AQA GCSE Physics P5 Electricity in the home
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
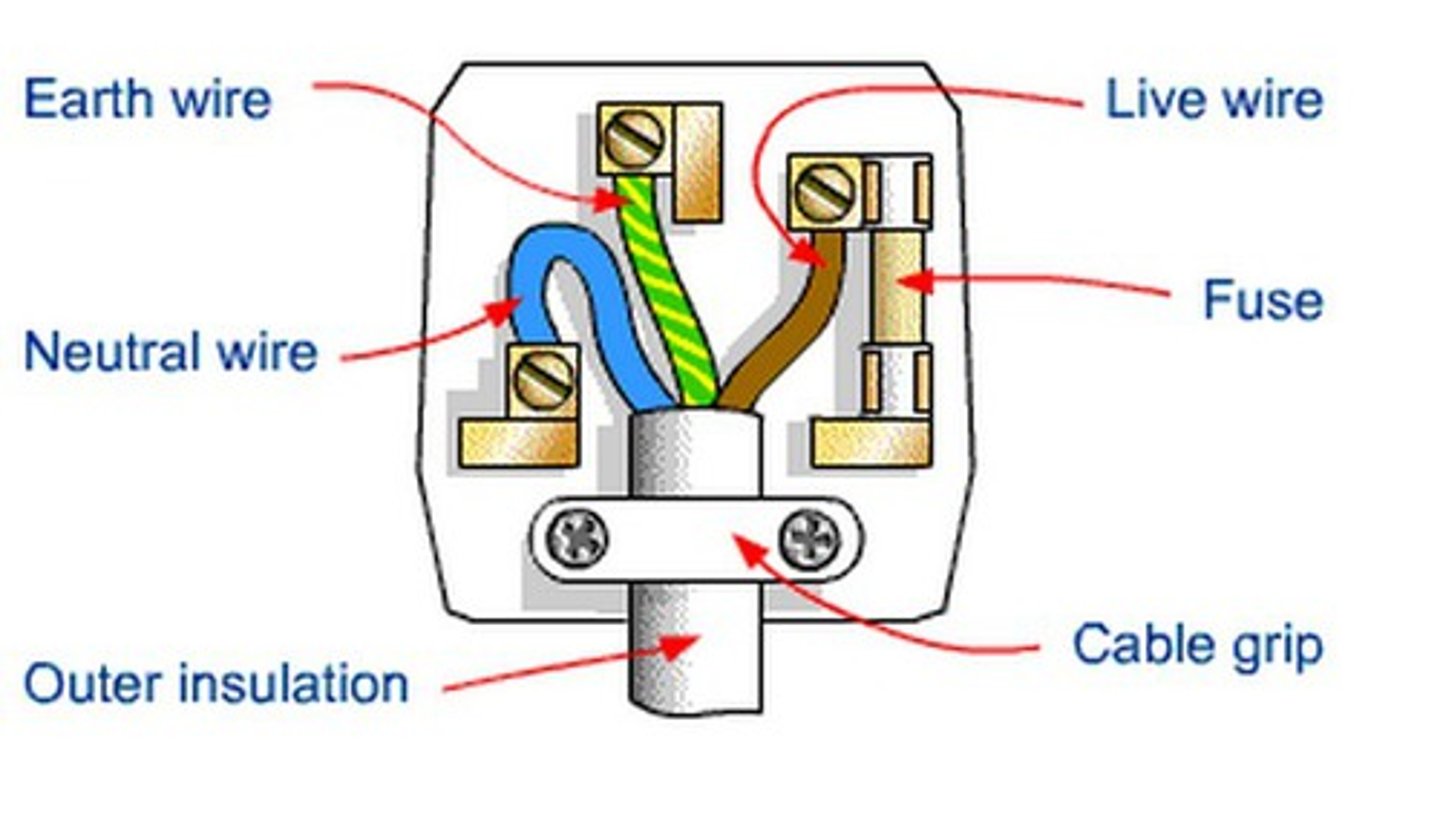
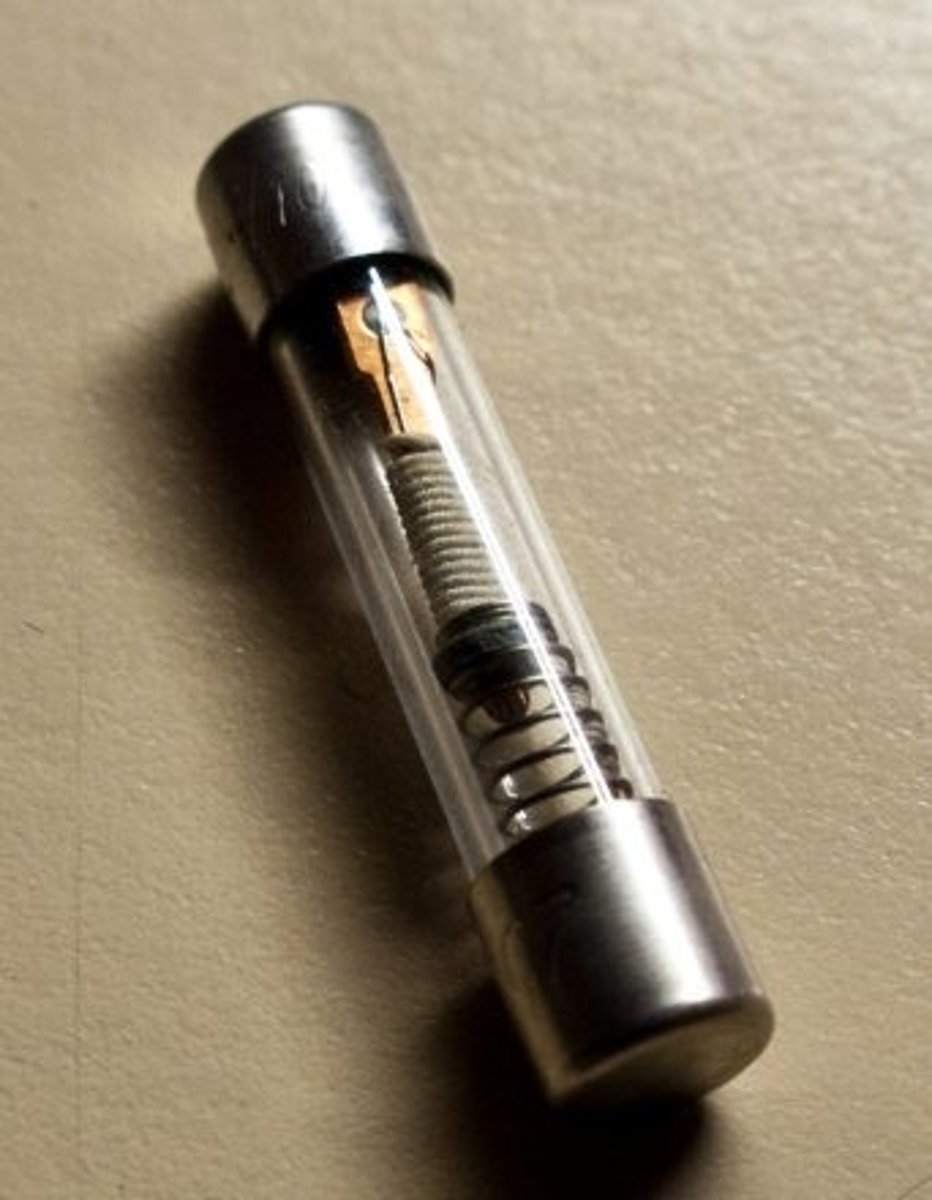
Fuse
This component melts and breaks the circuit when too much current flows
