Bot-Lec (Sem-1) - Chapter 5: Protists
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
Kingdom Protista
composed of simple eukaryotic organisms; most are aquatic; exhibit remarkable diversity where sizes range from single cells to large multicellular organisms
Chlamydomonas
unicellular, photosynthetic protist; a motile organism with two flagella and a cup-shaped chloroplast
locomotion
the ability to move from place to place
pushing out cytoplasmic extensions; flexing individual cells; waving cilia; lashing flagella
means of locomotion
photosynthetically; heterotrophically
how protists obtain nutrients
free-living
organism that does not depend on another for food or a place to live
symbiotic relationships
close, prolonged associations between two or more different organisms of different species that may, but do not necessarily benefit the members.
mutualism
symbiotic relationship in which both species benefit from the relationship
parasitism
symbiotic relationship in which one organism lives on or inside another organism and harms it
termites
have a mutualistic relationship with intestinal protozoa in order to digest cellulose
lichen
symbiotic association between a fungus and a photosynthetic organism (algae or cyanobacteria)
phylogeny
evolutionary history of a species
molecular data
evidence of phylogenetic relationships; for gene that codes for small subunit ribosomal RNA in different eukaryotes; for other nuclear genes (many of which code for proteins) in various protists
rRNA (ribosomal RNA)
an organelle that contains most of the RNA in the cell and that is responsible for ribosome function; used in classifying organisms in phylogenic analysis; faster replication
