Basics of Chemotherapy 1 - L9
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What is Malaria
it is a protozoa - unicellular prokaryote
many protozoa that effect humans e.g Pasmodium falciparaum
can be divided if tehy ahve an exo-erthretic stage or not
Falaciparum is common in areas aroudn water e.g. Africa, eastern Asia and central America countries
what is the Malaria cycle
have the Sprogonic cyle → Only happens in Mosquitoes
Have the erythrocyte stage → damage to erythrocytes (resd blood cells) due to production of Schizonts which are produced through asexual reproduction called sporigony
Sproziotes (transferred form mosquitoes) infect liver cells and mature and then rupture erythrocytes which can then re infect other erythrocytes
can be transferred back to misquotes when they feed on host
Have exo-erythrocyte stage → some malaria have this stage involved infection of liver cells, happen prior to erythrocytic stage
erythrocytic stge is still the major stage for reproduction of schizonts
what is major consequence of malaria
lysis of erythrocytes / destruction of red blood cells
Diagnosis of Malaria
Uncomplicated malaria → fever, shivering, jaundice, joint pain, stomach issues…
Severe Malaria → associated with neurological conditions e.g. loose consciousness, coma, cerebral hemorrhaging and ever organ faliue
Relapsing Malaria → occurring with malaria that has a large stage in liver, parasites remain dormant in liver until reactivated, once reactivated infect erythrocytes leading to malaria symptoms
what is important in chemotherapeutic regimes
that the host has a good immune system as its used to help the destruction of parasite
some patients present malaria and HIV at the same time which is a problem
drug treatments for malaria have 3 objectives
1) give drugs before establish infection - prevent infection of individual
2) drugs to kill parasite
3) drugs to stop transmission
why has malaria been eradicated in most parts of Europe, China and North America
due to irrigation of living spaces with mosquitoes, misquotes netting
educating local people
pesticides
what is the aim of chemotherapy
the target qualitative difference in the biochemistry of host and parasite and target these differences to then kill parasite
Folate pathway
Folate important in synthesis of DNA from nucleotides
humans get folate through diet
Parasites also get folate from diet and synthesis
Dihydropterate sythetase - use sulfonamides to inhibit this enzyme so cannot make folate
can still get enzyme from environment so inhibit enzyme Dihydrofolate synthase (also in humans but different on molecule level)
Drugs like trimethyprim (have small effect on human enzyme
Promethyamine no effect on human version of enzyme
So can combine the Dihydropteroate synthetase inhibitors (Sulphonamides) with dihydrofolate reductase inhibitors (specific for proteasome form ) to inhibit this pathway
Heme catabolism Pathway
in HUMANS → free haem leading to activation of uxygen species which can eb harmful so is controlled by enzyme haem oxygenase breaks down free haem into iron, Carbon monoxide and bilurin
In PARACITES → breask down haemaglobin as food sorce to relase AA, as tehy do this release toxic chemical heme, enzyem haem polymerase converes heme into hemozin which is a polymer of haem
can used Chloroquinne and quinine to inhibit this enzyme Haem polymerase and cause no effect on humans
now have some resistant strains
Artimisinin
Important drug that has low rates of resistance
Artmisinin is active when gets to digestive vacuole of paarsite whihc leads ot egneration of reactive oxygen species wich eveutually leads to death of parasite
