Chemistry Chapter 5
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
Thermochemistry
Study of energy changes occurring in physical or chemical change
Energy
Ability to do work
Work
Amount of energy transferred by a force over a distance, force exerted against the system
Kinetic energy
Energy of moving things
Potential energy
Stored energy of an object because of its position/bonds
Amount of energy absorbed or released
potential energy of bonds in reactants - potential energy of bonds in products
Heat
The transfer of thermal energy from warm to cool
Temperature
Average kinetic energy of molecules
warmer substance = faster molecules
Law of conservation energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, just rearranged
System
The substance undergoing chemical change
Surroundings
The system’s environment
Open
Matter and energy can move in or out
Closed
Energy can move in or out but not matter
Isolated
Neither matter nor energy
Heat of reaction: Bond breaking
Endothermic
Heat of reaction: Bond formation
exothermic
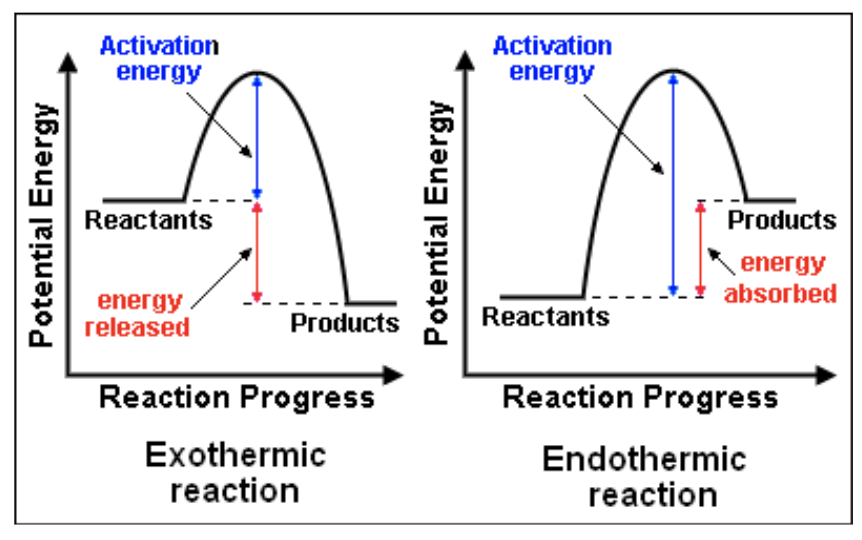
Exothermic reactions
Heat and energy is released, surrounding temp increases
Endothermic
Heat and energy are absorbed, decreases temp of surroundings
Draw a potential energy diagram of exo and endothermic reactions
Heat Capacity
Quantity of thermal energy required to raise 1g of a substance by 1℃
SI Units J/ g ℃
Calorimetry
Process of measuring energy changes during a physical/chemical change
Goal is to calculate energy entering or leaving system
Calorimeter
Device used to measure energy changes during physical/chemical change
Assumptions made in calorimetry calculations
Thermal energy absorbed by calorimeter/outside environment is negligible
Dilute aqueus soltuoins have the same density and heacapacity of water
Density: 1.00g/ml
Heat capacity: 4.18J/g℃
Calorimetry calculation for thermal energy absorbed or released in a chemical system

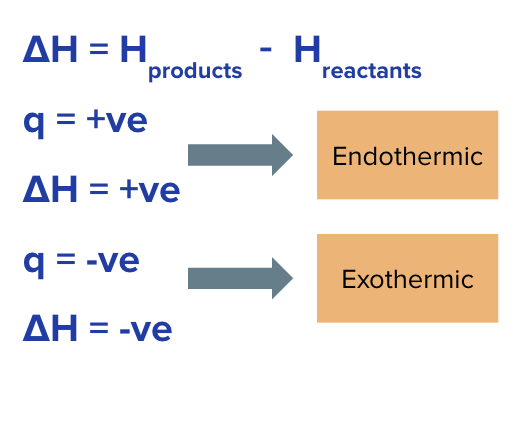
Negative value of q
System transfers thermal energy to surroundings = exothermic
positive value of q
system absorbs thermal energy from surroundings = endothermic
q system relationship to q surroundings
q system + q surroundings = 0
q system = - q surroundings
Enthalpy (H)
Heat content of a system at a constant pressure
Reaction with a gain or loss of energy
ENTHALPY CHANGE (ΔH), relative difference between Hreactants and Hproducts
Relationship between thermal energy and heat content
at constant pressure, enthralpy change equals the flow of thermal energy in or out of system
Molar Enthalpy Change (ΔHr)
Energy of change that occurs when 1 mol of substance undergoes physical, chemical, or nuclear change
J/mol
for example: ΔHvaporization
Calculation molar enthalpy change
ΔH = nΔHr
Bond Dissociation Energy
Energy required to break a chemical bond (average bond energies)
number of bonds in order of length
Single > double > triple
number of bonds in order of strength
Triple > double > single
Using bond energies to predict enthalpy change
(# of bonds broken in reactants) - (#of bonds formed in products)
Hess’s Law
For any reaction that can be written in steps overall ΔH is the same as ΔH sum for each individual steps
Standard Enthalpy of Formation ΔHf°
Change in enthalpy when 1 mol of substance is formed from its elements at SATP
Calculating enthalpy change
(sum of standard enthalpies of products) - (sum of standard enthalpies of formation of reactants)