Lesson 4 Electrical Signals and Voltage- Dependent Membrane Permeability
1/127
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
What causes the resting membrane potential (RMP), and how is it defined?
results from separation of charge across the cell membrane as defined by Vm = Vin-Vout
What is the distribution of charges on the neuronal cell membrane at rest?
the outer surface of the neuronal membrane has a cloud of positive charges, while the inner surface has a cloud of negative charges.
What maintains the separation of charge across the neuronal membrane?
the lipid bilayer, which acts as a barrier, and by the Na⁺/K⁺ pump, which actively moves ions to preserve the gradient
Why can’t ions diffuse freely across the membrane at rest?
Although a concentration gradient exists, ions cannot diffuse across the membrane because the lipid bilayer acts as a barrier; diffusion only occurs if an ion channel opens.
What is the membrane potential (Vm), and how is it defined?
it is the voltage difference across the membrane, defined as Vm=Vin−Vout
What is the typical range of the resting membrane potential (RMP) in neurons?
–60 mV to –70 mV.
What causes all electrical signaling in neurons?
it results from brief changes in the RMP that are caused by electrical currents [ions] flowing across the cell membrane.
What is depolarization?
changes in membrane potential that result in a less negative or more positive membrane potential.
What is hyperpolarization?
changes in membrane potential that result in a more negative membrane potential than the resting membrane potential (RMP).
What are electrotonic potentials?
They are passive responses of the membrane that do not lead to the opening of channels. These are depolarizing events, including small depolarizing or hyperpolarizing currents, that do not generate action potentials.
How does the size of the change in potential relate to the current pulse in electrotonic potentials?
With electrotonic potentials, the size of the change in potential is proportional to the size of the current pulse.
What happens when depolarizing events reach “threshold”?
They will lead to action potential generation.
How are ions distributed across the cell membrane?
unevenly across the cell membrane, no single ion species is distributed equally.
Which specific ions are concentrated outside the cell membrane, and which are concentrated inside?
Na^{+} and Cl^{-} are concentrated outside, while K^{+} is concentrated inside.
What does A^{-} represent in the context of ion distribution, and where are these molecules concentrated? Can they cross the membrane?
A^{-} represents various proteins/amino acids that are concentrated on the inside; such molecules cannot cross the membrane.
How do ionic concentrations in vertebrate nerve cells compare to those in the giant squid axon?
Ionic concentrations in vertebrate nerve cells are typically much lower than in the giant squid axon.
Despite differences in absolute concentrations, what similarity exists between ionic distributions in vertebrate nerve cells and the giant squid axon?
The ratio of external to internal ion concentrations are similar, and therefore the concentration gradients, are similar.
At rest, which ion are most open channels permeable to?
Potassium (K⁺) …that is, they are K channels
Are resting potassium channels voltage-gated?
No, such resting channels are not voltage-gated, and hence, they are typically open.
At rest, the resting potential would be expected to be very close to the electromotive force for which ion?
At rest, the resting potential would be expected to be very close to the electromotive force for K^{+} (due to its largest membrane conductance, g_K).
What is the typical resting membrane potential (RMP) of glial cells, and how does their ion distribution compare to neurons?
Glial cells have a typical RMP of about -75 mV, and their ion distribution is similar to that of any neuron at rest.
Why do K^{+} ions tend to move out of the cell at rest?
Because K^{+} ions are in high concentration inside the cell, they tend to diffuse down their concentration gradients, moving from the inside to the outside.
What happens as a result of K^{+} ions diffusing out of the cell?
A net positive charge accumulates on the outside, especially along the surface of the cell membrane, which in turn attracts the negative charges on the inside.
Why is the flux of K^{+} out of the cell self-limiting?
due to the electrical potential difference being generated by the growing charge separation; the greater the flow of K^{+}, the more charge is separated and the greater the potential difference.
What two forces are ions subject to?
(1) a chemical driving force, and (2) an electrical driving force.
What is the equilibrium for K^{+} (E_K)?