Artimistinin and Quinine are made form traditional chemicals that were used to treat malaria (like things that were found in plants )
so what are the main things that drugs attack in malaria
folate pathway
haem pathway
mitochondrial interaction and development of reactive oxygen species
Relationship between diseases of erythrocytes and malaria:
diseases like sickle cell anemia and glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency has shown low levels of these people catching malaria
this is because these diseases affect erythrocytes making it a less habitable environment for malaria and so less likely to get infected
how ever these diseases have higher rates of contracting other things
different scenarios of drug interactions and their effects on a host and a parasite:
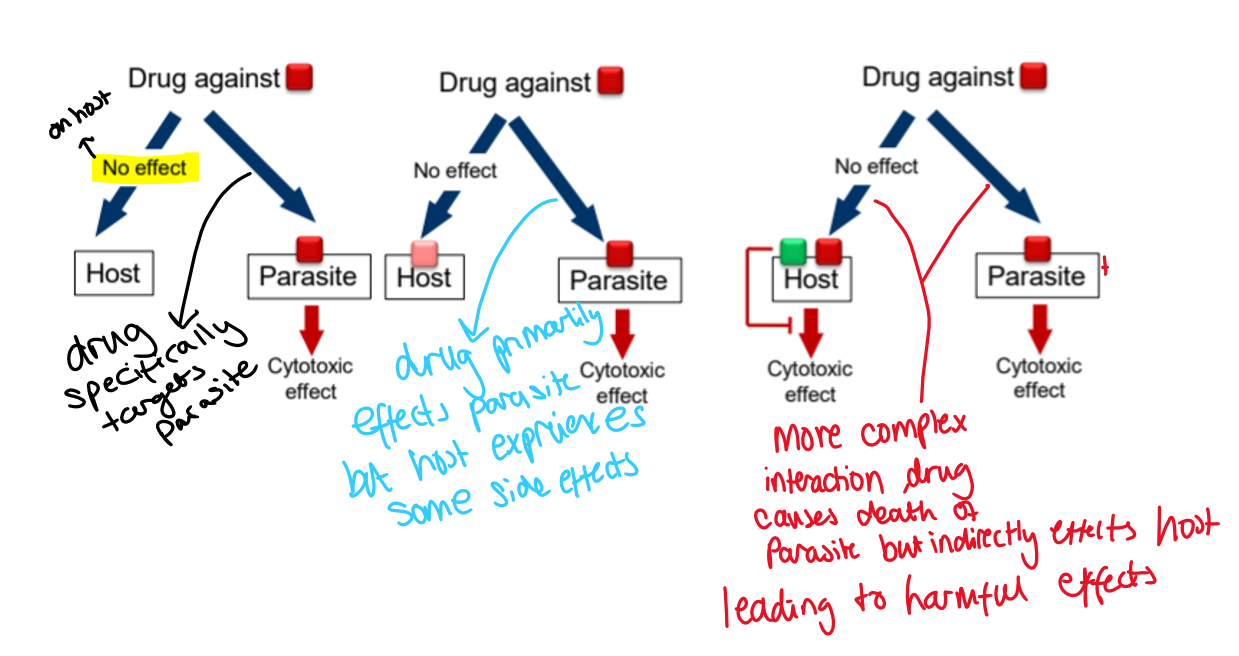
HIV infection
HIV is positively stranded RNA
It infects lymphocytes
binds to CD4 protein using GP120 glycoprotein on HIV molecule
binding causes interaction with Co-receptors call chemokine (type of GCPR)
this then allows HIV to fuse with cell membrane allowing RNA, reverse transcriptase and intergrase enzyme to move into cell
once in cell HIV RNA is transcribed into DNA through reverse tarscriptase
Then moves to nucleus where integrated into DNA using enzyme integrase
viral proetins then get tarscribed
proteins accumilate around cell surafce where protease causes them to form viral particle
then get released from lymphocytes into blood stream and infect other CD4 proteins
what is a nucleoside
Base + Sugar
base can be purine or pyrimidine
how to make a nucleotide form nucleoside
through addition of phosphate
in DNA backbone where is nucleotide added
at 3’ hydroxly group
what were the first drugs used to treat HIV
they were Reverse transcriptase inhibitors
this enzyme not present in humans as we do not convert RNA into DNA so a qualitative difference
what are the 2 types of reverse transcriptase inhibitors
Nucleoside RT inhibitors
Non-nucleoside RT inhibitors
Nucleoside RT inhibitors
they remove OH group from ribose ring
this means no DNA elongation can take place
e.g. ATZ has a nitrogen group instead of a OH group
when ATZ in cell gets converted into triphosphate nucleotide using host kinase
now it is in right form to be used as a subsutare in the trascription of RT
once its added ot the chain as no OH group elongation cannot contiues and it is then terminated and so no protein is formed
DAN polymerase has a lower affinity to ATZ compared
Non- Nucleoside RT inhibitors
can come in different shapes
Reverse transcriptase enzyme is like a 3 fingered shape
between first finger and thumb have catalytic site have NNRTIs biding site
between thumb and second finger have RNA site, where RNA is broken down
So when RNA comes in, it gets converted into complementary RNA DNA and leaves, the RNA then gets broken down by RNAase
NNRTIs work by binding to there site and inhibiting the production of complementary RNA DNA
mutations can occur causing resistance
E.g. Nevirapine
Integrase inhbitors
these drugs inhibit enzyme integrase which integrates RNA DNA into host DNA
e.g Raltegravir
HIV protease inhibitors
These drugs inhibit the cleave of structural proteins so do not get mature HIV
e.g. Indinavire
SO overall have drugs that can :
stop formation oh HIV DNA + HIV RNA
can inhibit integrase enzyme
can inhibit assembly of particle formation
inhibit binding to lymphocyteè , targeted for CCR5 and CXCR4
prevent fusion
what is important in a clinical setting for optimum therapeutic utility
THAT YOU COMBINE DRUGS