Earth pin
The longest pin that connects first for safety, potential of 0V
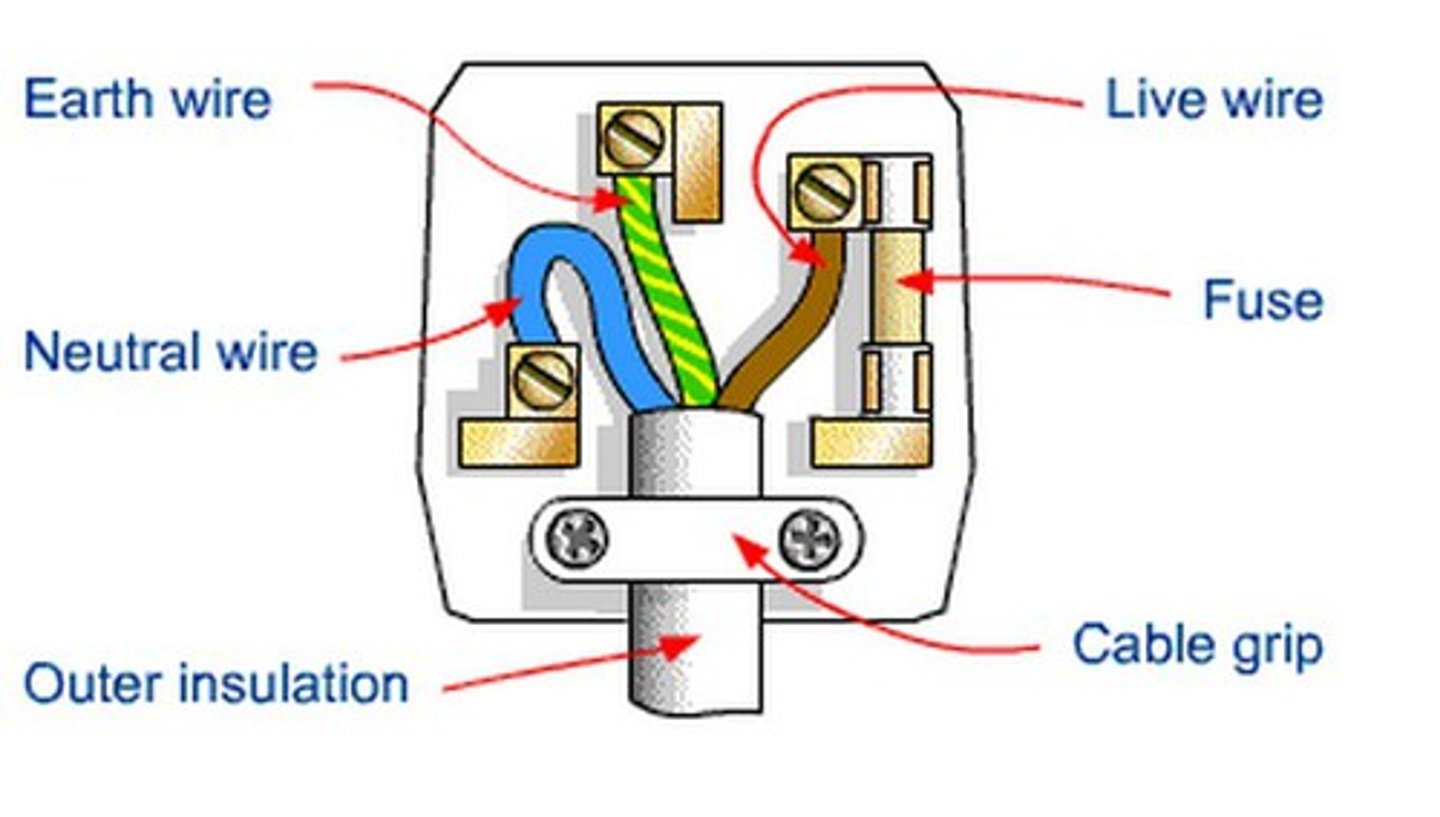
neutral wire
This wire completes the circuit and carries away current (potential of 0V)
Live wire
This wire supplies the current, mains potential of 230V in UK
It is connected in the live wire so the supply is cut off if the fuse melts.
Explain where the fuse is located.

outer metal case
What is the Earth wire connected to? (not the pin!)

