Chemistry Unit 1 Keyterms
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
variations of chemical elements that have the same amount of protons but different amounts of neutrons
Isotopic abundance
how much of each type of isotope an element has in nature
Dalton’s atomic theory
All matter is made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms
All atoms of an element are identical
Atoms of different elements are different
Atoms are rearranged to form new substances in chemical reactions, but they are unable to be created or destroyed
Thomson's Atomic Theory
All atoms contain negatively charged subatomic particles called electrons; pudding model
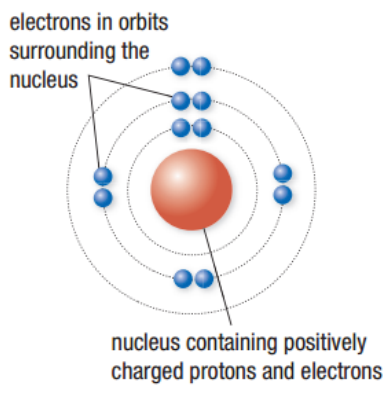
Rutherford’s Atomic Theory
Atoms have a nucleus surrounded by electrons called orbits
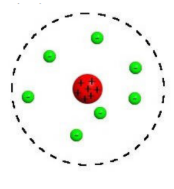
Bohr’s Atomic Theory:
Electrons move in fixed orbits that have fixed energy levels around the nucleus, and they can jump between these levels when energy is absorbed or emitted.