Anatomy - Tissues Quiz Study Guide
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What are the four types of tissues?
Nervous, Muscle, Epithelial, and Connective
Function of Nervous tissue?
Allows for communication to occur and the transmission of signals
Function of Muscle tissue?
Lines the hollow organs and allows for movement
Function of Epithelial tissue?
Forms boundaries between environments
Function of Connective tissue?
Supports, protects, and bonds structures, storage, transportation, immune function
What are the common functions of epithelial tissue?
They function to protect, secrete (sweat), and absorb (linings).
Where is epithelium located?
Coverings, linings, and glands.
What are three shapes of epithelium?
The three shapes of epithelium include squamous, cuboidal, and columnar.
What are the three layers of epithelium?
simple (single layer), stratified (more than one layer) , and the pseudostratified (appearance of more than one layer, but all cells are attached to the basement membrane).
What is transitional epithelium?
Modified stratified squamous epithelium. Found in the urinary bladder, ureters, and urethra. All cells at the basal layer are cuboidal or columnar
Endocrine vs Exocrine Glands (Epithelium)
Endocrine glands are surrounded by blood vessels and secrete their products into the blood for circulation around the body. Exocrine glands secrete their product into the duct of the gland which is connected to the outside of the body
Which type of tissue has a extracellular matrix?
Connective tissue.
Where is connective tissue found
Everywhere
What are the 3 classes of components of Connective tissue?
Cells, fibers, and ground substance (fibers and ground substance are included in the extracellular matrix)
What are the 3 different types of fibers found in connective tissue?
Reticular, elastic, collagen
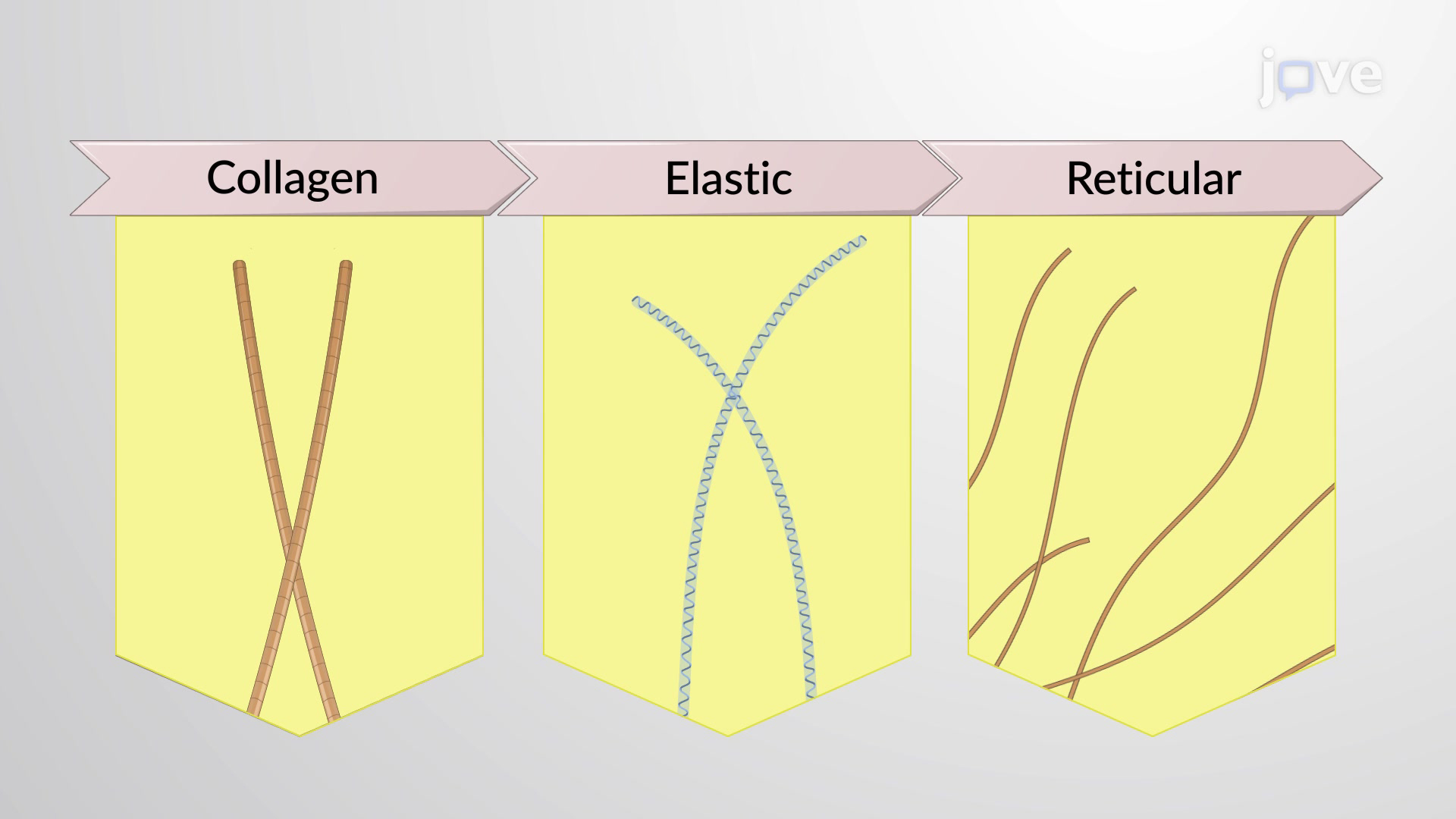
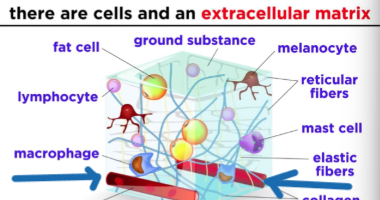
Connective tissue w/ cells and fibers and ground substance
What are the 3 classes of connective tissue?