nuclear genes
genes located on chromosomes found in the cell nucleus of eukaryotic cells; preferred for phylogeny
elevated evolution rate (sequence); biparental inheritance; multiple independent loci
reasons why nuclear genes are preferred for phylogeny
loci
point on the chromosome where the gene is found
ultrastructure
evidence of phylogenetic relationships; fine details of cell structure revealed by electron microscopy; often similar among protists that comparative molecular evidence suggests are monophyletic and evolved from a common ancestor
monophyletic
ALL descendants came from one common ancestor
Euglenoid (Euglenophyta)
mostly freshwater, flagellated, unicellular protist that moves by an anterior flagellum and is usually photosynthetic; Euglena sp.
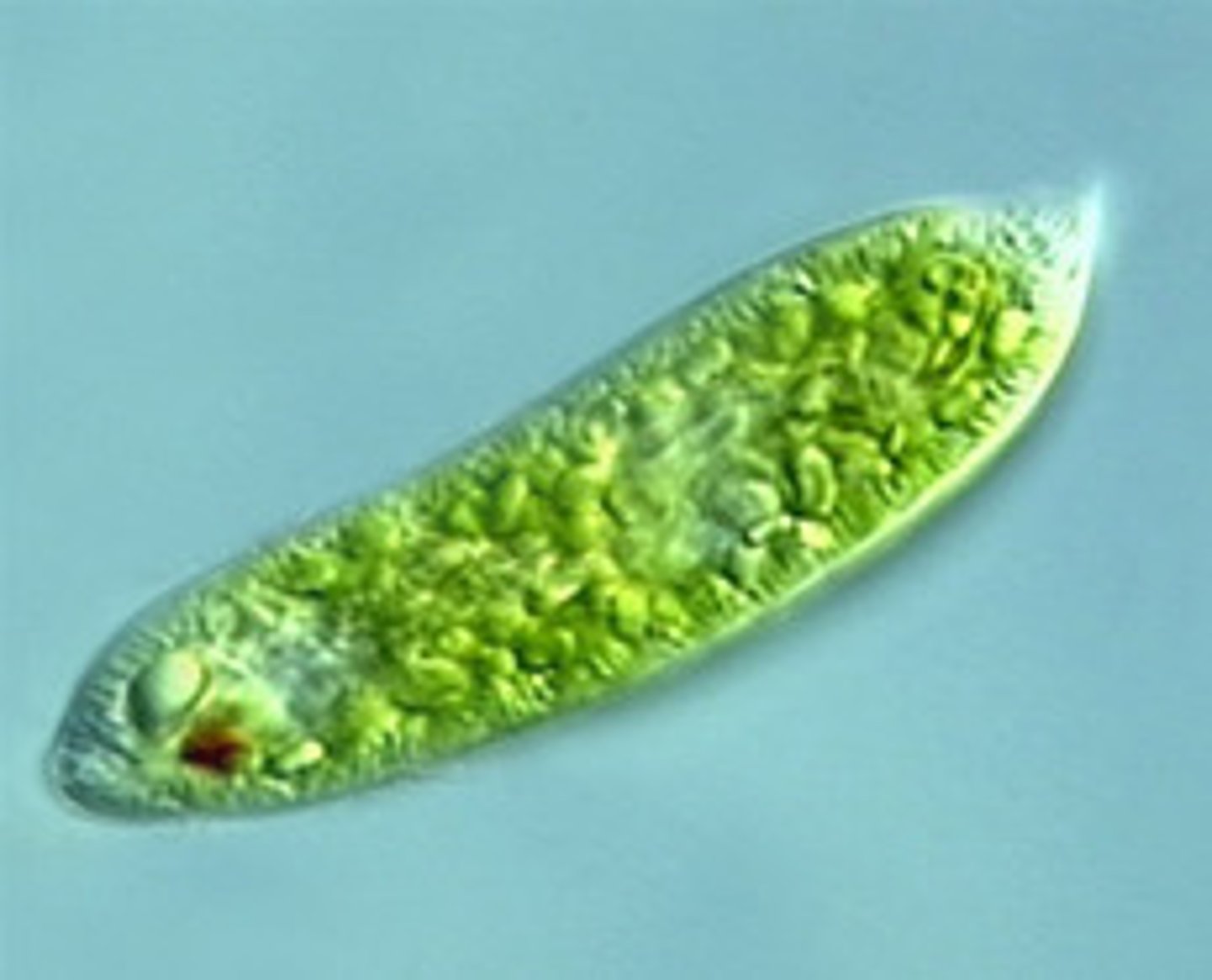
eyespot
A light-sensitive organelle that helps it react to light in certain protozoa
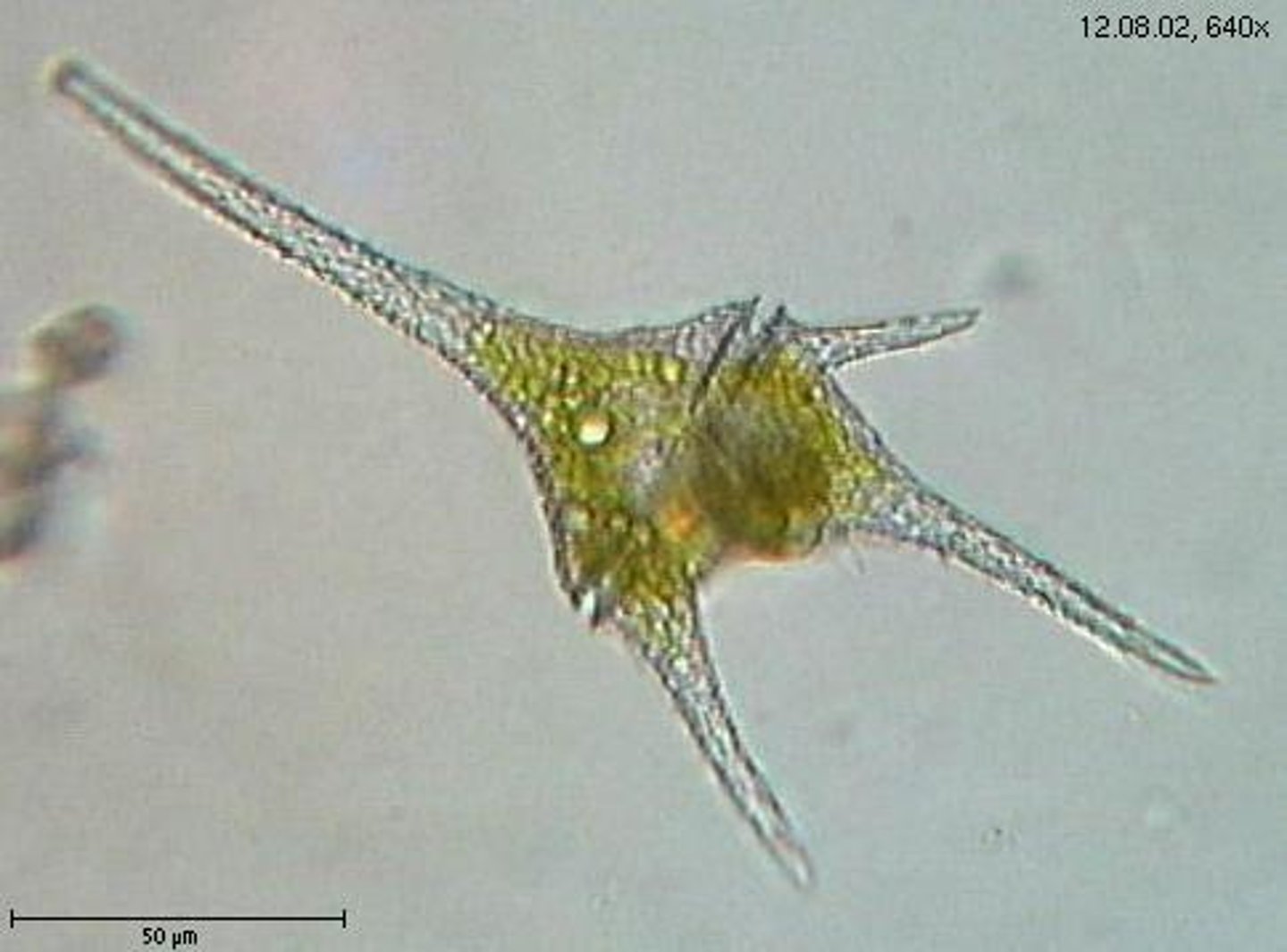
Dinoflagellates (Dinophyta/Pyrrophyta)
unicellular, biflagellated, typically marine protist; usually photosynthetic; brown pigment fucoxanthin, and is an important component of plankton; causes red tides (HAB: Harmful Algal Bloom)

eutrophication
excessive richness of nutrients in a lake or other body of water, frequently due to runoff from the land, which causes a dense growth of plant life and death of animal life from lack of oxygen
Pyrodinium bahamense
causes Paralytic Shellfish Poisoning (PSP); can lead to hypoxia; caused by high salinity + temperatures
hypoxia
lack of oxygen
Gymnodinium catenatum
