Chapter 11: Cell Division
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What is sexual reproduction? List its characteristics.
The fusion of two reproductive cells formed by each of the two parents
offspring inherits some of the genetic information from each parent
Fewer offspring growth takes more time
Need to find a mate
Changing environments
genetic diversity can be beneficial
Offspring may be less well adapted to current conditions
What is asexual reproduction? List its characteristics.
The production of genetically identical offspring from a single-parent
Simple, effective, efficient, and quick
Two cells that are genetically identical to the cell that produces them are produced.
Produce many offspring in a short period
Don't need to find a mate
In stable environments, genetically identical Offspring thrive
If conditions change, Offspring not well-adapted
What are the advantages and disadvantages of both asexual and sexual reproduction?
Asexual
Advantage: quick and efficient, creates many offspring, and simple
Disadvantage: no genetic diversity, offspring not adapted to new environments
Sexual:
Advantage: offspring adapt better to new environments, and genetic diversity
Disadvantage: takes longer, creates less offspring
Why is the surface area-to-volume ratio an important concept? How does it relate to cell growth/size? As a cell’s size increases, what happens to the ratio of its surface area to its volume?
As a cell grows, the surface area and volume increase; the larger the cell, the less efficient it becomes. If a cell has a smaller surface area to volume ratio, then it will be more efficient
In what type of cells does the cell cycle occur? (prokaryotes or eukaryotes
Prokaryotes: binary fission
Eukaryotes: cell cycle
What are the stages (phases) of interphase? What happens in each phase of interphase
G1: cells increase in size and synthesize (make) new organelles
S: DNA replication
G2: organelles and molecules required for cell division are produced
Chromosomes:
Threadlike structure within the nucleus that contains genetic information
sister chromatids (chromatids):
Single strand of DNA
Centromere:
The point at which two strands of chromosomes connect
spindle fibers:
a network of filaments that are formed during the cell division process
Centrioles:
a type of microtubules that helps form the mitotic spindle
Chromatin:
DNA tightly coiled around histone proteins
In what phase do cells duplicate their DNA?
Interphase (s Phase)
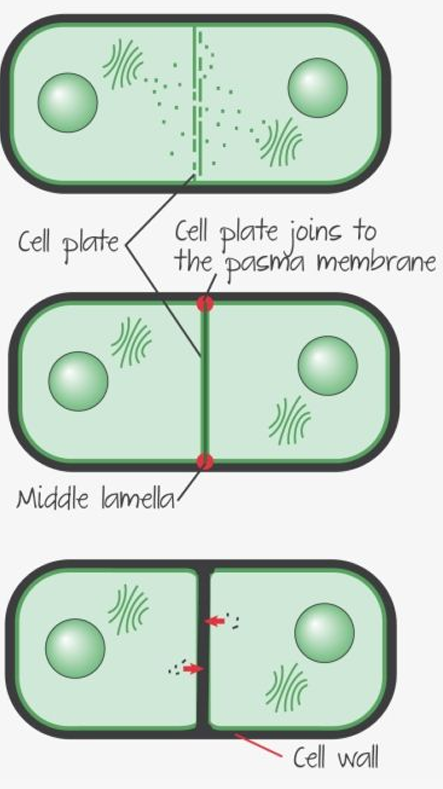
What is cytokinesis? How does this process differ in animal cells vs. plant cells?
Cytokinesis is the splitting of the cytoplasm into two. In plant cells, a cell plate forms halfway between divided nuclei, and then the cell plate joins the membrane, splitting the cell. In animal cells, microfilament rings form and pinch the cytoplasm, creating two cells.
How many chromosomes will the cell have after the S phase?
46
How many sister chromatids are present during prophase?
92
How many chromosomes will each new daughter cell have following mitosis?
23
What moves the chromatids during mitosis?
Miotic Spindle fibers
How does the DNA structure differ in each phase of the cell cycle? Why is this important?