The equilibrium for K^{+} (E_K) is reached when the electrical driving force on K^{+} is balanced by the chemical driving force, after K^{+} diffusion has proceeded to a certain point.
What condition defines E_K?
At E_K, the outward movement of K^{+} (driven by the concentration gradient) is equal to the inward movement of K^{+} (driven by the electrical potential difference across the membrane).
EK is derived using the Nernst equation:
Ex = RT/zF ln ([X]o/[X]i) where Ex is the equilibrium potential for ion X, [X]o is the extracellular concentration, and [X]i is the intracellular concentration.
What can be used to predict the electrical potential generated across the membrane at electrochemical equilibrium?
The Nernst equation can be used to predict the electrical potential that is generated across the membrane at electrochemical equilibrium (called the equilibrium potential).
What do the variables in the Nernst equation represent?
In the Nernst equation, E_x is the equilibrium potential for any ion X, R is the gas constant, T is the temperature in Kelvin, z is the valence (charge) of the ion, F is the Faraday constant, (the amount of charge in one mole of univalent ion), the brackets indicate concentrations of ion X, and ln is the natural logarithm.
How is the equilibrium potential defined?
in terms of the potential difference between the outside and the inside of the cell.
What potential is measured across the membrane when the concentration of K^{+} is higher inside the cell?
an inside-negative potential
What does the Nernst equation predict if the membrane potential is plotted against the logarithm of the K^{+} concentration gradient?
a linear relationship with a slope of -58 mV per tenfold change in the K^{+} gradient.
What would happen to the electrical potential (inside relative to outside) if the [K+ ] on the outside were replaced with 10mM Na+ and the K+inside were replaced by 1 mM Na+ ?
No membrane potential would exist, unless the membrane was permeable to Na+
If the membrane were permeable to sodium in the previous exercise, (That is, if the [K+ ] on the outside were replaced with 10mM Na+ and the K+inside were replaced by 1 mM Na+), what would be the membrane potential?
