Anatomy and Physiology: Vocal Tract and Larynx
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Define frontal
front or anterior
define dorsal
back side or posterior
define sagittal
vertical plan dividing body into right & left
define coronal
plane dividing into front/posterior
define lateral
away from the midline
deine medial
towards the midline
define superior
the top, above another structure
define interior
bottom, or below another structure
define anterior
towards the front, same as ventral in humans
define ventral
towards the belly side, same as anterior in humans
What are the 3 vocal subsystems
- respiration
- phonation
- resonance
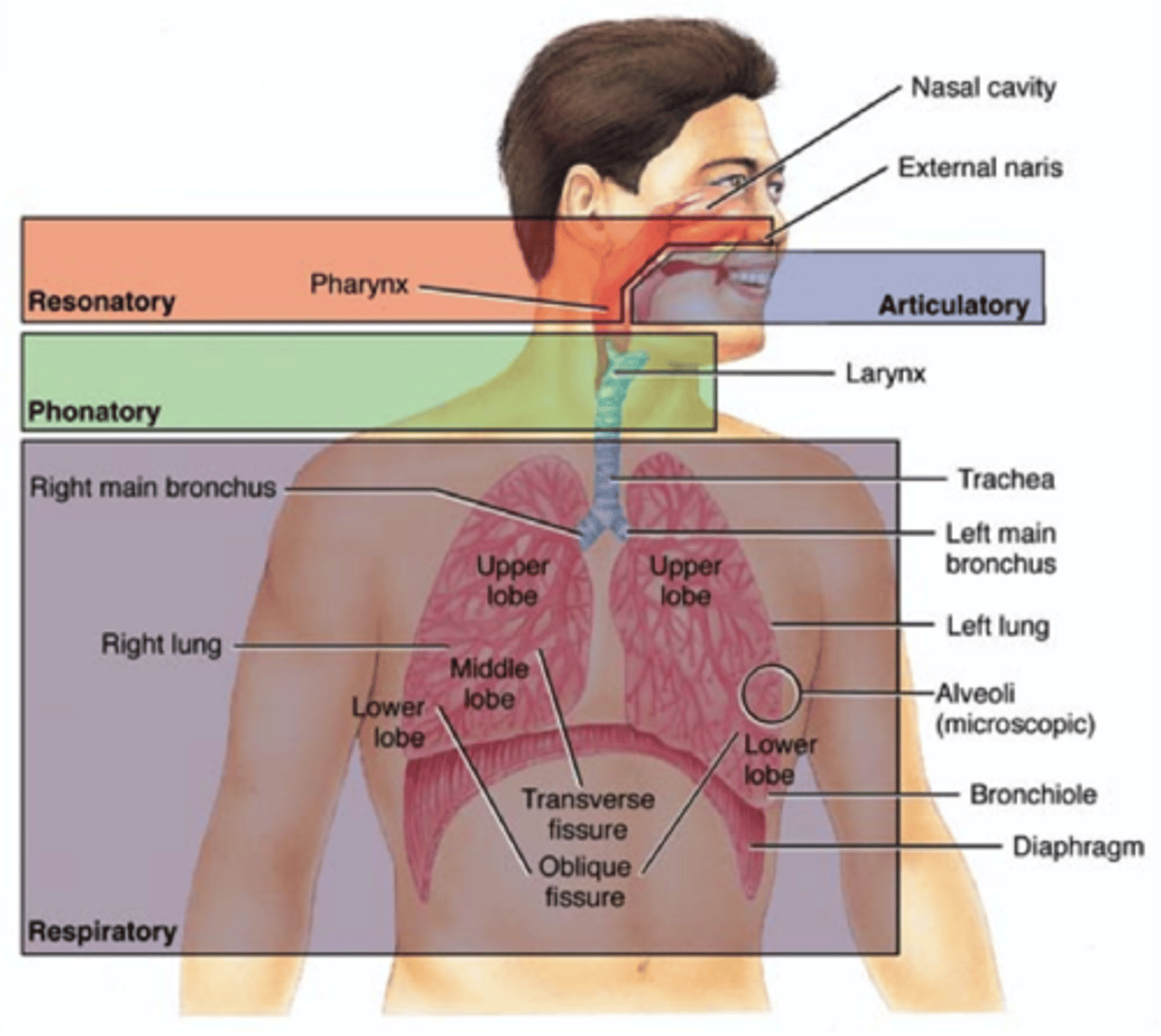
How does that car analogy relate to the vocal subsystems?
- respiration = gas (breathing) that makes the car go
- phonation = the engine (VF, what makes noise)
- Resonance = body of the car (shape of throat, mouth, and nose)
What makes up the vocal tract, how do they connect to the vocal subsystems?
- Nasal cavity (function as resonator)
- Oral cavity (functions as articulation and resonator)
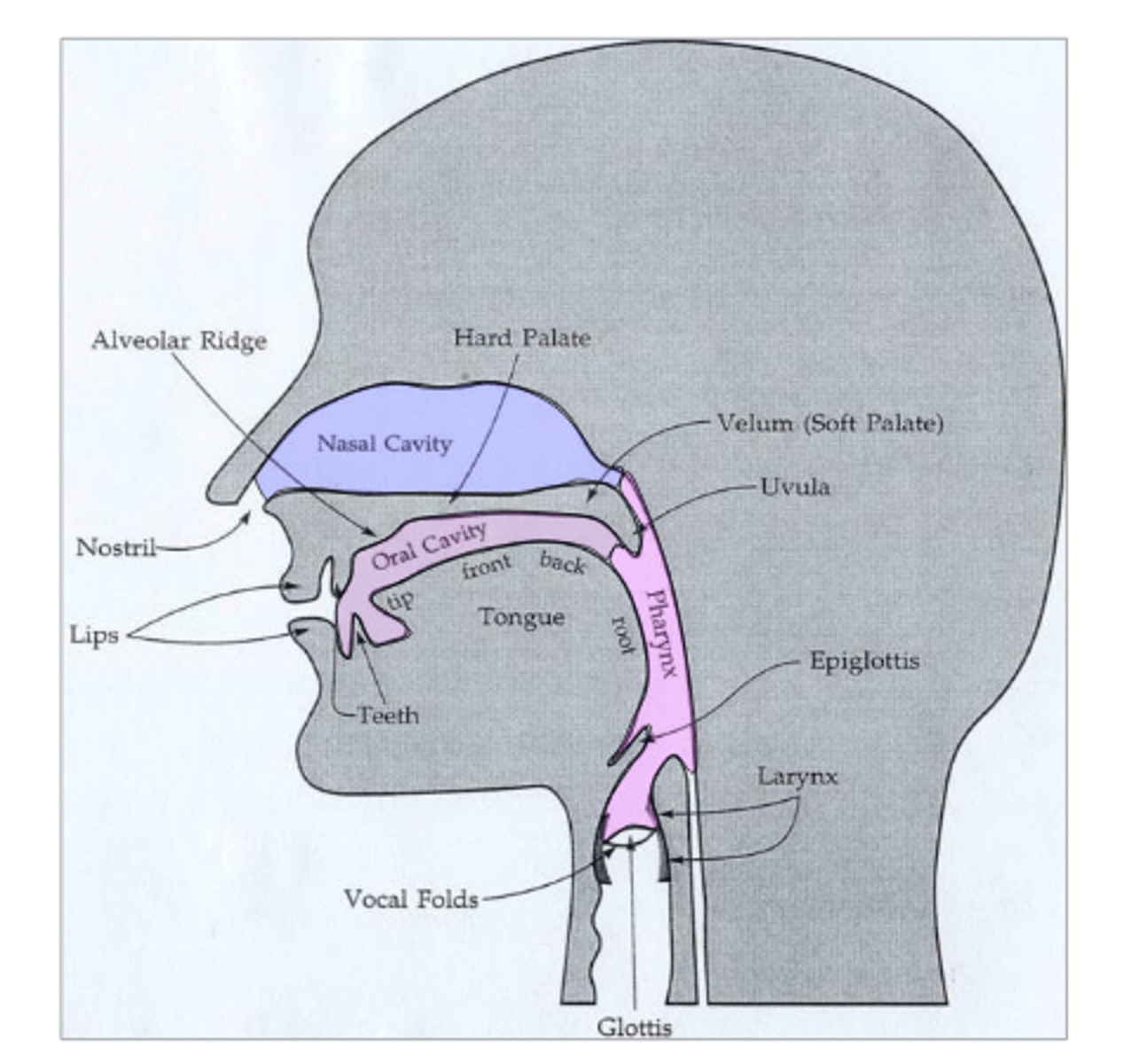
What is an important structure of the nasal cavity? When is it open and closed?
velopharyngeal port: opens during nasal sounds and closed on all other sounds
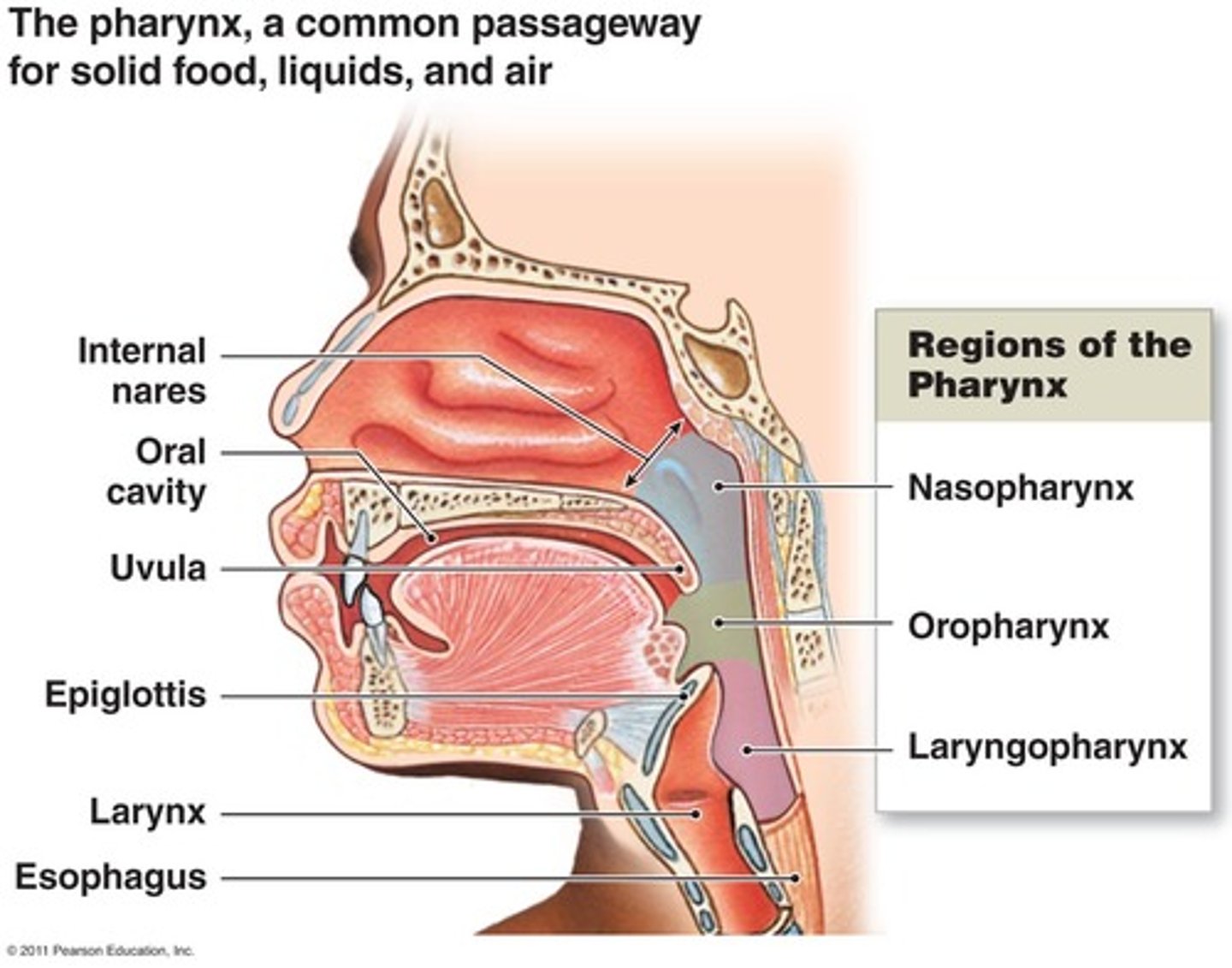
What are the 3 segments of the pharynx?
- nasopharynx
- oropharynx
- laryngopharynx
What are the functions of the larynx?
