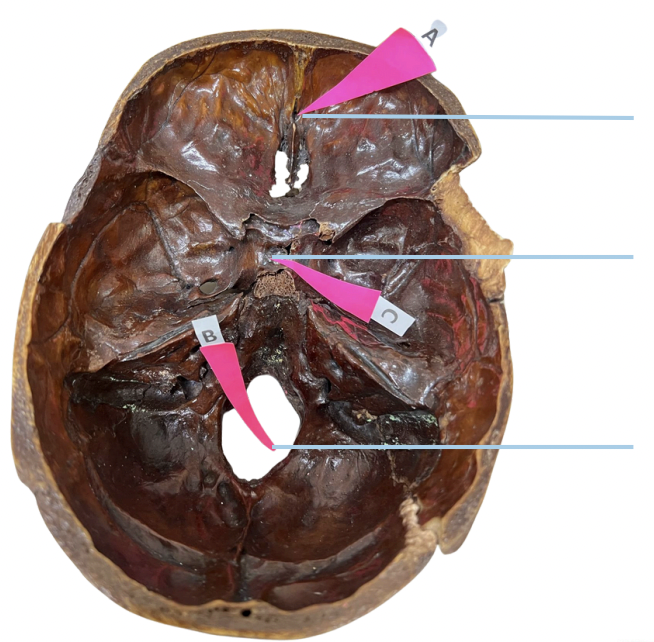
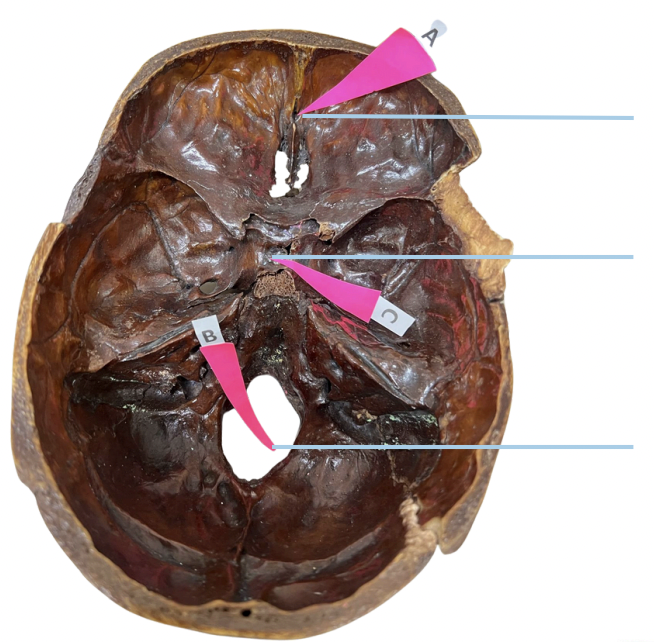
Sella Turcica
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as C.
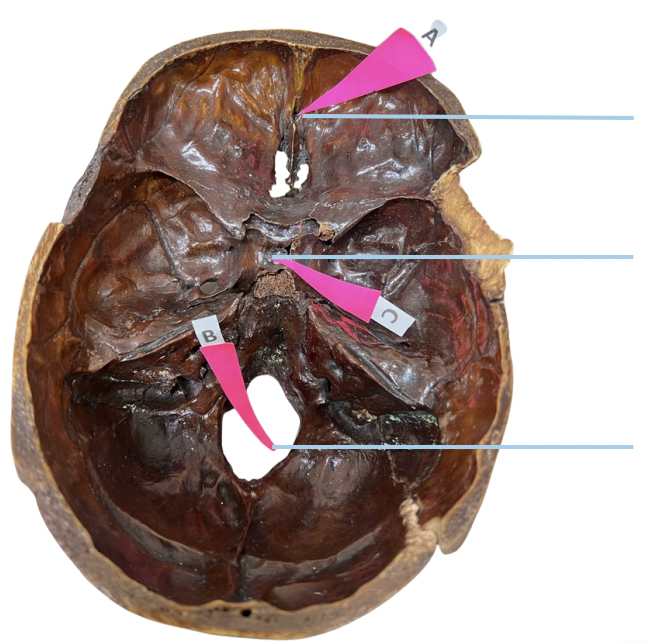
E. None of these (Spinal Cord)
The foramen magnum affords transit of the following, except for:
A. Medulla Oblongata
B. Spinal Cord and Meninges
C. Spinal Roots of Accessory Nerve
D. Vertebral Arteries
E. None of these
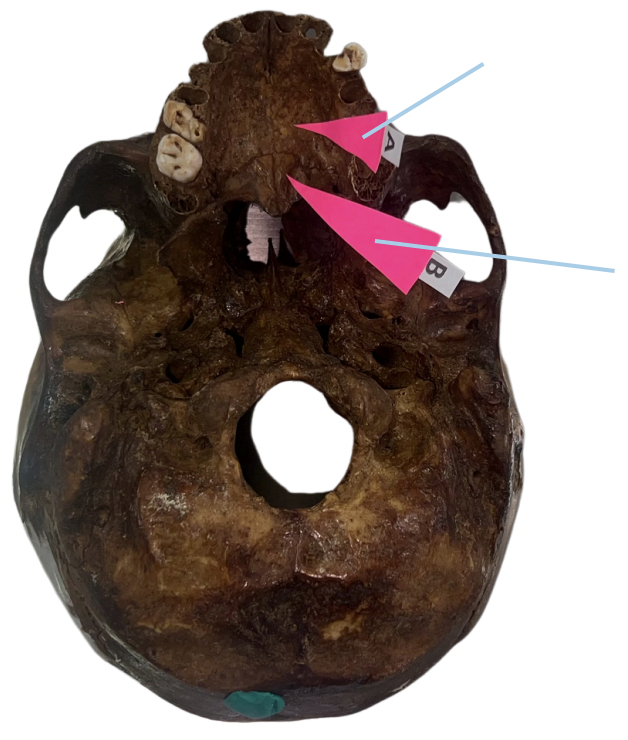
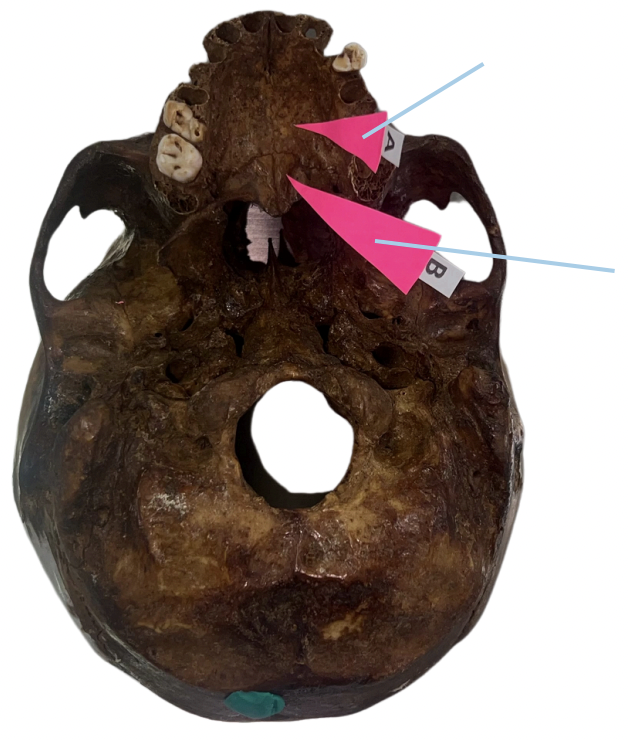