causes Neurotoxic Shellfish Poisoning (NSP); caused by high salinity + temperatures
fucoxanthin
a brown carotenoid pigment occurring in and generally characteristic of the brown algae, diatoms, and dinoflagellates
water mold (Oomycota)
a protist with a body consisting of a coenocytic mycelium and with asexual reproduction by motile zoospores and sexual reproduction by oospores
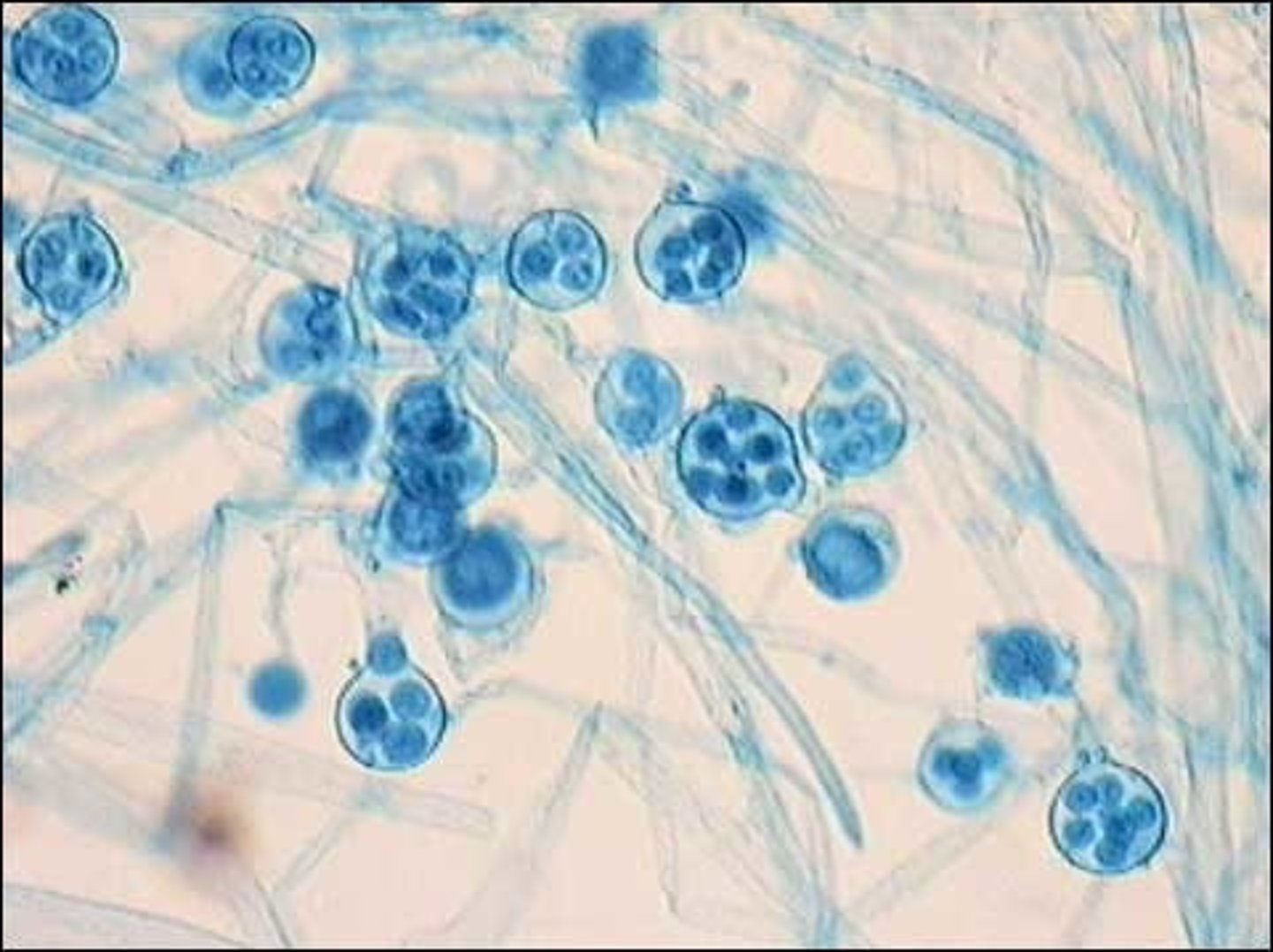
coenocytic
hyphae without septa
mycelium
mass of hyphae
diatom (Bacillariophyta)
usually a unicellular protist, covered by an ornate siliceous shell and containing the brown pigment fucoxanthin; important component of plankton in both marine and fresh water; used to make sandpaper
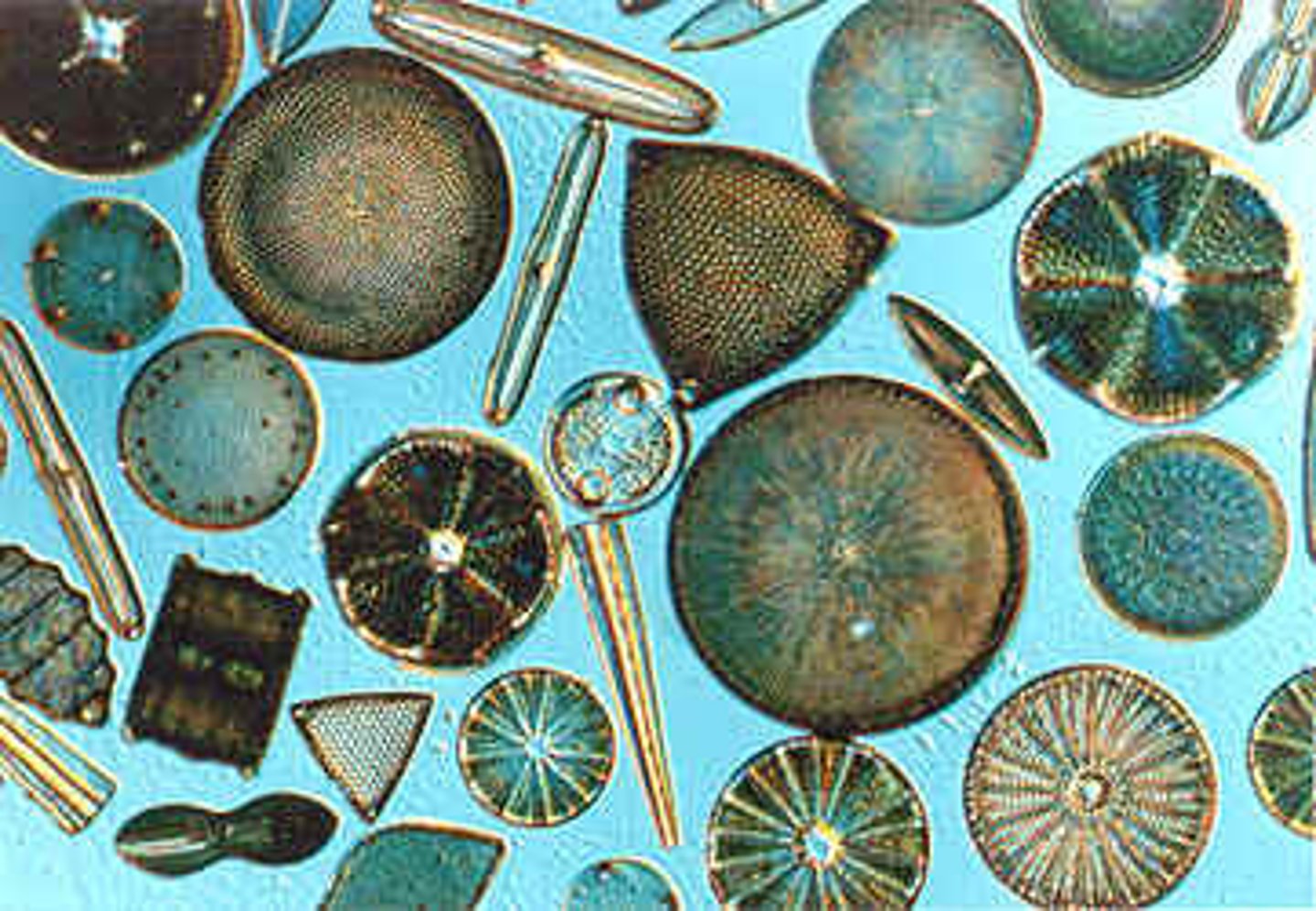

plankton
weak swimmers; carried by water current
bioluminescence
