Dentitions and Tooth Anatomy
1/43
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards reviewing types of dentitions, tooth anatomy, and related terminology.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
44 Terms
What is the term for natural teeth in the jaws?
Dentition
How many dentitions does a person typically have in a lifetime?
Two: primary and permanent
What is the first dentition present?
Primary dentition
How many incisors, canines, and molars are in the primary dentition?
8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 molars (total of 20 teeth)
What is the Universal Numbering System (UNS)?
A system used in the US to designate primary and permanent teeth.
What is the International Numbering System (INS)?
A two-digit code system for designating teeth, used internationally and recognized by the ISO and WHO.
What is the Palmer Notation Method?
A system using a right-angle symbol to indicate quadrants and arch, with tooth number placed inside.
What are the three dentition periods?
Primary, mixed, and permanent
When does the primary dentition period begin and end?
Approximately 6 months to 6 years of age, starting with the eruption of primary mandibular central incisors.
When does the mixed dentition period occur?
Approximately 6 to 12 years of age.
Why is the mixed dentition period sometimes called the 'ugly duckling stage'?
Because of the differences in tooth color, disproportionate tooth sizes, clinical crown heights, temporary edentulous areas, and crowding.
When does the permanent dentition period begin?
Typically after 12 years of age, with the shedding of the last primary tooth.
What is dental anatomy?
The area of dental sciences dealing with the morphology or form of the teeth, both the crown and root.
What is the alveolus?
The bone of the tooth socket that surrounds and supports each tooth.
What is the alveolar process?
The tooth-bearing part of each jaw.
What is occlusion?
The method by which the teeth of the mandibular arch come into contact with those of the maxillary arch.
In the D-A-Q-T system, what do the letters stand for?
D for dentition, A for arch, Q for quadrant, and T for tooth type
What is the difference between anterior and posterior teeth?
Incisors and canines are anterior (closer to the midline); molars and premolars are posterior (farther from the midline).
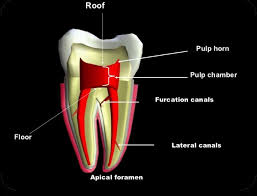
What is the function of the pulp cavity?
Houses the pulp chamber, pulp canal(s) with apical foramen(ina), and possible pulp horn(s).
What is the anatomic crown?
The part of the tooth covered by enamel.
What is the clinical crown?
The part of the anatomic crown that is visible and not covered by the gingiva.
What is the cementoenamel junction (CEJ)?
The area where the enamel of the crown meets the cementum of the root.
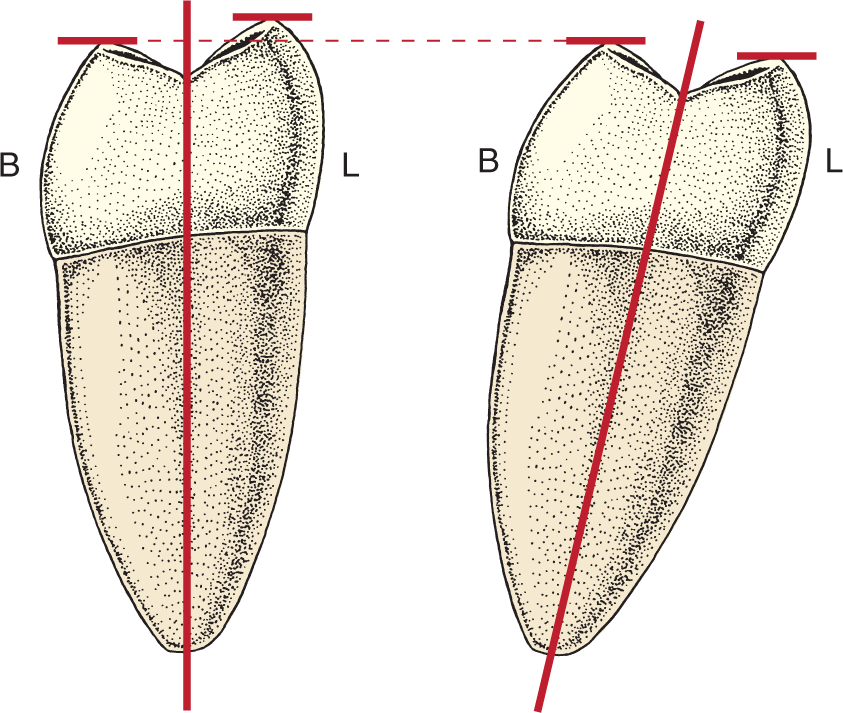
What is the root axis line (RAL)?