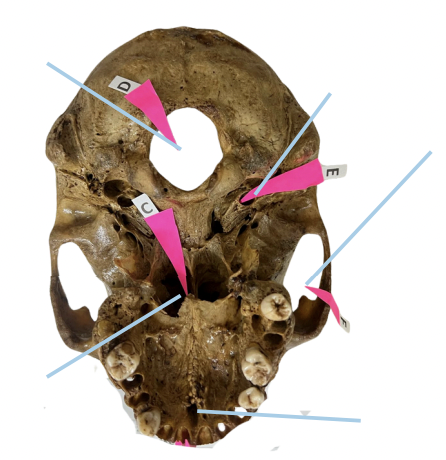
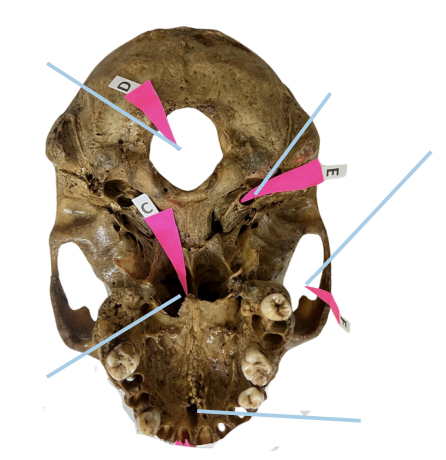
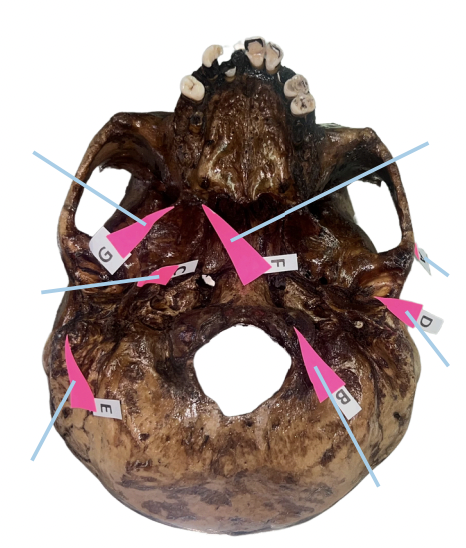
Alveolar Socket
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as A.
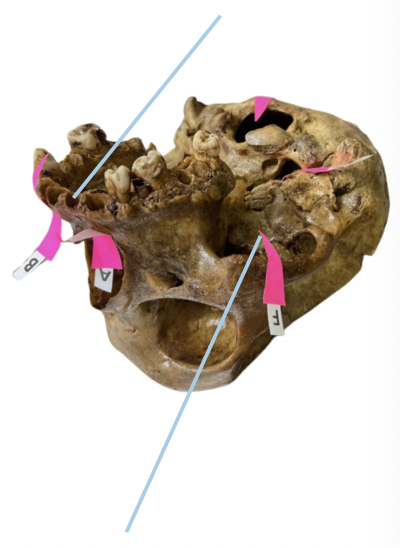
Incisive Foramen
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as B.
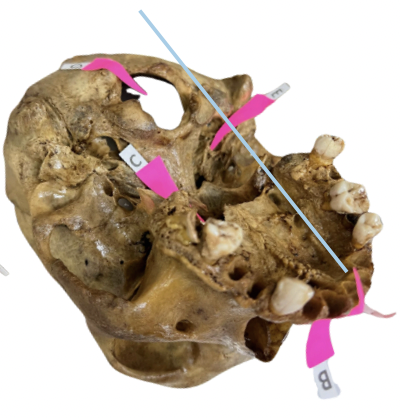
Choana
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as C.
Foramen Magnum
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as D.
