Organic Chemistry 12: Separations and Purifications
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
A/an [...] combines two immiscible liquids, one of which easily dissolves the compound of interest
extraction
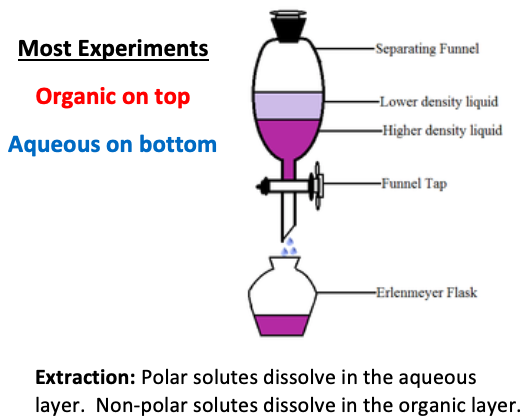
In an extraction, the [polar or nonpolar] layer is the organic layer and dissolves nonpolar compounds
nonpolar
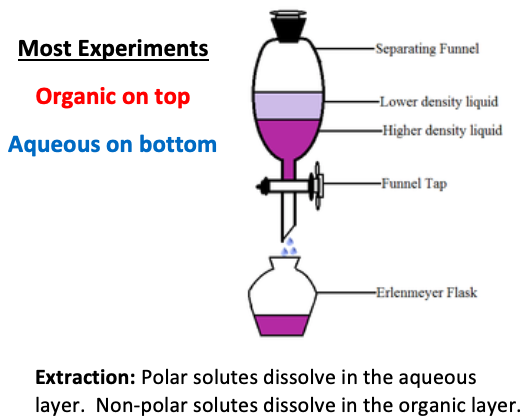
In an extraction, the [polar or nonpolar] layer is the aqueous (water) layer and dissolves compounds with hydrogen bonding or polarity
polar
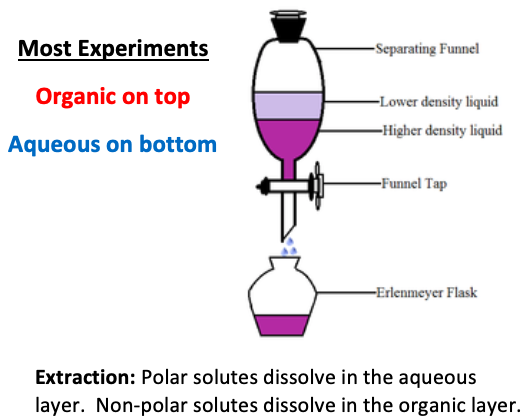
A/an [...] is the reverse of an extraction. A small amount of solute that dissolves impurities is run over the compound of interest
wash

During a filtration, a solid, also known as the [...], is isolated from a liquid, also known as the [...]
residue
filtrate