An imaginary line representing the long axis of a tooth, bisecting the root and crown in the cervical area.
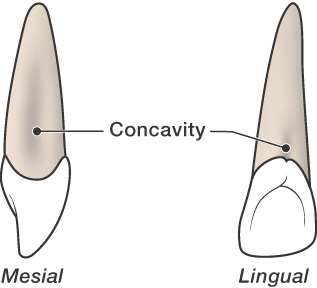
What are root concavities?
Depressions or indentations in the root surface. They can harvest bacteria and cause periodontal disease
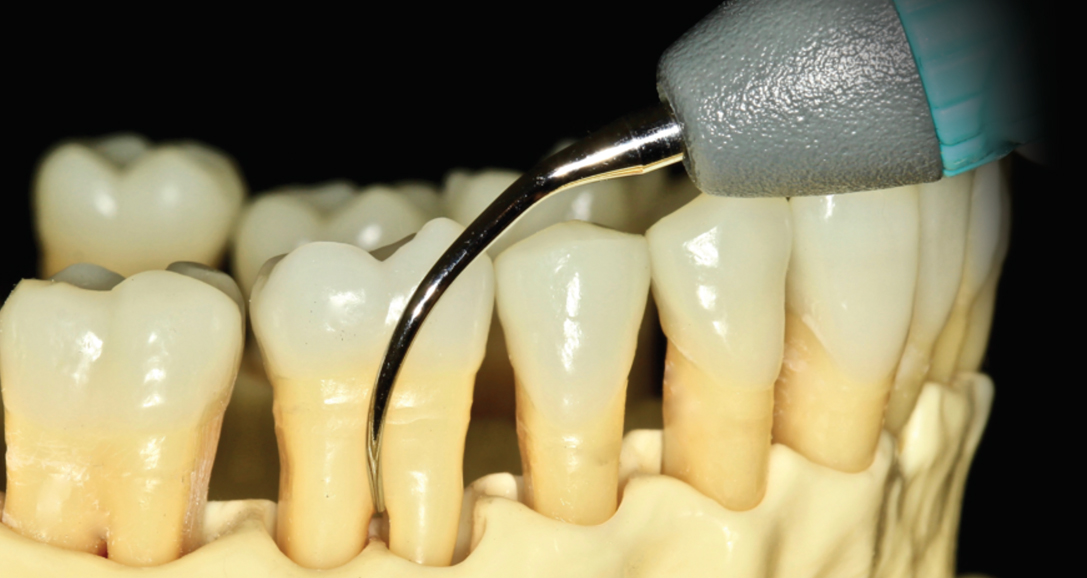
What is a furcation?
The area between two or more roots.
What is a full artificial crown?
A restoration that covers the entire anatomic crown area.
What are the five surfaces of a tooth?
Facial, lingual, masticatory, mesial, and distal surfaces.
What is the facial surface of a tooth?
The surface closest to the face; can be labial (closest to the lips) or buccal (closest to the inner cheek).
What are labial and buccal surfaces?
Labial is the facial surface closest to the lips, and buccal is the facial surface closest to the inner cheek.
What is the lingual surface?
The tooth surface closest to the tongue.
What is the masticatory surface?
The chewing surface on the most superior surface of the crown; incisal for anterior teeth and occlusal for posterior teeth.
