PBVD - Respiratory
1/167
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
What lung lobe is absent in the horse?
Middle
Which species have complete (non-fenestrated) mediastinum?
Cattle, goats, and pigs
In the nasal cavity from rostral to caudal what are the types of epithelium?
Squamous (nasal vestibule) —> olfactory epithelium (primarily nasal conchae —> pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium
Where are club cells predominantly found?
Bronchioles
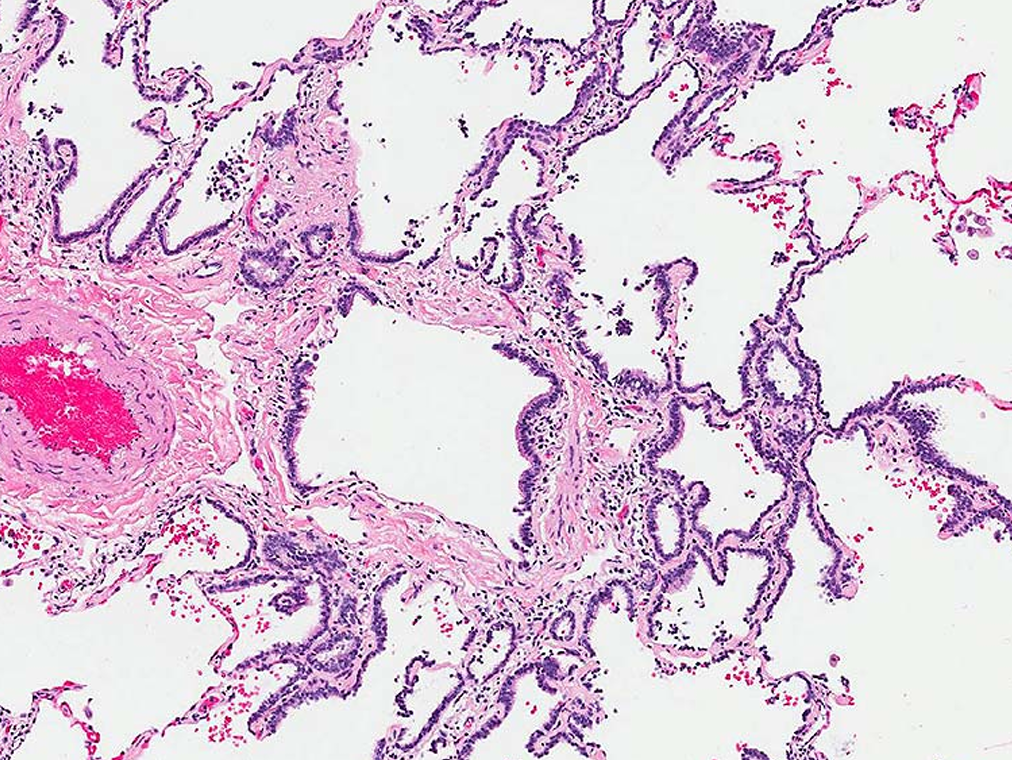
Term for this histologic change?
Lambertosis
What type of immunoglobulin is most important in the respiratory tract?
IgA
What are two types of infectious agents that classically cause severe hyperplasia of the BALT?
Mycoplasmas and retroviruses
T/F. Pneumoconiosis is a type of anthracosis.
False
Pneumoconiosis is a general term describing interstitial lung disease caused by deposition of carbon (anthracosis), asbestos, or silica (silicosis).
What size particles can gain access to the alveoli?
<2 um
In what species are the pulmonary intravascular macrophages predominantly responsible for removing circulating particles, bacteria, and endotoxin from the blood?
Cats, horses, ruminous, and pigs
Kupffer cells and splenic macrophages in dogs, rodents, and humans
What is the most frequent sarcoma of the nasal cavity?
chondrosarcoma
What is the most common round cell tumor of the nasal cavity and in what species is it most common?
Lymphoma; cats
In horses where is the most common location for nasal polyps?
Ethmoidal region
In cats where is the most common location for nasal polyps?
Nasopharynx and Eustachian tubes
In tracheal collapse what is the difference between dogs and horses?
Dogs: dorsoventral collapse
Horses: Lateral collapse forming a narrow vertical slit
Which portion of the trachea is most commonly affected by tracheal collapse in dogs?
a. cervical portion of the trachea
b. cervical and cranial thoracic portion
c. caudal thoracic only
d. entire length
Which portion of the trachea is most commonly affected by tracheal collapse in dogs?
a. cervical portion of the trachea
b. cervical and cranial thoracic portion
c. caudal thoracic only
d. entire length
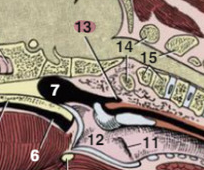
What is the anatomical structure labeled 13 called and in what species is it present?
