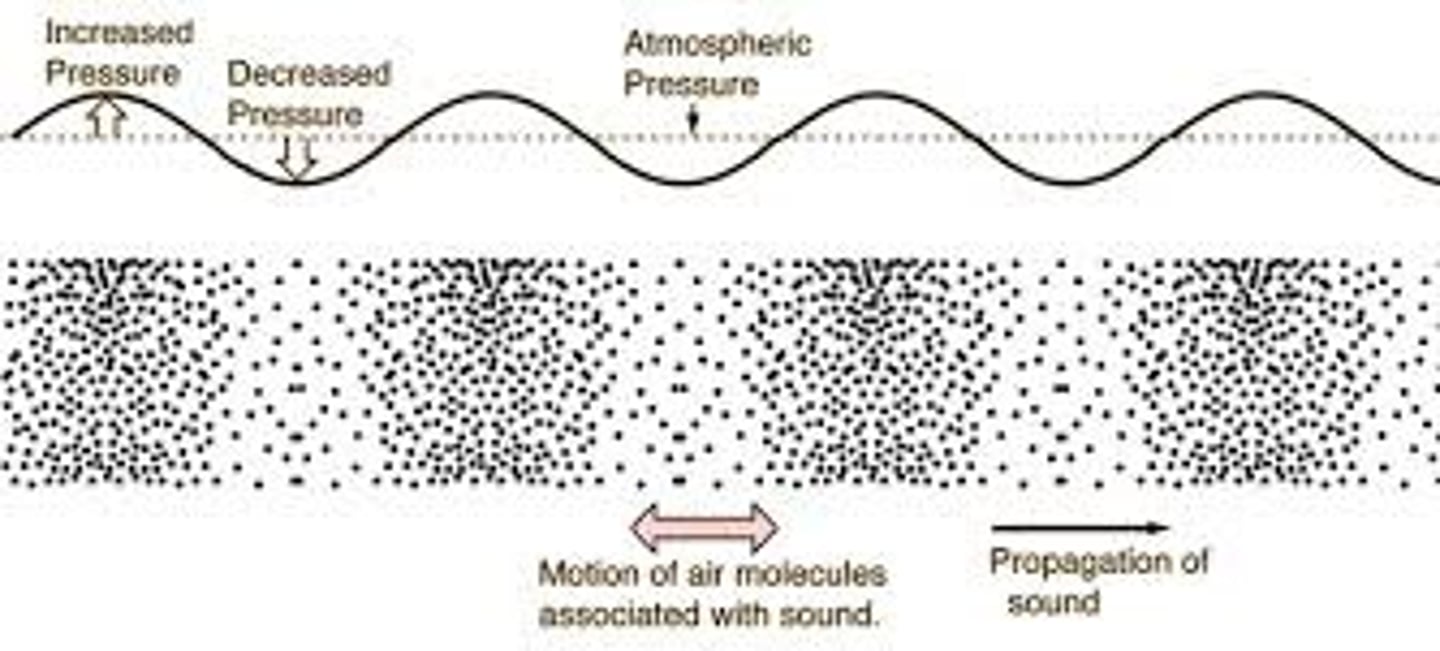
Waves
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
Any disturbance that transmits energy through matter or space is called a _________________
wave
How is energy (a wave) transmitted through a medium?
The energy causes the particles of a medium to vibrate (move back and forth). Collisions between neighboring particles transfer the energy .
***Remember: The particles of a medium are temporarily displaced from their resting position and are NOT carried along with the wave.
Material through which a mechanical wave travels
Medium - any matter (solid, liquid or gas)
All waves are classified as either ____ or ____.
Mechanical or Electromagnetic
Type of wave that requires a medium.
Mechanical waves
Type of wave that can travel through the vacuum of space - DOES NOT require a medium.