[... filtration] can be used to collect solid product, although generally [... filtration] is used for this purpose because it is faster
gravity filtration
vacuum filtration

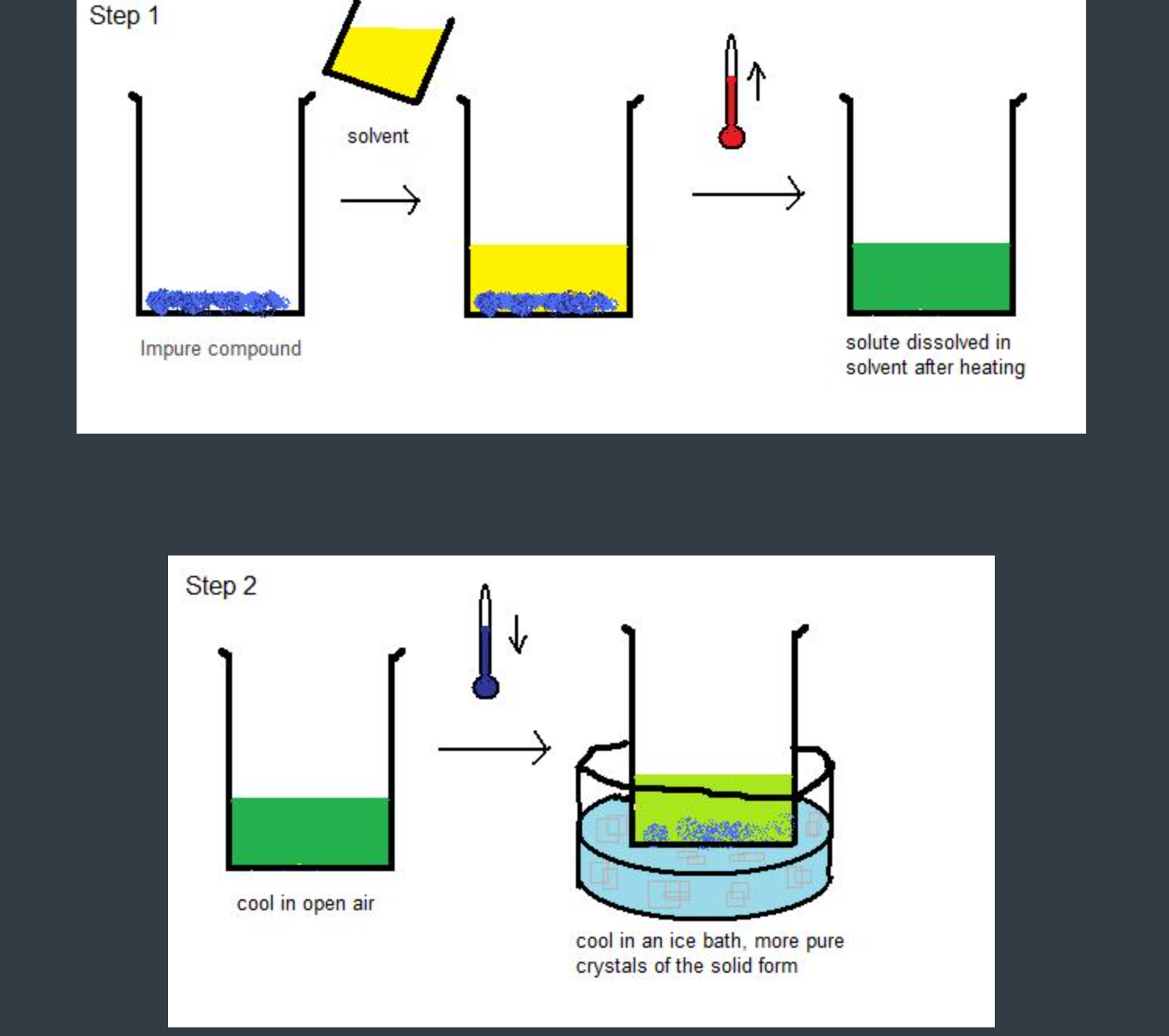
[...], also known as [...], is a procedure for purifying an impure compound in a solvent
recrystallization
fractional crystallization
- an impure compound is dissolved to prepare a highly concentrated solution at a high temperature
the solution is cooled
decreasing the temperature cause the solubility of the impurities in the solution and the substance being purified to creaceas
the impure substance then crystallized before the impurfires -assuming that there was impure substance there were imprttutes
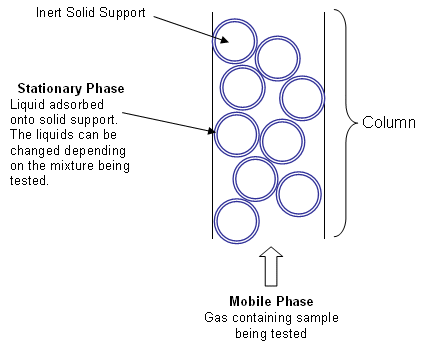
Chromatography is a laboratory technique for the separation of a mixture based on [...]