The membrane potential at equilibrium would be + 58 mV!
If the membrane were permeable to Cl- and the [Cl-]i was 10 mM and the [Cl-]o was 1 mM, what would be the membrane potential?
The membrane potential at equilibrium would be + 58 mV!
What does the membrane potential influence?
ion movement across the membrane
How can the membrane potential (Vm) be directly controlled in an experimental setup?
By connecting a battery.
How do K^{+} ions flow when the battery is turned off (i.e., when Vm is not externally controlled)?
K^{+} ions simply flow based on their concentration gradients.
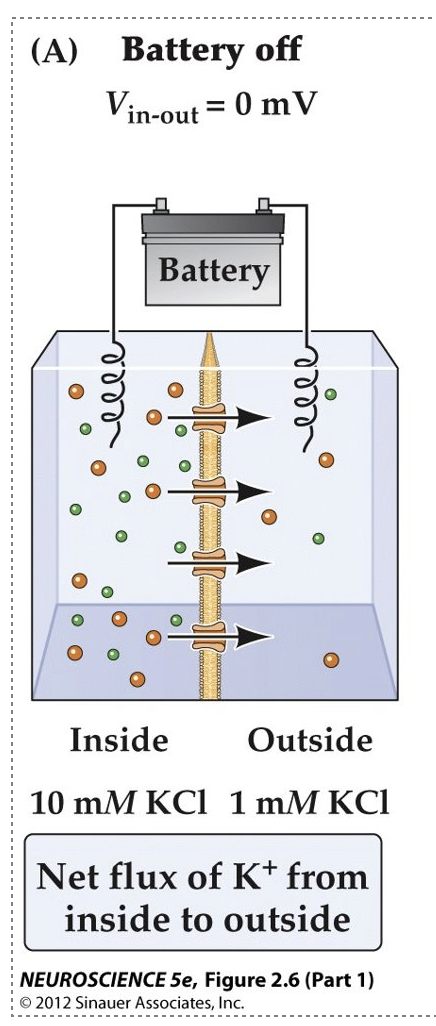
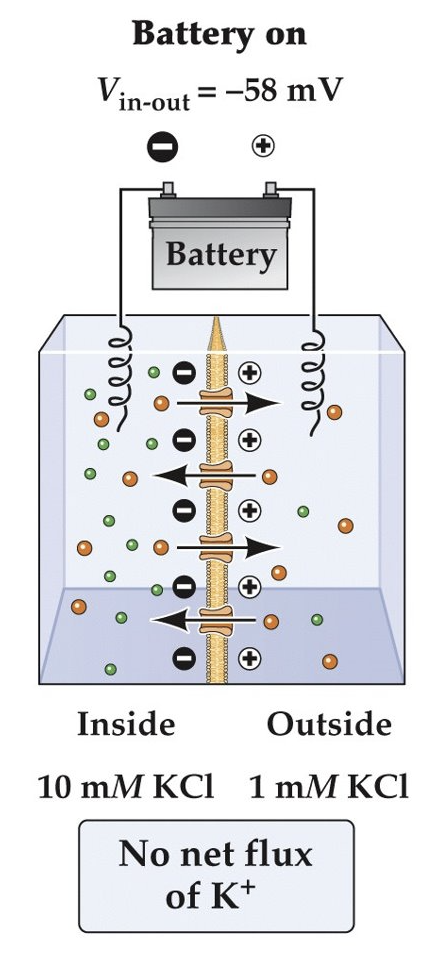
What happens to the net flux of K^{+} ions if the initial membrane potential (Vm) is set at the equilibrium potential for K^{+} (E_K)?
There will be no net flux of K^{+} ions.
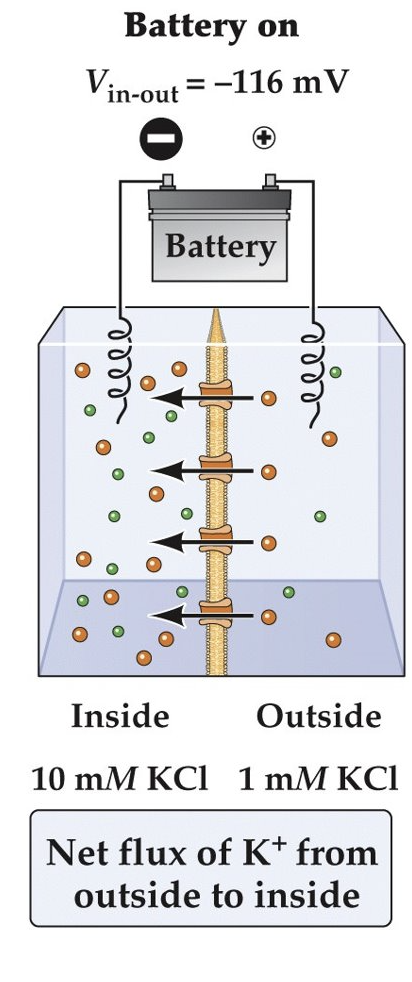
What happens to K^{+} ion movement if the membrane potential (Vm) is made more negative than E_K?
K^{+} will move against its concentration gradient, from outside to inside the cell.
Besides K^{+}, what other ions are neuronal cell membranes permeable to?
Na^{+} and Cl^{-}.
What happens if a cell membrane is permeable to more than one ion?
such ions would contribute to the driving forces acting on all permeable ions.
If a membrane were permeable to Na^{+} as well, by what forces would these ions be driven in?
These ions would be driven in by (1) the chemical gradient for Na^{+} and (2) the negative electrical potential across the membrane.
What effect would the influx of Na^{+} have on the cell's membrane potential, relative to E_K?
it would depolarize the cell, but only slightly from the equilibrium potential for potassium (E_K).
Why doesn't the membrane potential come close to the equilibrium potential for sodium (E_Na = +55 mV) despite Na^{+} influx?
The membrane potential doesn't come close to E_Na because there are many more resting K^{+} channels than Na^{+} channels in the membrane.
What factors determine the membrane potential (Vm) at rest?
Vm at rest reaches a balance between concentration gradients and electrostatic forces.
What happens to K^{+} equilibrium when the membrane potential (Vm) begins to depolarize away from E_K?
