Tubular secretion (urine formation) T2 W9
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
4 Terms
1
New cards
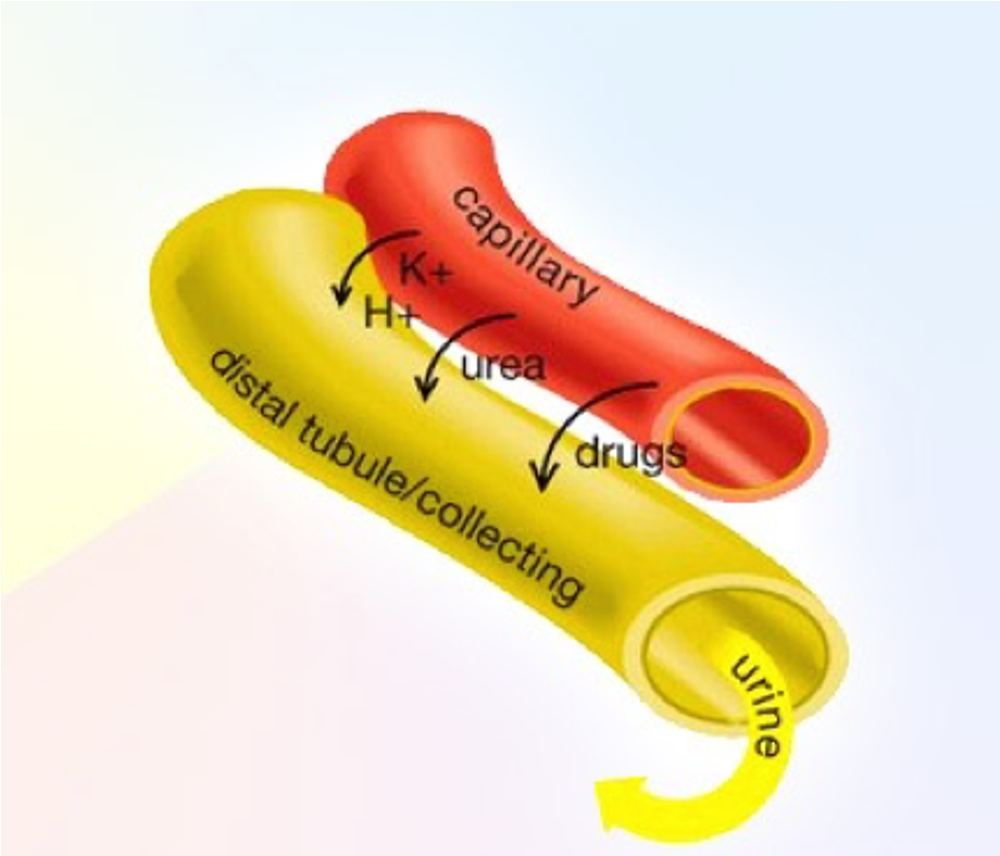
Tubular secretion
•Tubular secretion is a passive or active process in which selected substances in the blood are moved into the filtrate.
2
New cards
Tubular secretion function
Eliminating undesirable substances (wastes):
•Urea, uric acid, ammonium ions - passive transport.
Metabolites like drugs, hormones - active transport.
Ridding the body of excess potassium ions – active transport (controlled by aldosterone).
Controlling blood pH: when blood pH drops slightly, the renal tubules will actively secrete more H+ into the filtrate.
3
New cards
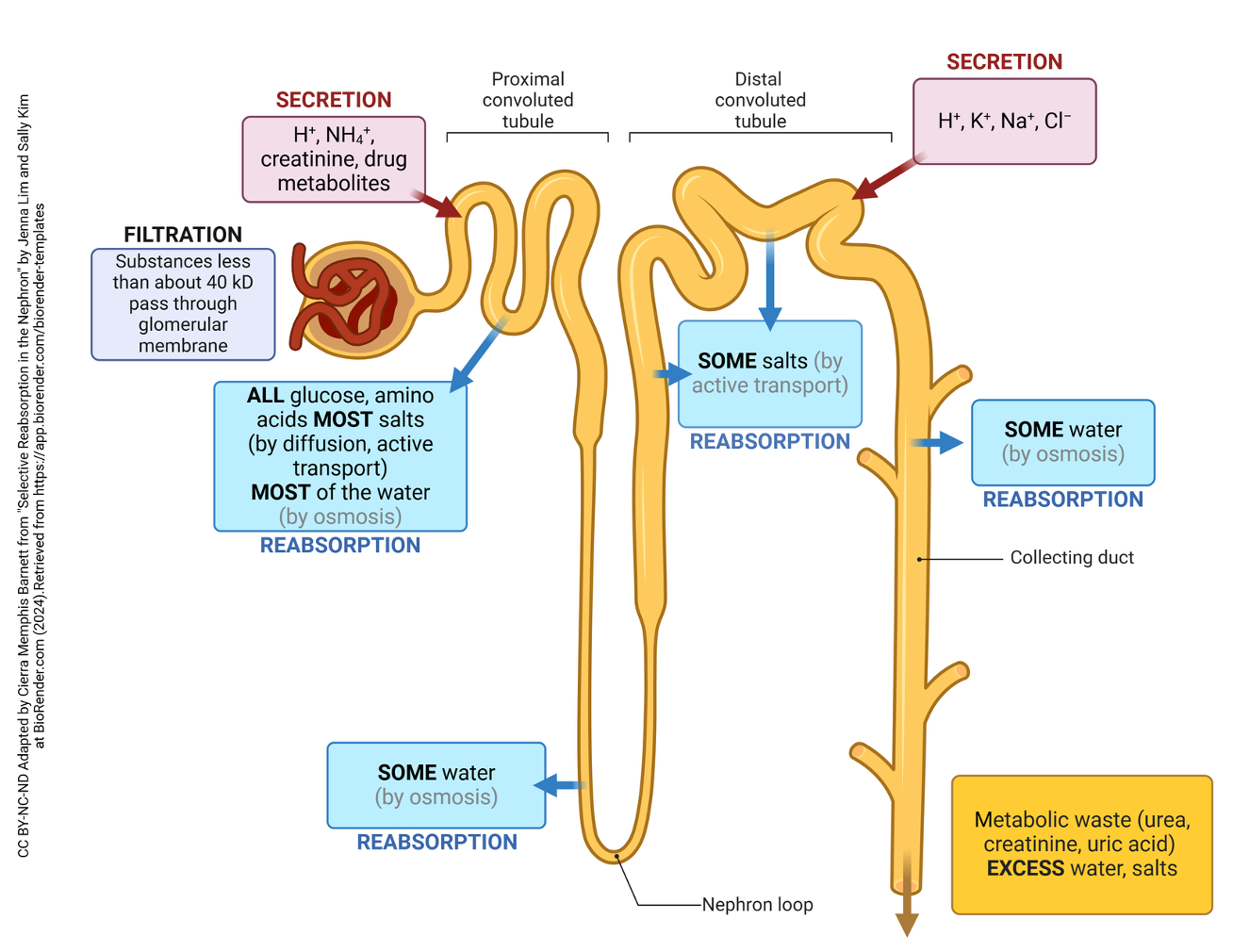
Where does tubular secretion occur
Along the renal tubule, especially the DCT.