- airway protection (closed during swallow)
- support during effort (closed)
- phonation (vibration)
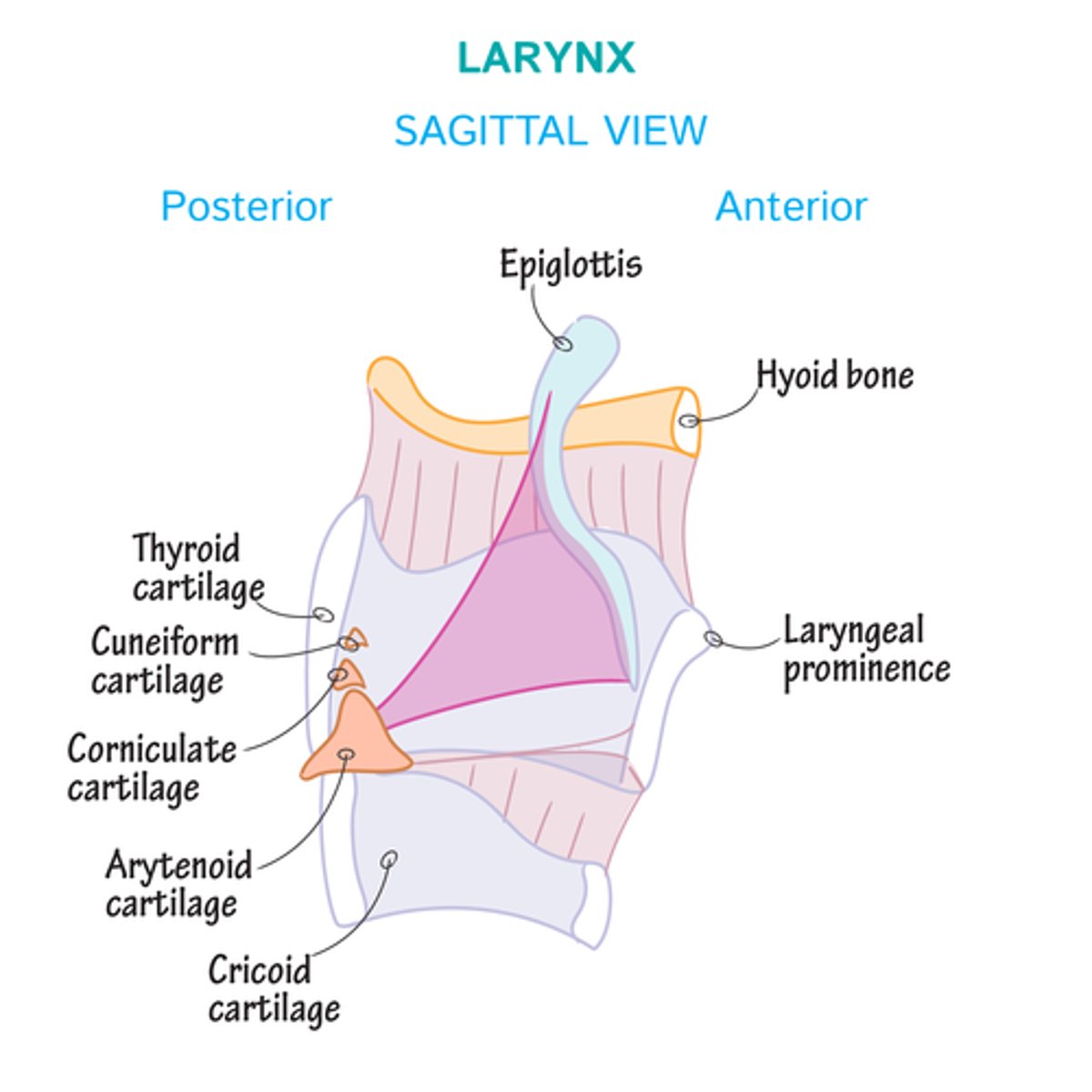
What is the larynx composed of?
- 1 bone
- 5 major cartilages
- 4 minor cartilages
- muscles
- ligaments and membranes
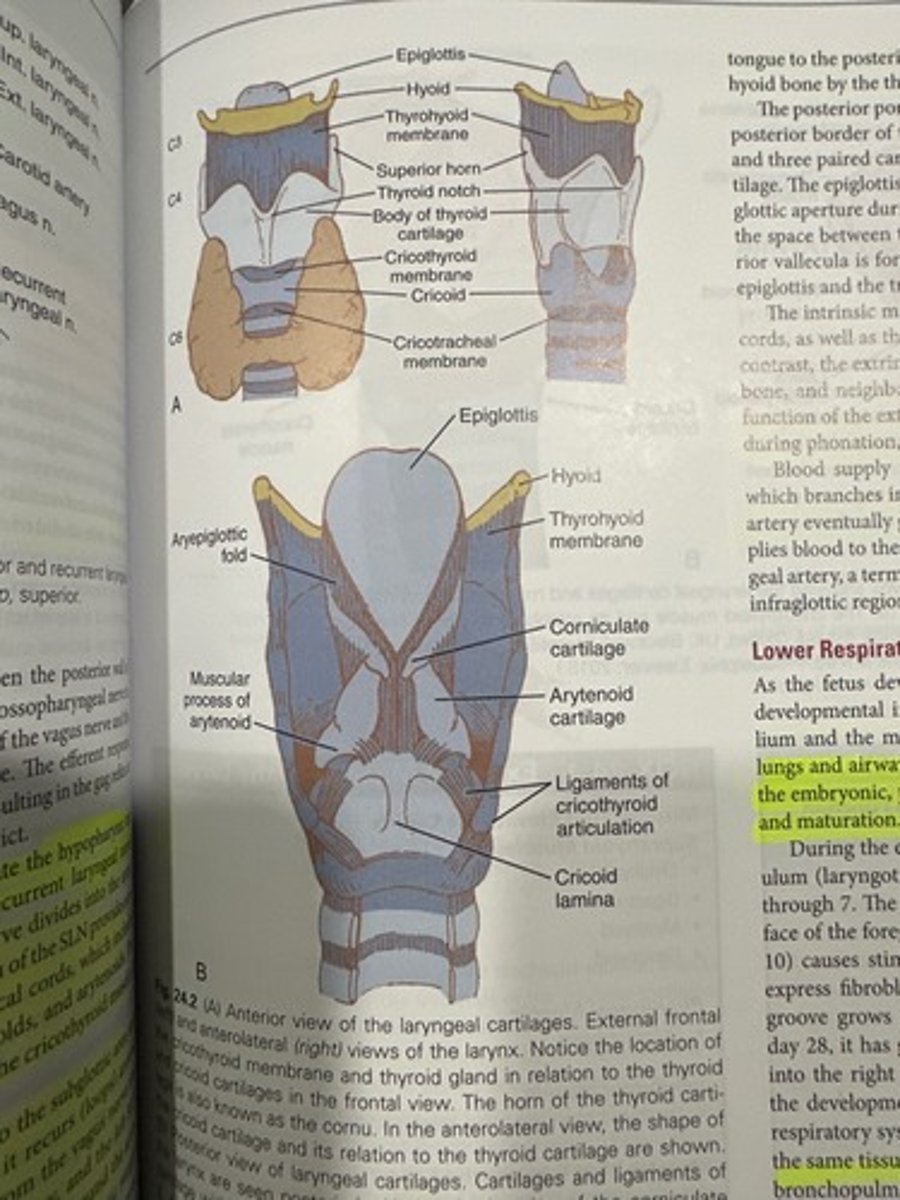
What are some characteristics of the hyoid bone?
- considered a bone of the tongue, pharynx, and larynx
- only bone in the body that does not articulate (meet)with another bone
- serves as superior border of the larynx
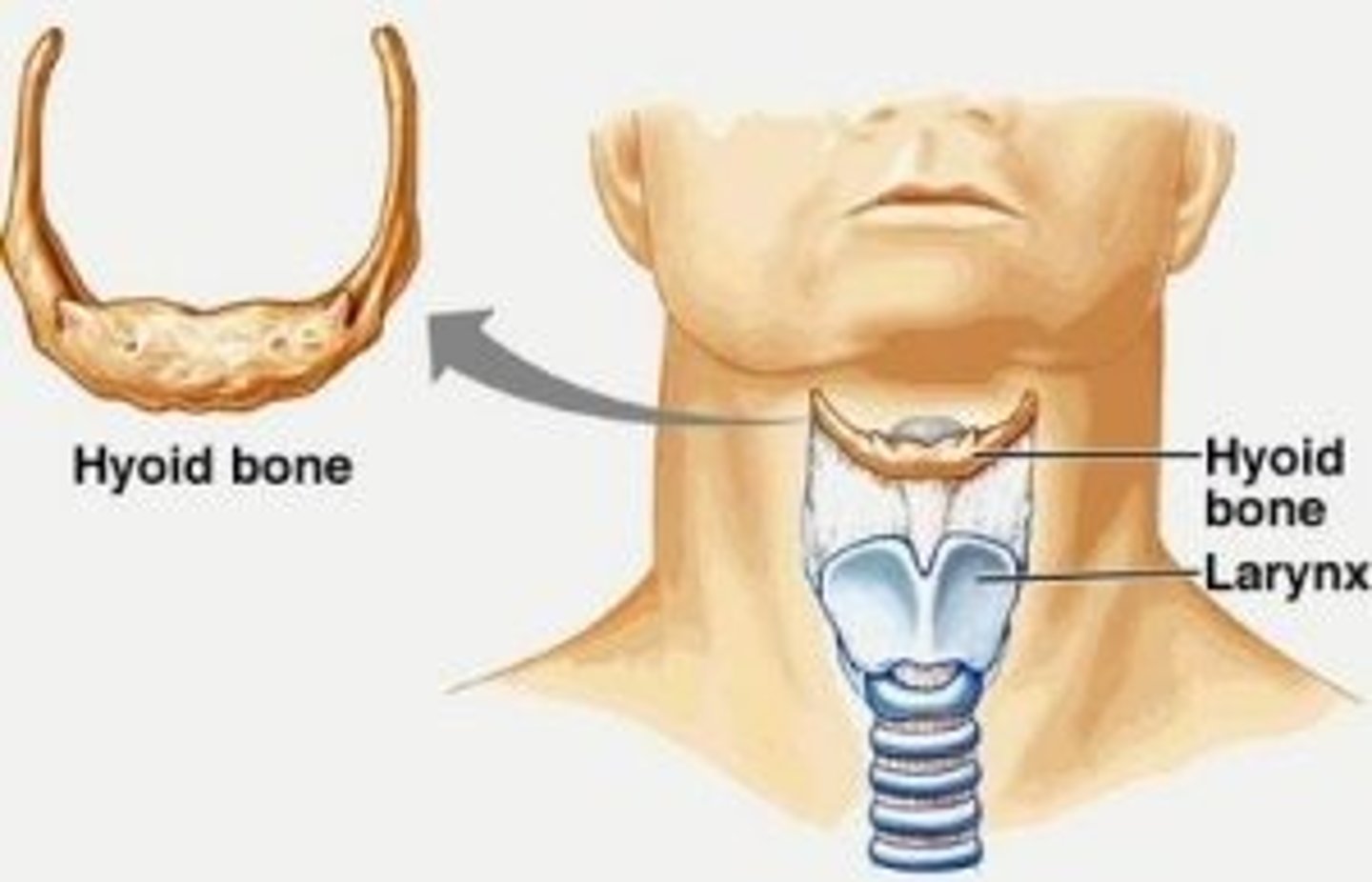
What are the major cartilages of the larynx (# = how many)
- cricoid (1)
- thyroid (1)
- arytenoids (2)
- epiglottis (1)
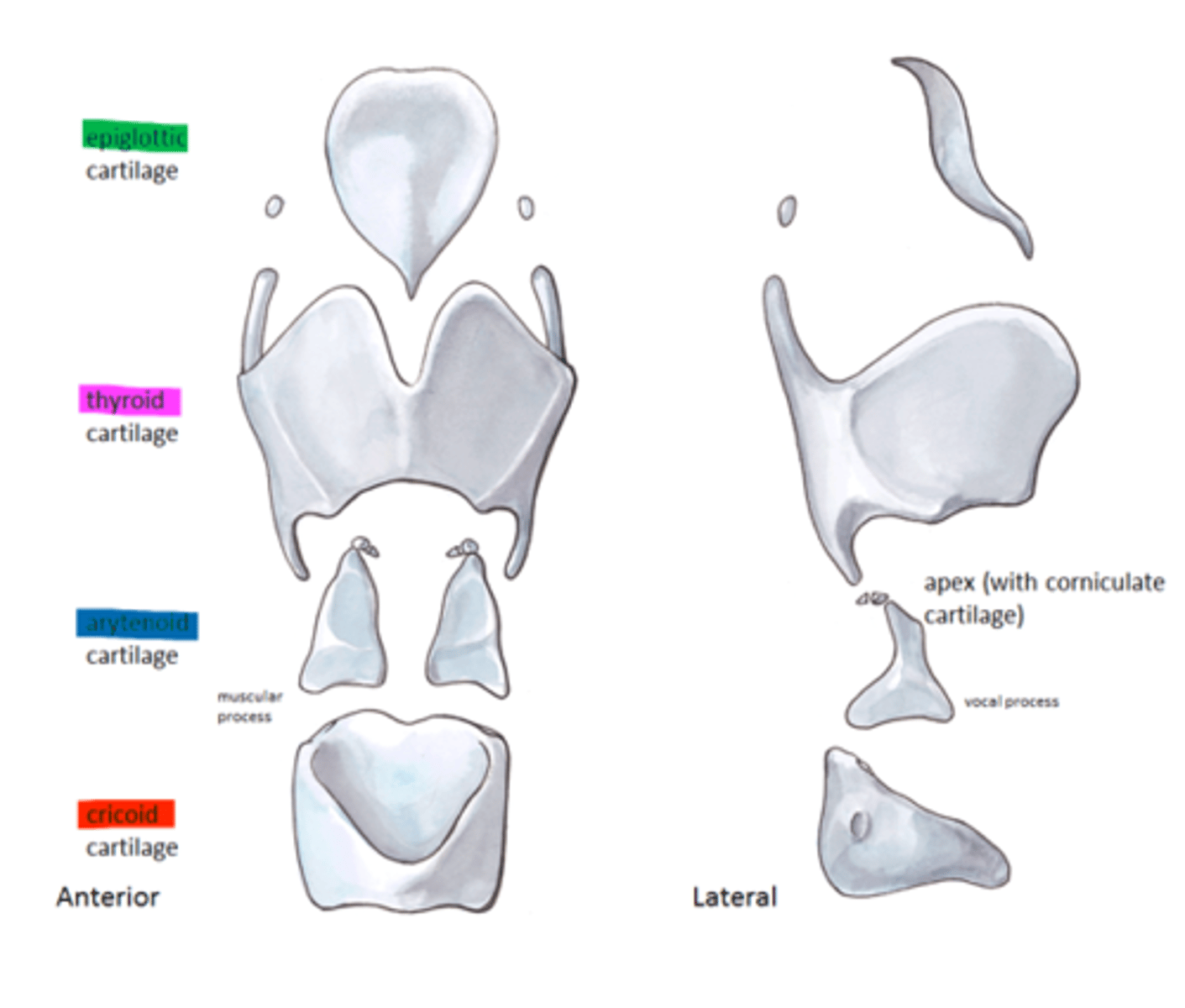
What are the minor cartilages of the larynx? (# = how many)
- corniculates (2)
- cuneiforms (2)
why are the corniculates & cuneforms considered minor cartilages of the larynx?