Supporting connective tissue (bone and cartilage (hyaline, fibrocartilage, elastic)),
Connective tissue proper (dense connective tissue/dense fibrous (regular, irregular, elastic))
Loose/Fluid Connective Tissue (blood/lymph)
What are the three types of muscle tissue?
skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle tissues
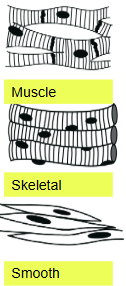
Which type of muscle is voluntary?
Skeletal muscle provides voluntary skeletal movement of the body.
Which type of muscle is found in our hollow organs?
Smooth muscle is found in our hollow organs.
Which muscle contracts as a single unit rather than individual cells?
cardiac muscle
Which muscle is non-striated?
Smooth muscle
Which muscle is multi-nucleated?
Skeletal
Skeletal Muscles pull on bones to create….
movement
Bones are connected to other bones with another connective tissue called…
ligaments
Skeletal Muscle attaches to bone with…
connective tissue called tendons
What are two characteristics of nervous tissue?
it's high excitability and it's conductivity.
Where is nervous tissue located?
It is found in the brain, spinal cord, and peripheral nerves.
What are the two types of cells found in nervous tissue?
Nervous tissue consists of neurons and neuroglia.
Which type of cell supports the communication cells?
The neuroglia supports the communication cells.
Whata re the cells that support the neurons called
glial or neuroglial cells
What do interneurons function to do
relay and process information between sensory and motor neurons
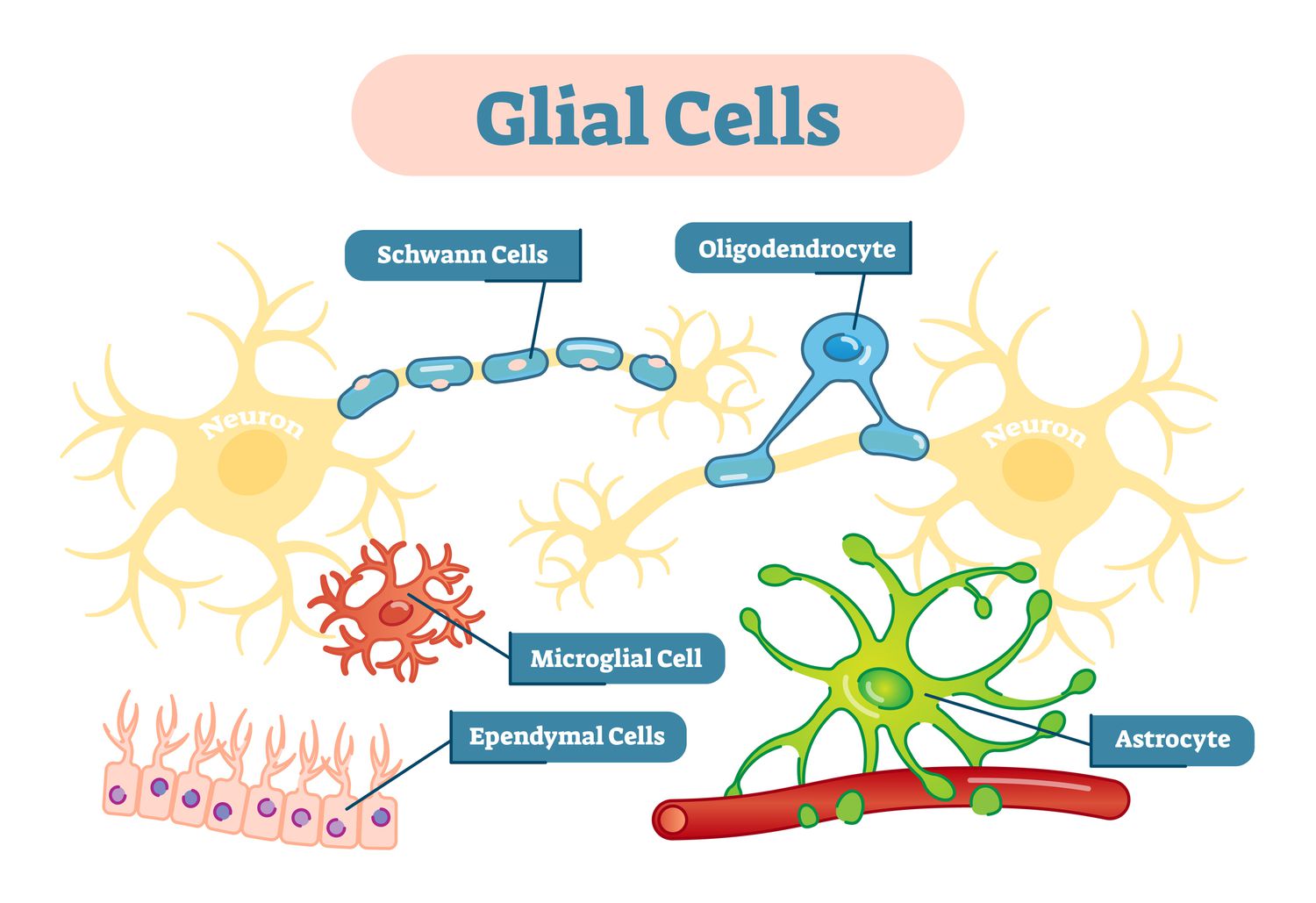
Glial Cells (Photo)
What is Multiple Sclerosis
An autoimmune disease that damages myelin in the CNS, slowing or blocking nerve signals
What are the cells of nervous tissue called?
Neurons
What do sensory neurons do?
Bring information from inside or outside the body to the CNS