how fast each component travels through a structure
the mixture is dissolved in a fluid called the mobile phase which carries it through a structure another material called the stationary phase
the various constituents of the mixture travel at different speeds causing them to separate
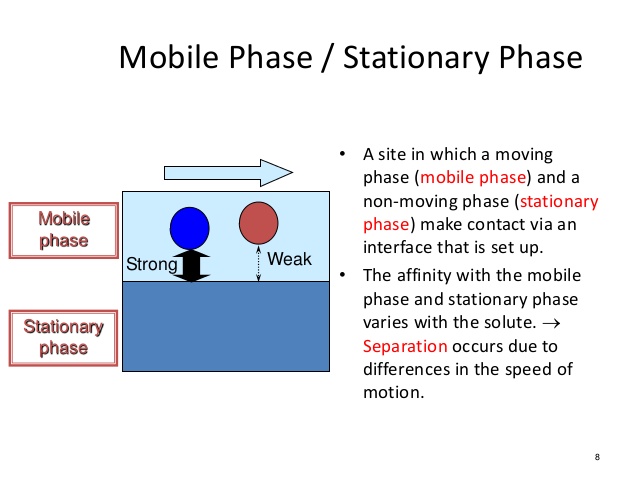
In chromatography, the stationary phase is typically [...] and this causes [...] molecules to elute slower
polar and polar
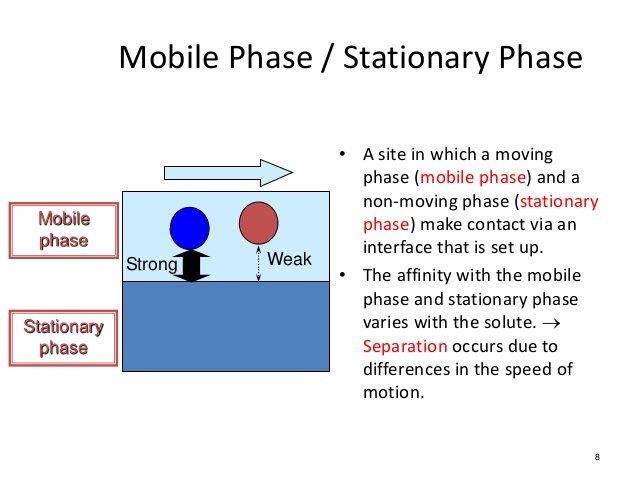
In chromatography, the mobile phase is typically [...] and this causes [...] molecules to elute faster
nonpolar
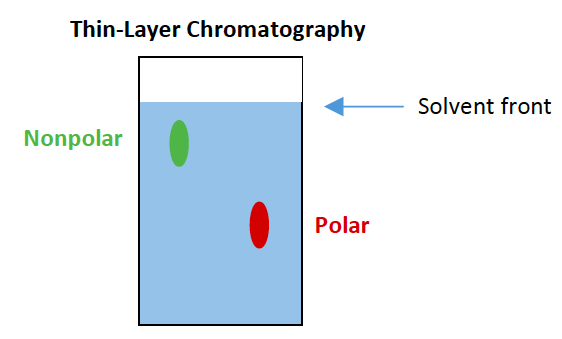
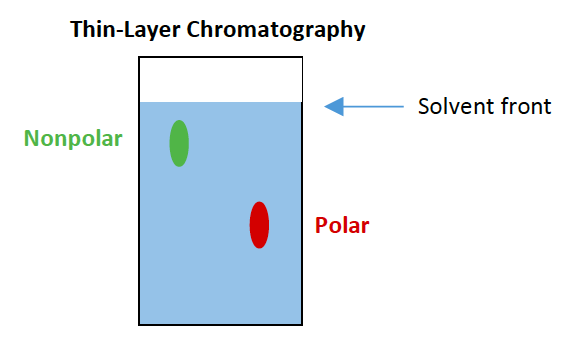
![<p><span>In a typical thin-layer chromatography setup, the spot that moves farthest is the </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> substance and the spot that moves the shortest distance is the </span><span style="color: mediumseagreen"><strong>[...]</strong></span><span> substance</span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/dcb58246-2e40-4b93-8598-5ef33aba7299.png)
In a typical thin-layer chromatography setup, the spot that moves farthest is the [...] substance and the spot that moves the shortest distance is the [...] substance
nonpolar and polar
the stationary phase is typically silica gel which is polar
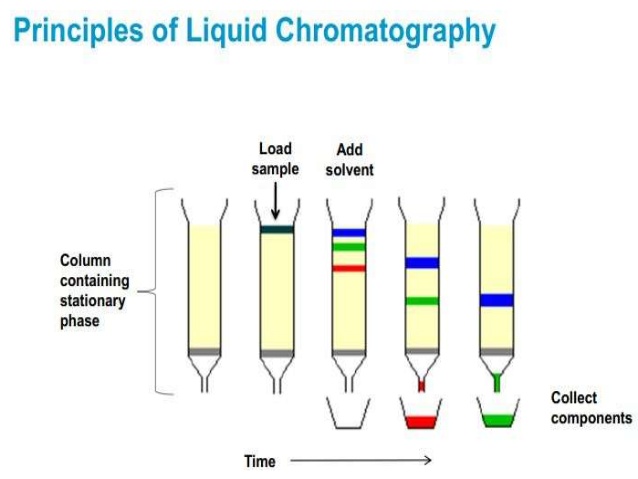