Blue
Colour of the neutral wire
Brown
Colour of the live wire
Green and yellow
Colour of the earth wire

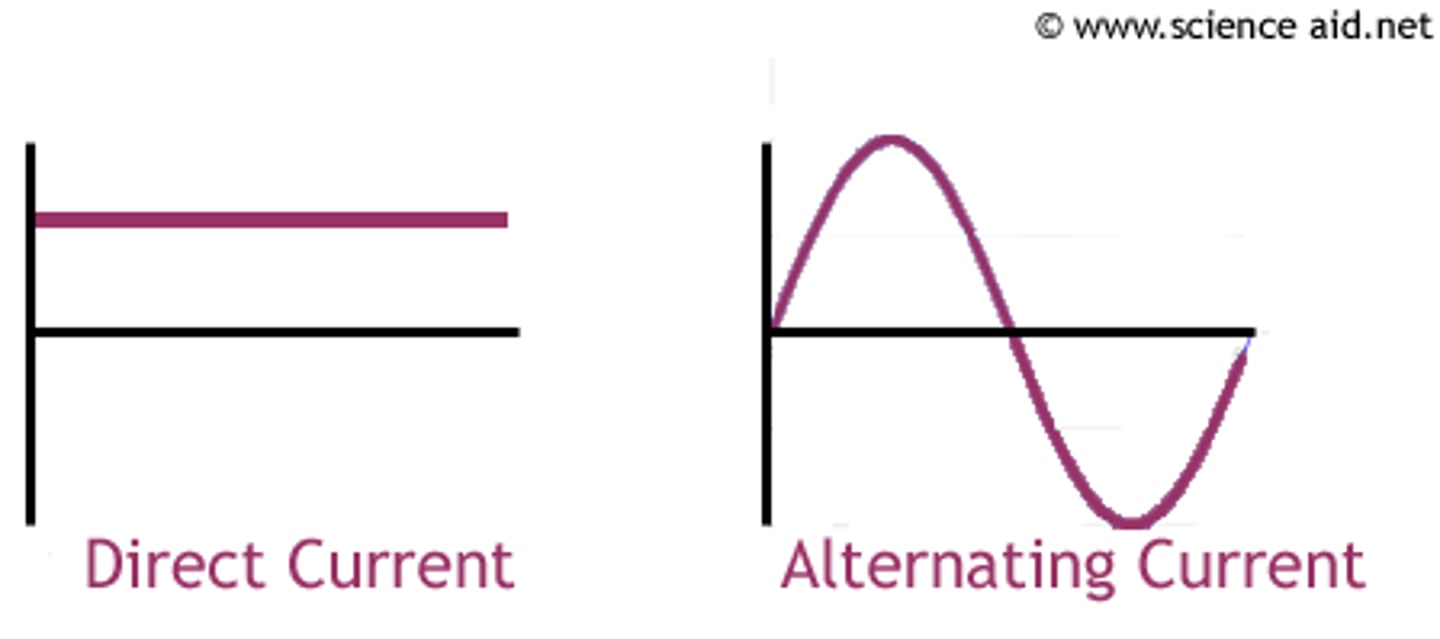
alternating current (a.c.)