4
New cards
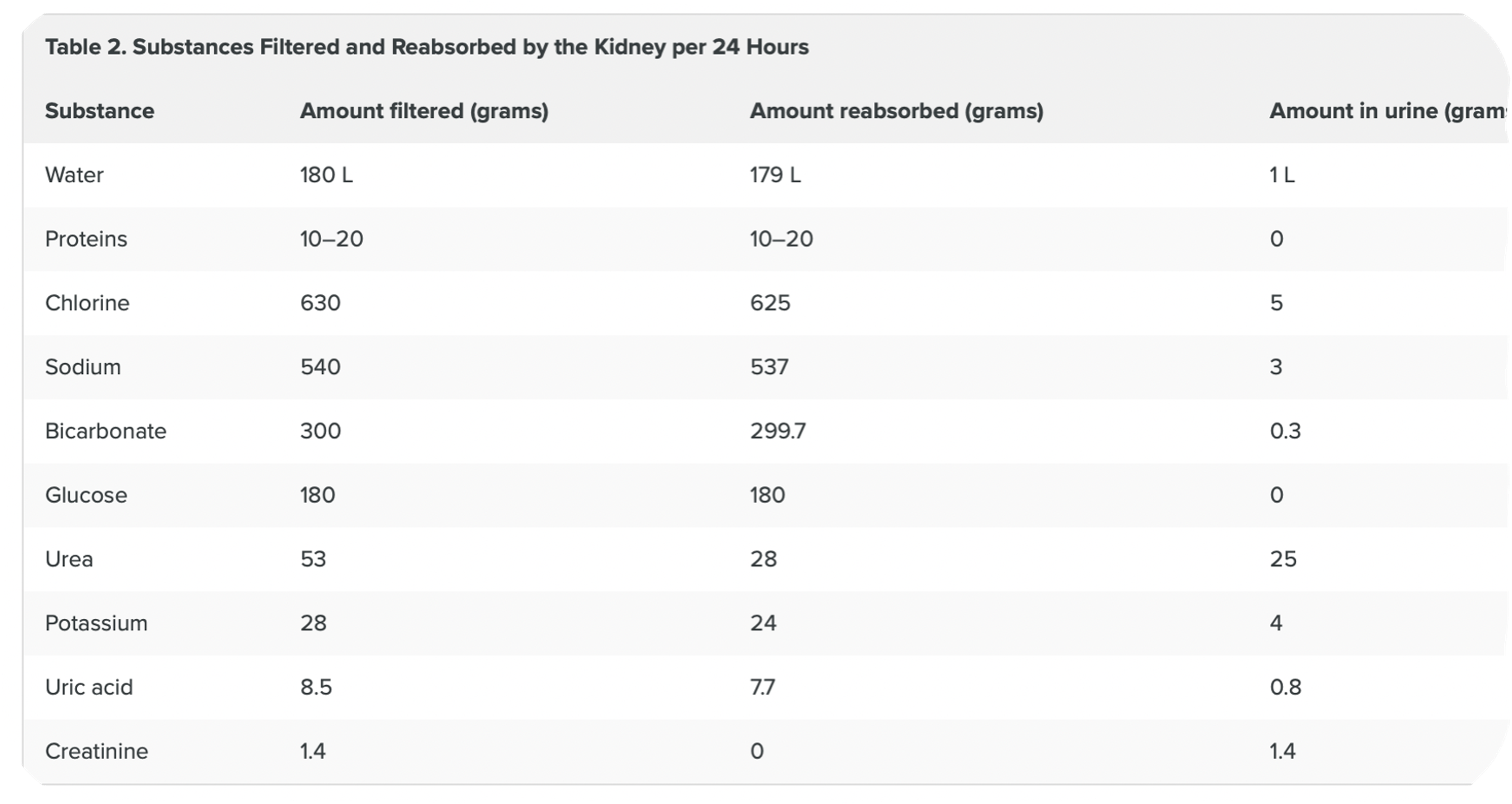
Table of substances filtered and reabsorbed by the kidney per 24hrs