may have no biological or communicative function
What are some important factors about the epiglottis?
- shapes like a leaf
- inverts and closes airway during swallowing to protect respiratory tract from aspiration
- botto "stalk" connects to the thyroid cartilage
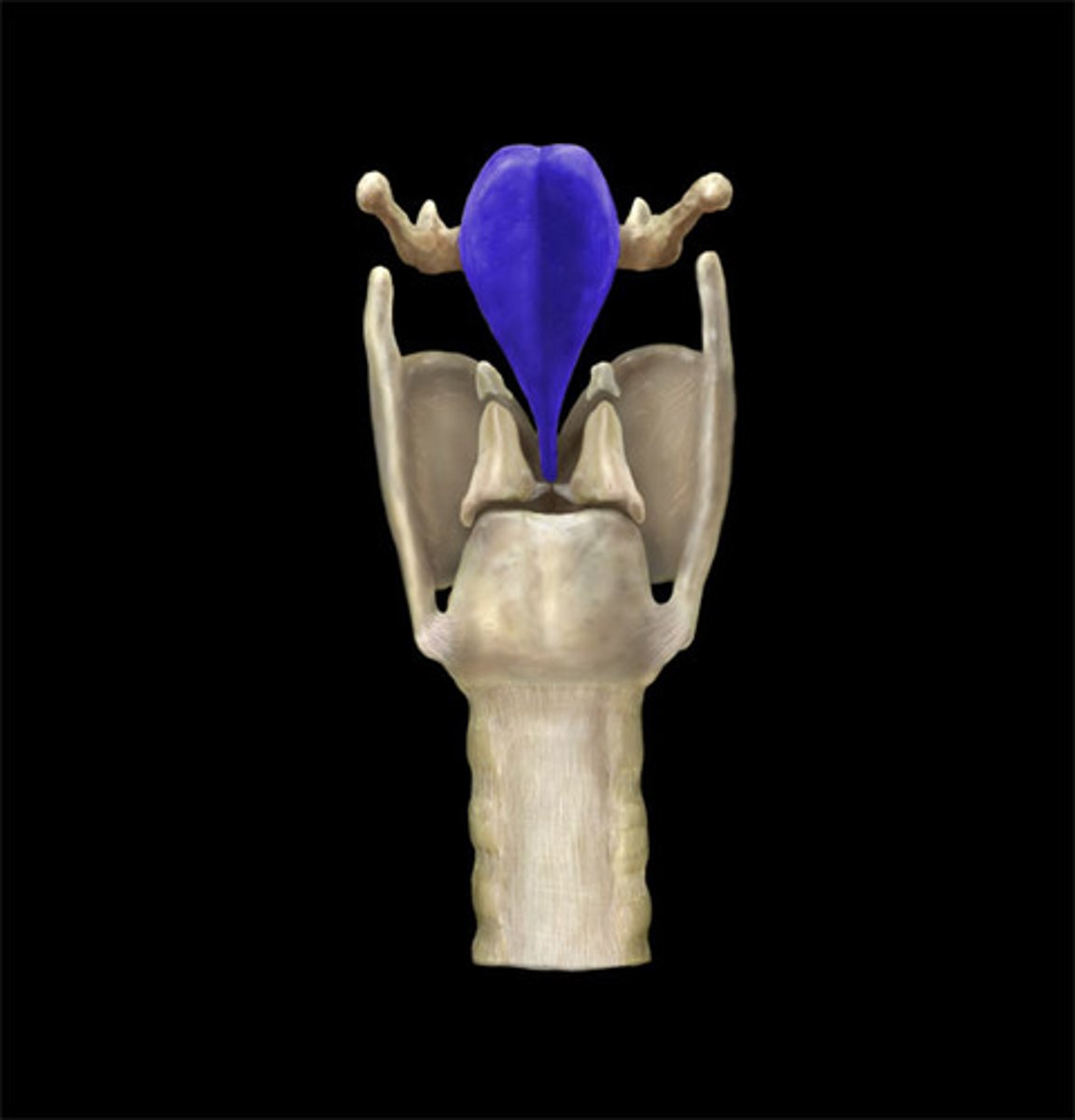
what are some important factors about the thyroid cartilage?
- largest of the laryngeal cartilages
- known as "adam's apple"
- shaped like front of ship
What do the inferior horns of the thyroid cartilage connect to and do?
connect to cricoid (pitch adjustment)
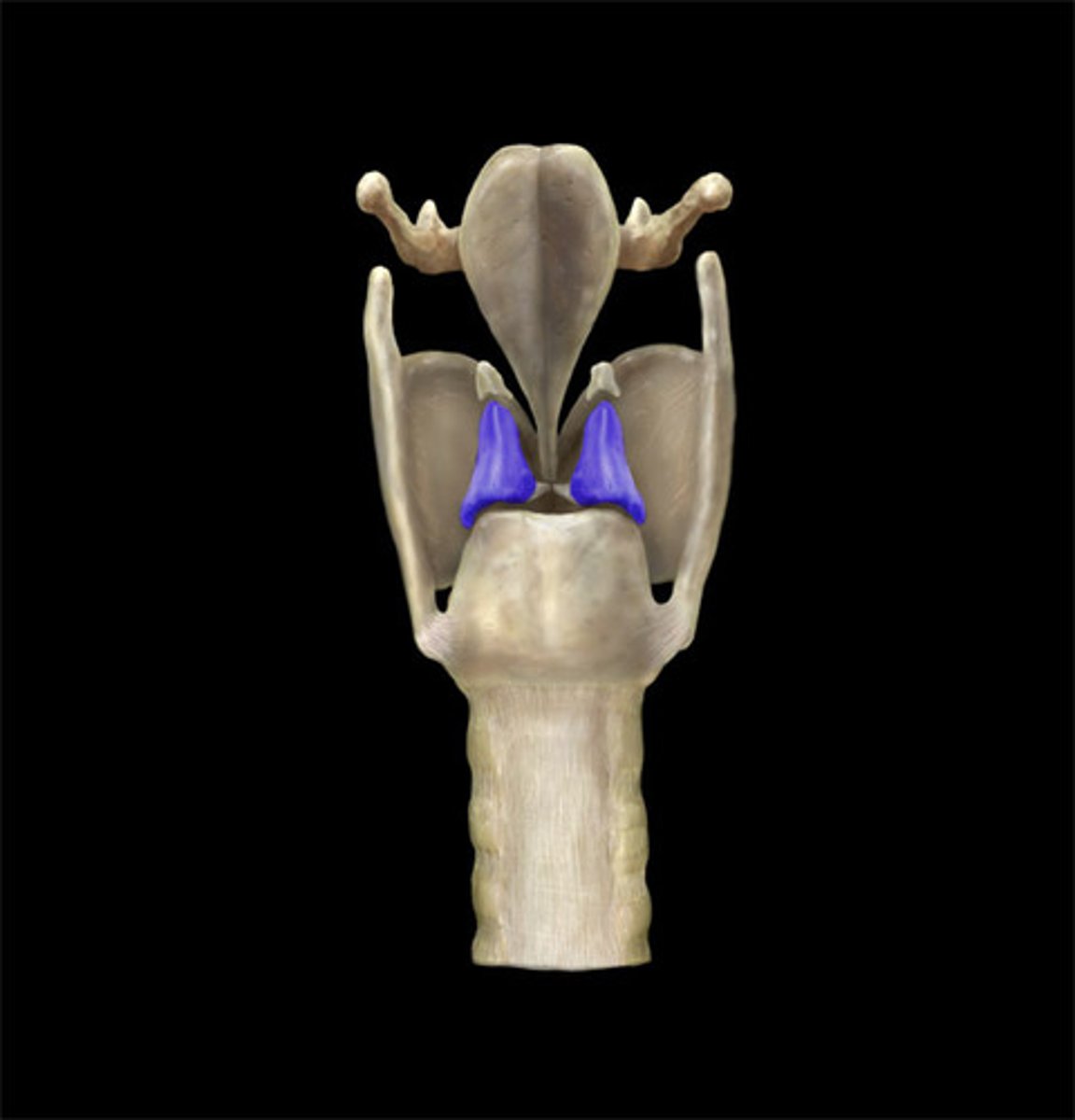
what are some important factors of the arytenoid cartilages?
- paired cartilages shaped like a pyramid
- "rockers and gliders"
- sit on the cricoid cartilage
- responsable for valving
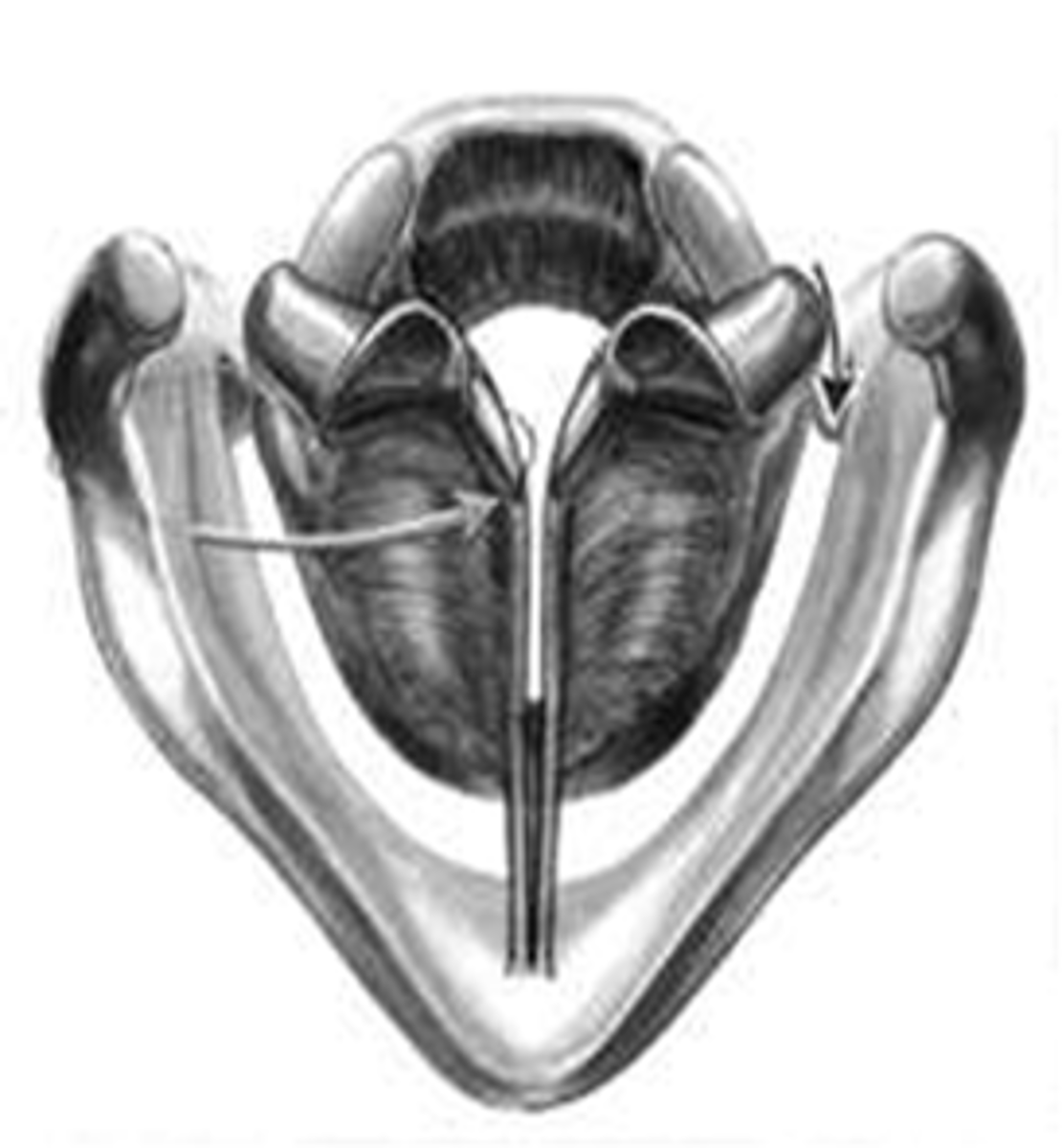
On the arytenoid cartilages, the farther projectioning anterior points are called what, when they meet what happens?
