3.4.3 addition polymers
polymer
a large, long-chain molecule formed from many small molecules joined together
monomer
small molecules that join to make polymers
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
polymer
a large, long-chain molecule formed from many small molecules joined together
monomer
small molecules that join to make polymers
addition polymer
large molecules made up of smaller molecules called monomers
no other products formed
addition polymer specific to organic chemistry
alkanes formed from alkenes (from crude oil) and substituted alkenes.
what is addition polymerisation?
what is the monomer?
the formation of large, long-chain molecules from lots of small molecules joining together with no other products.
alkenes from crude oil are the monomer.
how does addition polymerisation occur?
requires high temperature, high pressure and a catalyst.
to form the polymer, the double bond in the alkene opens up and joins one monomer to another.
what type of addition polymers are formed from high pressures and temperatures?
branched chain polymers with weak intermolecular forces.
branched = molecules cannot pack as closely together = less surface contact = weaker van der Waals between molecules.
LDPE, low density as molecules cannot pack as closely together.
what type of addition polymers are formed from lower pressures and temperatures?
straight chain polymers with strong intermolecular forces.
straight = molecules can pack closely together = more surface contact = stronger van der Waals between molecules = higher boiling point.
HDPE, high density as molecules can pack closely together.
what are addition polymers?
how they are named?
give examples of addition polymers
they are named using ‘poly(name of alkene monomer)’.
e.g. LDPE, HDPE, both formed from the monomer ethene.
repeating unit of addition polymers
shows the arrangement of atoms that are repeated in the polymer chain
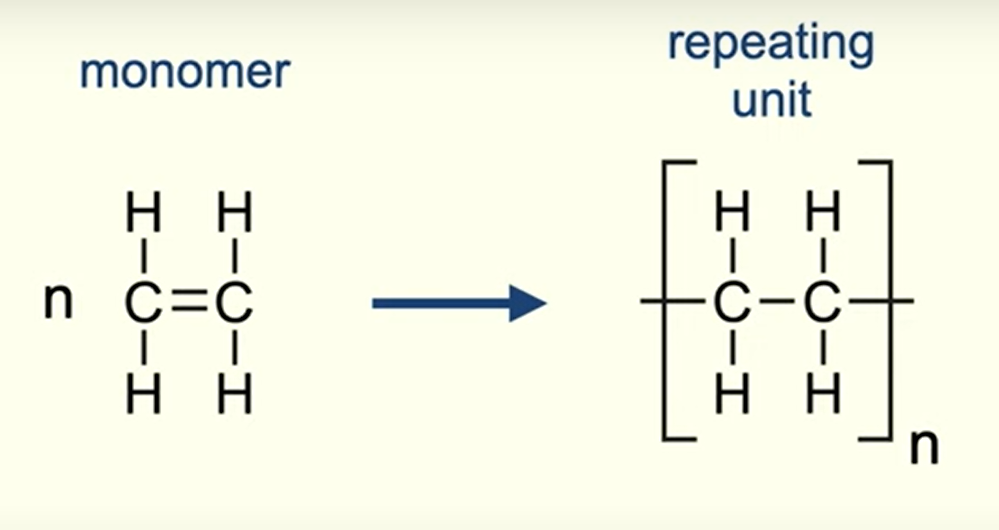
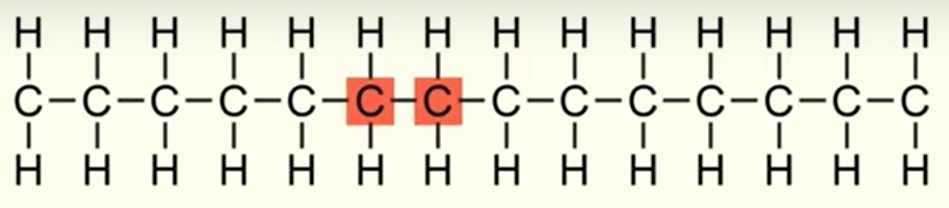
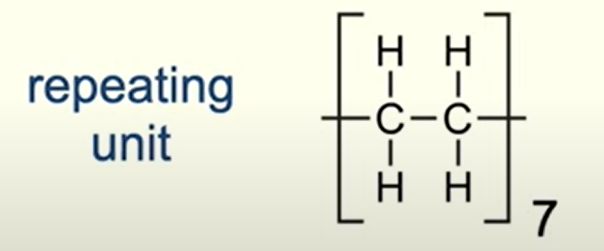
how many repeating units are present in this polymer?
n = 7
choose the correct option:
E-Z isomers of an alkene form polymers with the same / different repeating unit(s).
the same
what happens at the ends of an additon polymer?
C atoms at the ends only have 3 bonds.
during polymerisation, other molecules are added to cap the ends of the polymer chain.
why do polymers have higher melting points than their monomers?
polymers are bigger/longer molecules/have more electrons.
so they have stronger van der Waals forces between molecules.
compare the reaction conditions for making LDPE and HDPE.
LDPE high temp, HDPE low temp.
LDPE high pressure, HDPE low pressure.
LDPE oxygen is needed, HDPE ziegla-natta catalyst is needed and the alkenes/chains bond to the catalyst’s surface.
compare the properties of LDPE and HDPE.
in LDPE molecules are loosely packed due to branching.
in HPDE molecules are tighly packed.
LDPE is flexible and soft.
HDPE is stiff/rigid and hard.
compare the uses of LDPE and HDPE.
LDPE is used in plastic bags and cling film.
HDPE is used in buckets and plastic bottles.
what does PVC stand for?
poly(chloroethene)
what are plasticisers and what is their role?
small molecules added in between polymer chains.
cause chains to move further apart.
so weaken the intermolecular forces between chains.
so chains can move over each other.
so polymer becomes more flexible (/less brittle).
example of the use of plasticisers
using plasticisers makes PVC flexible.
flexible PVC is relatively soft.
using plasticisers also makes PVC waterproof.
.
PVC is rigid, and the chains are attracted to each other by van der Waals forces and dipole-dipole forces.
using plasticers weakens these intermolecular forces.
rigid PVC must be used to make:
plastic pipes
window frames
flexible PVC must be used to make:
flooring
electrical insulation in cables
clothing
guttering (?)
a use of poly(propene)
used to make carpets
what is polystyrene?
what is polystyrene used for?
what is the side group in the monomer of polystyrene?
poly(phenylethene).
used to make foam food containers and drinks cups.
the side group in phenylethene is benzene.
define non-biodegradable
not broken down by microorganisms in the environment
why are addition polymers unreactive?
they contain many C-C and C-H bonds.
these bonds are non-polar and (relatively) strong, so are difficult to break.
what is an advantage of the lack of reactivity of addition polymers?
their lack of reactivity makes them useful molecules, e.g. they can be used for containers for food and drinks without the polymer reacting with the contents.
what are a disadvantage of the lack of reactivity of addition polymers?
their lack of reactivity makes them non-biodegradable.
this means they can pollute the environment for decades or longer.
this is harmful to wildlife, e.g. seabirds can become tangled in polymer waste or consume it, which can be fatal.