As soon as Vm begins to depolarize away from E_K, K^{+} is no longer in equilibrium, as it was before Na^{+} started to move.
The reduction in the negative driving force on K^{+} into the cell means what?
There is now a net driving force on K^{+} out of the cell, attempting to counter the influx of Na^{+}.
When is a new resting potential reached during this process?
when the increased outward movement of K^{+} is balanced by the inward movement of Na^{+}.
How is the magnitude of ion flux defined?
it is the product of its electrochemical driving force (the sum of electrical and chemical driving forces) and the conductance of the membrane to the ion. This can be expressed as: ion flux = (electrical driving force + chemical driving force) x membrane conductance.
APs are generated by
the flow of ions across cellmembrane
What significant discovery did Cole and Curtis make in 1939 concerning action potentials?
that ion conductance across the cell membrane increases greatly during an action potential (AP).
What was the primary implication of Cole and Curtis's observation about ion conductance during an action potential?
Their observation was the first evidence that an action potential results from changes in the flux of ions through channels in the membrane.
What two fundamental questions arose after it was understood that action potentials involved changes in ion flux?
(1) which specific ions are responsible for the AP, and (2) how is membrane conductance regulated?
What observation did Hodgkin and Katz make that provided insight into the ions responsible for the action potential?
that the amplitude of the action potential (AP) is reduced when the external concentration of sodium is lowered.
What characteristic describes the mechanism governing the increase in pNa^{+}?
The mechanism governing the increase in pNa^{+} is sensitive to V_m.
What is the primary electrical signal generated by neurons?
The action potential (AP).
From what does the action potential (AP) arise?
Changes in membrane permeability to specific ions.
For most axons, what specific permeability changes constitute the action potential?
These changes consist of a rapid and transient rise in Na^{+} permeability followed by a slower and prolonged rise in K^{+} permeability.
Under what condition is an action potential (AP) initiated?
The AP is initiated when and only when the neuronal membrane potential becomes more positive than threshold.
Regarding ion permeabilities during an AP, what is their dependence?
Both Na^{+} and K^{+} permeabilities are voltage-dependent, increasing as the membrane potential depolarizes.
What question remains regarding Na^{+} permeability during an AP?
But how does this increase in Na^{+} permeability actually occur?
From where does much of the evidence for understanding ionic permeability (in APs) come?
voltage clamp studies.
What must be done to understand how membrane potential affects permeability?
The membrane potential must be controlled while simultaneously measuring the permeability changes.
What problem arises when trying to study how membrane potential affects permeability?
Any change in membrane potential that produces an action potential causes additional uncontrolled changes in membrane potential.
What did the voltage clamp method allow researchers to do?
to understand ionic permeability at any membrane potential by clamping the membrane potential at any level desired
What does the voltage clamp technique prevent
It prevents changes in membrane current (Im) from influencing the membrane potential (Vm).
Who developed the voltage clamp technique, and what does it allow scientists to do?
Kenneth Cole, it allowed scientists to clamp the voltage at a desired value and observe changes in membrane conductance by measuring the currents that flowed across the membrane
What is the primary function of the Goldman Equation?
it is used to predict the membrane potential (V_m) at electrochemical equilibrium (Eeq) when more than one ion is crossing the membrane.
What key factors does the Goldman Equation consider for a real neuron?
It takes into account the concentration gradient and the relative permeability of several ions, which is typical of a real neuron.
What is the formula for the Goldman Equation?
V=58logPK[K+]o+PNa[Na+]o+PCl[Cl−]iPK[K+]i+PNa[Na+]i+PCl[Cl−]oV=58logPK[K+]i+PNa[Na+]i+PCl[Cl−]oPK[K+]o+PNa[Na+]o+PCl[Cl−]i
In the Goldman Equation (V = 58 \log \frac{PK [K^+]o + P{Na} [Na^+]o + P{Cl} [Cl^-]i}{PK [K^+]i + P{Na} [Na^+]i + P{Cl} [Cl^-]o}), what do V and P_x represent?