Electromagnetic waves
Sound, water and seismic waves are examples of this type of wave
Mechanical wave
True or False: Sound can be heard in a vacuum.
False: A vacuum is empty space (no matter). Sound waves must have a medium (matter) in order to travel. Sound waves are mechanical waves.
UV, Infrared, x-rays, visible light, gamma, microwaves, radio waves are examples of this type of wave
Electromagnetic wave
This wave washes up on tiny beaches
Microwaves, ha, ha - just a joke!
True or False:
Waves carry energy and matter from one place to another
FALSE - Think Nemo!
Waves carry energy, NOT matter
True or False
The particles in a transverse wave move PARALLEL to the direction that the wave is traveling
FALSE - The particles in a transverse wave move PERPENDICULAR to the direction that the wave is traveling
True or False:
The particles in a longitudinal wave move parallel to the direction that the wave is traveling
TRUE dat yo!
(Longitudinal waves cause the particles of the medium to vibrate back and forth along the path that the wave travels.)
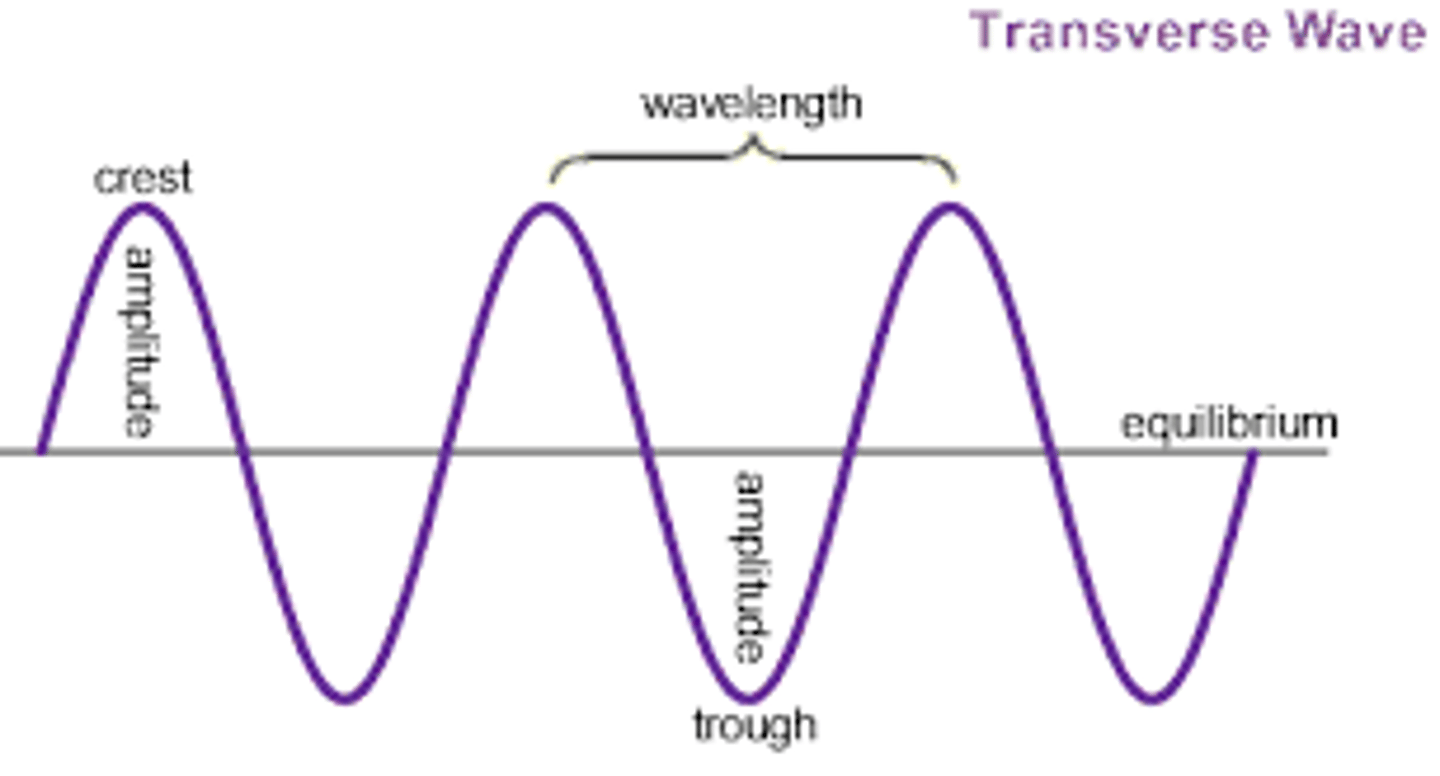
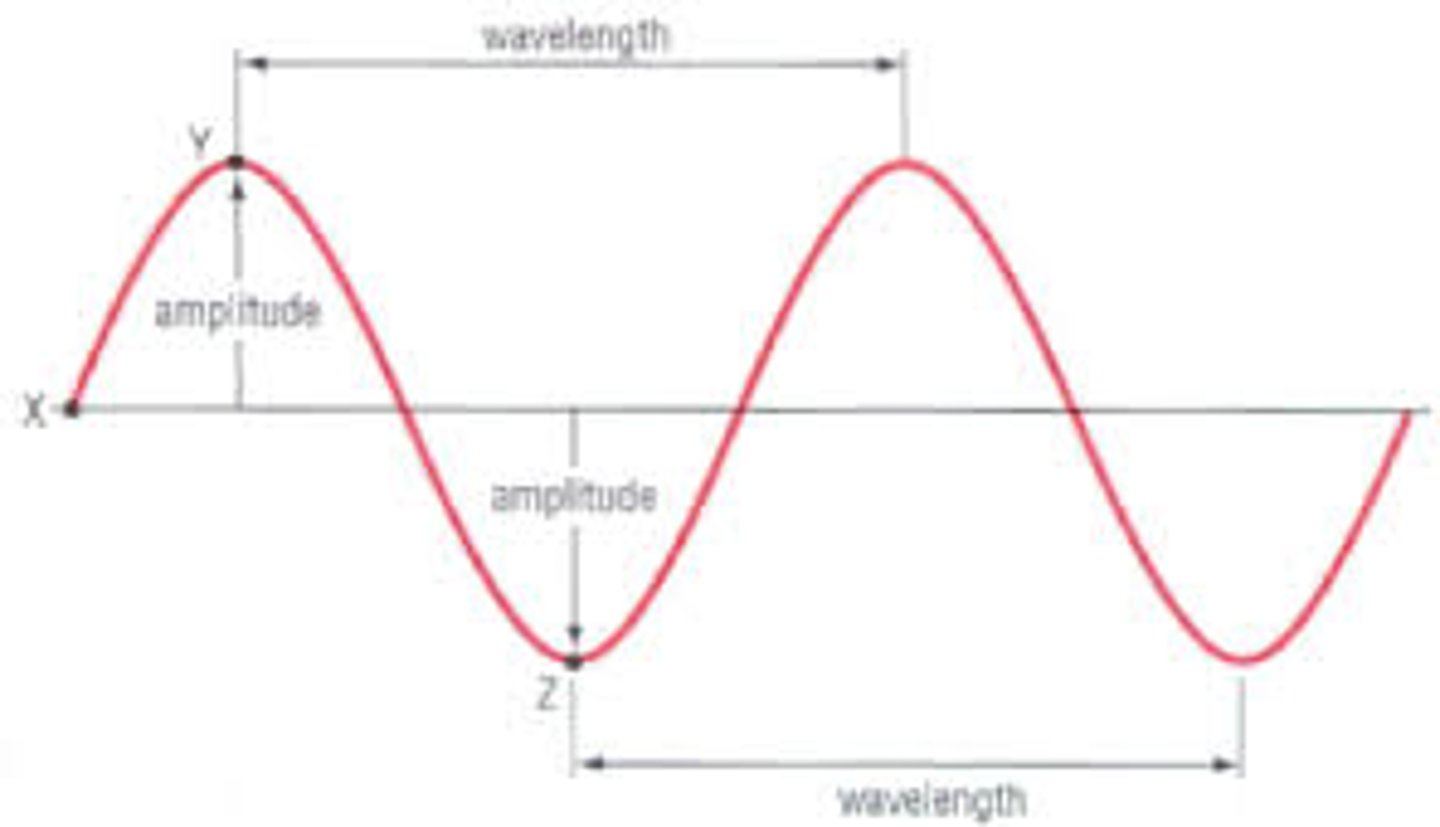
Draw a typical transverse wave - label the crest, trough, wavelength & amplitude
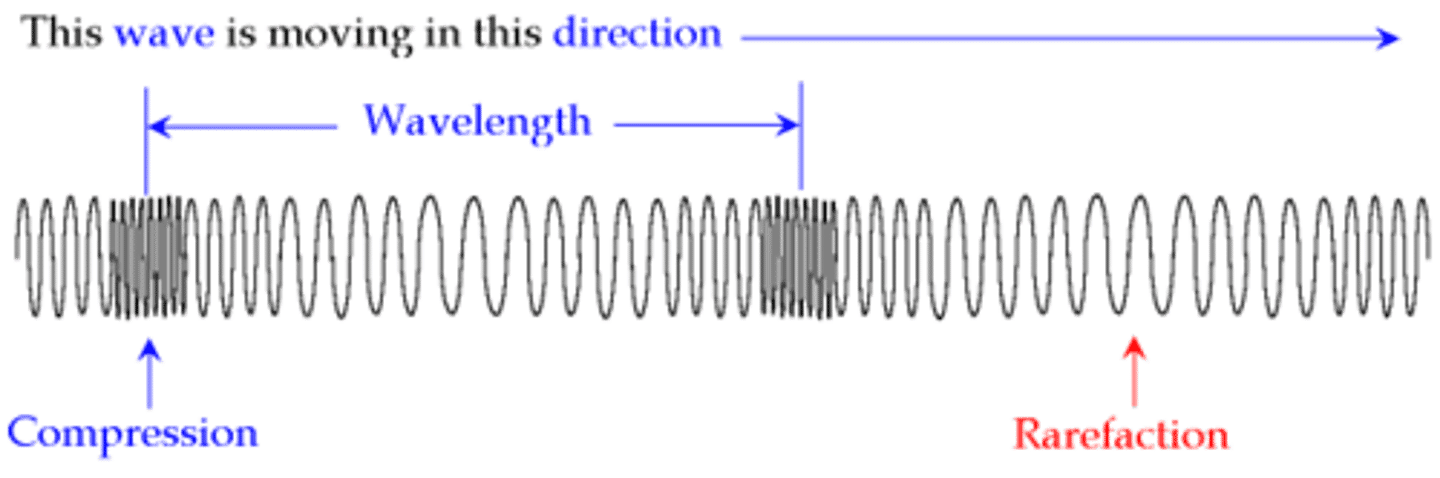
Draw a typical longitudinal wave - label the compression, rarefaction, wavelength & amplitude
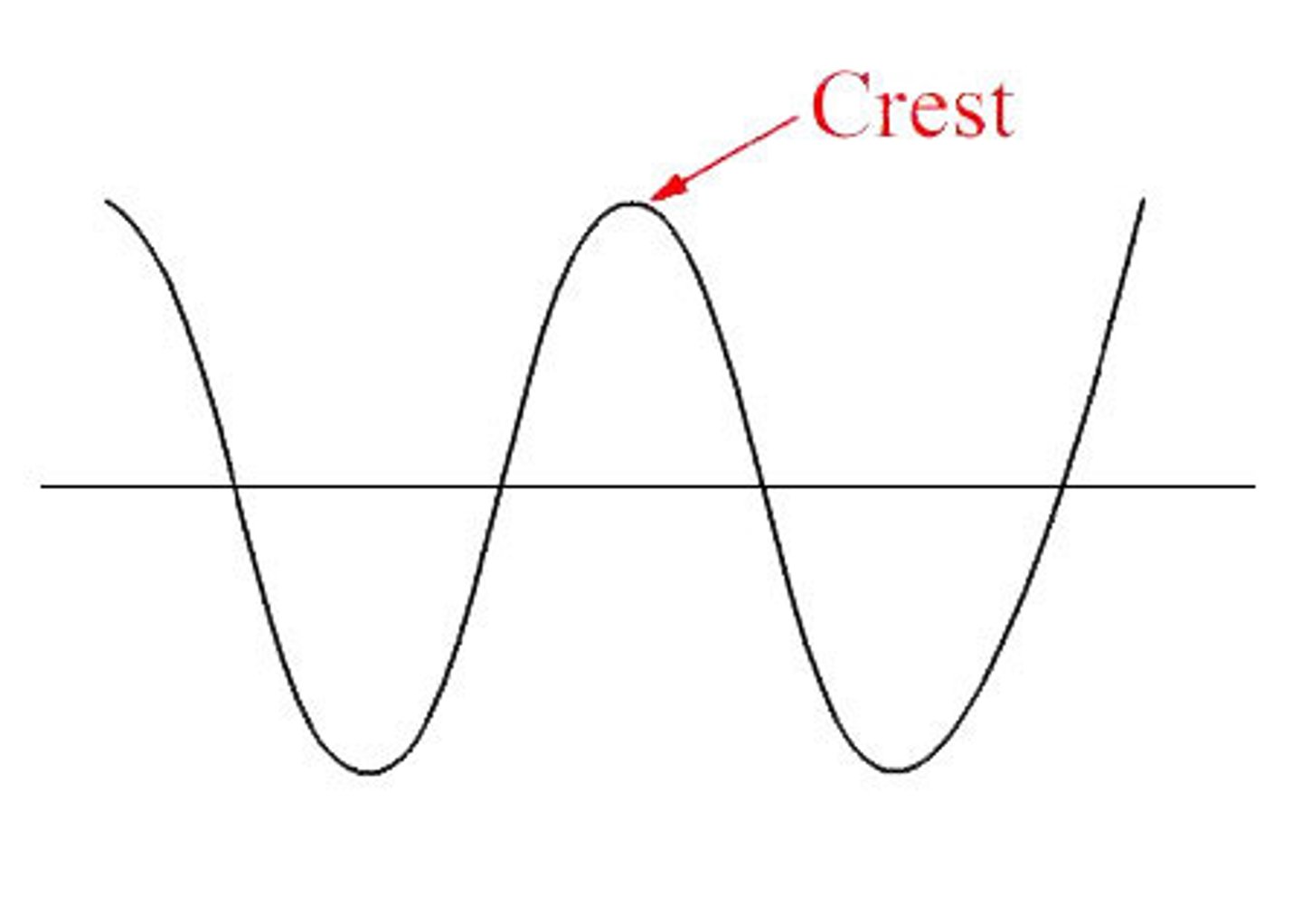
What is a crest?
Nope, not a brand of toothpaste - IT IS THE HIGH POINT OF A TRANSVERSE WAVE!
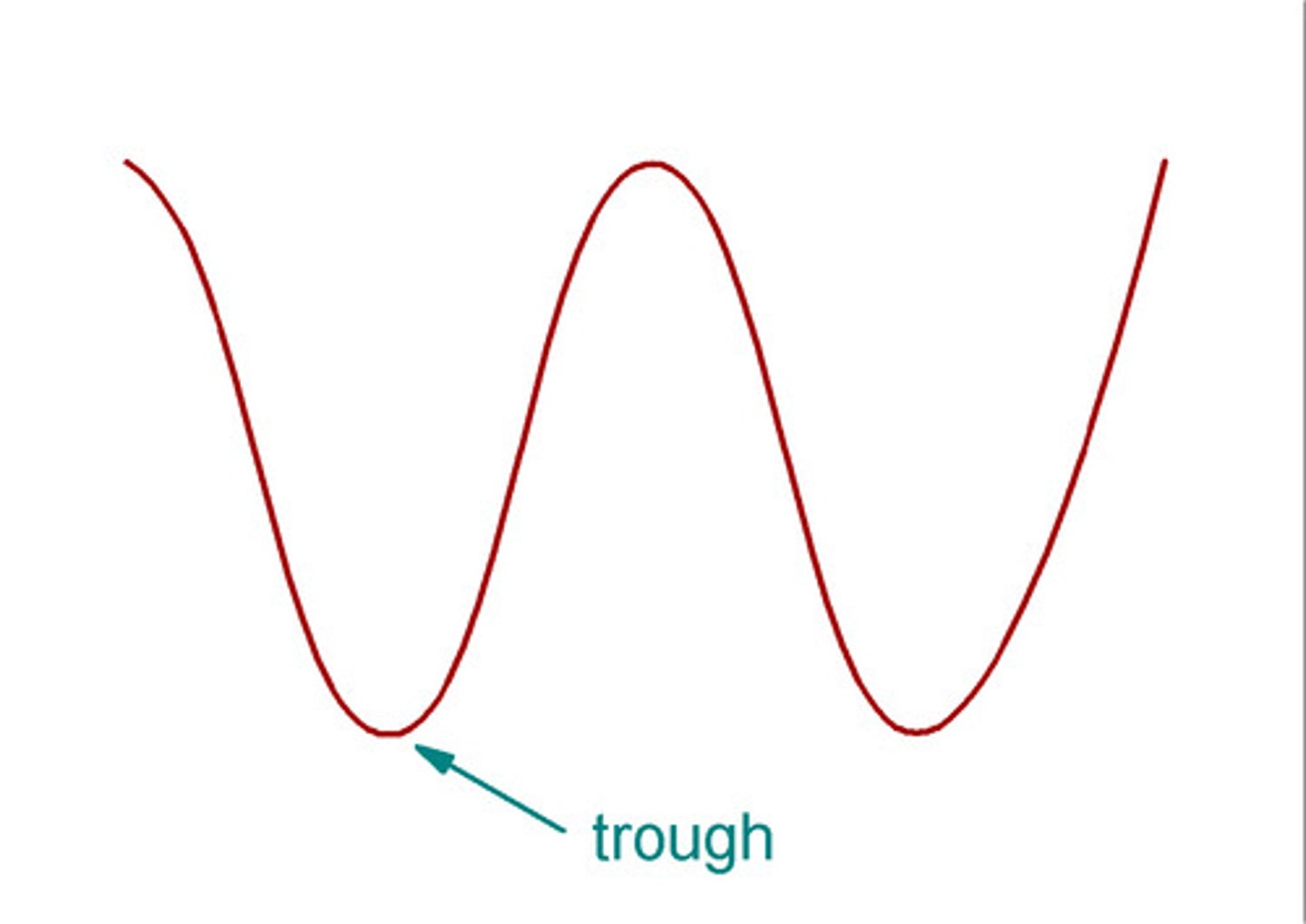
What is a trough?
True, it is a long narrow bucket from which farm animals eat, but that is NOT the answer.
IT IS THE LOW POINT OF A TRANSVERSE WAVE!