Carotid Canal
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as E.
Zygomatic Fossa
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as F.
B. Nasopalatine Nerve
The incisive foramen permits passage of:
A. Sphenopalatine Artery
B. Nasopalatine Nerve
C. Sphenopalatine Vein
D. ALL OF THESE
Posterior Nasal Spine
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as A.
Styloid Process
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as C.
Mastoid Process
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as D.
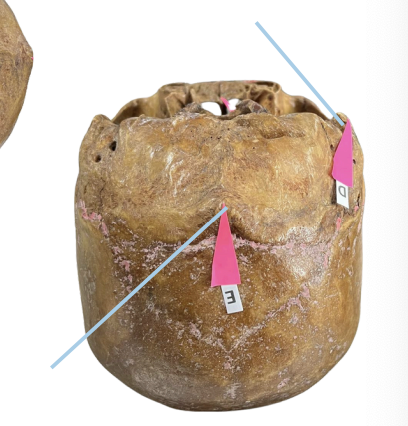
Inion
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as E.
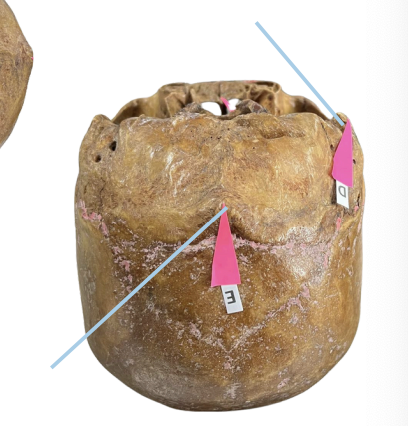
A. Men
The inion is more prominent amongst:
A. Men
B. Women
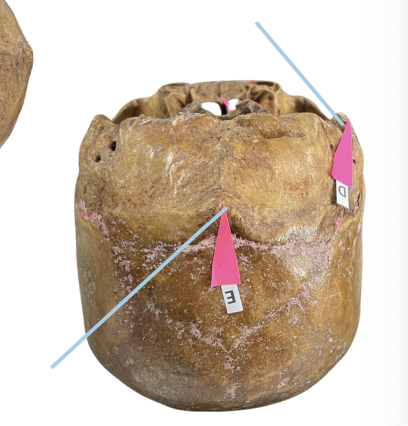
Anterior Nasal Spine
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as F.
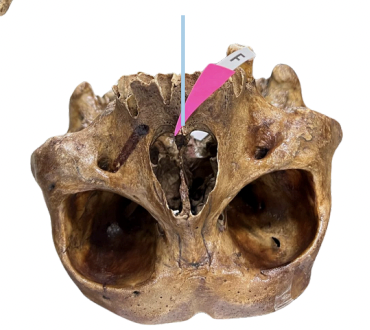
Zygomatic Arch
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as A.
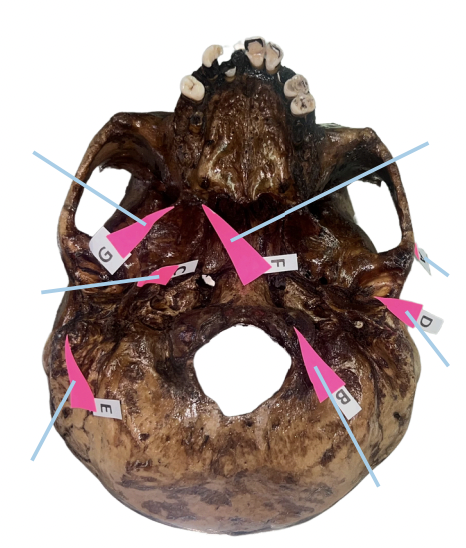
Occipital Condyle
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as B.
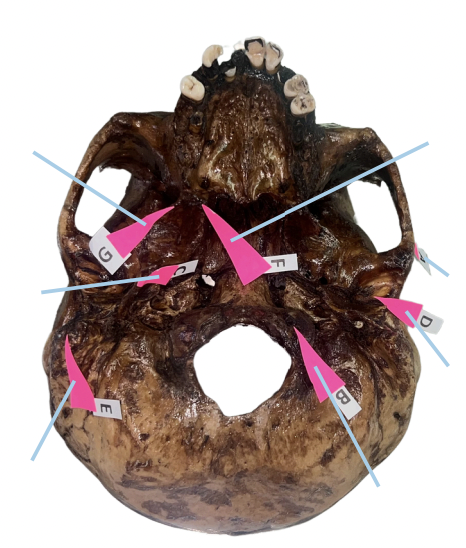
Styloid Process
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as C.
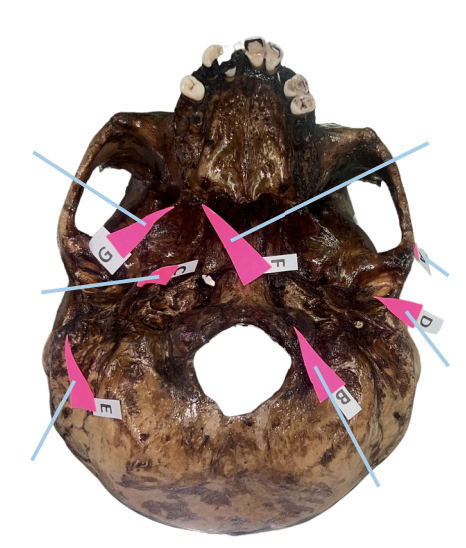
Petrotympanic Fissure
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as D.