vocal processes, when face each other and meet at the midline, and adduct (close)
What are some important facts of the cricoid cartilage?
- signet ring
- second largest laryngeal cartilage
- provide stable round entry into airway
- lower facets connect to thyroid (cricothyroid joint)
- upper facts connect to arytenoids (cricoarytenoid joint)
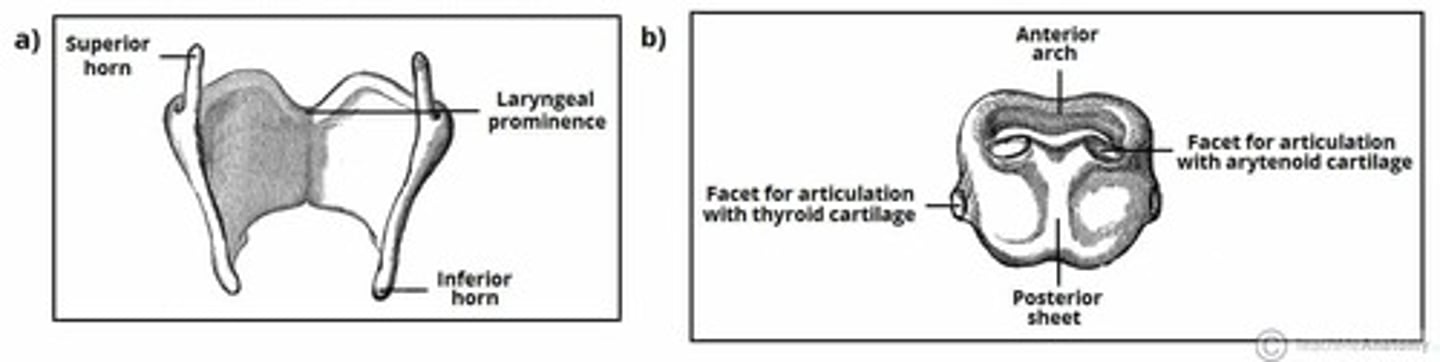
What are some factors of the corniculate cartilages?
- paired cone shaped cartilages that sit on the apex (top) of each arytenoid
What are some factors of the cuneiform cartilages?
- cone shaped, placed in each aryepiglottic fold
What are the 2 types of laryngeal muscles?
- extrinsic muscles
- intrinsic muscles
Where are extrinsic muscles, what do they do, and what is their prominent role?
where: attached at one end of the cartilage of the larynx and to a bony structure outside the larynx
what: move the larynx as a whole
role: swallowing
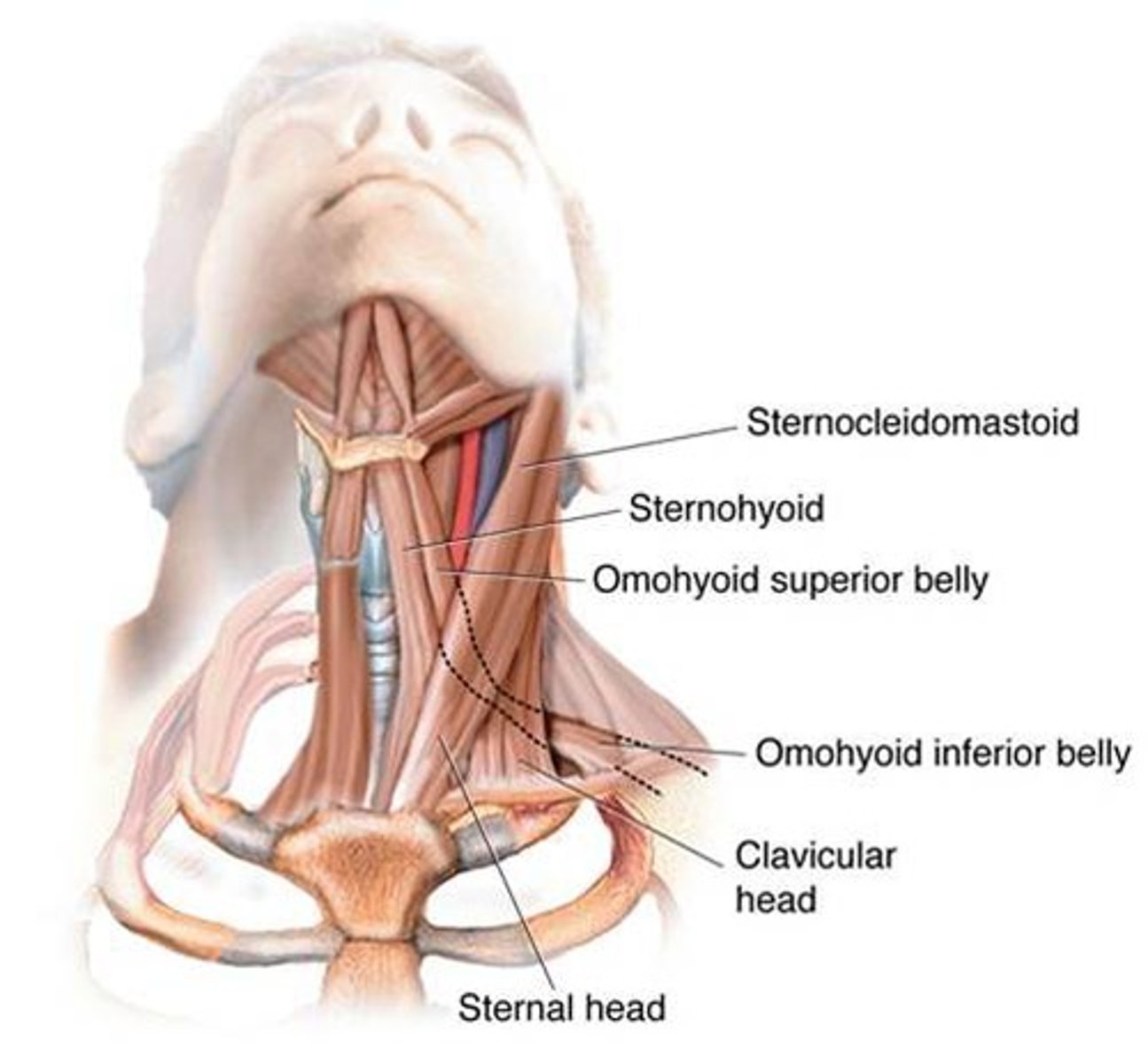
What are the 2 types of extrinsic muscles?
- elevator of larynx
- depressor of larynx
What are the extrinsic elevators/suprahyoids of the larynx?
- stylohyoid
- mylohyoid
- digastric
- geniohyoid
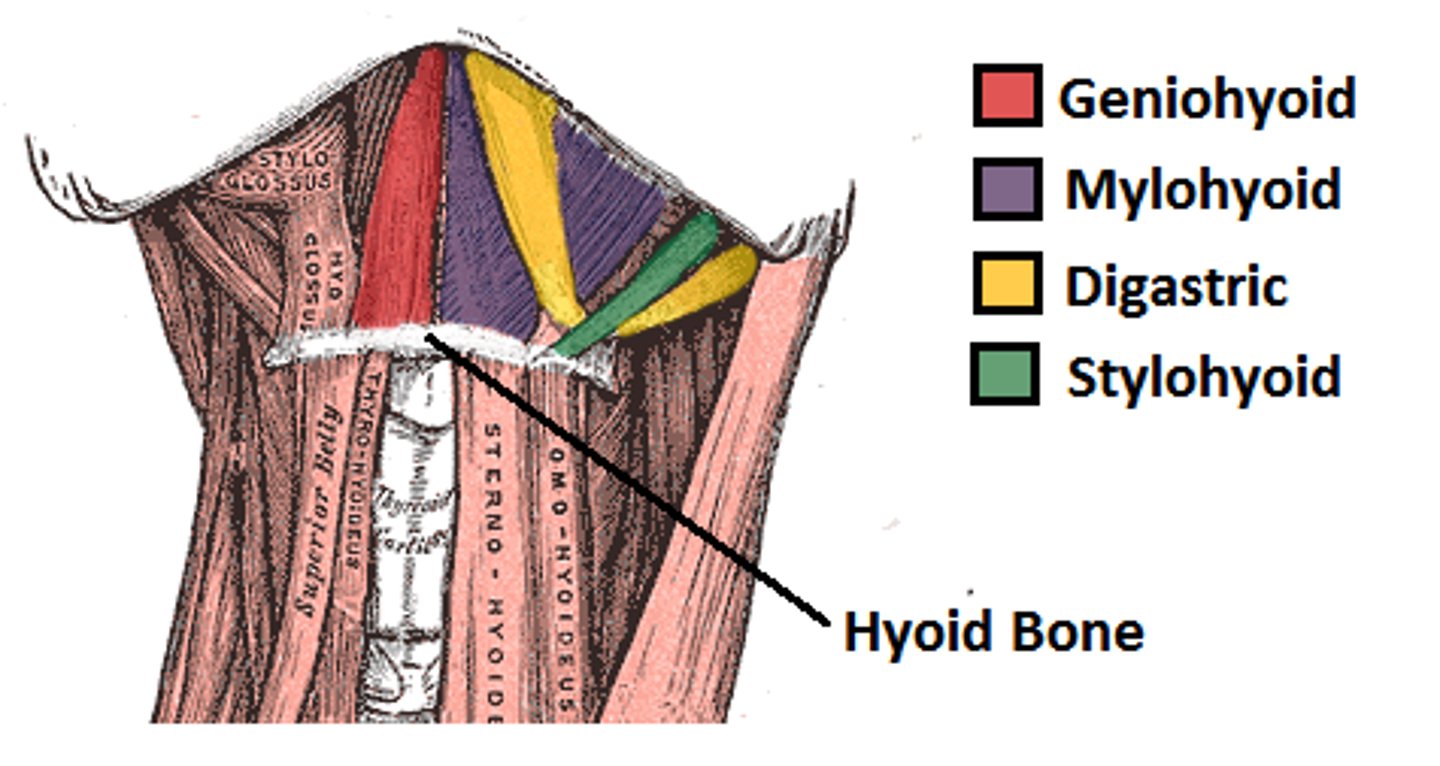
What are the extrinsic depressors/infrahyoids of the larynx?