Pharyngeal diverticulum
Pigs
What is the main cause of emphysema in animals?
Obstruction of outflow of air
What are hyaline membranes composed of?
Plasma proteins, necrotic type 1 pneumocytes, and Pulmonary surfactant
What are the three phases of diffuse alveolar damage (acute interstitial pneumonia)?
Exudative
Proliferative
Fibrotic (chronic)
What are the most common bacterial isolates from septic pulmonary emboli?
Fusobacterium necrophorum and Trueperella pyogenes
Erysipelothrix
Staphylococcus aureus
Strep suis and equi
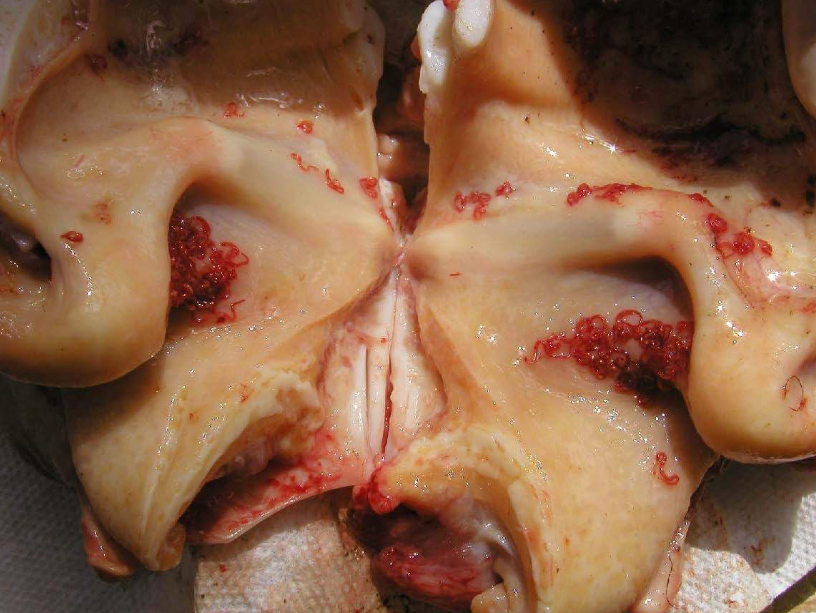
Ox. Cause?
Mammomonogamus laryngeus
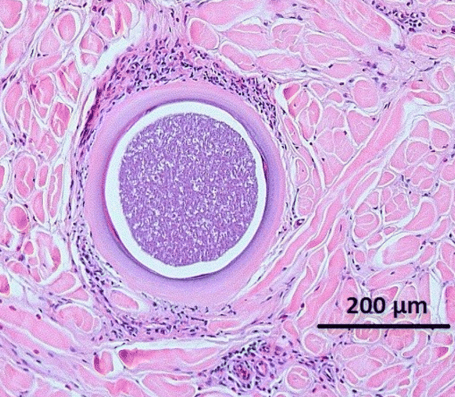
Ox. Cause?
Besnoitia spp.
What is the histologic Hallmark of chronic interstitial pneumonia?
Fibrosis of the alveolar walls
What are the two most common bacteria isolated from the lungs of aborted calves?
Brucella abortus and Trueperella pyogenes
What cells are immune reactive to TTF-1?