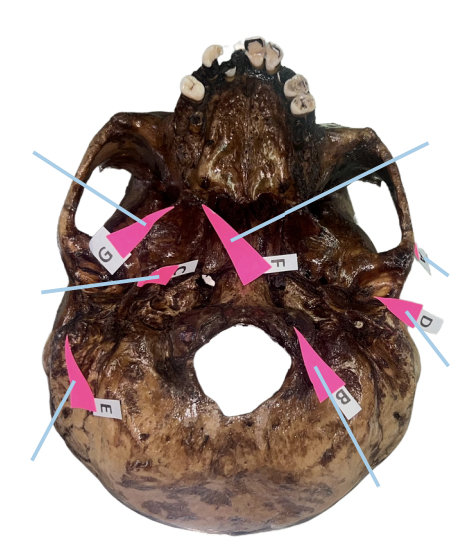
Mastoid Process
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as E.
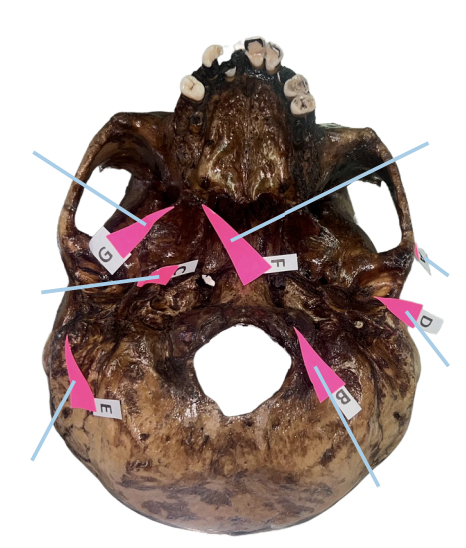
Hamulus
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as F.
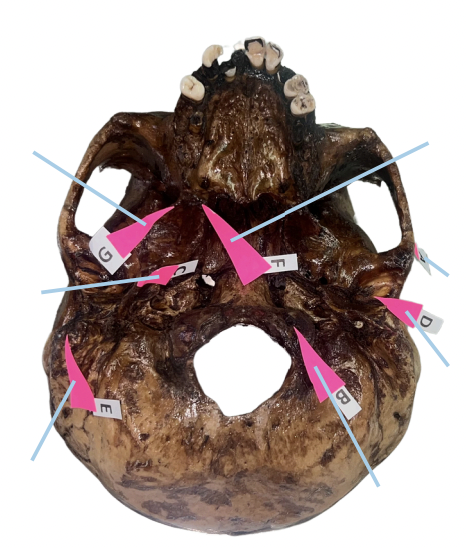
Civinini Process
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as G.
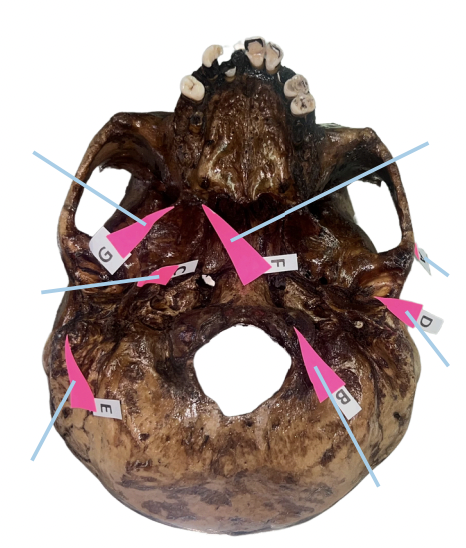
Chorda Tympani Nerve
What nerve passes through the “petrotympanic fissure” and what is the function of that nerve to the tongue?
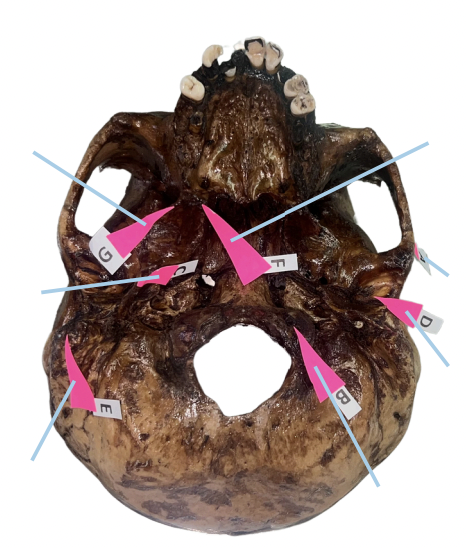
C (Styloid Process)
Which of these is involved if its length from the undersurface of the cranial base exceeds 3 cm and offers sudden, shooting, and sharp pain to the oropharyngeal area when turning the head on the affected side (Eagle Syndrome)?