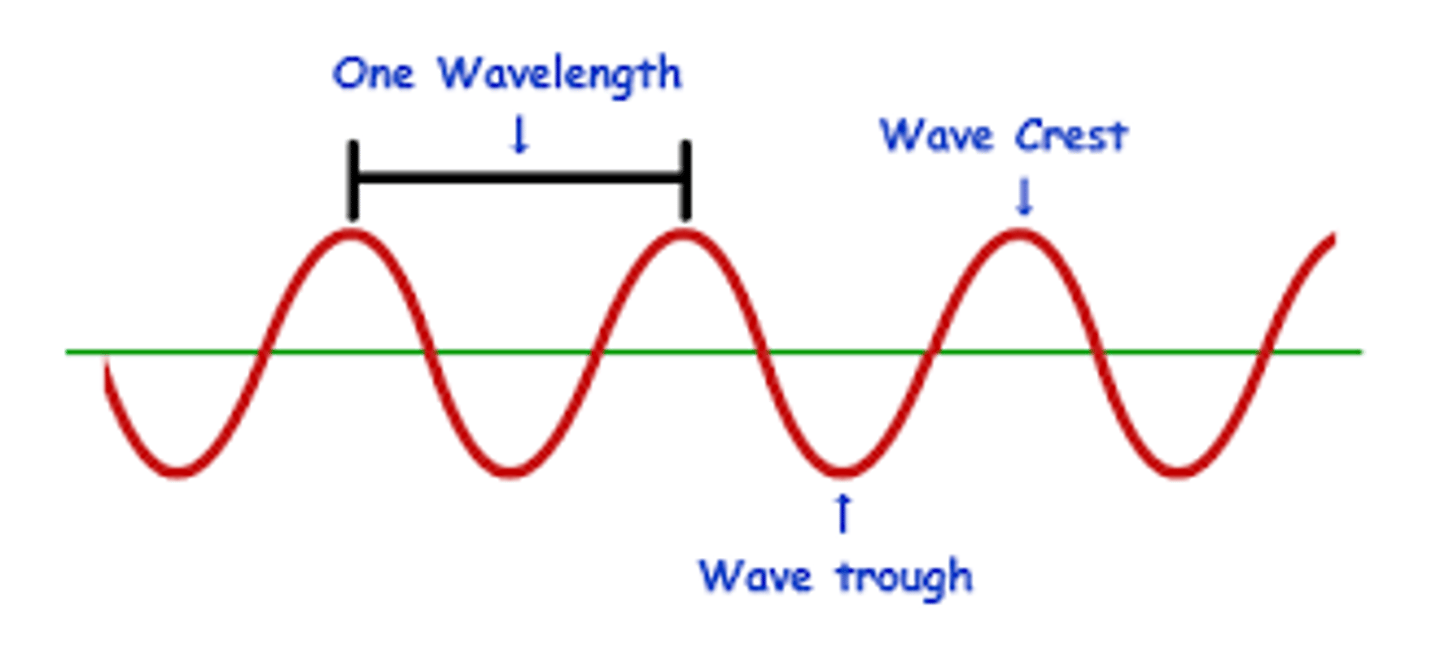
The distance from crest to crest OR trough to trough in a transverse wave is its ___.
wavelength
Identify the part of a longitudinal wave where particles of the medium are crowded together
compression
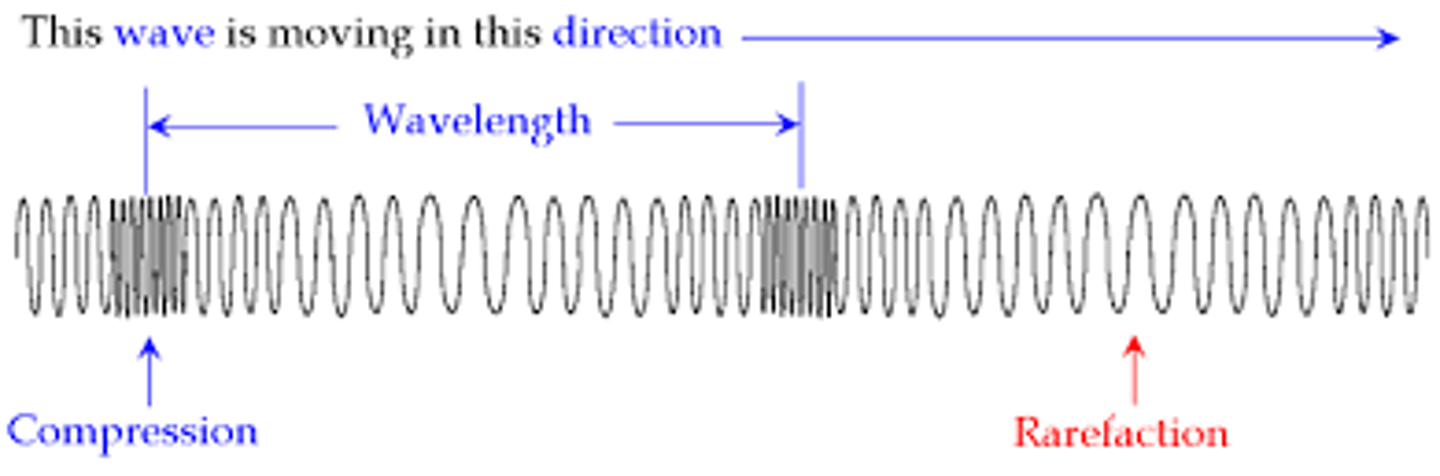
Identify the part of a longitudinal wave where particles of the medium are further apart (less crowded).
rarefaction
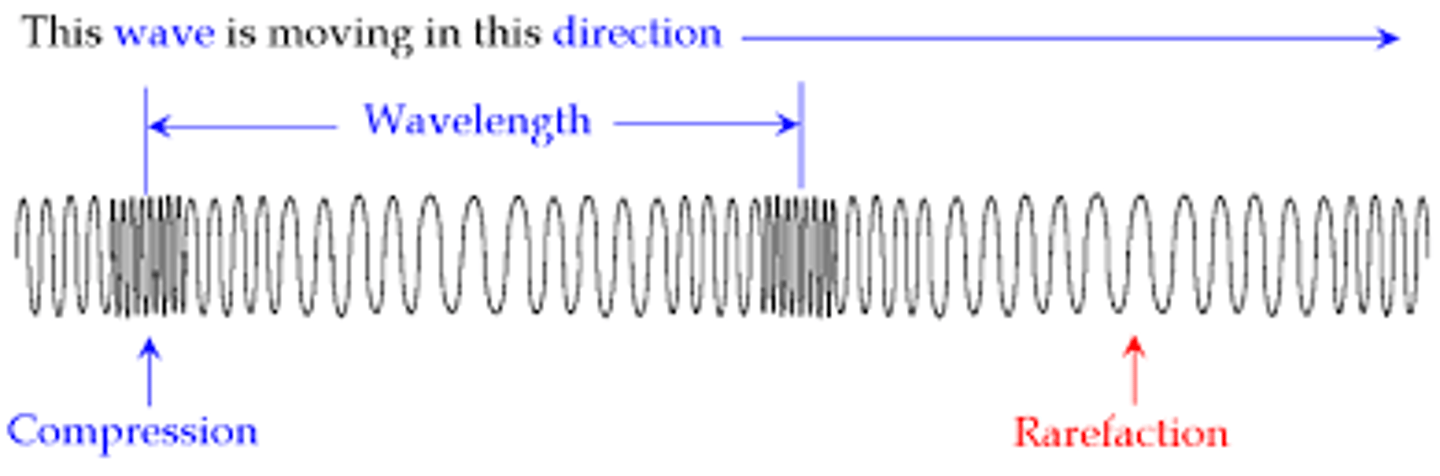
The distance from compression to compression OR rarefaction to rarefaction in a longitudinal wave is its ___.