- thyrohyoid
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- omohyoid
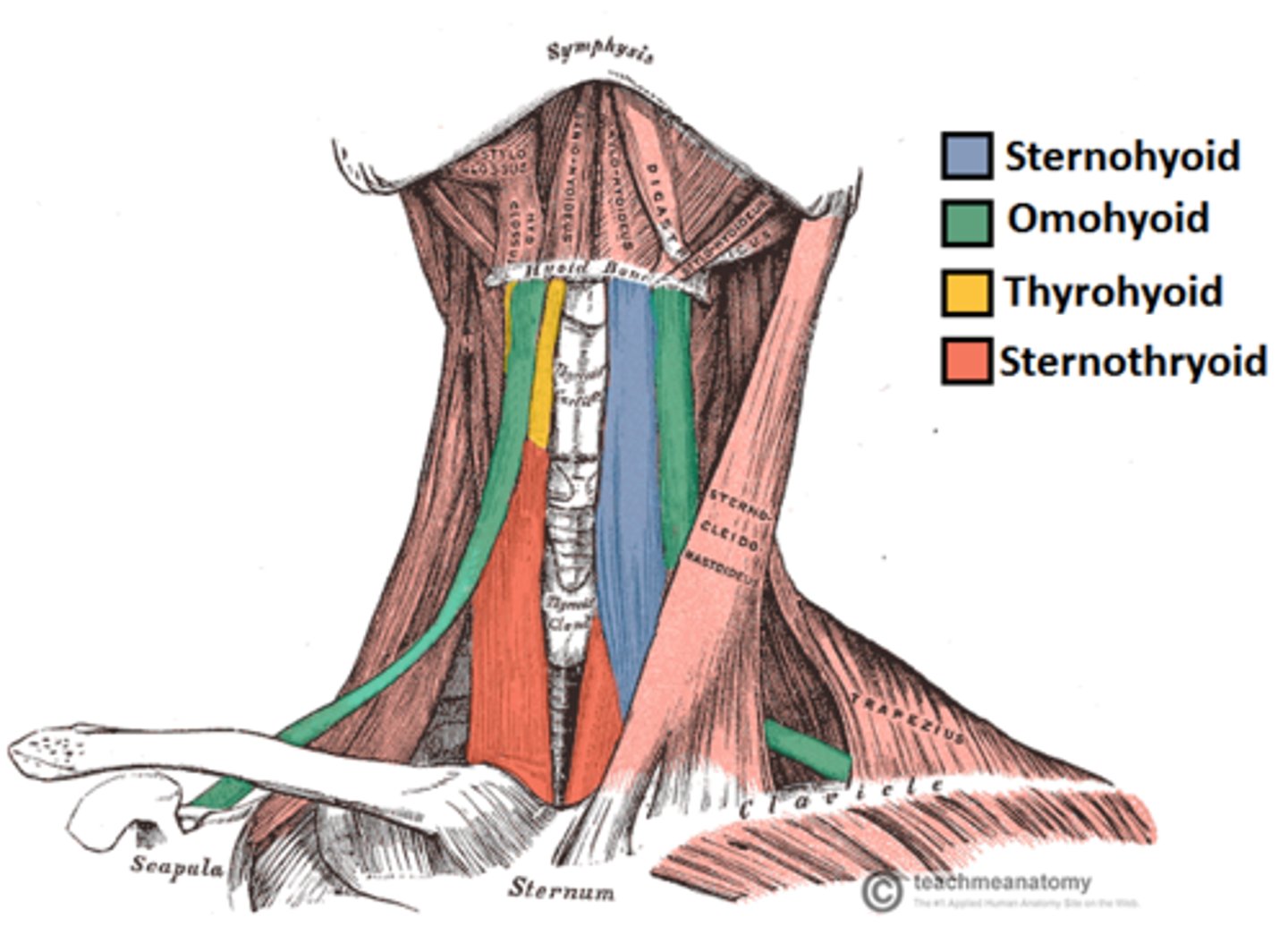
Where are intrinsic muscles, what do they do, and what is their prominent role?
where: both ends are attached to cartilages of the larynx
what: some abduct, adduct, or cause tension
role: phonation
What are the intrinsic muscles of the larynx?
- cricothyroid
- thyroartenoid
- lateral cricoarytenoid
- posterior cricoarytenoid
- transverse arytenoid
- oblique arytenoid
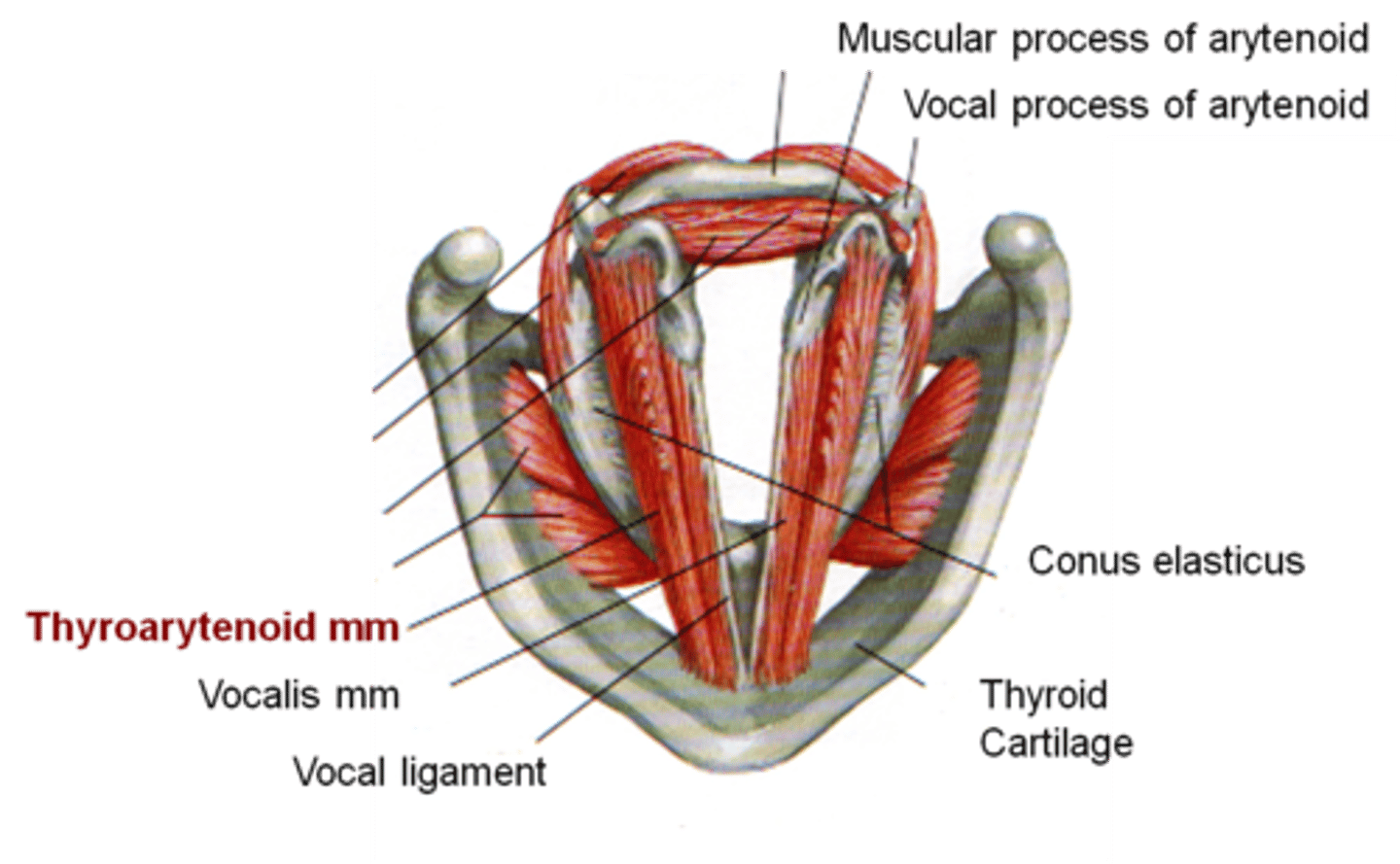
Who is the thyroarytenoid closely related to?
vocalis muscle
What is the function of the thyroarytenoid?