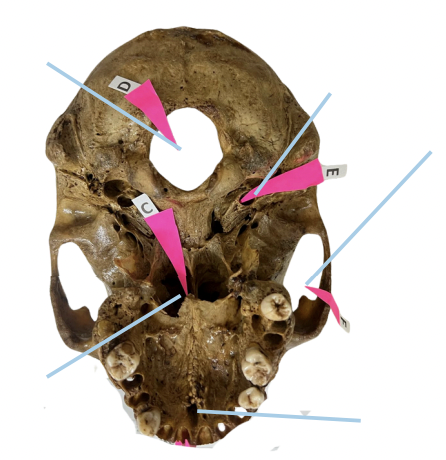
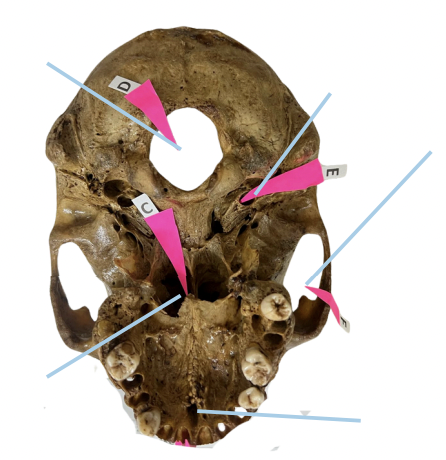
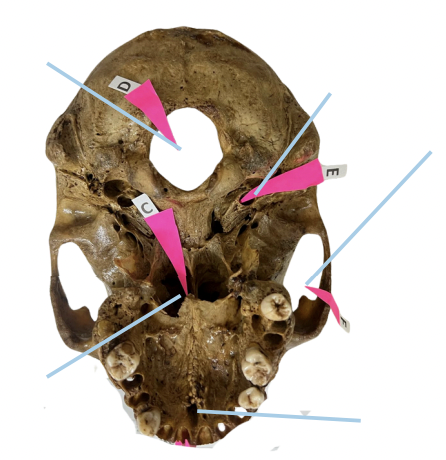
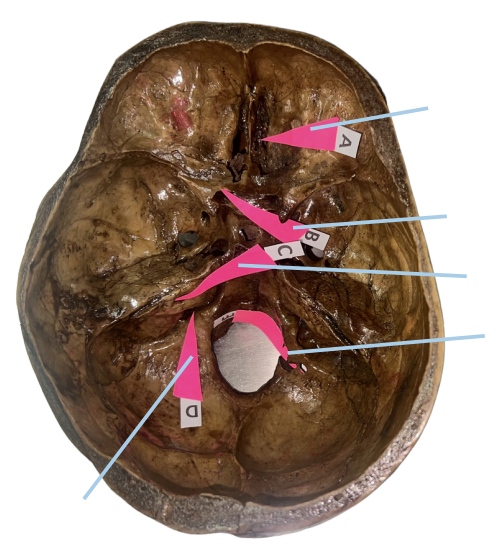
Cribriform Plate
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as A.
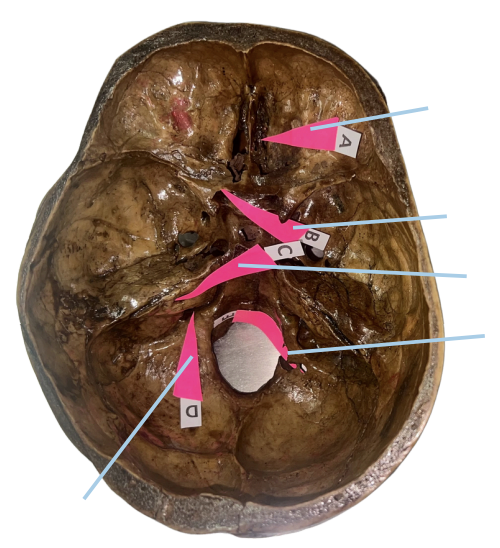
Optic Canal
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as B.
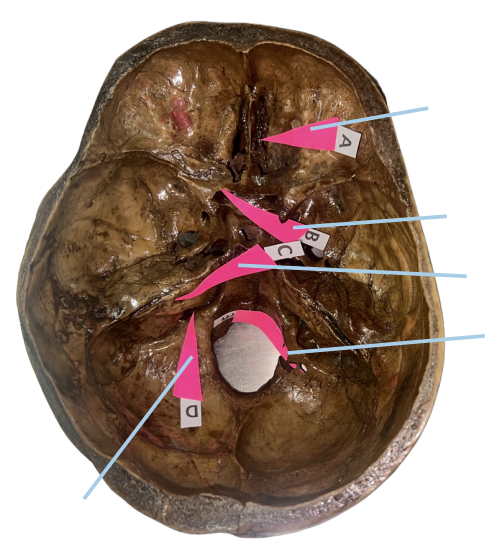
Internal Acoustic Meatus
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as C.
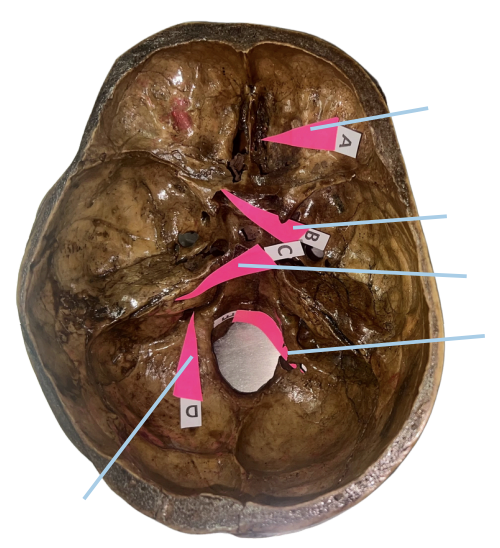
Jugular Foramen
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as D.
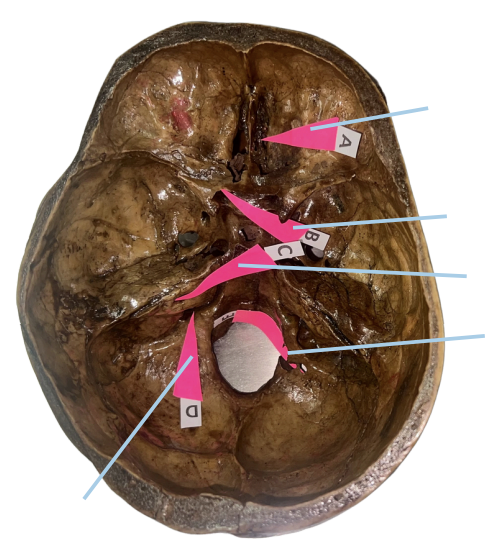
Hypoglossal Canal
Identify the structure of the skull labelled as E.