In liquid chromatography, [...] is a common stationary phase while [...] or another nonpolar liquid is used as the mobile phase
silica
tuluence
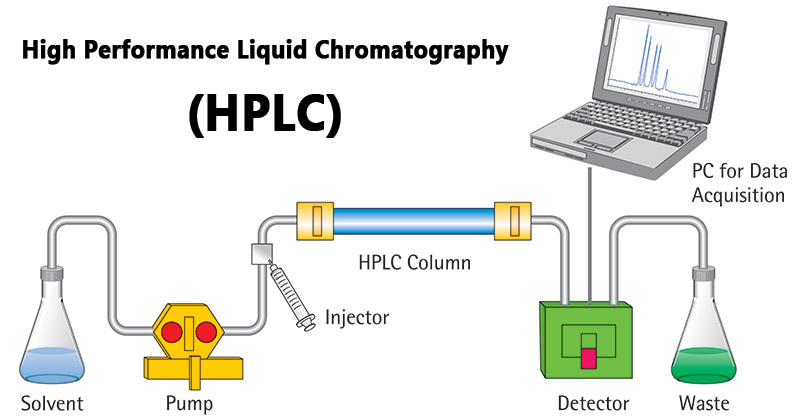
[... chromatography] relies on pumps to pass a pressurized liquid solvent containing the sample mixture through a column filled with a solid adsorbent material
high-performance liquid chromatography
this gives HPLC higher resolving power
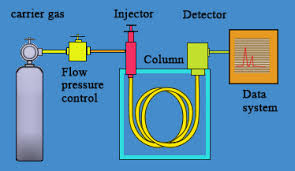
In gas chromatography, the liquid sample is vaporized before separation. Molecules are separated based on their [...] and [...]
polarity and boiling point
the stationary phase is a thin layer of material applied to the inside of the column
typically the polarity if the stationary phase matches that of the solute
the mobile phase is an entry gase
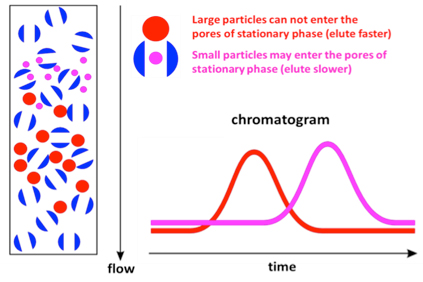
Gel-filtration chromatography separates molecules based on their [...]
size
also known as size-exclusion chromatography
smaller molecules enter the porous gel beads causing them to elute slower
larger molecules do. not fit in the pores so they elute faster
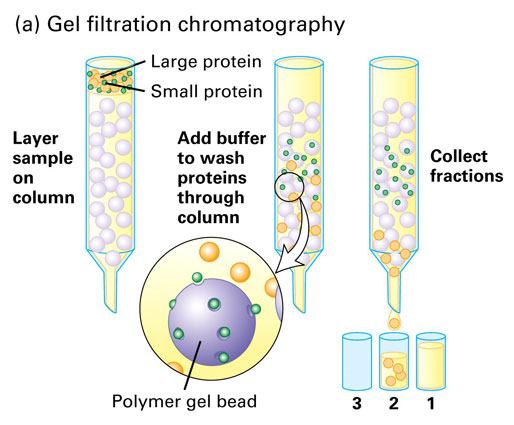
In size-exclusion chromatography, large molecules will elute [first or last]
first
larger molecules do not fit in the pores so they elute faster
smaller molecules enter the porous gel beads causing them to elute later
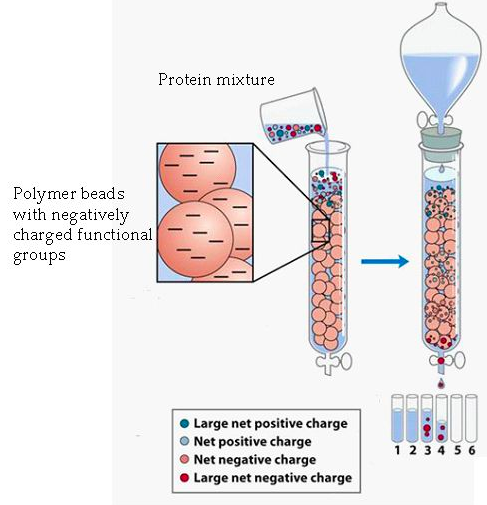
Ion exchange chromatography separates proteins by their [...]