Club cells and type II pneumocytes
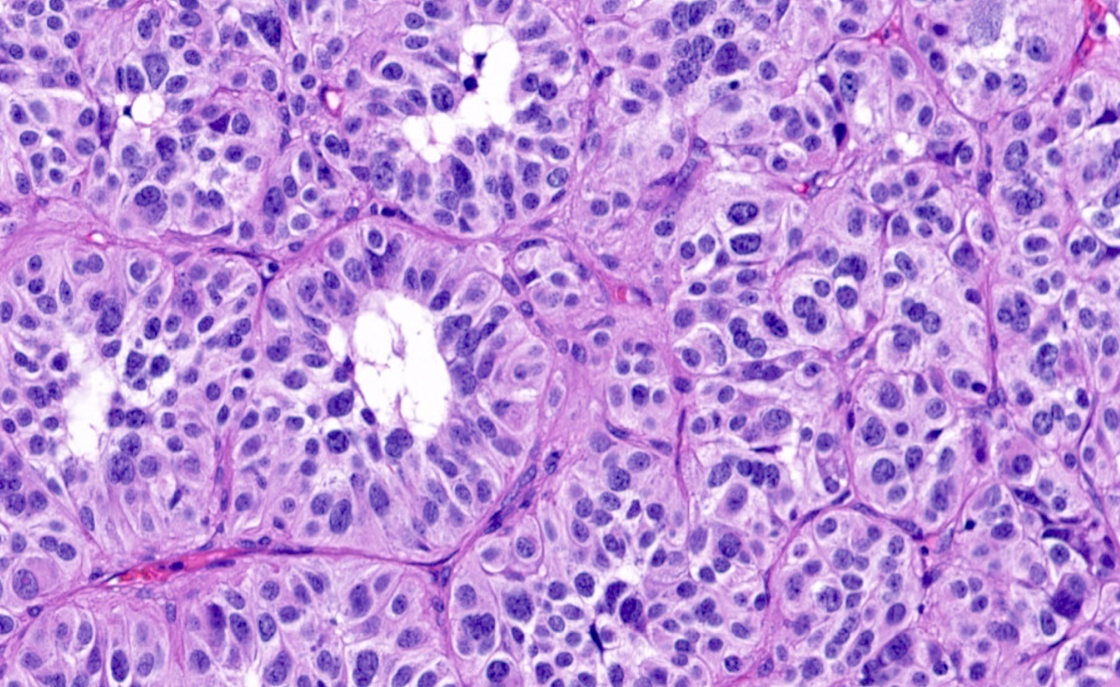
Dog, Lung. Most likely diagnosis and cell of origin?
In horses where does this type of tumor arise?
Carcinoid
Neuroendocrine
Reported in the nasal cavity of horses
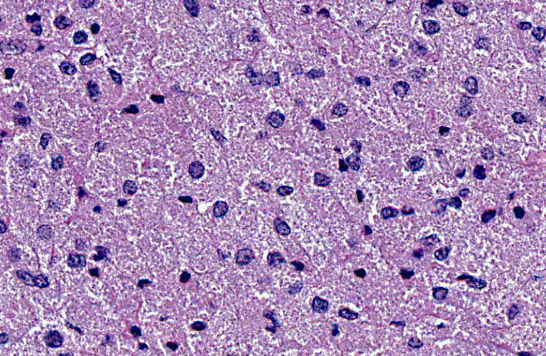
Horse, lung.
Diagnosis? Additional diagnostics?
Cytoplasmic granular material represents what?
Granular cell tumor
PAS positive granules; cells are S100+
Accumulation of lysosomes
Key histo feature of lymphomatoid granulomatosis?
Tumors formed by large pleomorphic mononuclear cells with a high metallic rate that grow around blood vessels and invade and destroy vascular walls
Mixed population of B&T lymphocytes
In which species is congenital mesothelioma common?
Calves
In horses nasal amyloidosis is composed of what type of amyloid?
AL amyloid
What muscles are affected to cause “roaring” in horses?
The dorsal and lateral cricoarytenoid muscles; mostly on the left side
What are the key histologic features of equine asthma syndrome?
Goblet cell hyperplasia
Plugging of the bronchioles with mucus
Smooth muscle hyperplasia in bronchi and bronchioles
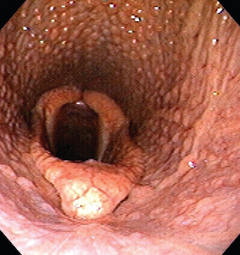
MDX and species?
Pharyngeal lymphoid hyperplasia
Horse
What cranial nerves are in close proximity to the guttural pouch?
VII, IX, X, XI, and XII
Most common infectious agent of guttural pouch mycosis?
Aspergillus fumigatus
Most common cause of guttural pouch empyema?
Strep equi equi (strangles)
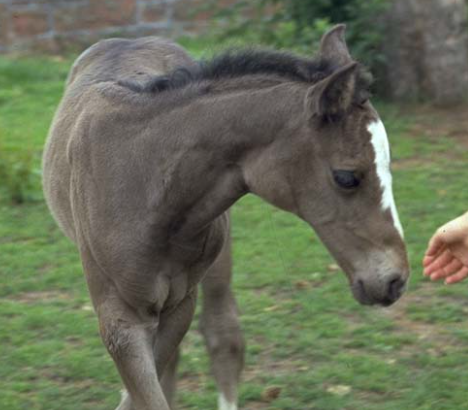

Most likely diagnosis?
Guttural pouch tympany
What are the two equine influenza viruses and which one jumped into dogs?