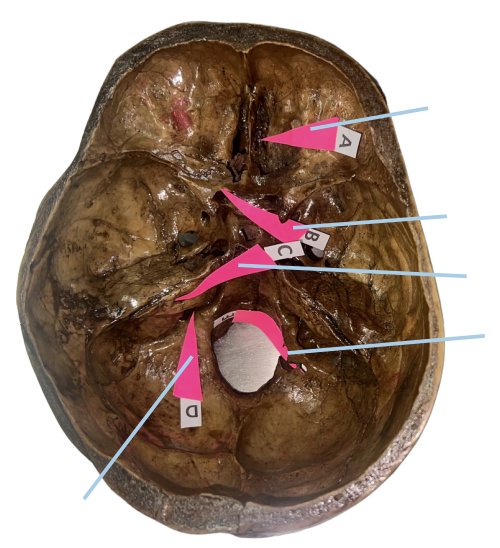
A (Cribriform Plate)
Which permits the passage of CN I Rootlets?
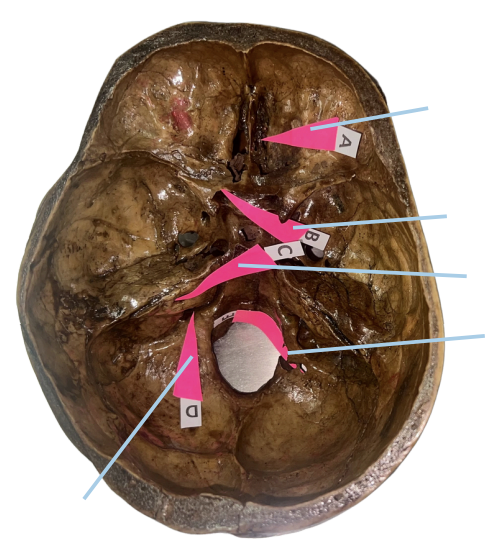
B (Optic Canal)
Which permits the passage of CN II + Ophthalmic artery?
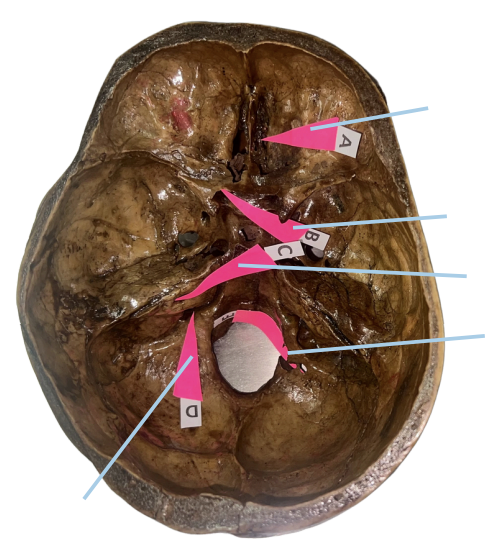
C (Internal Acoustic Meatus)
Which permits the passage of CN VII + CN VIII?
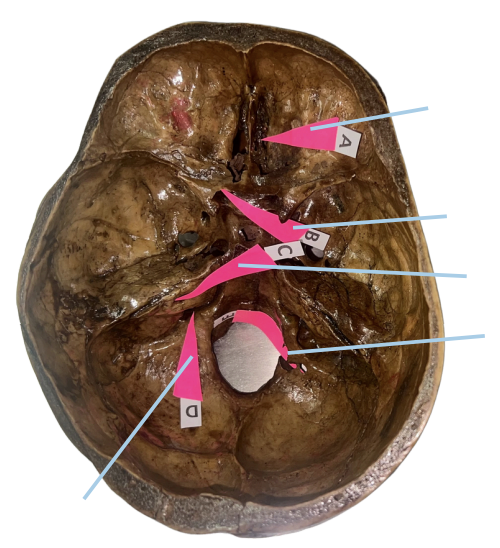
D (Jugular Foramen)
Which permits the passage of CN IX + CN X + CN XI?
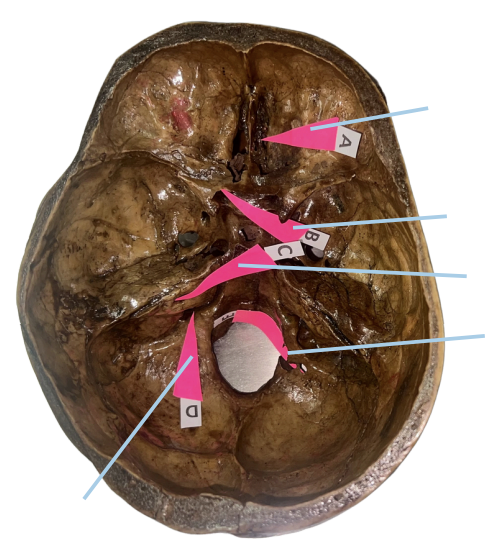
E (Hypoglossal Canal)
Which permits the passage of CN XII?
