organisms and population
1/58
Earn XP
Description and Tags
botany
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
what is ecology
study of interaction b/w living organisms and its environment
basic unit of ecology and functional unit of ecology
basic unit= organism
functional unit= ecosystem
levels of biological organisation
macromolecules
cell, tissues, organs, organisms
population
communities
ecosystem
biomes
biosphere
ecology at organism level is
physiological ecology
how an organism functions to adapted in an environment in survival and reproduction
population ecology benefits
helps to understand genetics and evolution
many forces like natural selection work on population
four main levels of ecology
organism
population
communities
biome
population is group of same
species
population attributes are
birth rate
death rate
sex ratio
population density
birth rate/ death rate formula
change in population/ initial population
population increasing or decreasing can be determined in age pyramid by
pre reproductive individuals more than reproductive then population increasing or lowermost section big
pyramid shape for increasing, stable and decreasing population
triangular
bell shaped
urn shaped
Four ways to measure population density
total number
biomass cover
relative density
indirect count
population growth equation
Nt+1 = Nt + [ (B+I) - (D+E) ]
in normal conditions which factor important to control population growth
natality and mortality
in newly colonised area which factor most important
immigration
maximum reproductive fitness measure is
r value
or intrinsic rate of natural increase
maximum number of individuals which ecosystem can support
K carrying capacity

sum total of all factors which limits population size
environmental resistance= K-N/K
N= population size
which growth seen under unlimited resources
Exponential growth
J curve
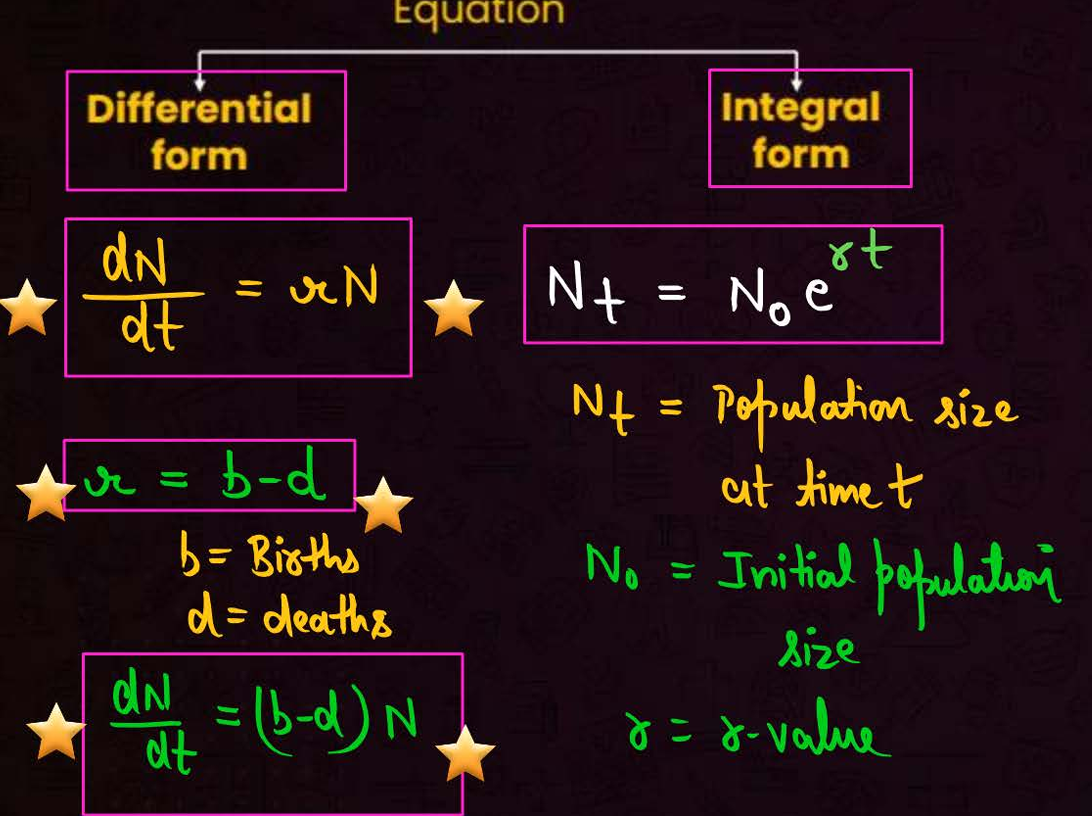
differential and integral form of exponential curve
growth seen under limited conditions
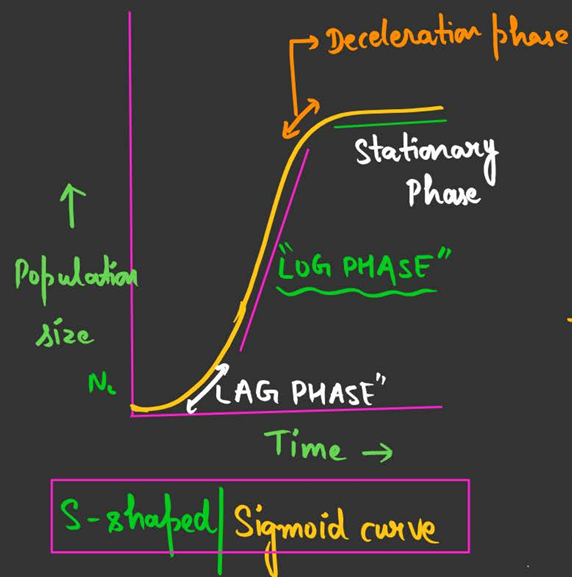