H7N7 and H3N8
H3N8 jumped into dogs
What is a common cause of respiratory morbidity in SCID foals?
Equine adenovirus infection
What are the two syndromes caused by Burkhoderia mallei?
Glanders: Granulomatous and ulcerative respiratory disease that exudes copious pus
Farcy: Severe suppurative lymphangitis; nodular thickening of extended segments of the lymph vessels with draining tracts
What is the causative agent and main lesions of pseudoglanders?
Melioidosis
Burkholderia pseudomallei
Abscesses with a thick wall and yellow-green exudate in internal organs throughout the body
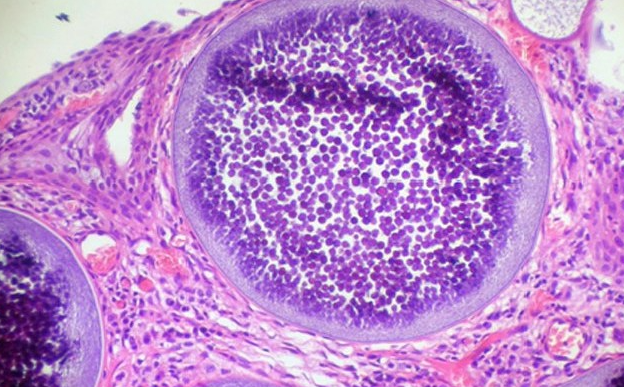
Cause; histo description; most common location?
Rhinosporidium seeberi
large (300-400 um) sporangium containing thousands of endospores
Nasal mucosa
Histo lesions of equine influenza?
Necrotizing and proliferative bronchiolitis with DAD
Cause of equine viral rhinopneumonitis?
EHV-1 and EHV-4
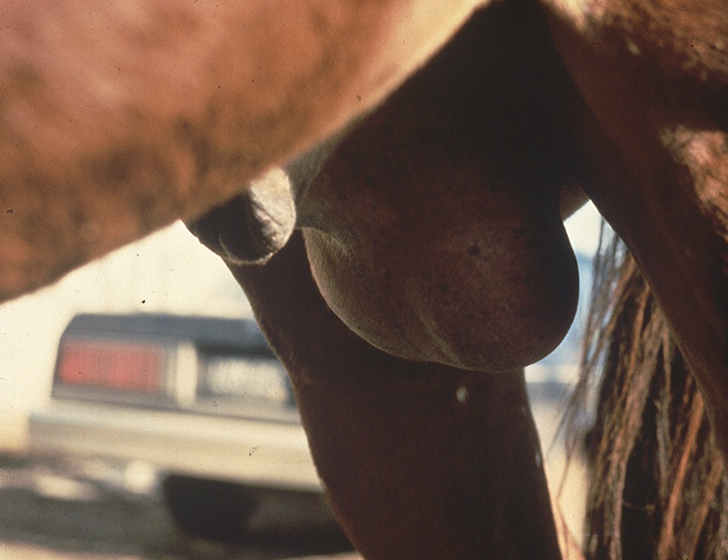

Horse. Cause?
Equine viral arteritis
Equine Arterivirus
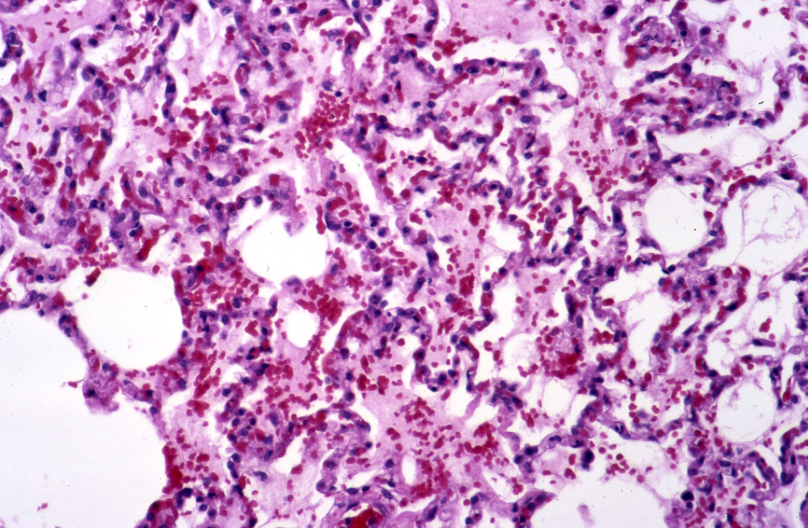
Horse. Likely cause?