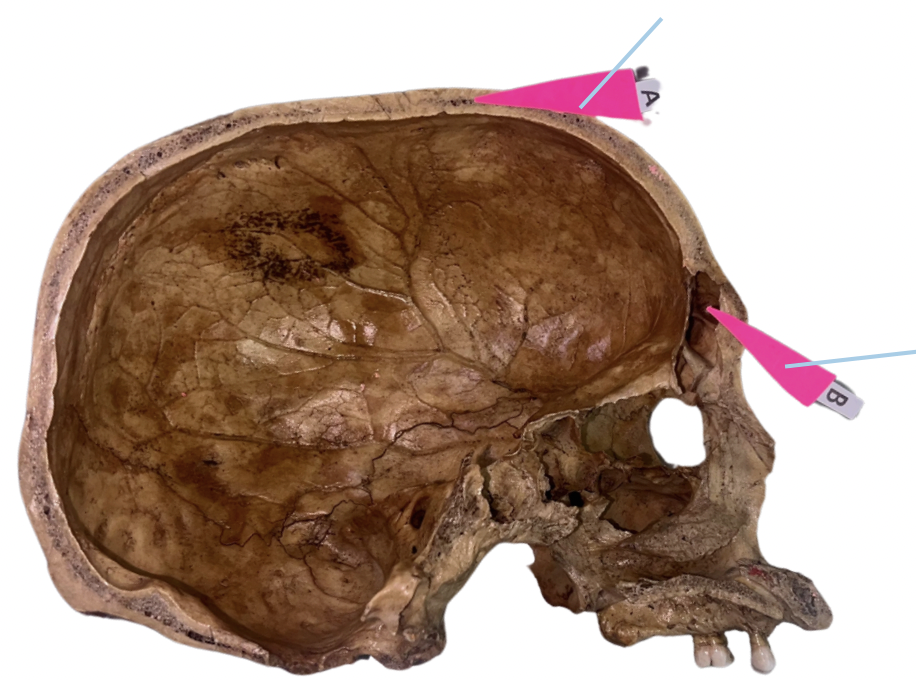
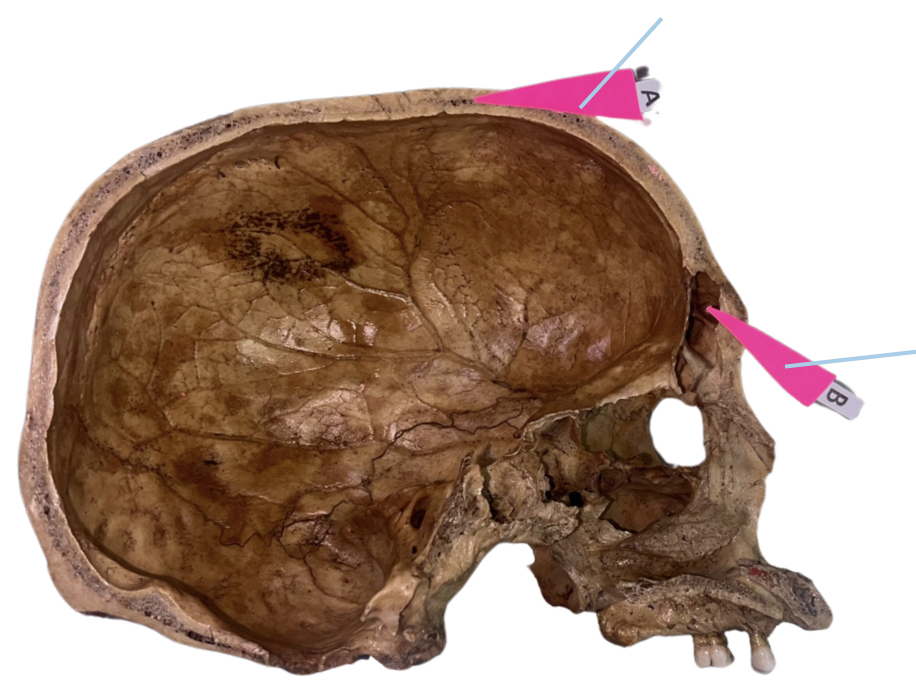
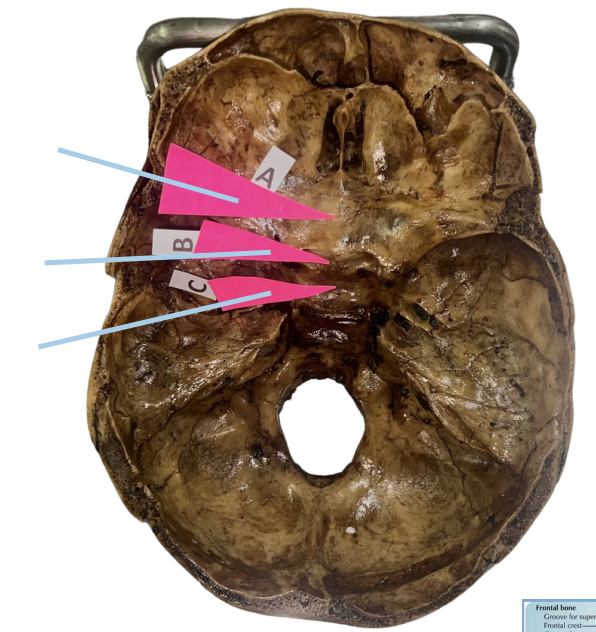
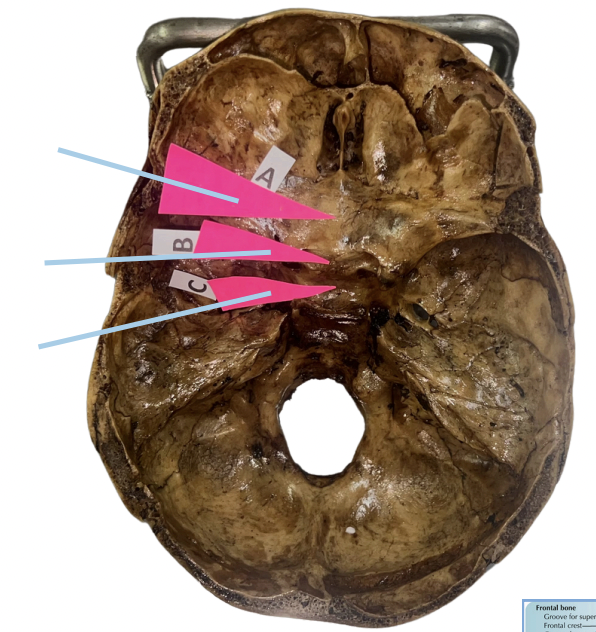
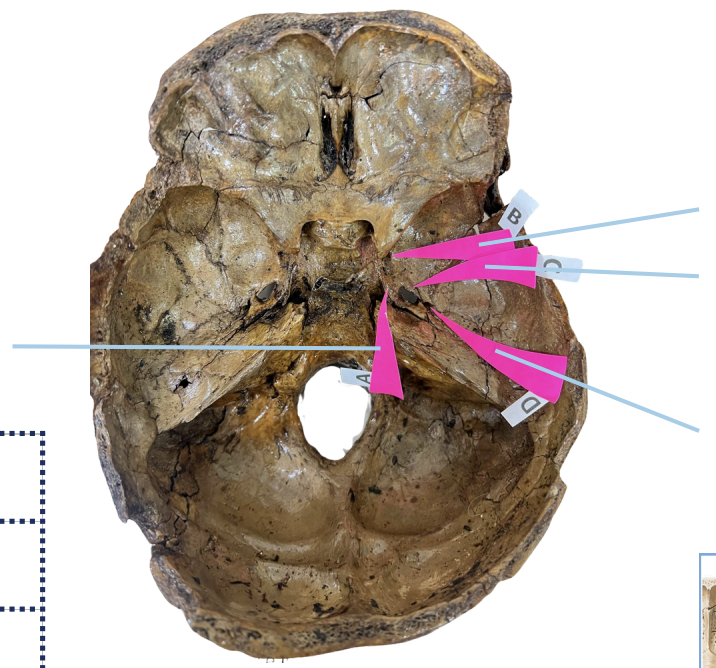