logistic growth
more realistic
sigmoid curve
most common in nature
eg. bacteria growing in a petri dish
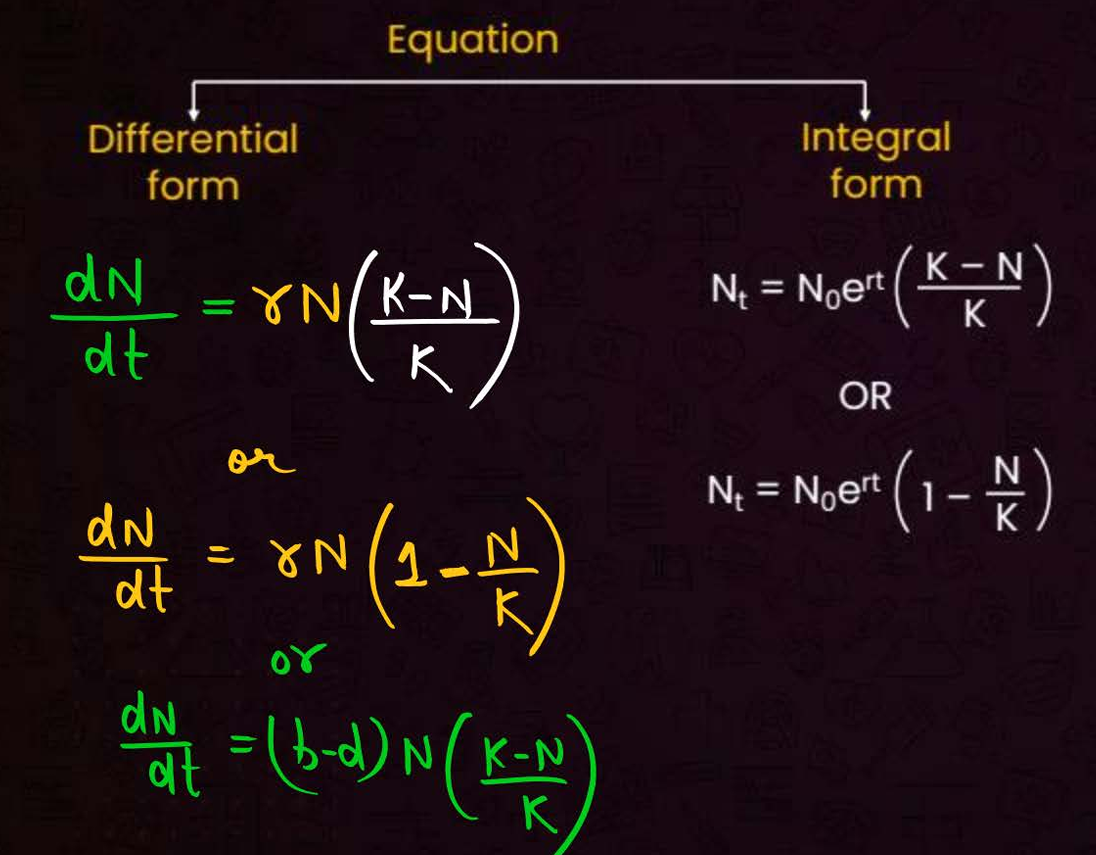
differential and integral form for logistic growth
show all phases of logistic growth
Magnitude of (r)intrinsic rate for Norway rat, flour beetle
0.015
0.12
In ____, r value for human population in india was_____
1981
0.0205
which organisms breed once in lifetime
bamboo
pacific salmon fish
which organism produce many small sized offspring
oysters
pelagic fishes
why do population grow more slowly as they approach carrying capacity
density dependent factors lead to fewer births and increased mortality
interspecific competition is more severe than intraspecific competition
true false
false
intraspecific is more severe
inter or intra specific competition more potent for evolution
interspecific
siberian cranes in bharatpur wetlands
less than 10
darwin observed which growth while developing his theory for natural selection
exponential growth
animals realise fully its innate potential and increase in number even elephants
darwinian fitness is measured by
high ‘r’ value
max reproductive fitness
in which interaction, interacting species live closely
predation parasitism commensalism
herbivores are also predator
true false
true
prickly pear cactus wrcked havoc in _____ in the year_____ and brought in control by_____
australia
1920’s
cactus feeding moth
assertion- predators help in maintaining species diversity
reason- they reduce the intensity of competition among prey animals
true and correct explanation
starfish pisaster a predator is found in
rocky intertidal communities of american pacific coast
what happened when starfish pisaster was removed
more than 10 species of invertebrates became extinct within a year because of interspecific competition
nearly ___ percent of insects are phytophagous (plant sap feeders or other parts)
25 percent
which plant produces highly poisonous cardiac glycosides
Calotropis
chemicals extracted from plants on a commercial scale
nicotine
strychnine
quinine