- body of VF (vocal fold)
- shorten distance between the thyroid & arytenoid cartilages = lower pitch
- increase longitudinal tension of VF = pitch modification
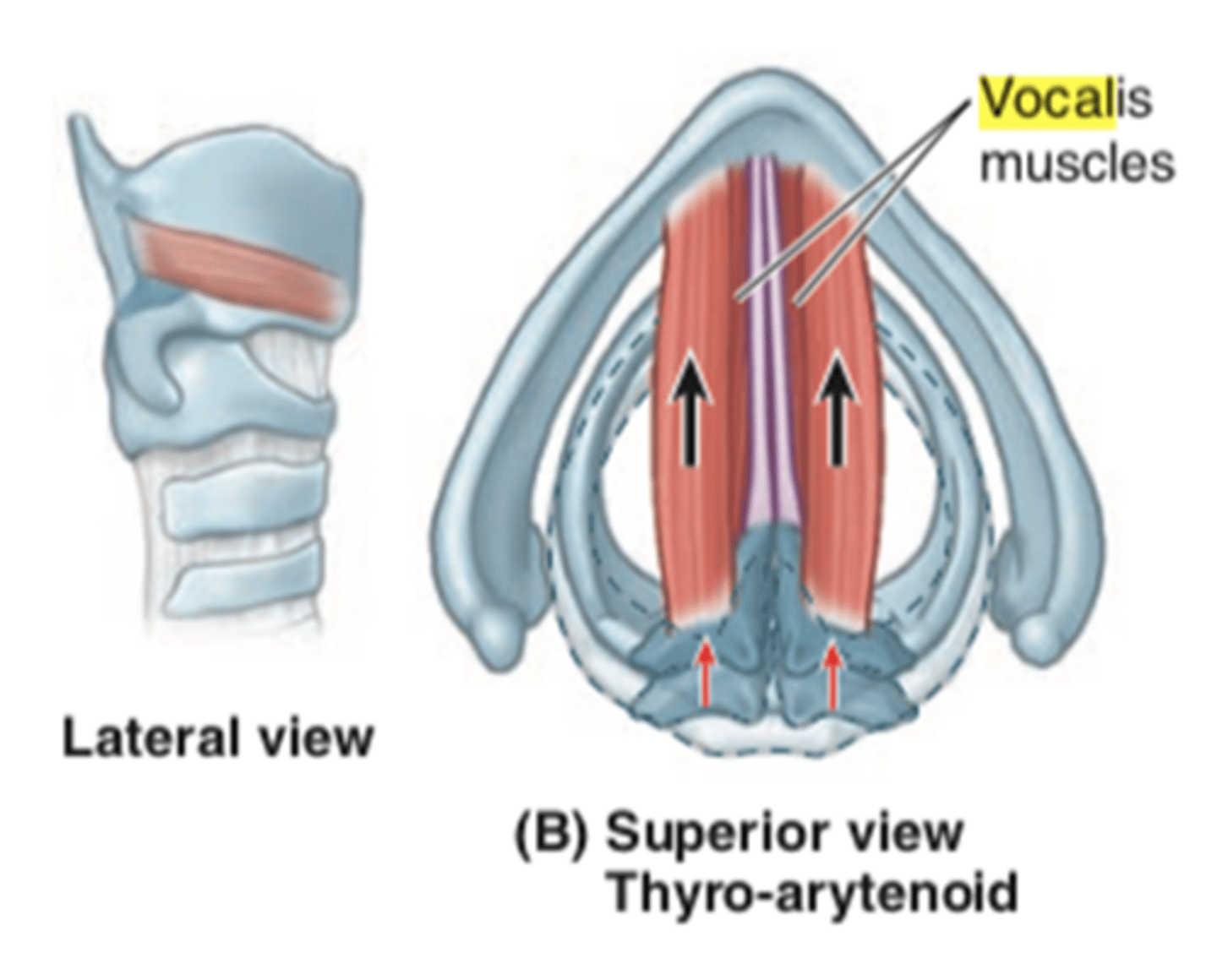
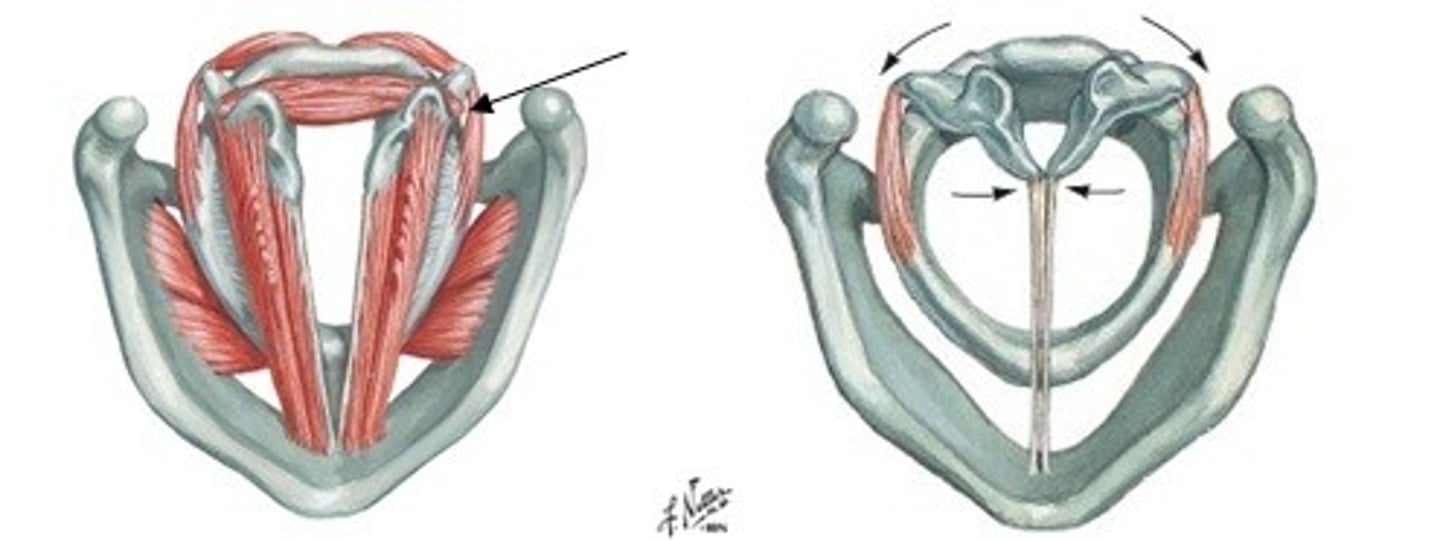
who is the ONLY abductor (open) of the VF (vocal folds)
posterior cricoarytenoid (PCA, Pull Cords Away)
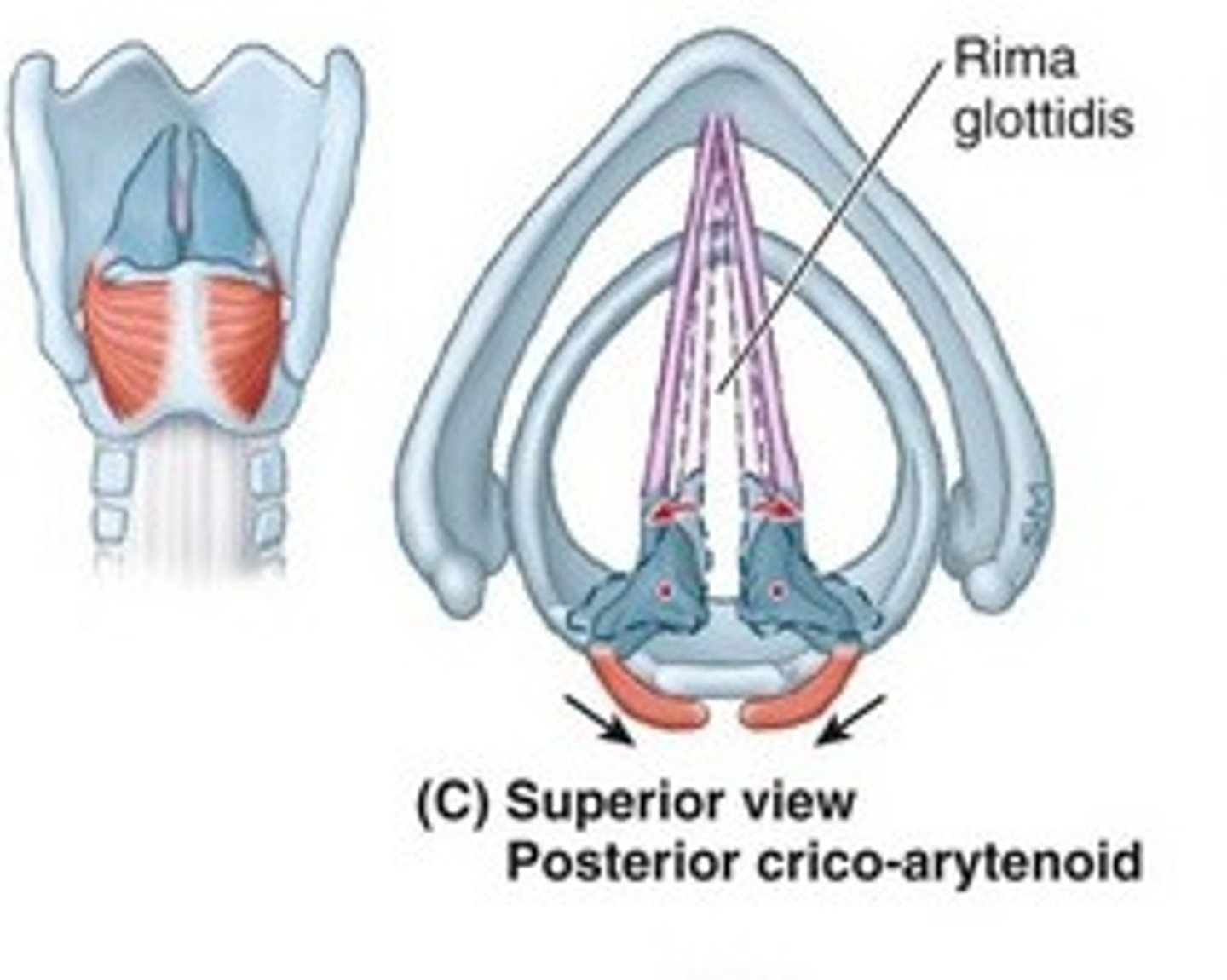
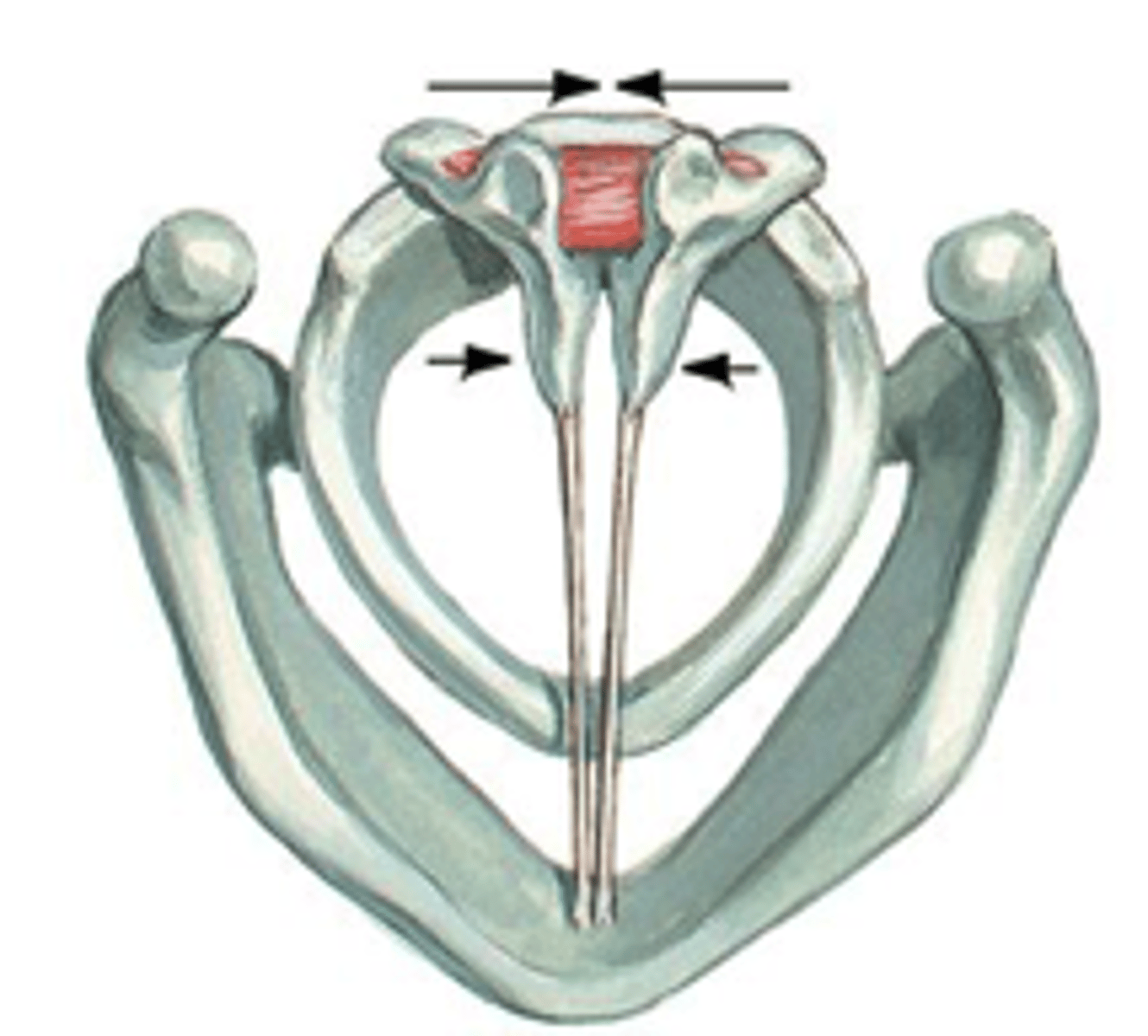
Who are the adductors (close) of the VF?
- lateral cricoarytenoid
- transverse arytenoid
- oblique arytenoid
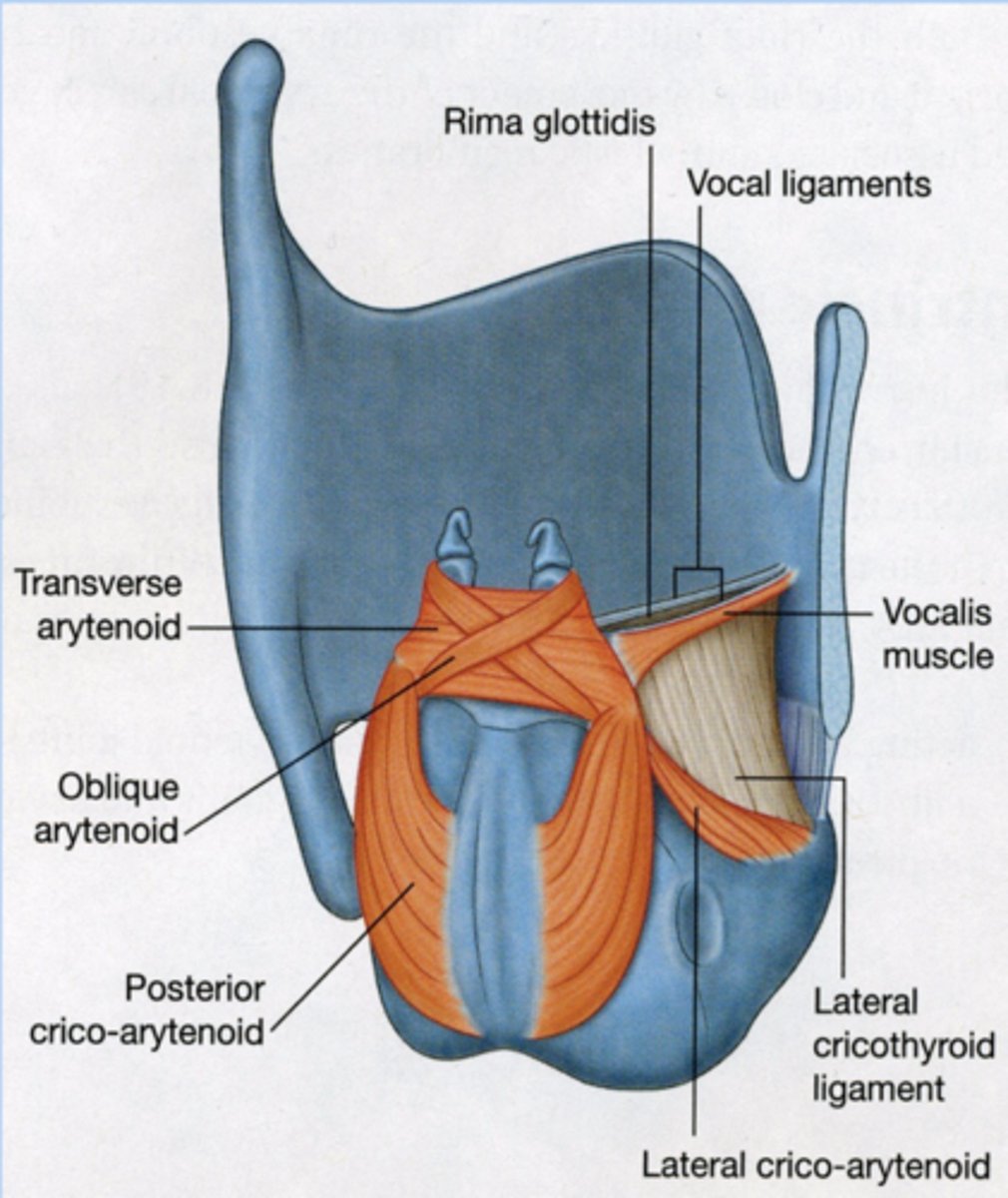
what is the look and function of the lateral cricoarytenoid?