V represents the voltage across the membrane, and P_x represents the relative permeability of the membrane to each specific ion X.
How does the Goldman Equation relate to the Nernst equation?
The Goldman Equation is an extended version of the Nernst equation. It is necessary when the membrane is permeable to more than one ion, as the Nernst equation only considers the equilibrium potential for a single ion. (the Nernst equation doesn’t consider
permeability)
Under what condition does the Goldman Equation simplify to the Nernst equation?
If the membrane is permeable only to K+, all terms involving Na+ and Cl− drop out (since their permeabilities, PNa and PCl, would be zero), reducing the Goldman Equation to the Nernst equation for K+.
What technique did Hodgkin and Huxley use to understand permeability changes underlying the action potential (AP)?
The voltage clamp technique.
What hypothesis did Hodgkin and Huxley test regarding action potentials?
that membrane potential-sensitive Na^{+} and K^{+} permeability changes are both necessary and sufficient to produce an AP.
What was Hodgkin and Huxley's initial question to determine if neuronal membranes have voltage-dependent permeabilities?
They asked if ionic currents flow across the membrane when the potential is changed.
What happens when the membrane is hyperpolarized by 65 mV?
There is a brief capacitive current or a redistribution of charge across the membrane.
What happens to ion flow after the membrane is hyperpolarized?
there is very little ion flow across the membrane.
How did Hodgkin and Huxley characterize the membrane's response to depolarization compared to hyperpolarization?
They observed a "very different response" during depolarization from that observed during hyperpolarization.
Describe the sequence of currents observed by Hodgkin and Huxley following the capacitive current when the membrane was depolarized.
A rapid rising inward current (a positive charge entering the cell) was produced, which then gave way to a more slowly rising, delayed outward current.
What did Hodgkin and Huxley's observation that depolarization elicits ionic currents establish?
It established that the membrane permeability of axons is indeed voltage-dependent.
These experiments showed that ionic permeability is voltage-sensitive, or voltage-dependent
However, it did not identify the ions involved or the types of permeability involved
Describe the sequence of currents observed when the membrane is depolarized by 65mV.
There is a brief capacitive current, followed by a longer-lasting transient inward current and a delayed outward current.
What did Hodgkin and Huxley observe regarding current flow at negative membrane potentials below the resting potential?
They noticed that no appreciable current flows at negative membrane potentials below the resting potential.
What did Hodgkin and Huxley observe about current flow at membrane potentials more positive than the resting potential?
They noticed that at more positive potentials, current not only flows but also reverses its polarity (changes in magnitude).
What was the goal of Hodgkin and Huxley in examining ionic permeability?
They wanted to understand ionic permeability by examining how the properties of the inward and outward currents changed as the membrane potential was varied.
What did Hodgkin and Huxley determine about membrane current using the voltage clamp method?
They determined that the membrane current behaved differently depending upon the membrane potential.