African horse sickness virus; orbivirus
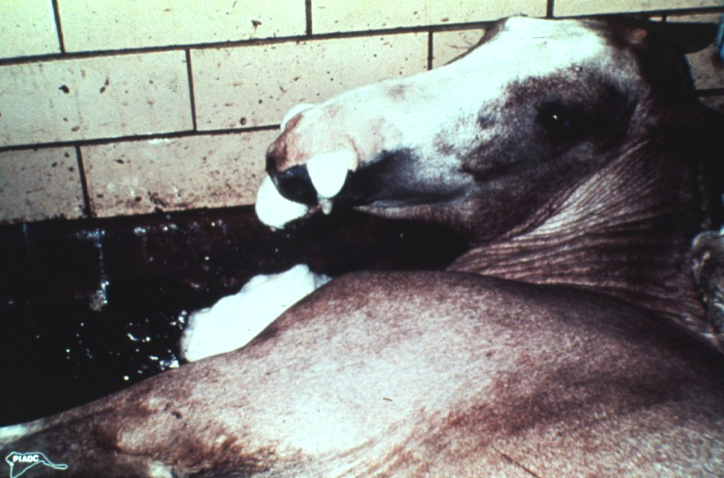
African horse sickness. Four forms of the disease?
African horse sickness
Pulmonary
Cardiac
Mixed
Mild
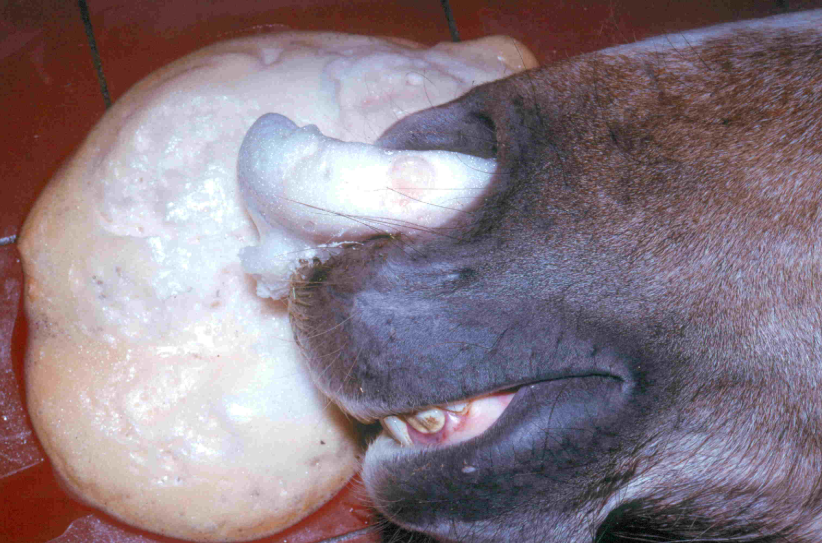
Two main differentials?
Hendra virus
African horse sickness virus
Viruses that causes (3) equine multinodular pulmonary fibrosis?
EHV-5
AHV-4
AHV-5
Which of the following is associated with Rhodococcus equi survival in host macrophages in horses?
a. VapA
b. VapB
c. VapC
d. VapN
Which of the following is associated with Rhodococcus equi survival in host macrophages in horses?
a. VapA (horses)
b. VapB (pigs)
c. VapC
d. VapN (cattle and goats)
Key histologic lesion of pulmonary Rhodococcus equi in horses?
MF/C pyogranulomatous bronchopneumonia progressing to areas with discrete pyogranulomas
What % of horses with pulmonary Rhodococcus equi have intestinal rhodococcosis?
50%
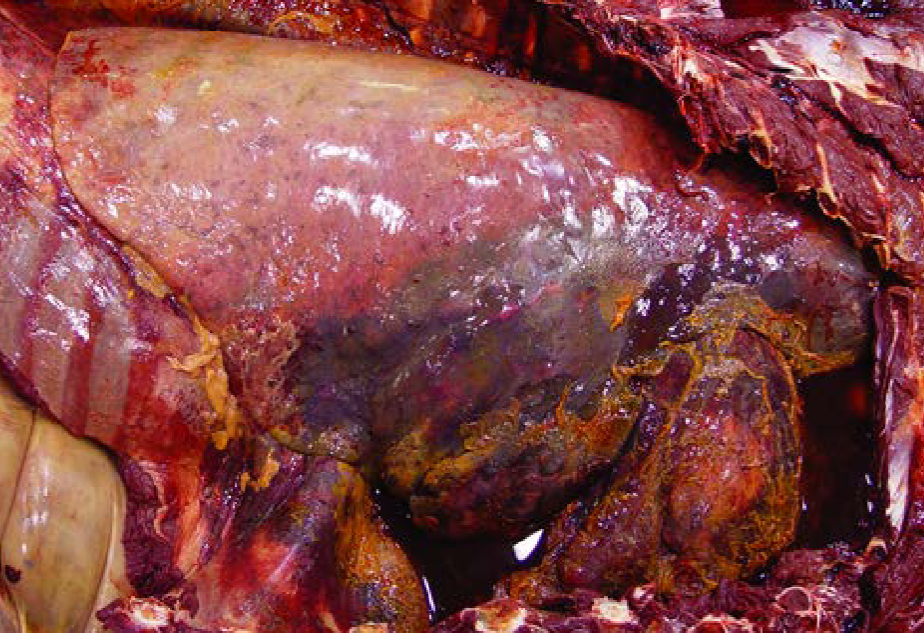
Horse. Name four predisposing events.