look: fan-shaped
function: medial compression of VF, possibly the strongest adductor
what is the look and function of the transverse arytenoids?
look: inner (between) arytenoid
function: moves arytenoids together for forceful closure
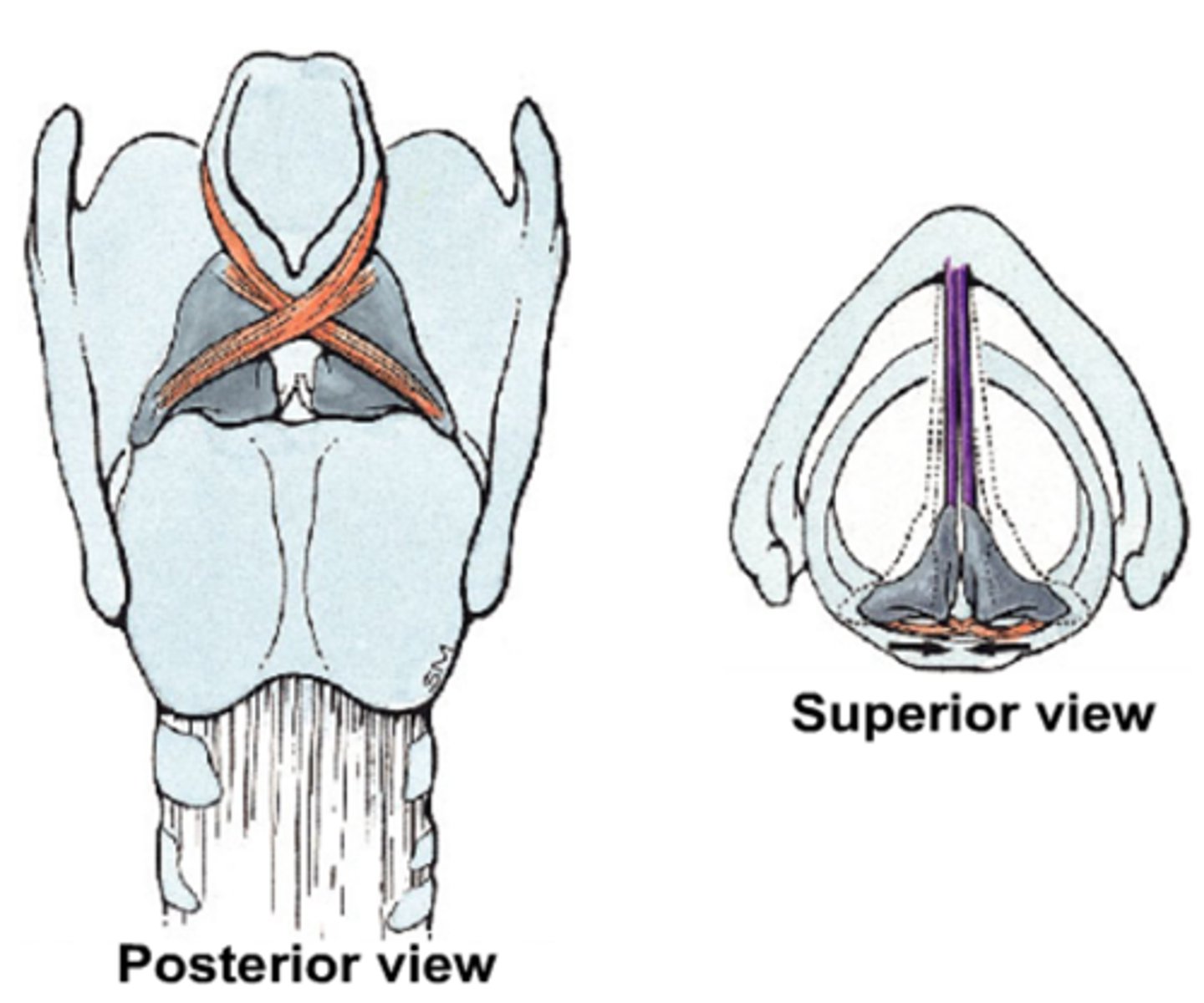
what is the look and function of the oblique arytenoid?
look: x-shaped
function: contributes to arytenoid rocking (pitch control)
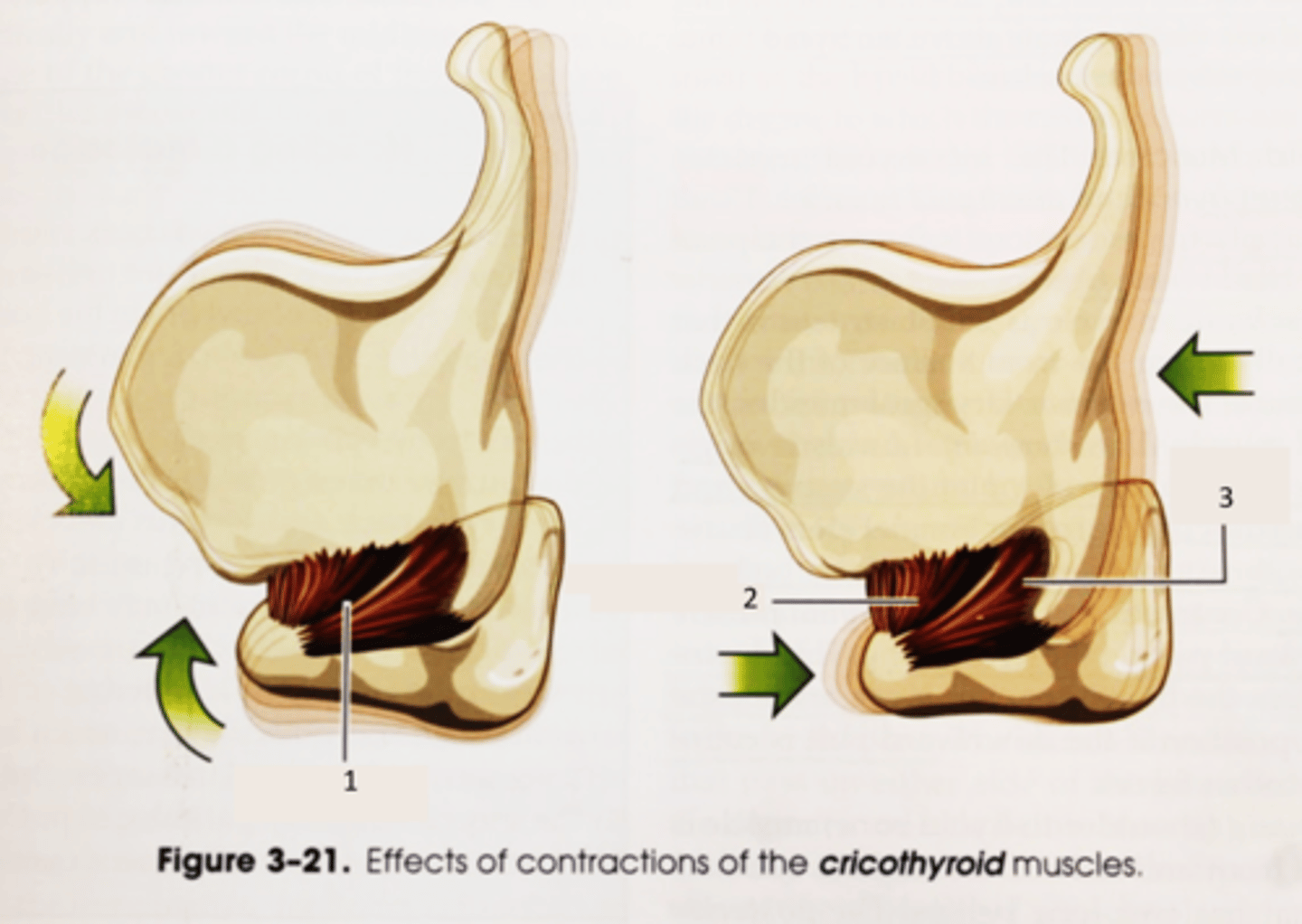
What does the cricothyroid muscle do?
- increase and decrease length of VF (the largest contributor to pitch control)
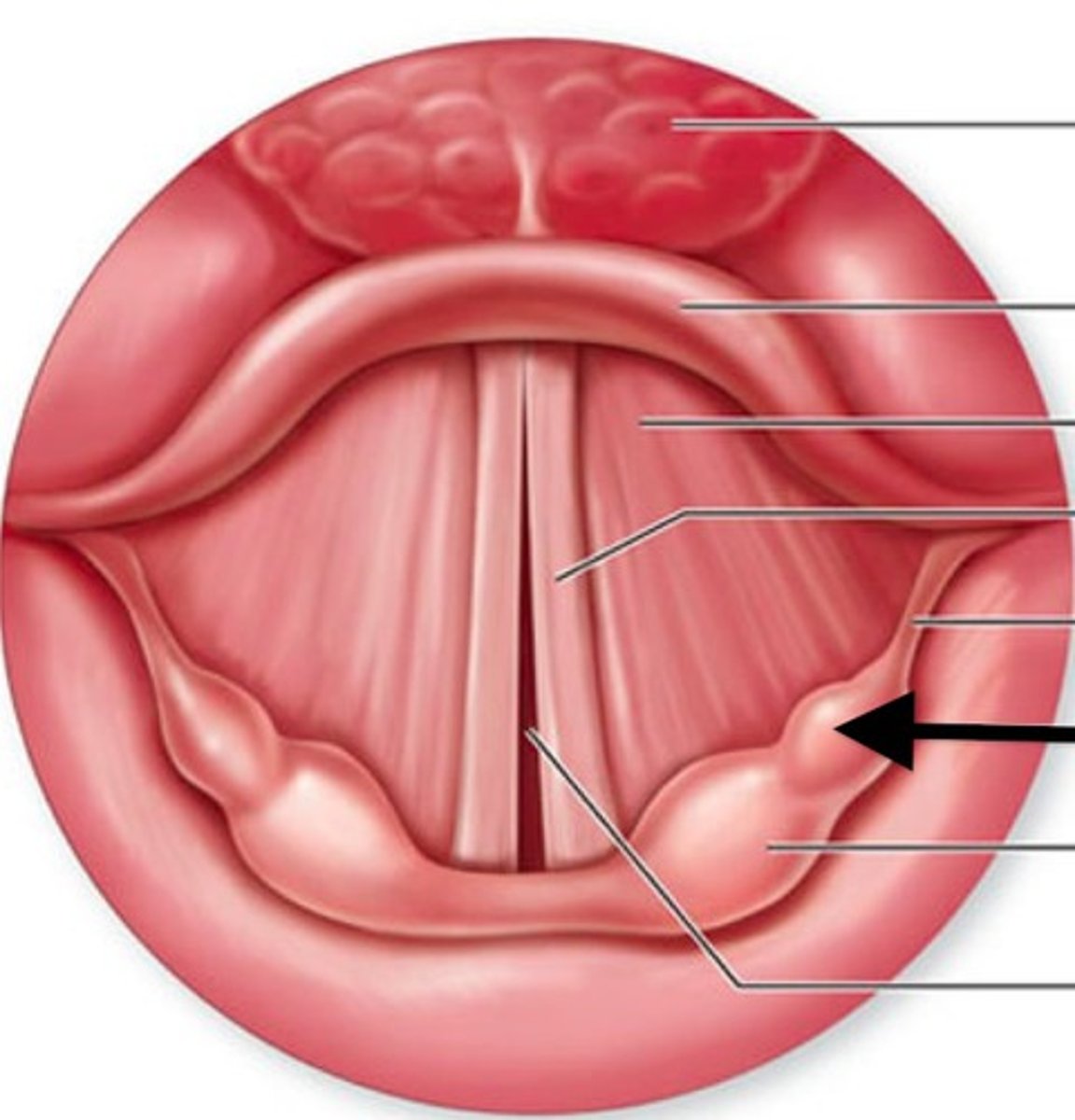
what 3 things make up the true vocal folds?
- thyroartenoid muscle
- vocalis muscle
- vocal ligament
What are the 5 layers of the true vocal folds? (outside -> inside)
1. epithelium
2. superficial layer of the lamina propria
3. intermediate of the lamina propria
4. Deep layer of the lamina propria
5. Vocalis muscle
Of the 5 layers of the true vocal folds, what makes up the cover, transitional, and body?
cover: epithelium & superficial layer
transitional: intermediate & deep layers
body: vocalis muscle
What are some characteristics of the epithelium?
- thinnest layer
- mucosal layer of stratified squamous
- varies in thickness along the length of VF, thickest in the middle
What are some characteristics of the superficial layer of the lamina propria?
- "Reinke's space"
- highest elastic: stretch and vibrate
- along with epithelium, most susceptible to damage
what are some characteristics of the intermediate and deep layers of the lamina propria?