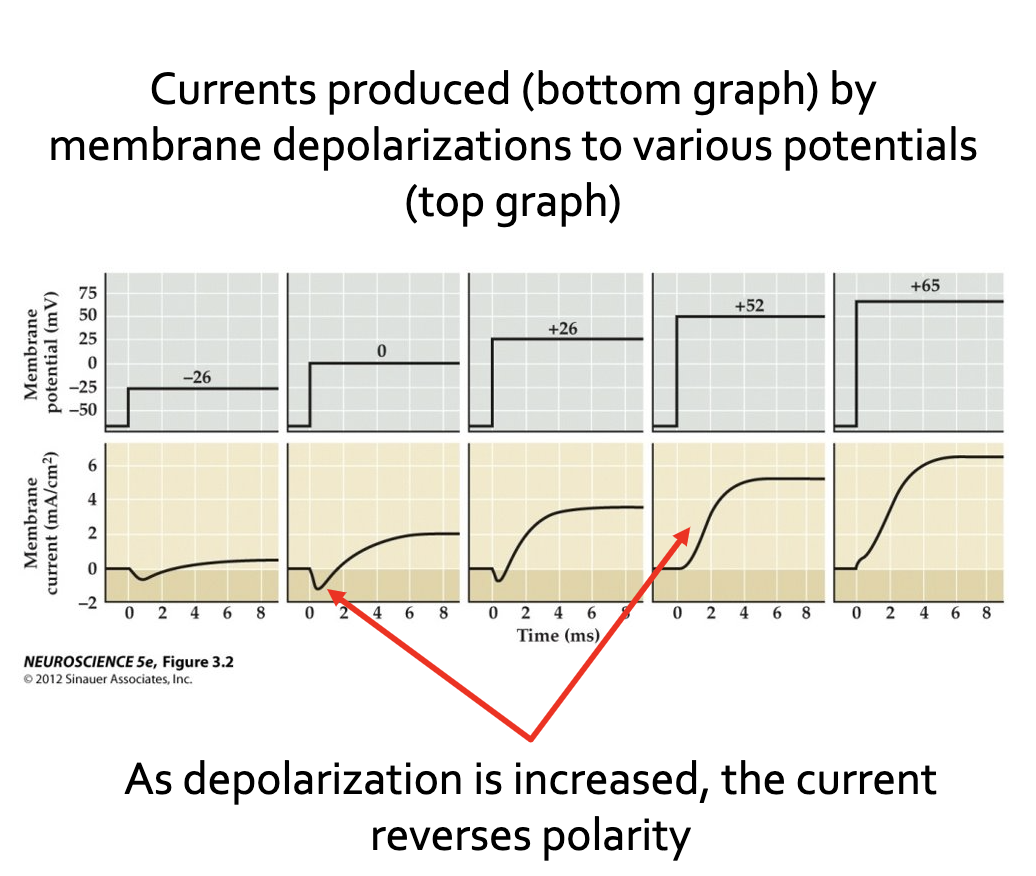
How do the two different membrane responses appear when their magnitudes are plotted as a function of membrane potential?
They are more noticeable
What did Hodgkin and Huxley observe about the early current flow at a clamped membrane potential of +52 mV?
No early current flows at +52 mV when the membrane is clamped at this potential.
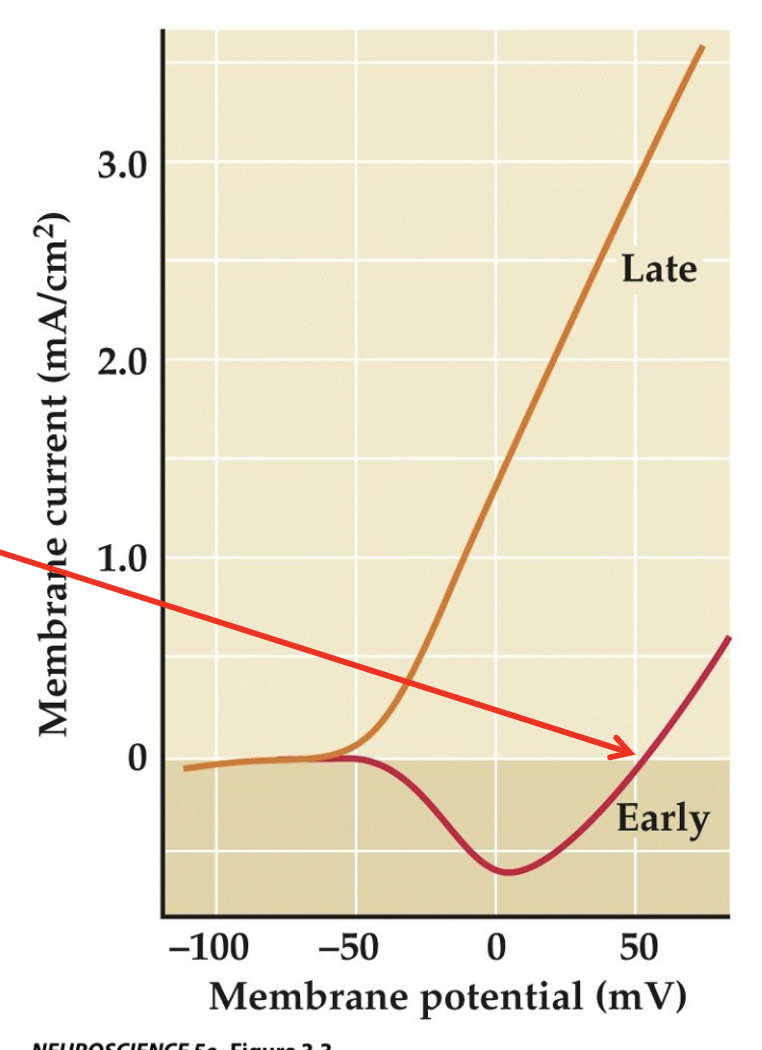
For squid neurons with [Na^+]o = 440 mM and [Na^+]i = 50 mM, what is the predicted equilibrium potential for sodium (E_{Na}) according to the Nernst equation?