net charge
the column is filled with charged beads: either positivity or negativity charged
cation exchange; negatively charged beads: negatively charged proteins elute first
anion exchange: positively charged beads positively charged proteins elute first
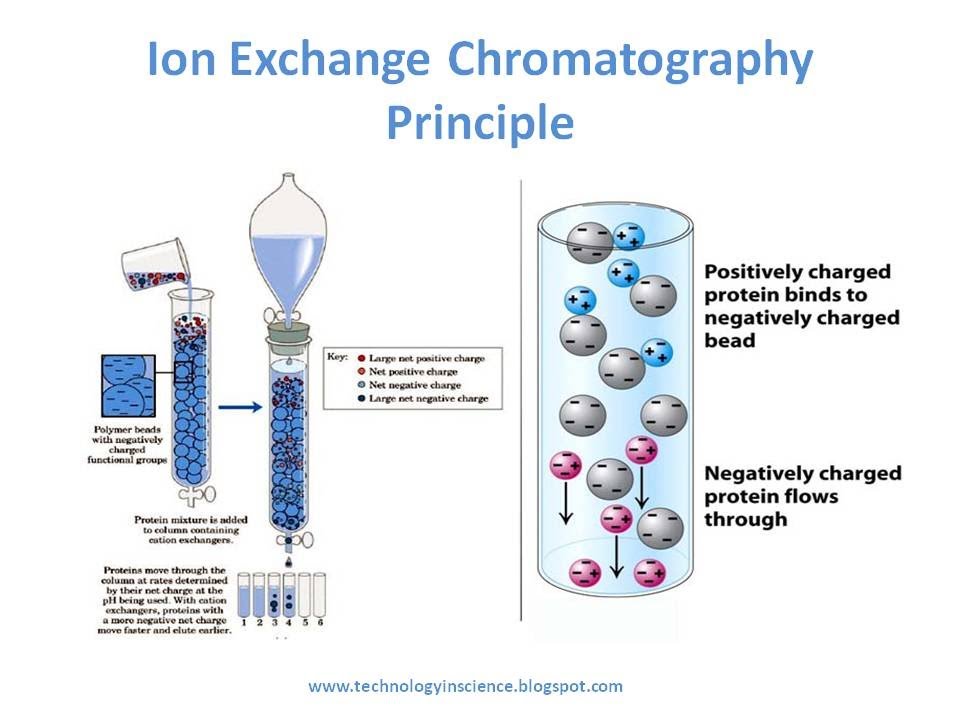
In anion exchange chromatography, the beads are [positively or negatively] charged and this causes [positively or negatively] charged proteins to elute first
postivitely, positivity
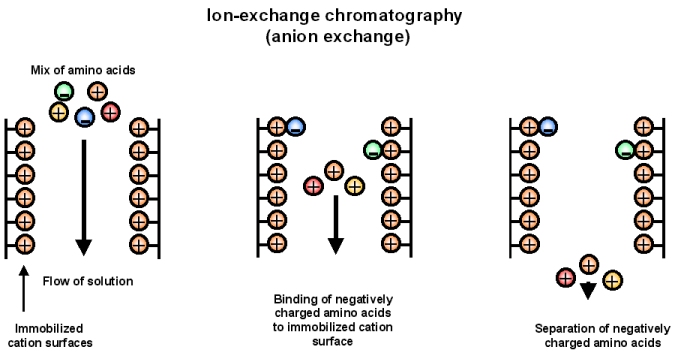