wavelength
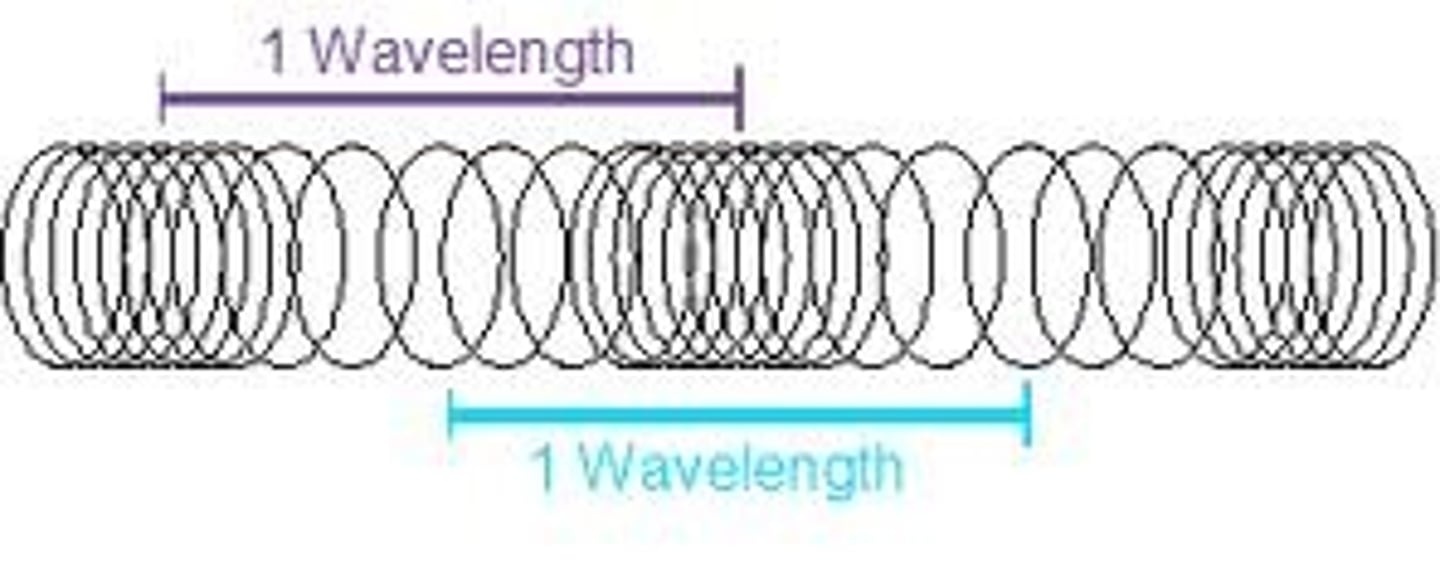
The amount of energy in a wave is called its ____. (Also referred to as the HEIGHT of a wave)
Amplitude
The distance from resting point of the medium to the crest or from resting point of the medium to the trough is called its ____.
Amplitude
Relationships:
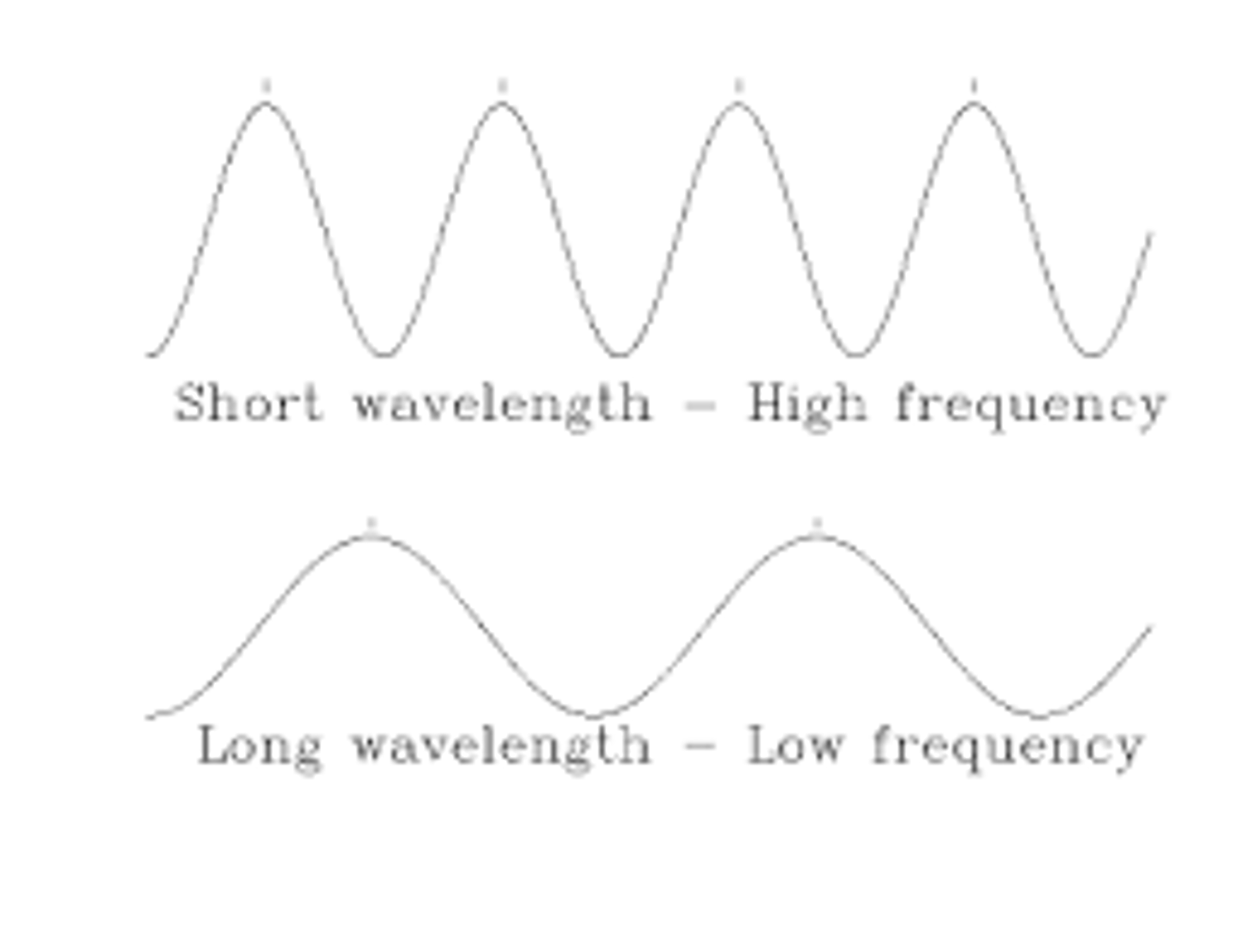
As the wavelength increases, the frequency _____.
decreases - the frequency of a wave is indirectly related its wavelength
Relationships (True or False):
The amplitude of a wave is directly related to its wavelength.
FALSE - Wavelength has NO EFFECT on the amplitude of a wave.
Relationships (True or False):
The amplitude of a wave is indirectly related to its frequency.
FALSE - Frequency has NO EFFECT on the amplitude of a wave.