Long distance travel
Confined with head raised and tied
Strenuous exercise
General anesthesia
What is the most common isolate in cases of equine pleuropneumonia?
Streptococcus zooepidemicus
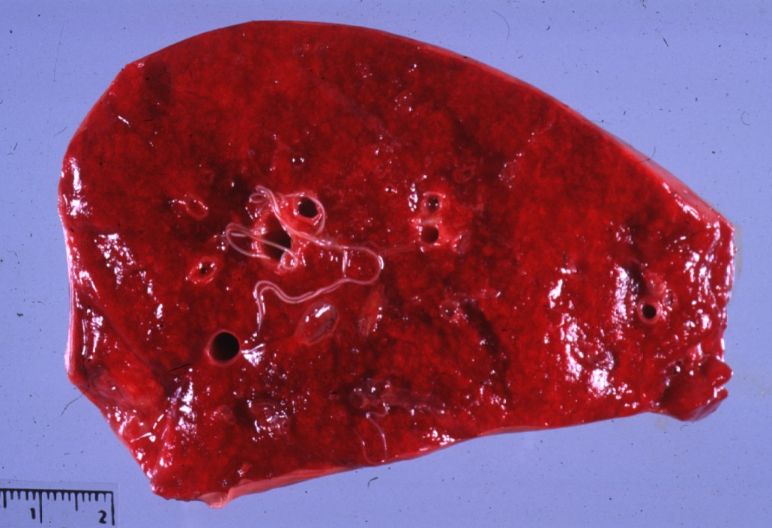
Horse. Cause and predisposing factor?
Dictyocaulus arnfieldi
Pastured with donkeys that tolerate large numbers and can spread to horses
Not very pathogenic
Can cause eosinophilic bronchitis
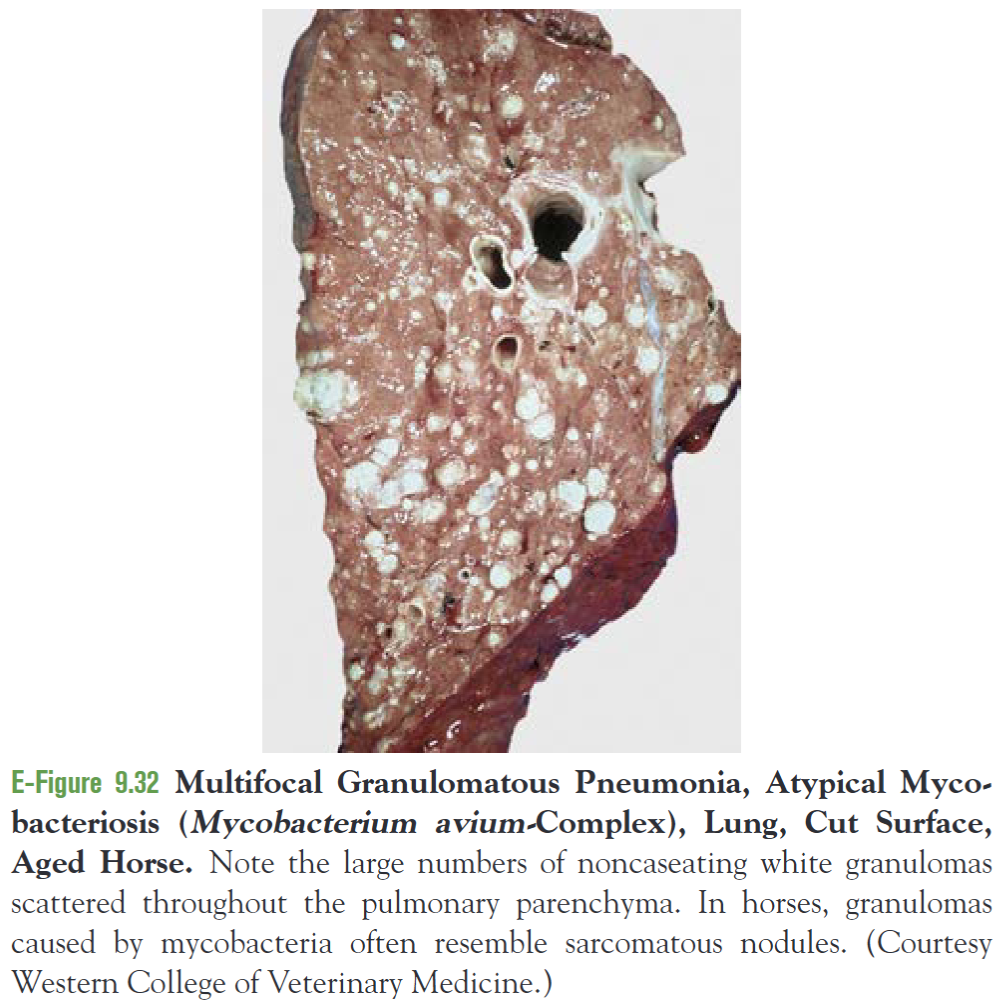
How does pulmonary mycobacteriosis in horses differ from ruminants ad pigs?
