UCM GenBioII Final - Animal Behavior
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Ethology
study of animal behavior
genetic influence
behavior hardwired into genes
physiological mechanisms
hormones or neuronal mechanisms influence behavior
developmental influence
imprinting
learning
innate behaviors
performed without thought, cannot be modified by learning
reflex actions
involuntary and rapid response to a stimulus (innate behavior)
kinesis / taxis
movement away from heat, or towards light (innate behavior)
fixed action patterns
predictable series of actions triggered by a cue one triggered it goes to completion (innate behavior)
ex) egg retrieval in geese
learning
modification of behavior through experience
can be simple of complex
habituation
when an animal stops responding to a stimulus after repeated exposure (learned behavior)
ex) crows with scarecrows
imprinting
highly specific type of learning, occurs at a particular age or life stage aka critical period (learned behavior)
associative learning
conditioned behaviors that have a positive or negative association between a stimulus and a response
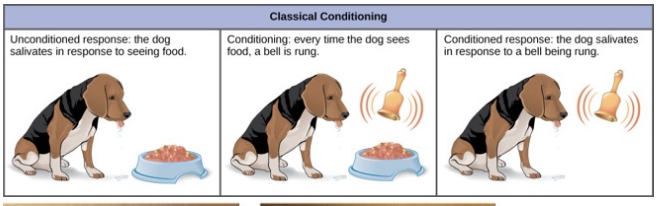
classical conditioning
response to one stimulus becomes associated with a second unrelated stimulus
operant conditioning
an animal’s behavior is reinforced by a consequence either a reward of a punishment
recipient benefits, actor benefits
cooperative
recipient benefits, actor is harmed
altruistic
recipient is harmed, actor benefits
selfish
recipient is harmed, actor is harmed
spiteful
sexual selection if often working against _______
natural selection
when traits increase reproductive success, they can be selected for even if they reduce survival
ex) mating with a colorful lizard instead of the camouflage lizard results in offspring with a lower chance of survival due to their bright colors
reproductive success in the HEAVILY investing sex is limited by _________
time and energy
reproductive success is the LIGHTLY investing sex in limited by _________
number of mates
members of the sex subject to strong selection will be competitive
intrasexual selection
members of the sex subject to weak selection will be choosy
intersexual selection (female choice)
intersexual selection benefits
females can acquire resources from male
male display as an indicator of genetic quality
choosy females have offspring with higher fitness
good genes hypothesis