- vocal ligament
- intermediate made of both elastic and collagen
- deep made of mostly collagen (damage here is more long term)
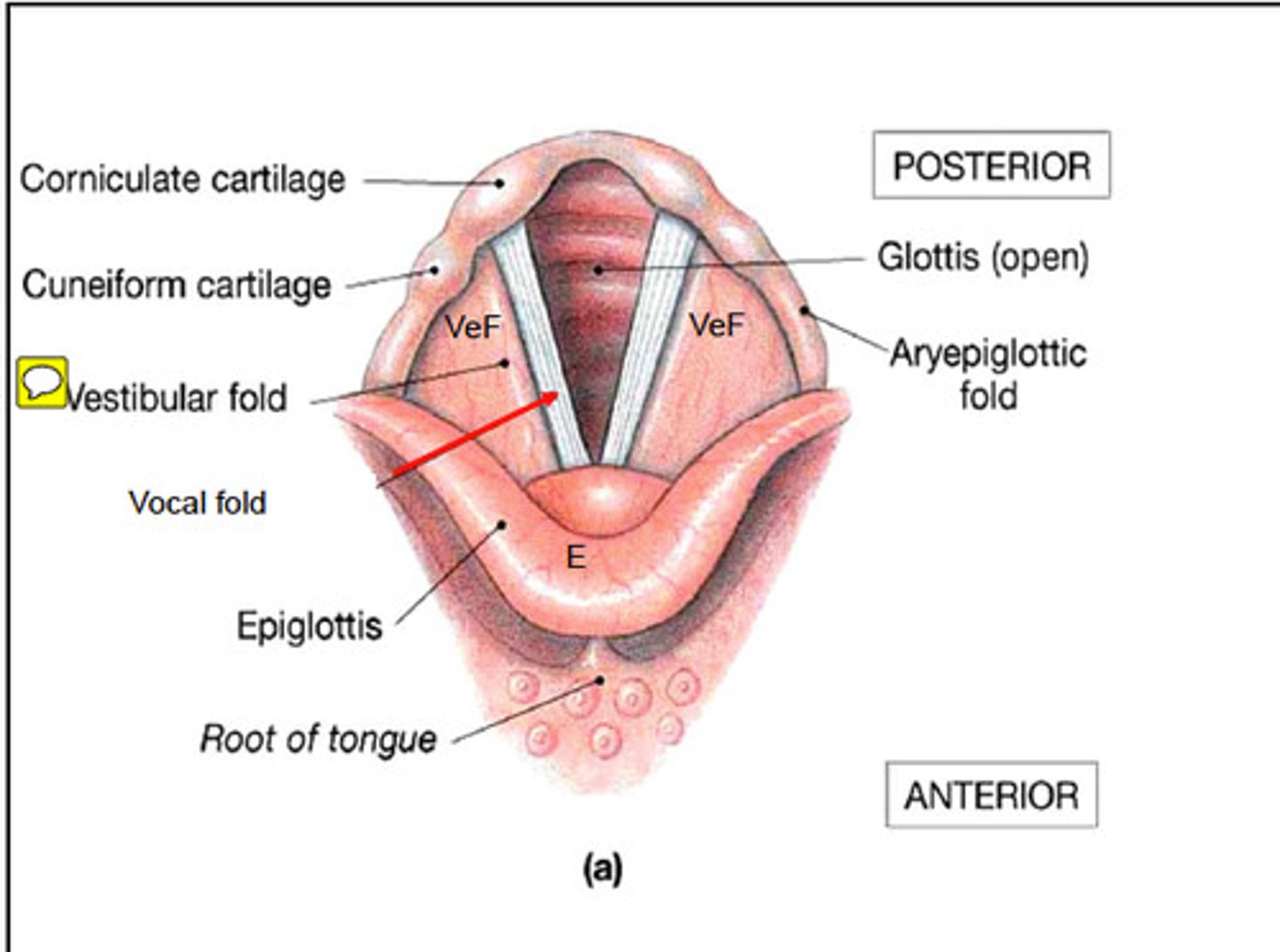
what is the glottis?
"chunk" of space between the vocal folds, and immediately below it is the trachea
what are the ventricular folds?
- aka false vocal folds
- area next to true VF
- adduct for swallowing, grunting, and coughing
- NO ROLE IN PHONATION
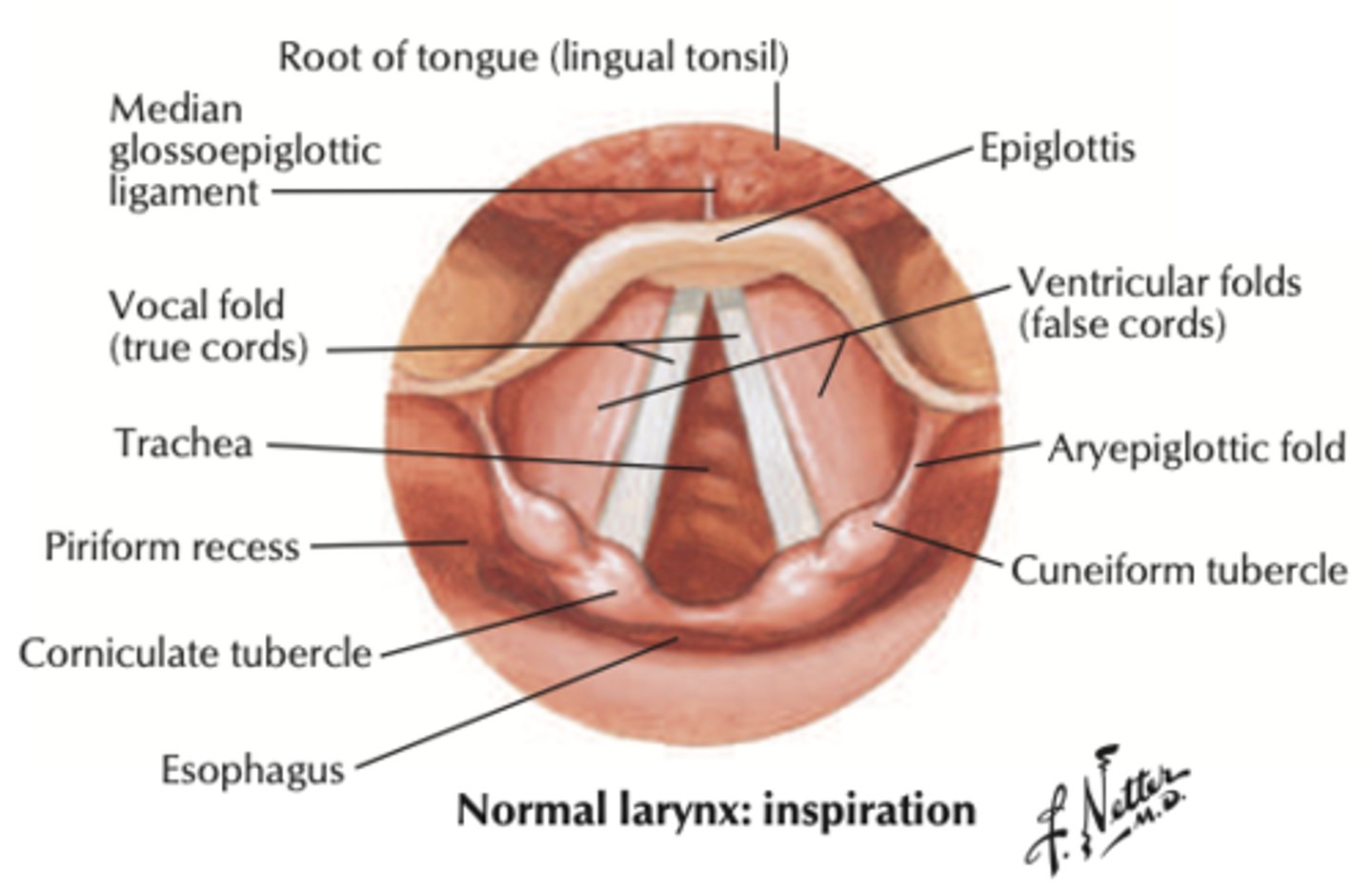
What is the ventricle?
space (thin furrow) between true VF and the ventricular folds
what are the aryepiglottic folds?
- large structure above the ventricular folds, connecting the lateral wall of the larynx to the arytenoids on each side
- first line of defense for preserving the airway
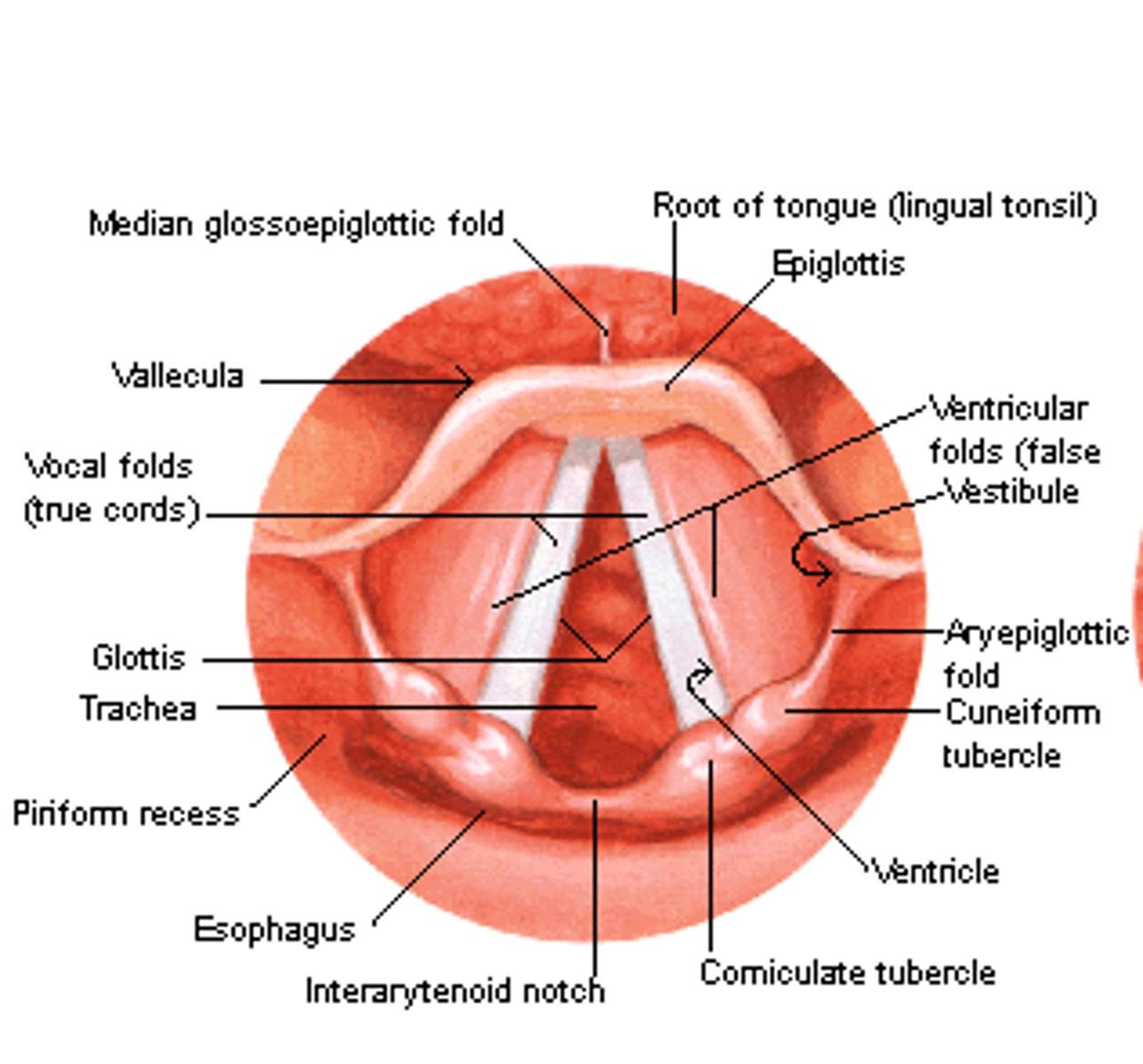
what are commissures?
where the vocal folds meet
- always an anterior commissure
- only posterior commissure when VF adducts (close/meet)
what is the main nerve of the larynx?
vagus nerve
what are the 2 branches of the vagus nerve?
- superior laryngeal nerve
- recurrent laryngeal nerve
what are the 2 further branches of the superior laryngeal nerve
internal and external branches
What do the interior and external superior laryngeal nerves do?
internal: sensory
External: motor for cricothyroid
What does the recurrent laryngeal nerve do?
- all motor function to other laryngeal muscles
- sensory to subglottic
Why is there damage mostly to the recurrent laryngeal nerve when doing surgery?
Due to its placement around the heart