The nodules are smooth, gray, solid, and sarcomatoid and do not have grossly visible necrosis or calcification.
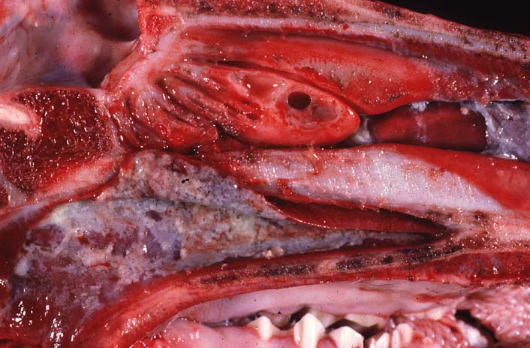
Ox. MDX and cause.
Fibrinonecrotic nasopharyngitis
Infectious bovine rhinotracheitis; bovine herpesvirus-1
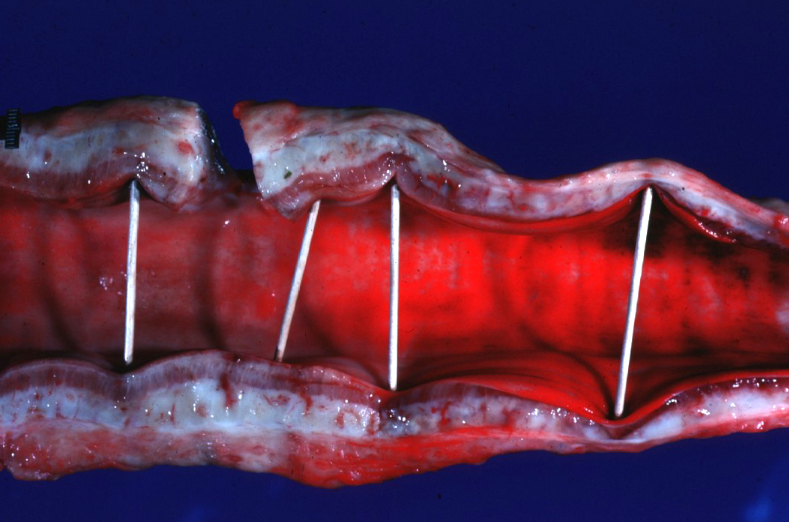
Ox. Which is true about this lesion?
a. Most common in the early spring in feedlot cattle
b. Most common in the summer in cattle on lush pasture
c. Most common in the early spring in cattle on lush pasture
d. Most common in the summer in feedlot cattle
Ox. Which is true about this lesion?