What is the mesial surface?
The surface closest to the midline.
What is the distal surface?
The surface farthest away from the midline.
What is the proximal surface?
The mesial or distal surface between adjacent teeth.
What is the interproximal space?
The area between adjacent tooth surfaces.
What is the contact area?
The area where the crowns of adjacent teeth in the same arch physically touch on each proximal surface.
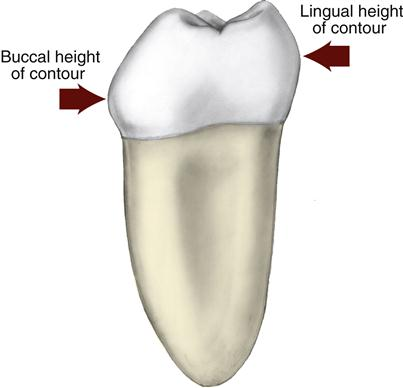
What is the height of contour?
The greatest elevation of the tooth either incisocervically or occlusocervically on a specific surface of the crown.
What are embrasures?
Triangular-shaped spaces between two teeth, created by the sloping away of the mesial and distal surfaces.
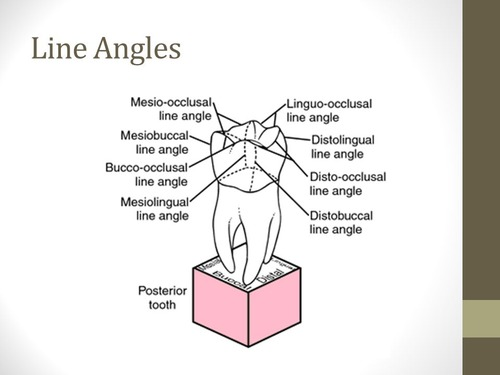
What is a line angle?
The junction of two crown surfaces, derived by combining the names of those two surfaces.
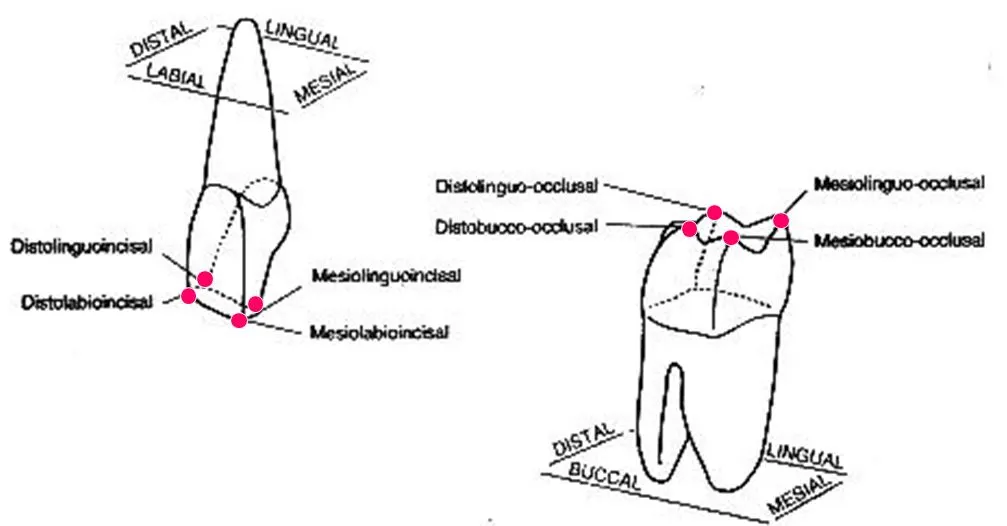
What is a point angle?
The junction of three surfaces of the crown, named from those three surfaces.
What is the function of incisors?
Biting and cutting food during mastication.
What is the function of canines?
Piercing or tearing food during mastication.
What is the function of premolars?
Assisting canines in piercing and tearing and assisting molars in grinding food.
What is the function of molars?
Grinding food during mastication.