Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
Adaptations of single celled organisms
Short diffusion distance (thin membrane and thin and flat cell)
Large SA : vol ratio (usually long and flat)
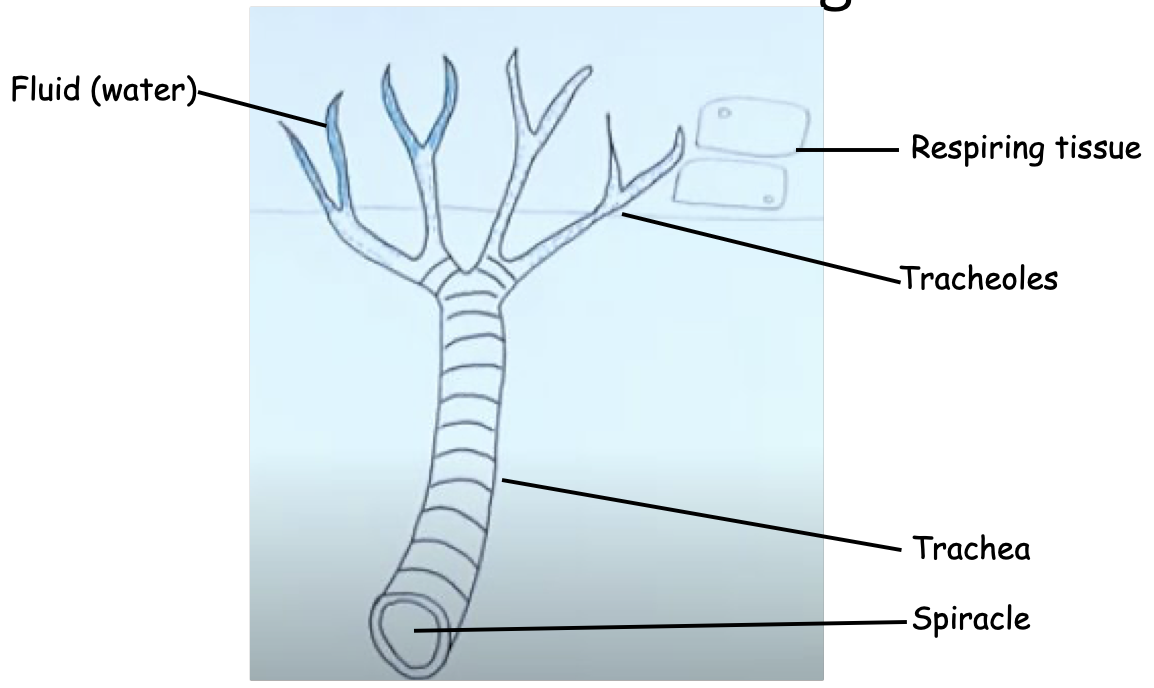
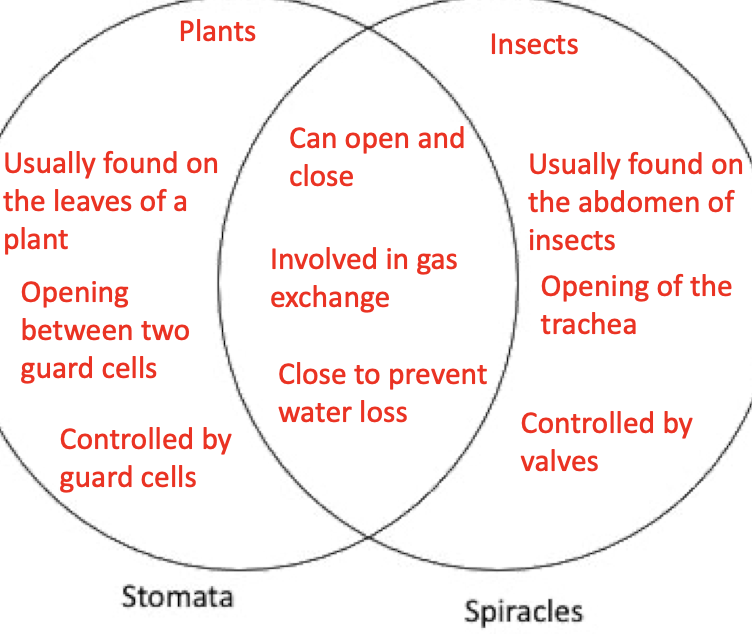
Spiracles
Pores on surface that can open/close to allow diffusion
Tracheae
Large tubes full of air that allow diffusion
Tracheoles
Smaller branches from tracheae, permeable to allow gas exchange with cells
Why do the trachea not collapse?
Trachea are supported by strengthened rings made of cartilage to prevent them from collapsing.
How is a tracheole different to a tracheae?
The trachea divide into smaller dead-end tubes called tracheoles
Describe 3 ways in which respiratory gases move in and out of the tracheal system
Along a diffusion gradient: O2, spiricle to respiring products; CO2, respiring cells to spircles
Mass transport
The ends of the tracheoles are filled with water
Limitations of the tracheal system
Relies mostly on diffusion, only effective if there’s a short diffusion pathway.
Explain how an insect’s tracheal system is adapted for gas exchange
Tracheoles have thin walls - short diffusion pathway
High numbers of highly branched tracheoles - short diffusion pathway, large SA:vol ratio
Tracheae provide tubes full of air - so faster rate of diffusion
Contracting of abdominal muscles changes pressure in body, causing air to move in/out - maintains concentration gradient for diffusion
Fluid in end of tracheoles drawn into tissues by osmosis during exercise; as fluid is removed, air fills tracheoles; so rate of diffusion to gas exchange surface increases as diffusion is faster through air
Adaptations in terrestial insects that allow efficient gas exchange while limiting water loss
Thick waxy cuticle/exoskeleton - increases diffusion distance so less water loss (evaporation)
Spiracles can open to allow gas exchange and close to reduce water loss (evaporation)
Hairs around spiracles - trap moist air, reducing water potential gradient so less water loss (evaporation)
Stomata vs Spiricles