This current is constantly changing direction (supplied by the mains)
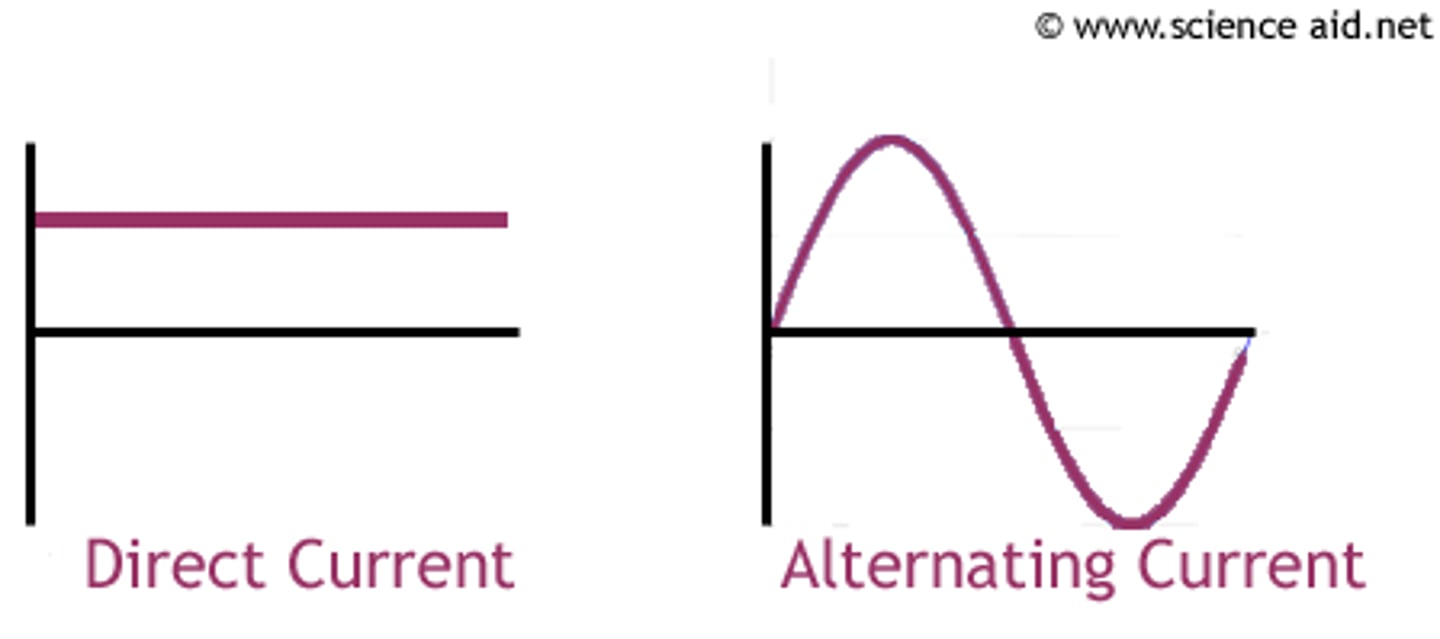
direct current (d.c.)
This current always flows in the same direction (supplied by cells and batteries)
Power
= p.d. x current (P=VI)
Energy
=Power x time (E=Pt)
p.d. x charge (E=QV)
electrical energy transferred = (equation)
Charge
= Current x time (Q=It)
p.d.
= current x resistance (V=IR)
current² x resistance
= Power (P=I²R)
Efficiency
= useful power output/total power input (x100%)
hii
All the equations
Ω
Units of resistance
Watts
units of power
Joules
units of energy
seconds
units of time
Amps
units of current
Volts
units of p.d.
% or ratio (decimal)
units of efficiency
Coulombs
units of charge
current in wires(or friction of moving parts) (This causes…)
This causes heat energy loss in appliances
A smaller proportion of energy is wasted, higher proportion of energy is usefully transferred
describe an appliance with a higher efficiency in terms of energy
If a fault causes the outer metal case to become live, high current flows down the low resistance earth causing the fuse in the live to melt, stopping the current from flowing.
How do the earth wire and fuse work together?
The appliance has insulation covering the wires and the outer case so no earth wire is needed as the case cannot become live.
Explain the meaning of double insulated ( in terms of a plug)
There is a p.d. between you (0V) and the appliance (230V) so a current will flow through you to earth.
WHY do you get a shock from a 'live' appliance?