the production of light by living organisms
silica
component of diatom shell
golden alga (Chrysophyta)
a protist that is biflagellated, unicellular, and photosynthetic, and contains the brown pigment fucoxanthin
brown alga (Phaeophyta)
a predominantly marine; photosynthetic protist that is multicellular and contains the brown pigment fucoxanthin
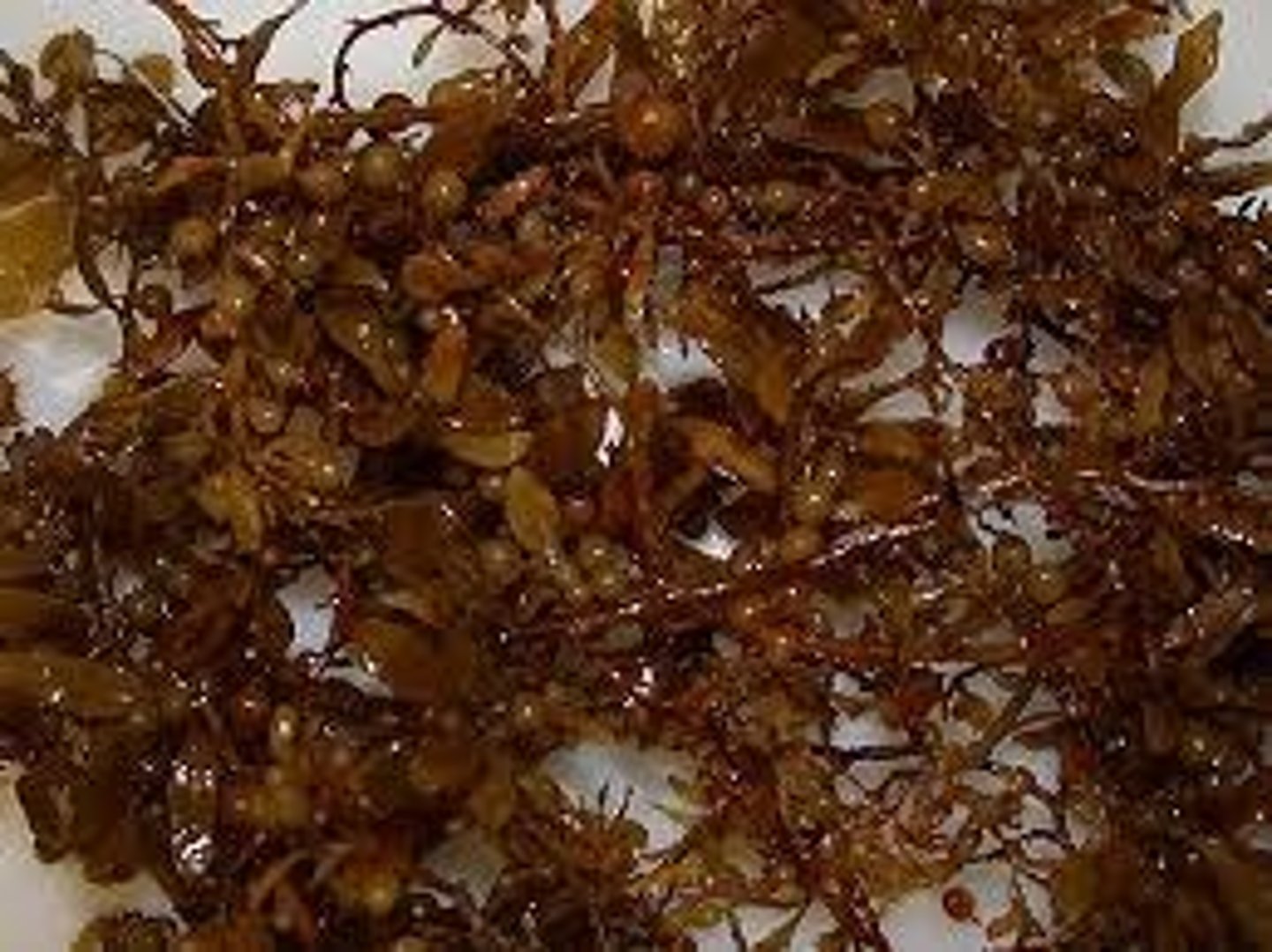

Laminaria; Fucus; Ectocarpus; Sargassum (lusay)
brown algae
blade; stipe; holdfast
parts of brown algae: leaf; stem; root
Macrocystis pyrifera
giant kelp; multicellular brown algae; has gas-filled floaters which allows buoyancy
red alga (Rhodophyta)
diverse group of photosynthetic protists that contain the pigments phycocyanin and phycoerythrin
Polysiphonia; Kappaphycus; Gracilaria; Bosiella
red alga
phycocyanin
blue pigment
phycoerythrin