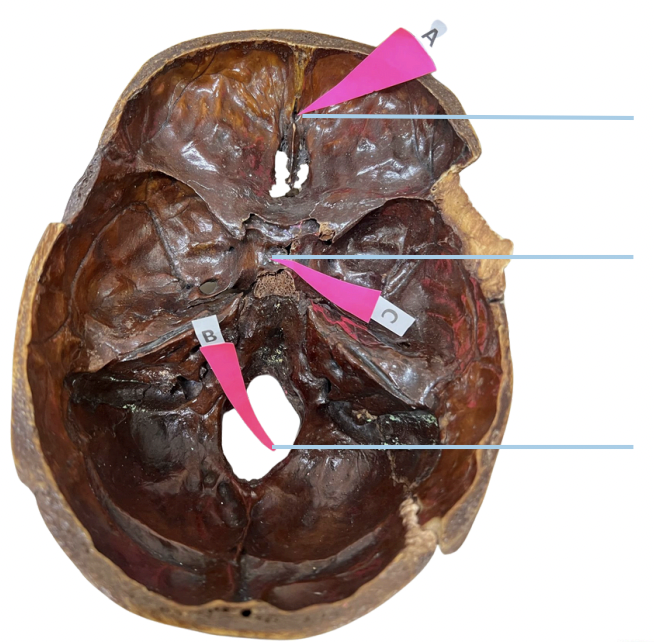
Frontal Crest
Identify the structure of the basicranium labelled as A.
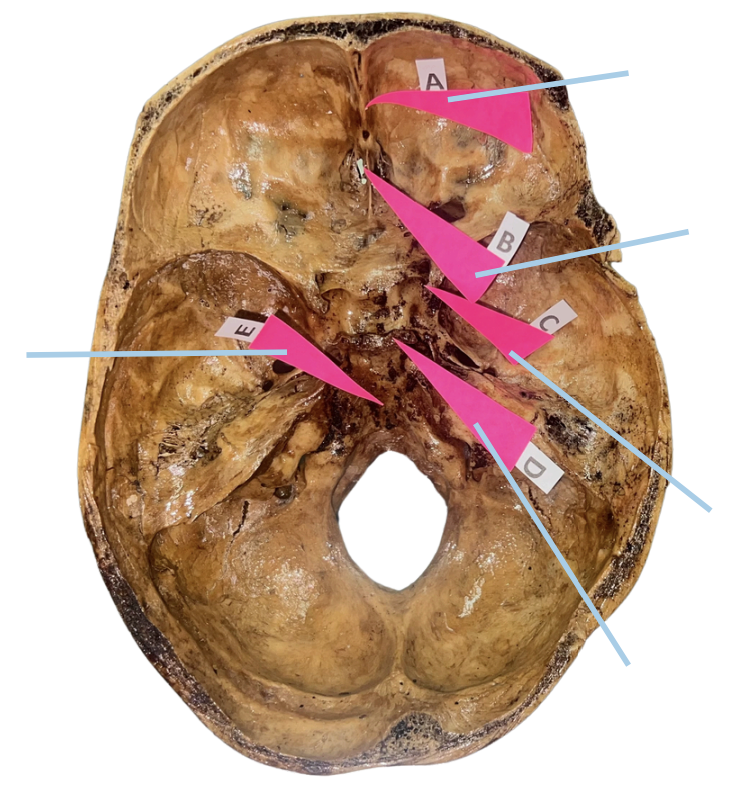
Crista Galli
Identify the structure of the basicranium labelled as B.