In cation exchange chromatography, the beads are [positively or negatively] charged and this causes [positively or negatively] charged proteins to elute first
negativity
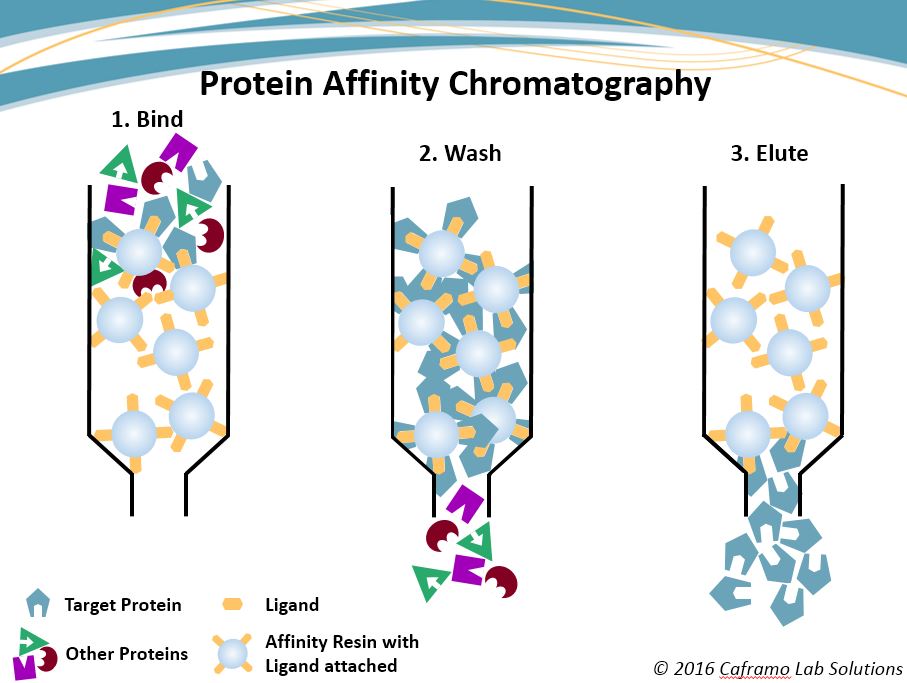
Affinity chromatography separates proteins based on [...]
their affinity for a specific ligand
beads are bound to a specific ligand and proteins with a high affinity for that ligand will bond to the breads
proteins with a low affinity for the ligand will elute first
In a typical thin-layer chromatography setup, the stationary phase is made up of [substance] which is [polar or nonpolar]