caffeine
opium
competitive exclusion principle was given by
Gauss
competitive release example
connells elegant field experiment
on the rocky sea coasts of scotland larger and superior barnacle balanus dominates and excludes smaller cathamalus. if balanus is removed then cathamalus expands
competitive co existence or resource partitioning given by
mc arthur
competitive co existence or resource partitioning examples
coexistence of 14 darwins finches
5 species of warblers
competition can occur b/w two unrelated species and related species also
true
unrelated species like visiting flamingoes and resident fishes compete for zooplankton
competition occurs only in limited resources
competition occurs in unlimited resources
true false
false
true
herbivores and plants are more affected by competition than plants
true false
true
competition is best defined as a process where
fitness of one species is significantly lower in presence of other species
what is gauss exclusion principle
two closely related species competing for the same resources cannot coexist indefinitely and inferior one will be eliminated eventually
commensalism examples

amensalism examples
J shaped growth curve can be observed for
algal bloom
mosquitos and insects in rainy seasons
adaptations in parasites
host specific
loss of unnecessary sense organs
loss of digestive system
presence of adhesive organs and suckers
high reproductive capacity
complex life cycle
examples of ectoparasite like cuscuta
cuscuta or amarbel is found growing on hedge plants and is devoid of chlorophyll and leaves but has houstorial roots that derive nutrition from xylem and phloem of plant
female mosquito is not considered a parasite why
they don't live on or in a host for an extended period and don't rely on it for their sole survival
the anatomical and morphological features of endoparasites are greatly simplified
high reproductive potential
complex life cycle
true false
true
niche explains
functional role of an organism in its habitat
no two species in same habitat have same niche