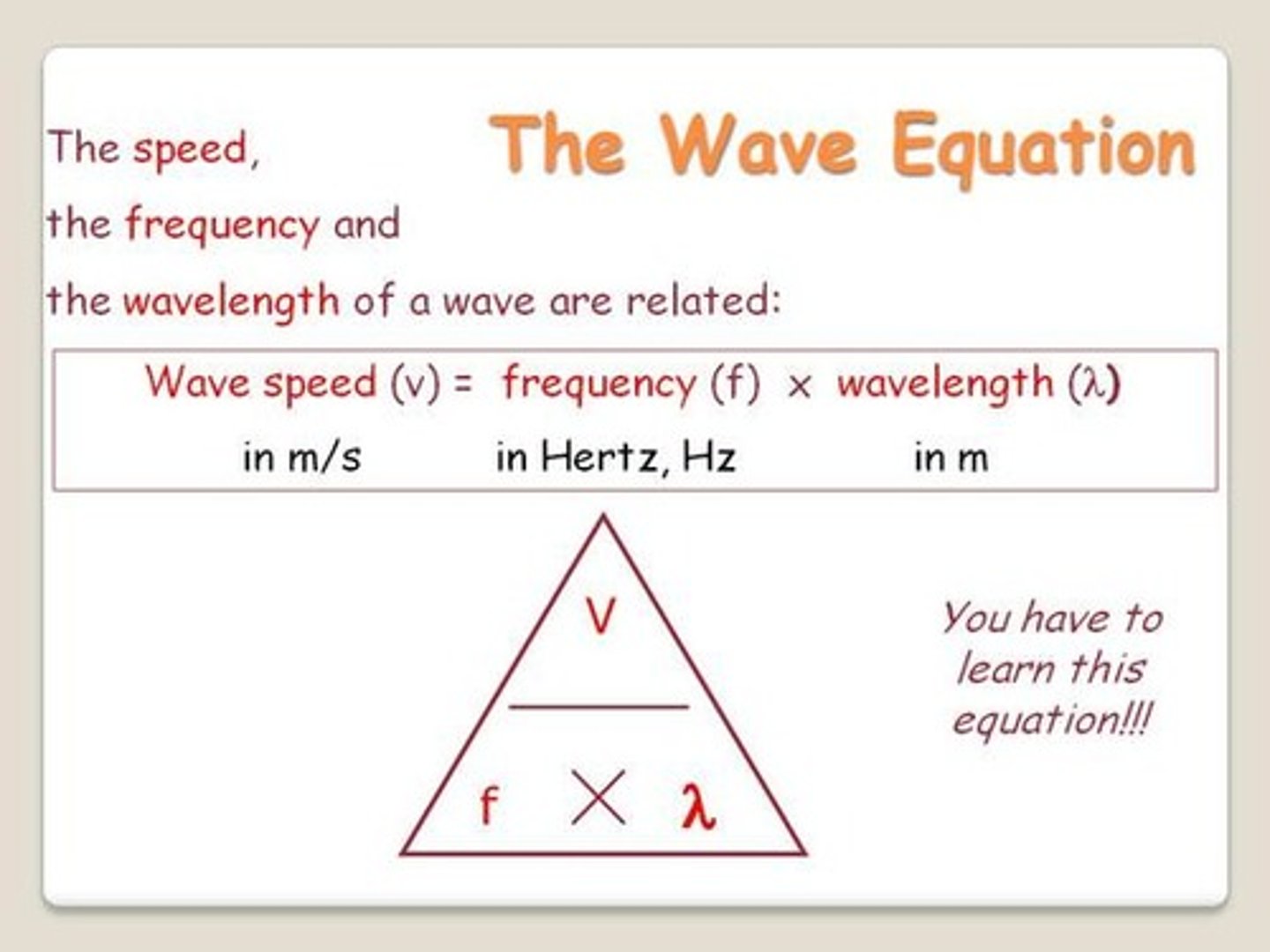
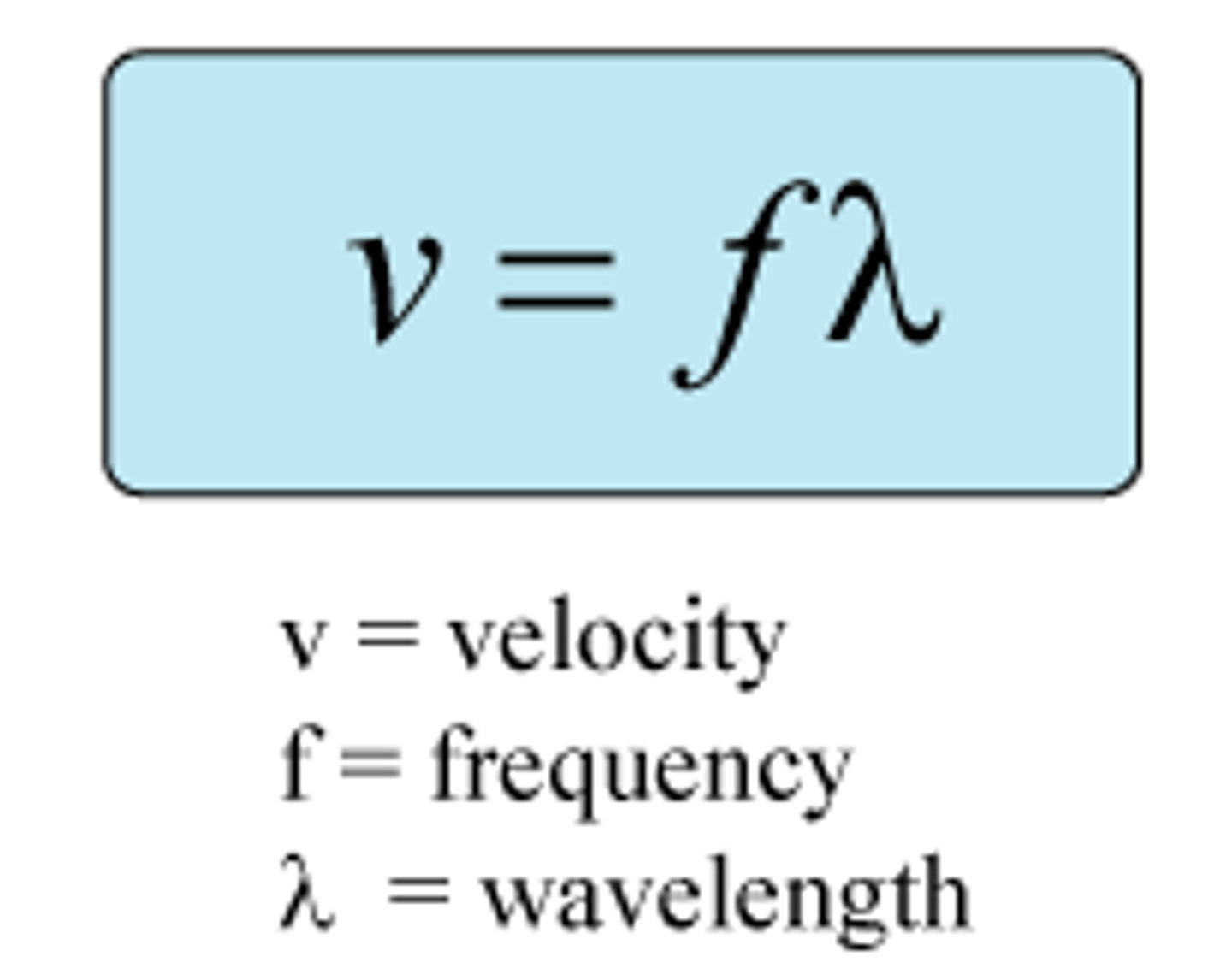
What is the formula for wave speed?
wave speed = frequency x wavelength
A wave that is a combination of longitudinal and transverse waves is called a _________________
surface wave (water waves are an example of surface waves)
Define wave frequency.
Frequency is the number of waves in a certain amount of time.
What is the unit for frequency?
Hertz (Hz)
1 Hz = 1 wave/second
True or False:
If amplitudes are equal, high frequency waves have MORE ENERGY than low frequency waves.
TRUE! IF amplitudes are equal, high frequency waves carry more energy than low frequency waves.