red pigment
green alga (Chlorophyta)
diverse group of protists that contain the same pigments as land plants (chlorophylls a and b and carotenoids)
Micrasterias; Spirogyra; Volvox; Ulva (sea lettuce); Codium fragile (dead man's fingers); Chara (stonewort)
green alga
Chara sp. (stonewort)
closely related to plants; distributed in fresh water
chlorophyll alpha
the key light-capturing pigment that participates directly in the light reactions
chlorophyll beta
an accessory pigment
carotenoids
an accessory pigment, either yellow or orange, in the chloroplasts of plants; by absorbing wavelengths of light that chlorophyll cannot, carotenoids broaden the spectrum of colors that can drive photosynthesis
isogamy; anisogamy; oogamy
reproduction in green algae
isogamy
production of equal-sized gametes
anisogamy
sexual reproduction by the fusion of dissimilar gametes
oogamy
large non-motile egg, smaller motile sperm
plasmodial slime mold (Myxomycota)
a protist whose feeding stage consists of a multinucleate, amoeboid plasmodium
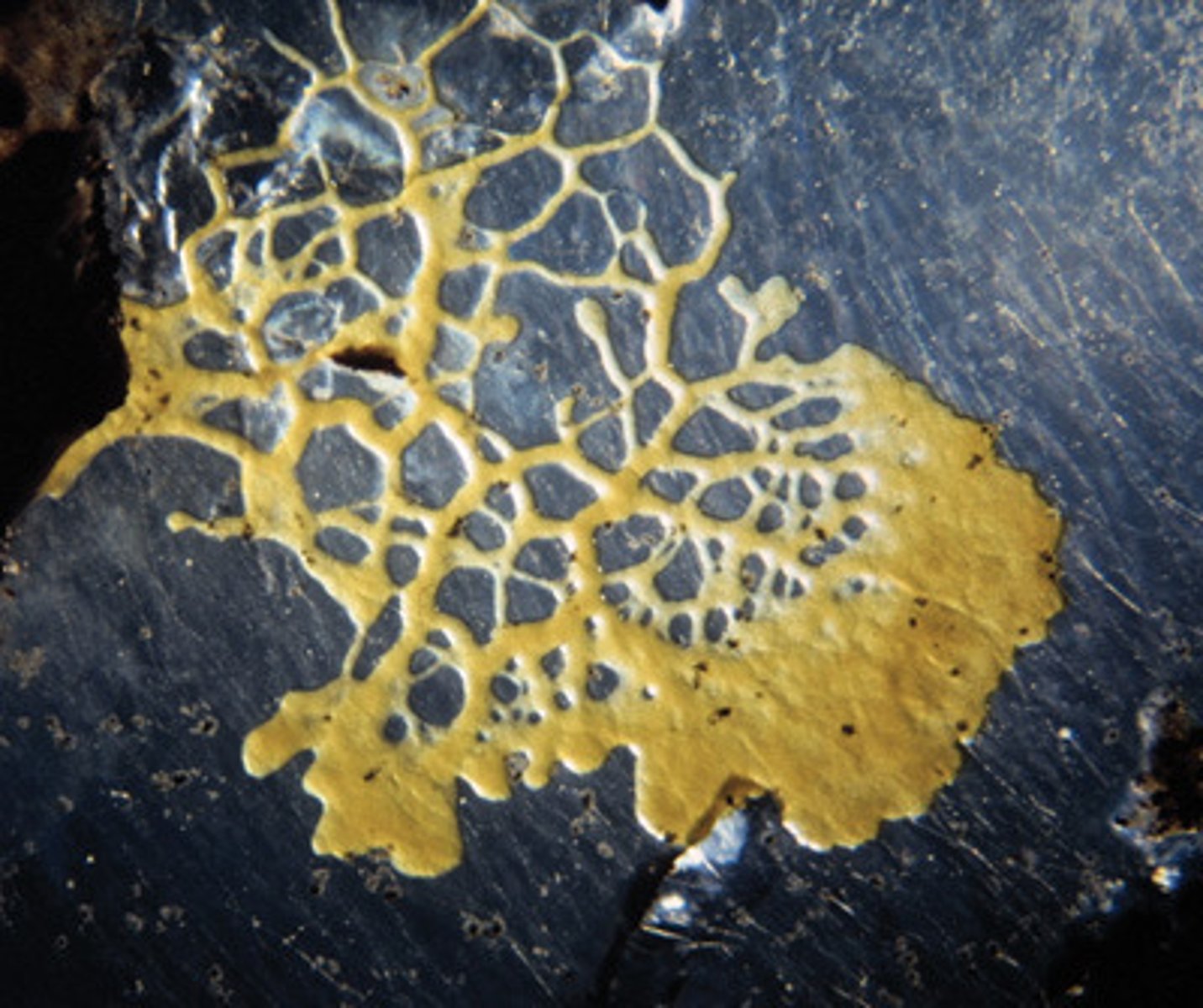
Physarum polycephalum
plasmodial slime mold; bright yellow
amoeboid
cell that moves and engulfs debris with pseudopods
plasmodium
causes malaria
conjugation
process in which paramecia and some prokaryotes exchange genetic information
cellular slime mold
a protist whose feeding stage consists of a unicellular, amoeboid organism that aggregates to form a pseudoplasmodium during reproduction
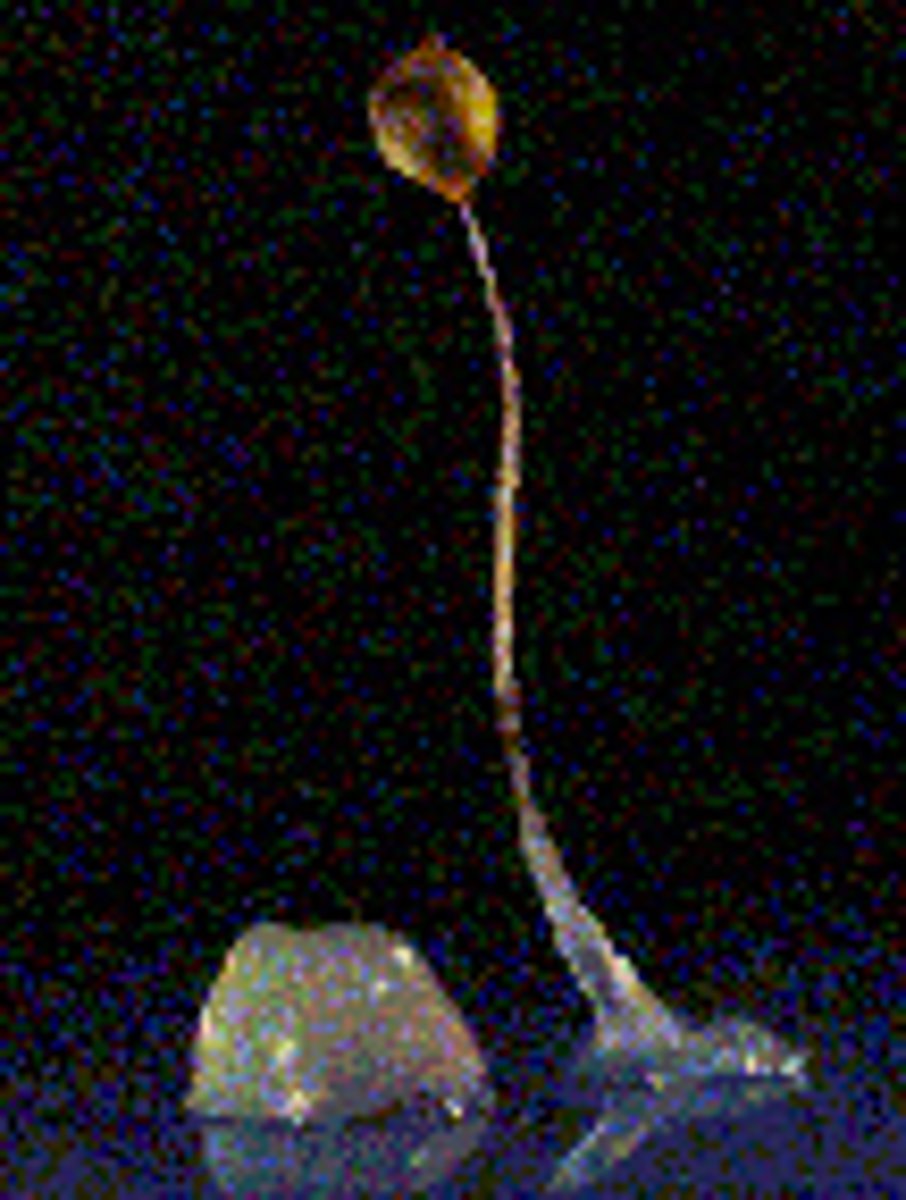

pseudoplasmodium
a slightly motile aggregation of cells that produces fruiting bodies, which in turn produce spores