230V
UK mains voltage
50Hz
UK mains frequency
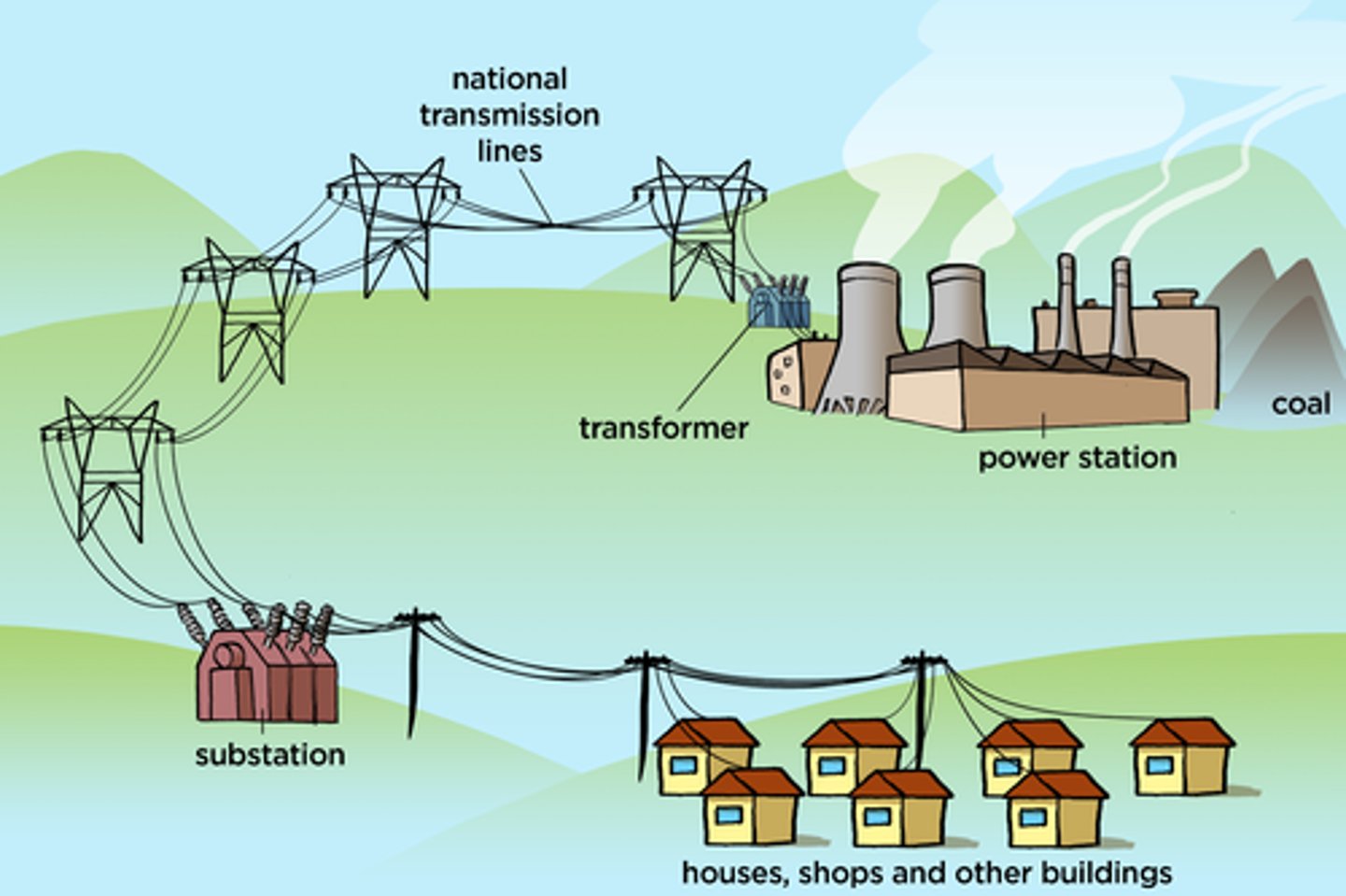
Step-up transformer
Increases the voltage (so decreases the current) in the national grid.
Step-down transformer
Decreases the voltage (so increases the current) in the national grid.
For the same power, a high voltage means a low current. Low current means cables stay cooler so a smaller proportion of heat energy is wasted so the efficiency of the national grid is higher.
Why is energy transferred at a high voltage through the national grid?
It has live, neutral and earth wires
Describe 3-core cable
It has live and neutral wires only, no earth is needed as the appliance is double insulated
2-core cable
Brass: hard, strong and a good conductor
What are plug pins plug are made of & why?
Plastic: a good insulator so you don't get a shock
What is the plug outer case is made of & why?
Copper: very good conductor of electricity
What are cables and wires are made from & why?
A system of cables and transformers linking power stations to consumers.
What is the national grid?
For safety to reduce the chances of an electric shock being fatal
Why is the voltage stepped down to go into homes?