silica gel which is polar
polar molecules are slowed by the stationary phase, nonpolar molecules are repelled by the stationary phase and elute first
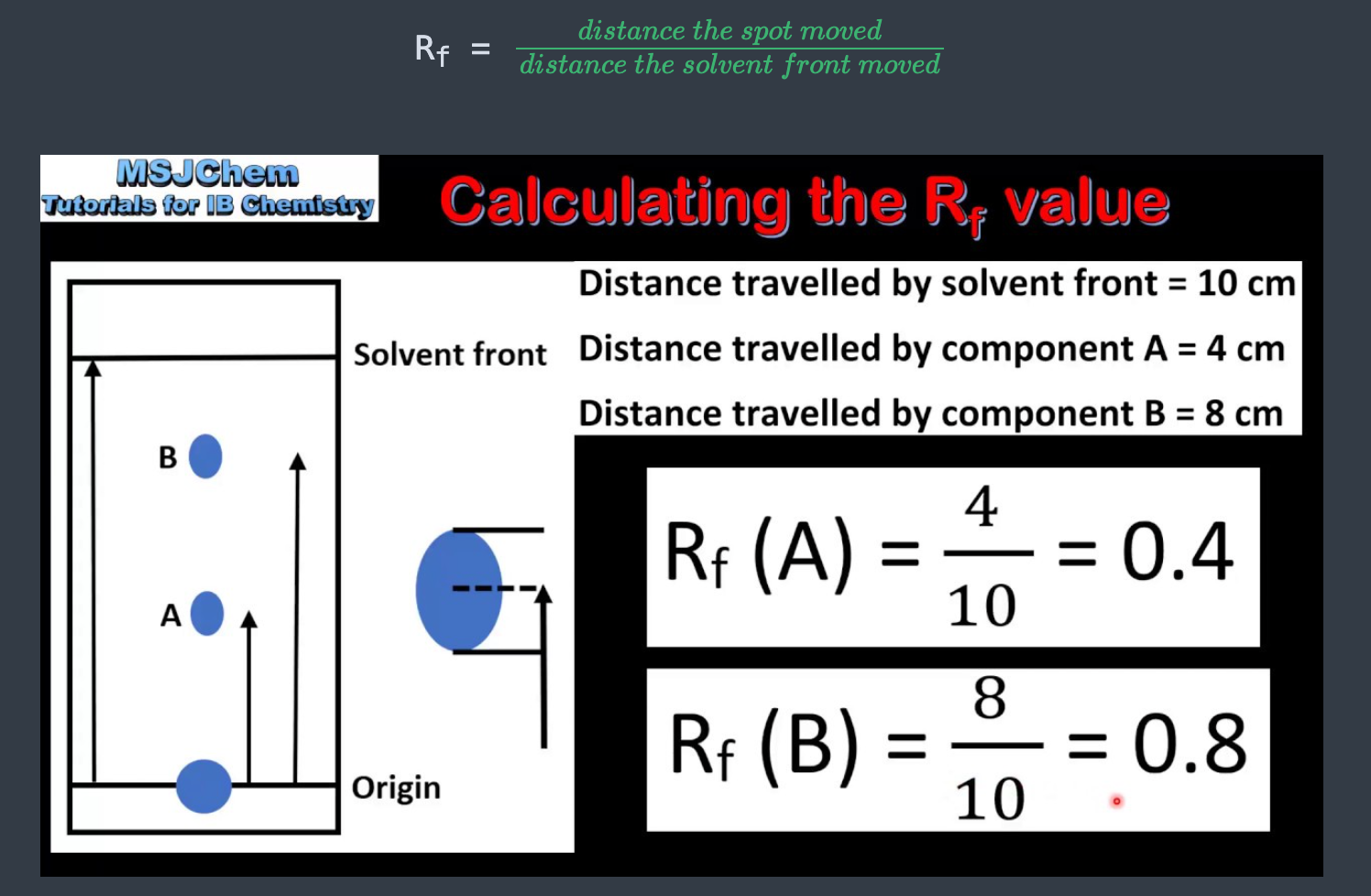
The retention factor in thin-layer chromatography is:
Rf = [...]
A distillation separates liquids according to differences in their [...]
boiling points
the liquid with the lowest BP vaporizes first and its collected as the distillate
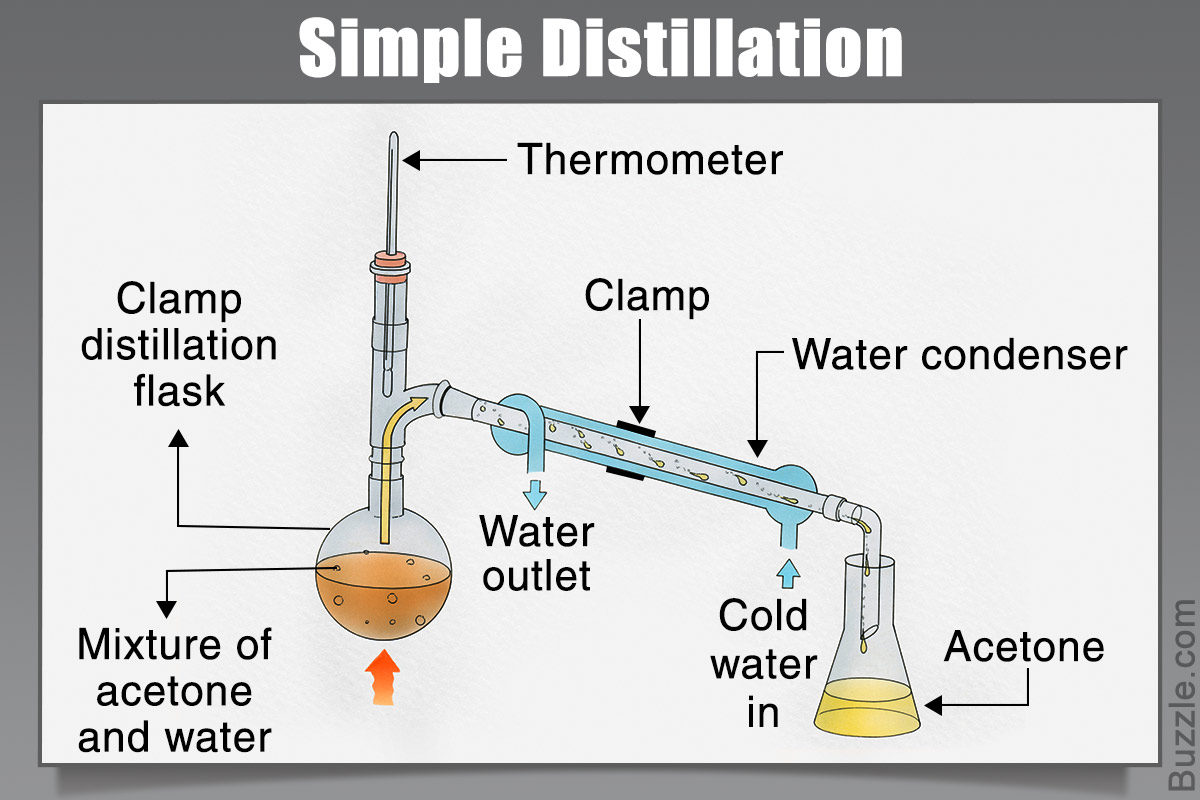