For this concentration gradient, E_{Na} should be +55 mV (as predicted by the Nernst equation).
What does the absence of early current flow at E_{Na} indicate about the nature of this current?
that this early current is carried by the entry of Na^+ into the axon
What did Hodgkin and Huxley observe when they removed external sodium during their experiments?
They found that the early current was reversed in polarity, becoming an outward current.
Why did the removal of external sodium cause the early current to reverse its polarity and flow outward?
it would make E_{Na} negative; if permeability to sodium is increased under this condition, sodium should flow outward (here, the electrochemical gradient has been reversed).
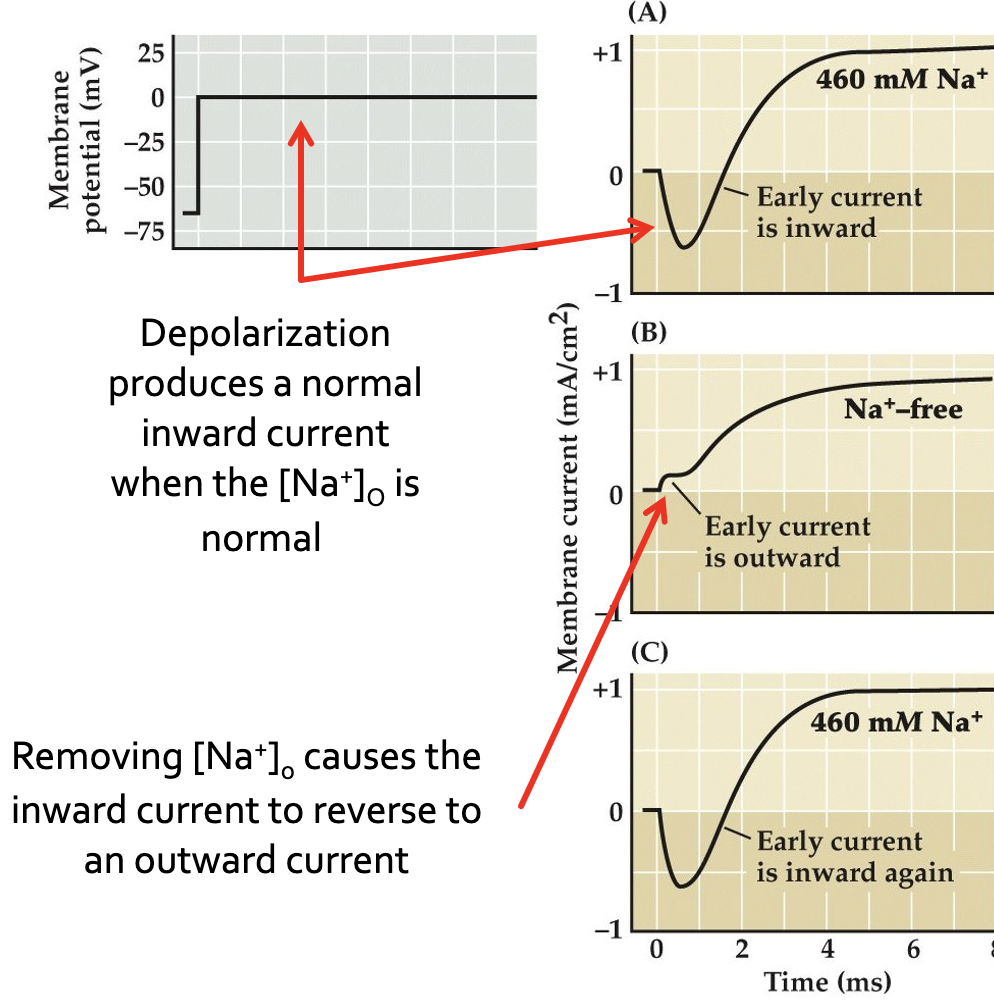
What happened to the reversed current when the external sodium concentration ( [Na^+]_o ) was restored?