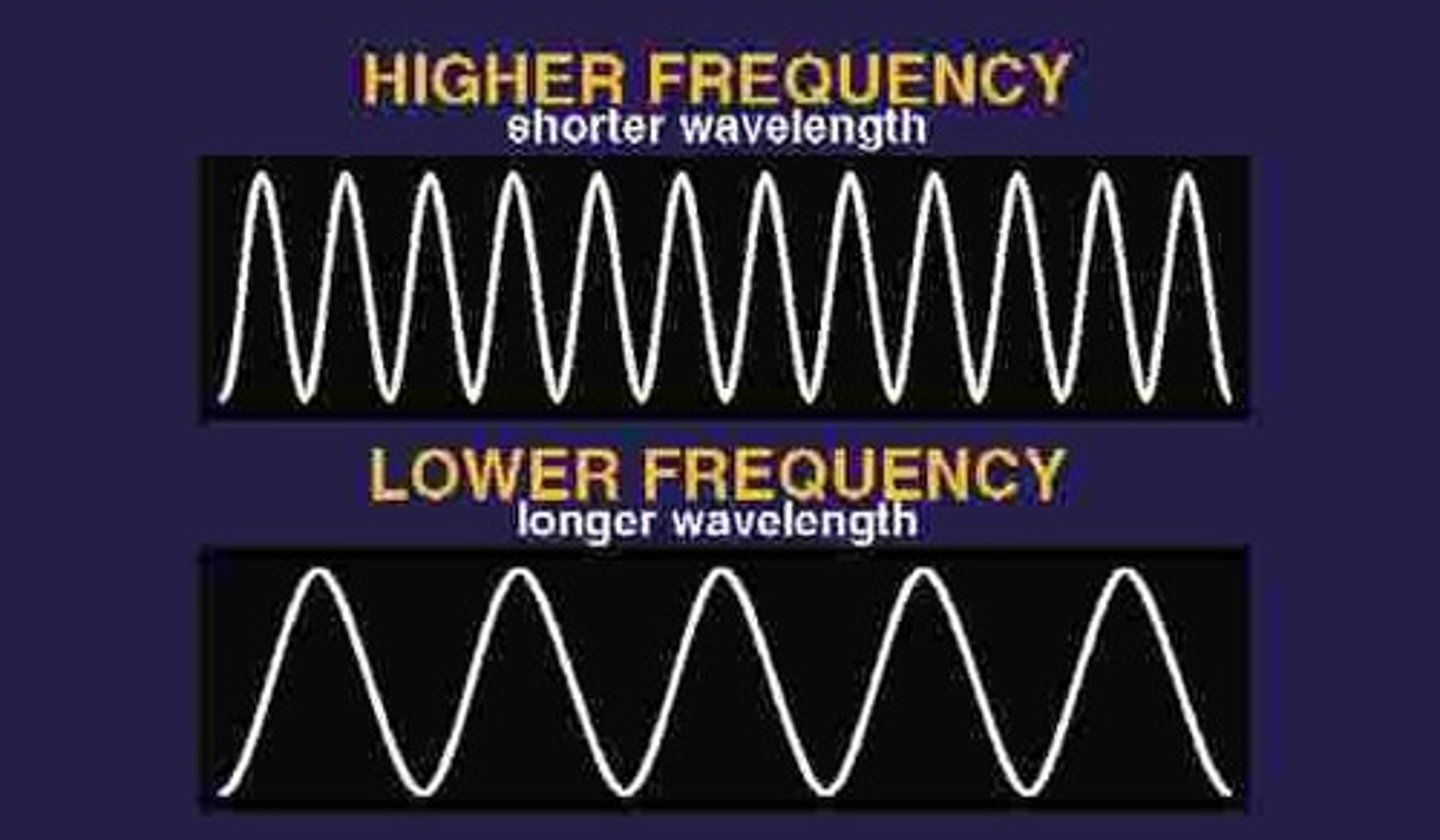
Calculate the frequency of a wave with a speed of 30cm/sec and a wavelength of 10cm.
30cm/sec divided by 10cm
= 3 waves per second or 3Hz.
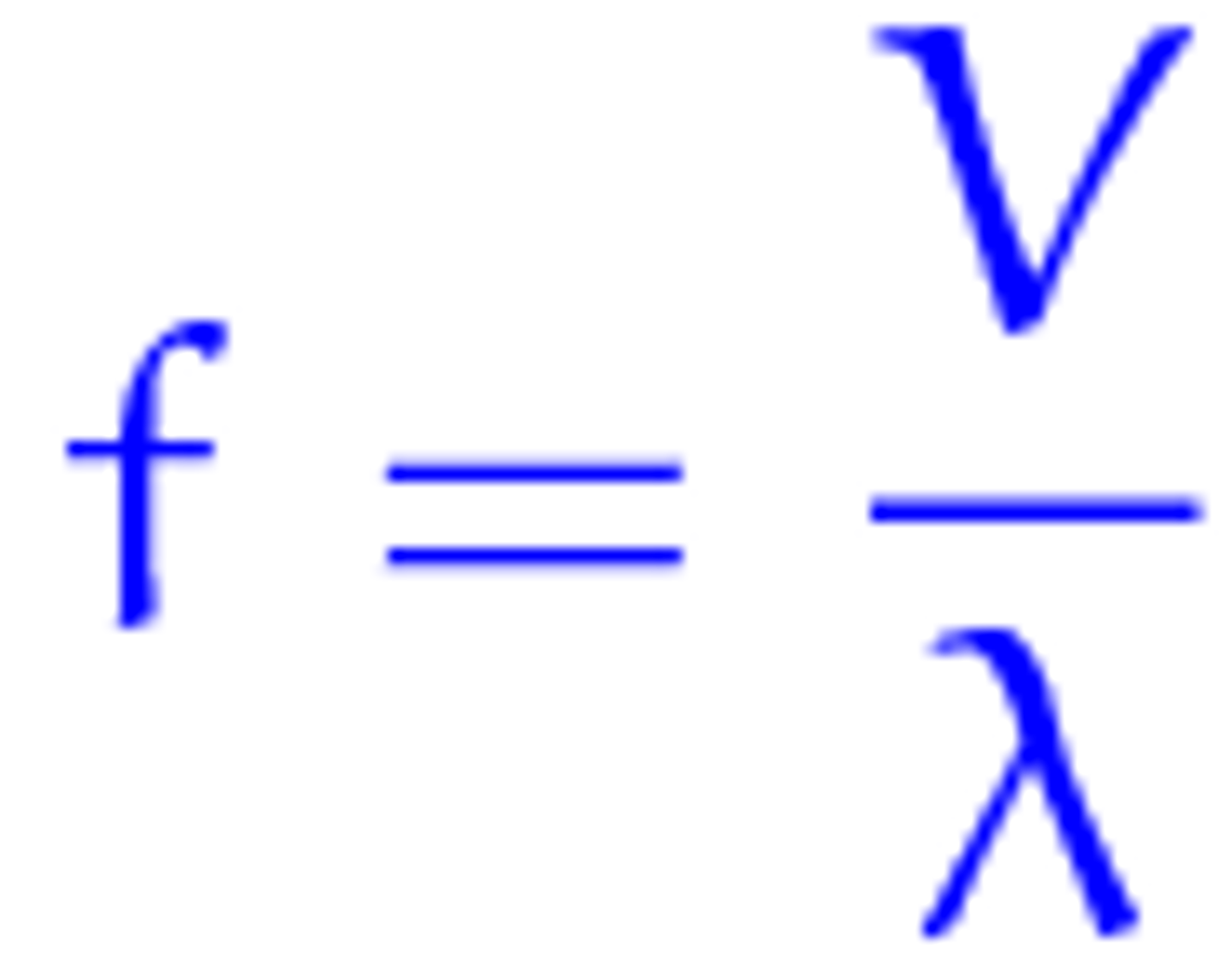
Calculate the wavelength of a wave with a speed of 20cm/sec and a frequency of 5cm.
20cm/sec divided by 5cm
= 4 cm
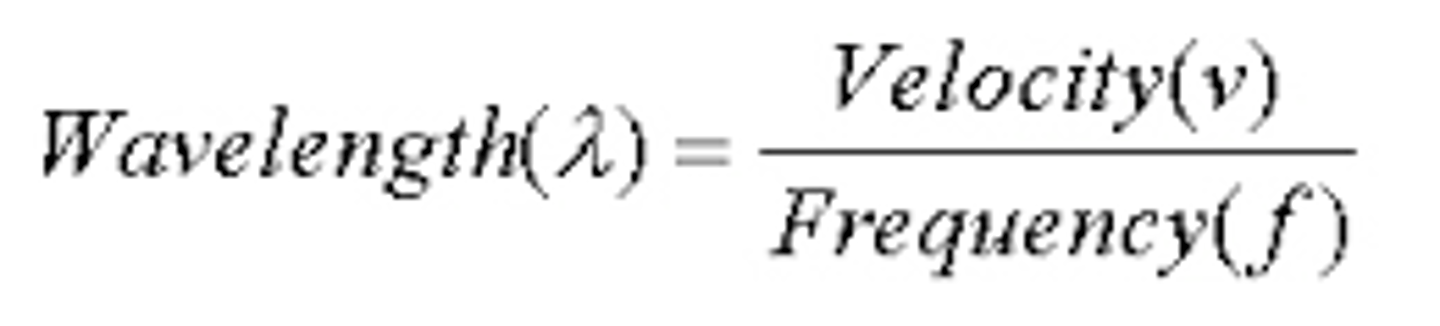
Calculate the speed of a wave with a wavelength of 5cm and a frequency of 12 Hz.
