Chapter 1. Investment Appraisal - Net Present Value
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Investment decisions
These are one part of corprate financial strategy, along with financing and dividend decisions.
Financing Decisions
Businesses need funding to invest in capital, to pay expense and for working capital
This relates to the decisions about where this money comes from, and is primarily about balancing
It can come from ;-
Equity - Investment from owners/shareholders
Debt - Money from lenders such as banks or bonds
Retained earnings - Unspent/accumulated profits from prior periods
Net Present Value (NPV)
The difference between the present value of cash inflows and the present value of cash outflows for a project.
Generally A positive Project should be accepted.
Takes into account the time value of money by ‘discounting’ future cash flows, this effectively is the cost of capital.
Superior project appraisal technique to others
Internal Rate of Return (IRR)
This looks at an investment in terms of the optimal rate of return for the company, rather than the net value.
Payback period
the length of the time taken for an investment to make a return on the initial expenditure
Return on Capital Employed (ROCE)
This compares a company’s capital with its earnings
Dividends Decisions
Funds can be returned to shareholders in the form of dividends payments
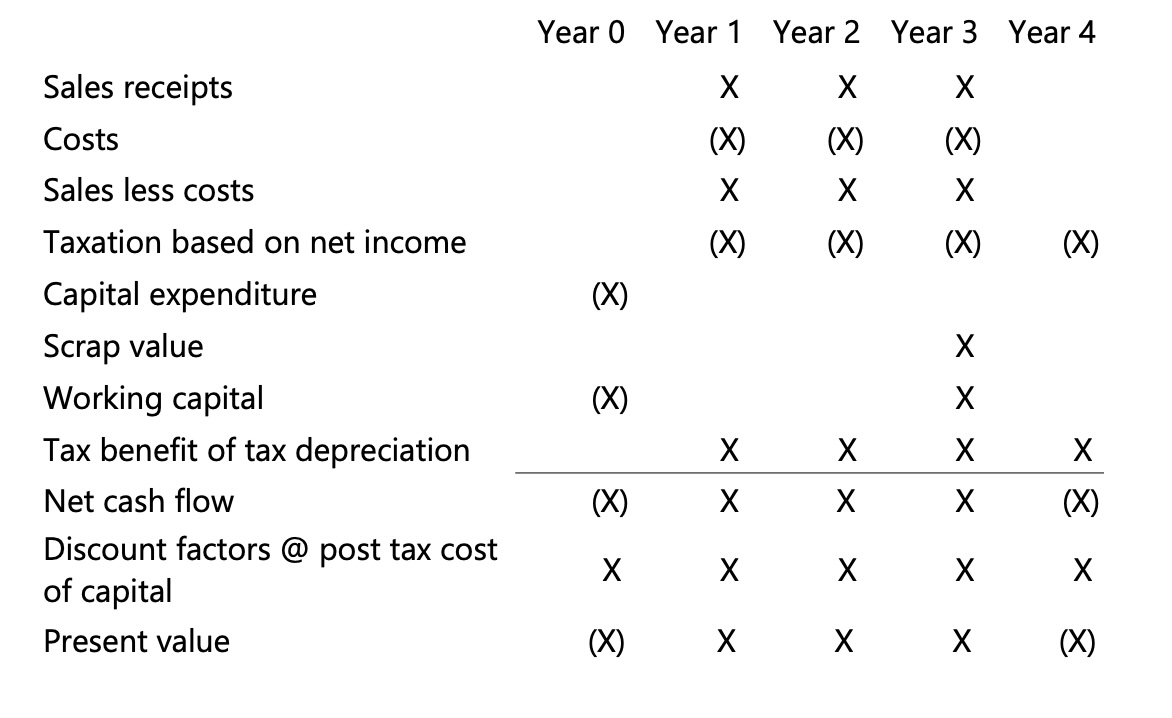
NPV Proforma
Cash outflows that occur at the begninng of a project occur now (Year 0)
Cash outflows or inflows that occur during any particular year are all treated as if they occurred at the end of the financial year.
Remember “If you are specifically told that cash outflow or inflow occurs at the start of a year, include it as the end of the previous year”
NPV things to remember
Recognise which costs are relevant i.e
Legal fees are a sunk cost - already been paid whether it goes ahead or not
Tax in NPV
Simple part of the calculation and you will simply need to follow the instructions given (%)
Written down allowance
the annual amount claimed each year (which is taken off the total asset value for the following year’s balance)
Cash flows with Inflation
Real terms - the amount that you would spend if you were to buy a product today
Perpetuities
relies on a constant and consistent cash flow that continues forever. to calculate an infinite NPV
Annuities
a financial instrument which is purchased for an initial sum which then pays out the same amount each and every year until a definitive end date.