This reversal of polarity was again reversed back to normal
Why was the outward current determined to be caused by an ion other than sodium?
The outward current was not really affected by the removal of external sodium, indicating it was due to the flux of a different ion.
What is the strongest evidence that the late outward current is due to K^+ efflux from the neuron?
The strongest evidence is that the amount of K^+ efflux from the neuron is correlated with the magnitude of the late outward current.
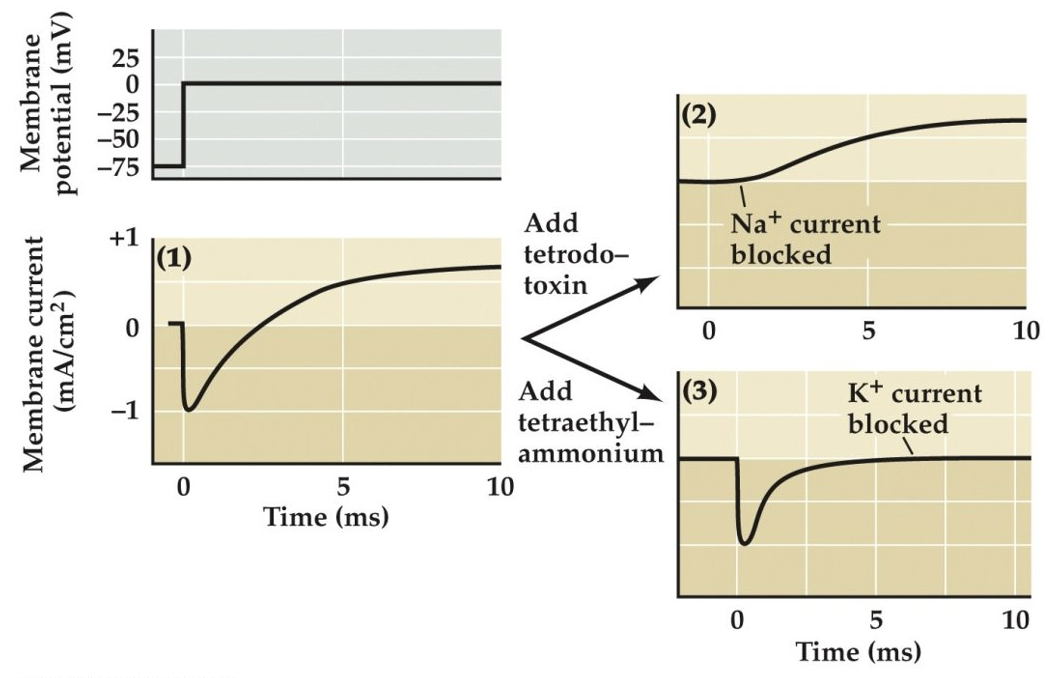
What initial observation suggested that there are two different mechanisms of ionic permeability during an action potential?
The fact that the inward current was transient, while the delayed outward current was sustained, suggested two different mechanisms of ionic permeability.
How were these two different ionic permeability mechanisms confirmed?
These two different mechanisms were confirmed by using drugs that block each current separately.
Which drugs selectively block Na+ current and K+ current, respectively?
Tetrodotoxin (TTX) blocks Na+ current, while tetraethylammonium (TEA) blocks K+ current.