In g1, it's not condensed
2 phase is replicated
G2 its xs
Prophase condensing full-on xs
Metaphase- condensed xs
Anaphase- chromatids are pulled apart
Telaphase- condescend and on opposite sides of the cell
Mitosis- entangled together
Cytoskensies- retangle within each other still
stages of mitosis
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
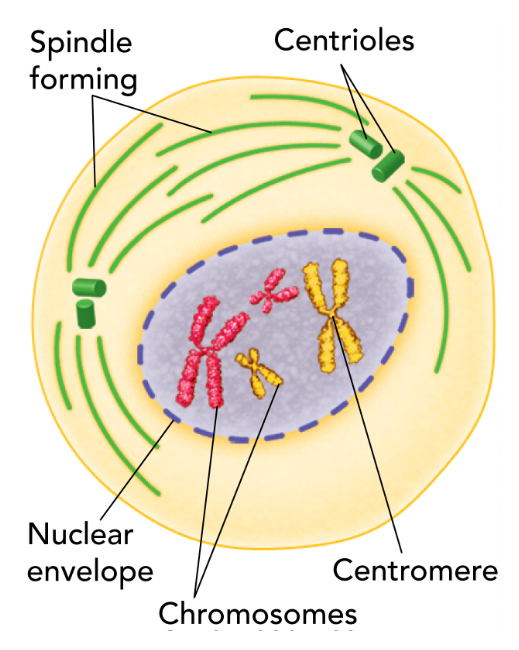
prophase
nucleus condenses and chromosomes become visible
centrioles go to side of the cell
spindle starts to form
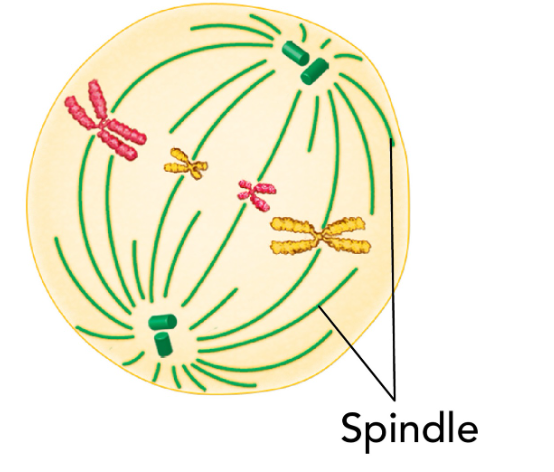
metaphase
shorterst phase
chromosomes line up in the center of cell
nucleus and its membrane dissasembles
miotic spindle attaches to centrioles
anaphase
sister chromatids are pulled apart and move along the spindle fibers in opposite ends in the cell
the spindel fibers are getting disasembles until chromosomes are esch on one side of the cell
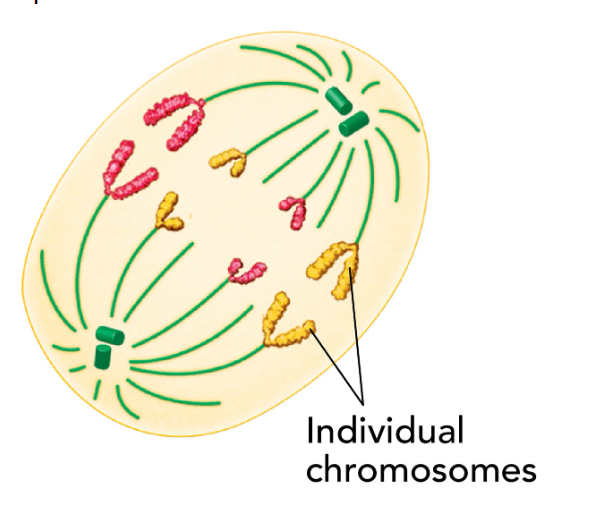
in anapahse when do the the spindle fibers stop dissasembleing
chromosomes are completely seperted and movement stopped
telaphase
nuclear envolope reforms
chromosomes retangle tmeselves with chromatin
nucleus becomes visible
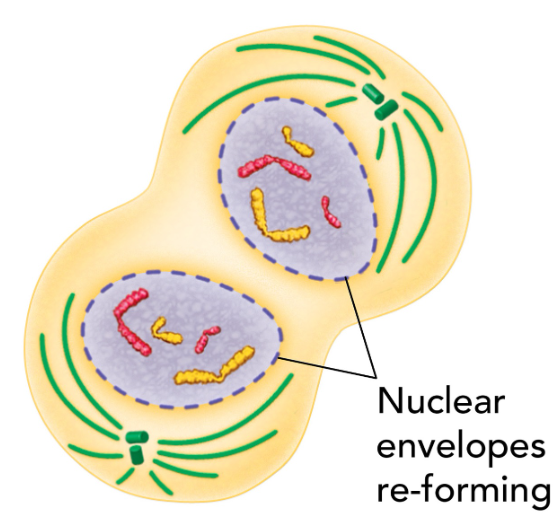
when mitosis is complete what continues
cell divison
cytokeneisis in animal cells
microfilimant ring forms
pinchs the cytoplams
2 cells created
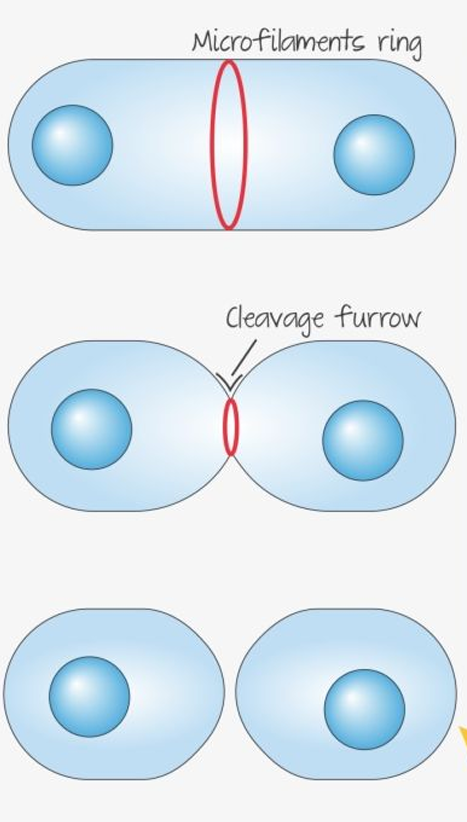
cytokenesis in plant cells
cell plate forms hald way between divided nuclei
cell plate joins membrane, splitting the cell