Simple distillation can be used if the boiling points are under 150°C and are at least [#°C] apart
25 °C
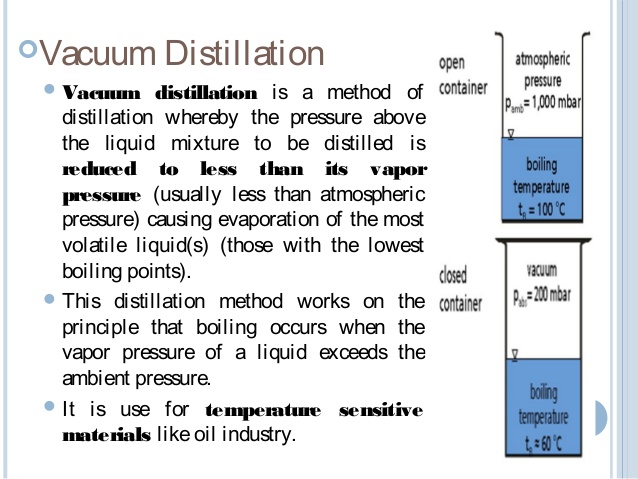
Vacuum distillation should be used if the boiling points are over 150°C to prevent degradation of the product. The vacuum [...], which decreases the BP of the liquid
lowers the air pressure
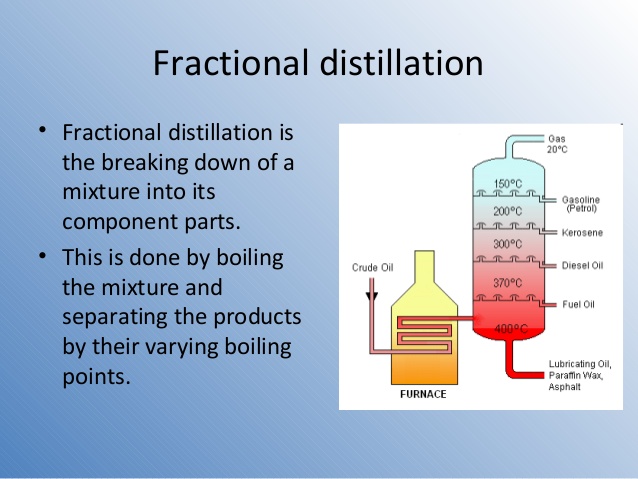
Fractional distillation is a process by which components in a mixture are separated into different parts (called fractions) according to their different [...]
boiling points.