(12 hz) times (5 cm)
= 60 cm/sec
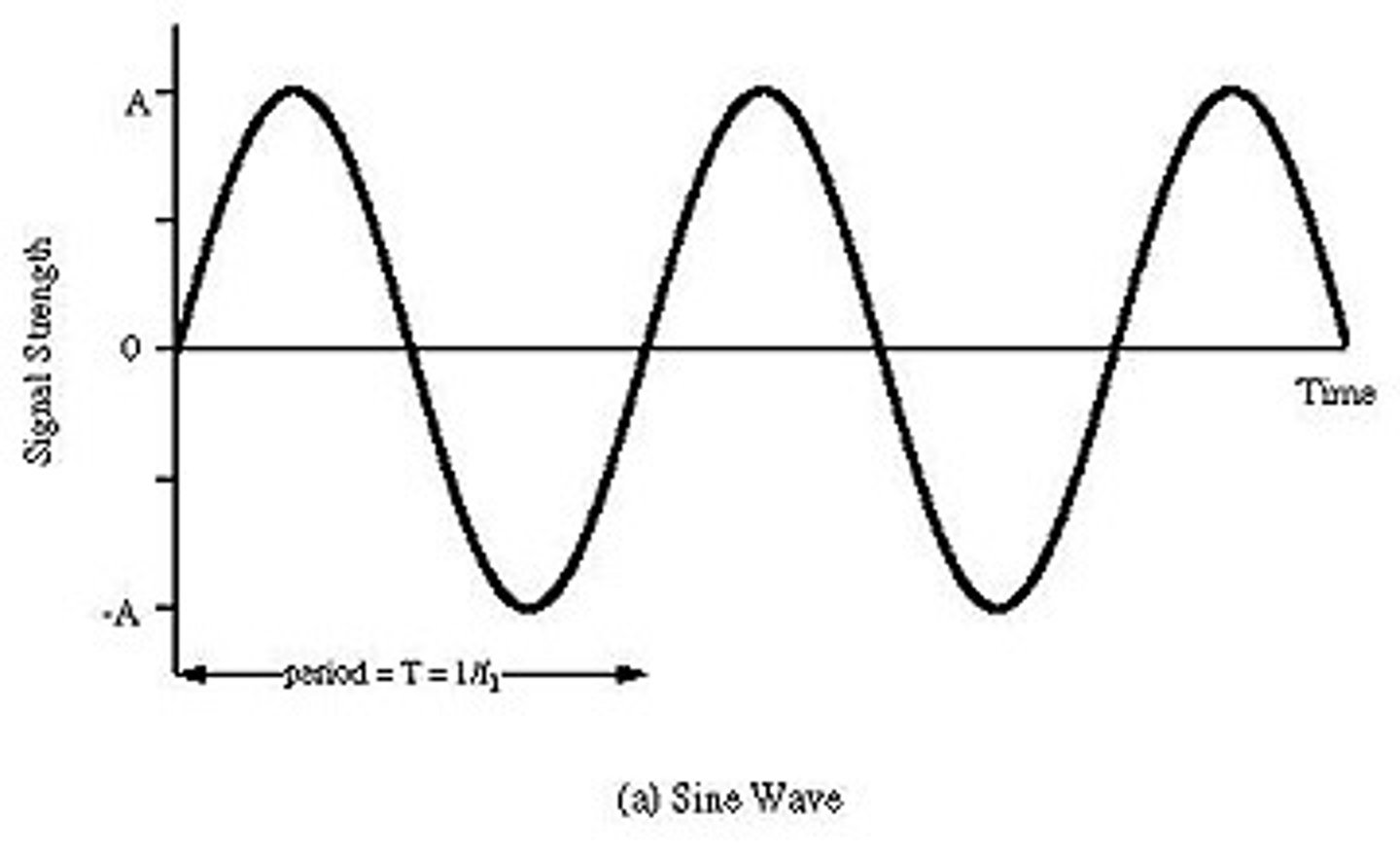
How many waves are in the following diagram?
3 waves total (1 crest + 1 trough = 1 wave)
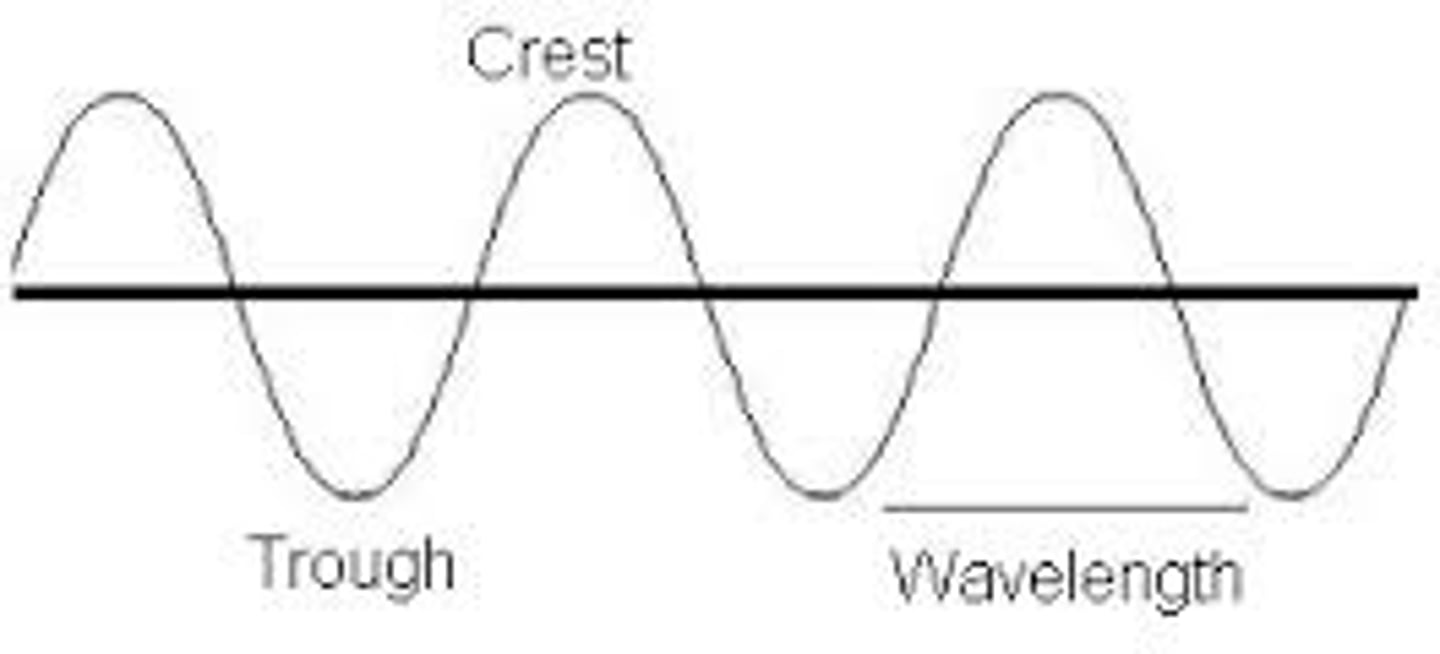
How many waves are in the following diagram?
2.5 waves (1 crest + 1 trough = 1 wave)
there are 3 crests & 2 troughs in this wave
How many waves are in the following diagram?
4 waves
(1 compression + 1 rarefaction = 1 wave)
there are 4 compressions & 4 rarefactions in this wave