a. Most common in the early spring in feedlot cattle
b. Most common in the summer in cattle on lush pasture
c. Most common in the early spring in cattle on lush pasture
d. Most common in the summer in feedlot cattle (Tracheal edema and hemorrhage syndrome of feeder cattle)
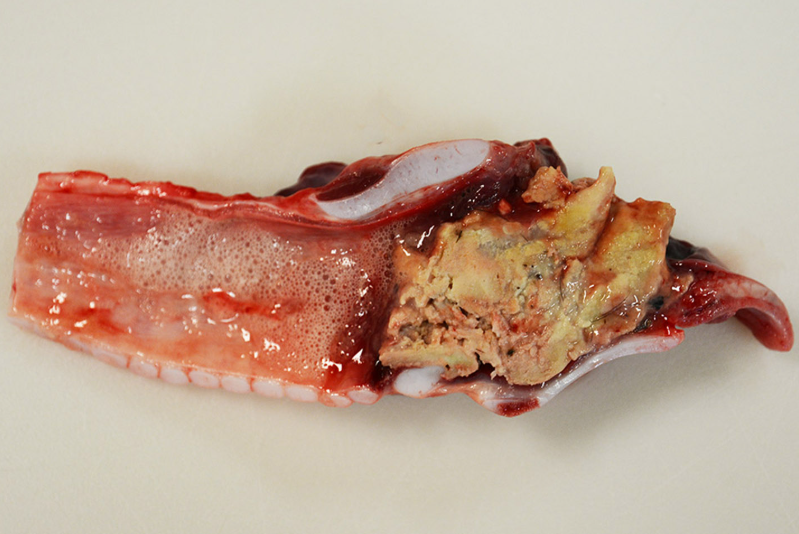
Calf. MDX and cause.
Severe, extensive necrotizing laryngitis
Fusobacterium necrophorum
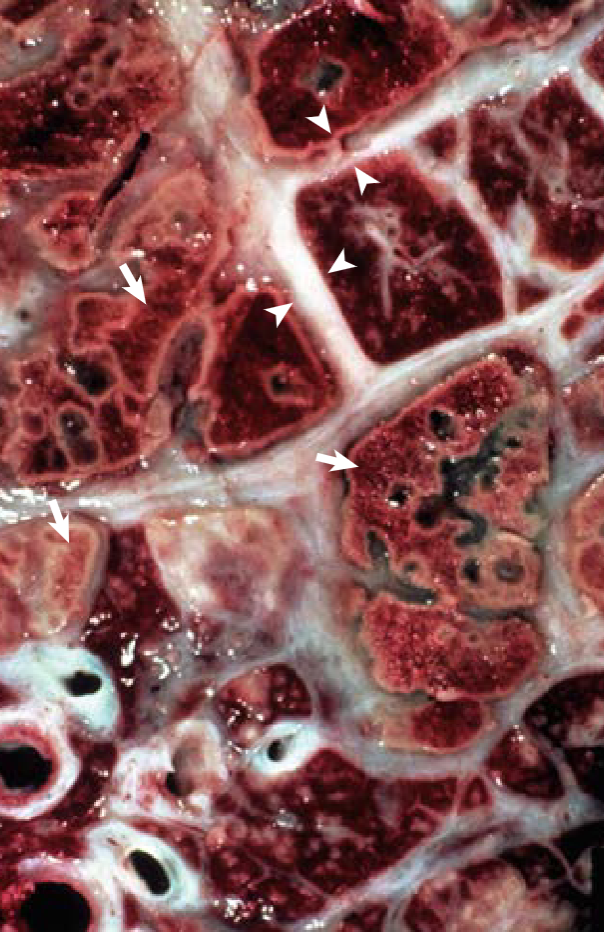
Ox. Most likely cause?
Mannheimia haemolytica
This is a sequestrum
What are the six bacterial species involved in shipping fever?
Mannheimia haemolytica
Histophilus somni
Pasteurella multocida
Biebersteinia trehalosi
Mycoplasma bovis
Mycoplasma mycoides mycoides
What are the four virulence factors of Mannheimia haemolytica and which is most important?
Leukotoxin (Rtx)
Lipopolysaccharide
Polysaccharide capsule
Iron regulated outer membrane protein
What is the etiologic agent of hemorrhagic septicemia and what are the gross lesions?
Pasteurella multocida serotypes 6:B and 6:E
Edema, hemorrhage, and hyperemia in many organs
Histophilus somni most important virulence factors?
Lipo-oligosaccharide (LOS) triggers apoptosis of bovine endothelial cells
Immunoglobulin Fc binding proteins interferes with host response
What are the 8 forms of Histophilus somni in cattle?
Septicemia
Thrombotic meningoencephalitis
Pneumonia and pleuritis
Myocarditis
Arthritis
Ophthalmitis and conjunctivitis
Otitis
Abortion
What is the most severe effect of Mycoplasma bovis?
Bronchiectasis
What are the 6 syndromes caused by Mycoplasma bovis?
Pneumonia
Arthritis
Otitis
Mastitis
Abortion
Keratoconjunctivitis
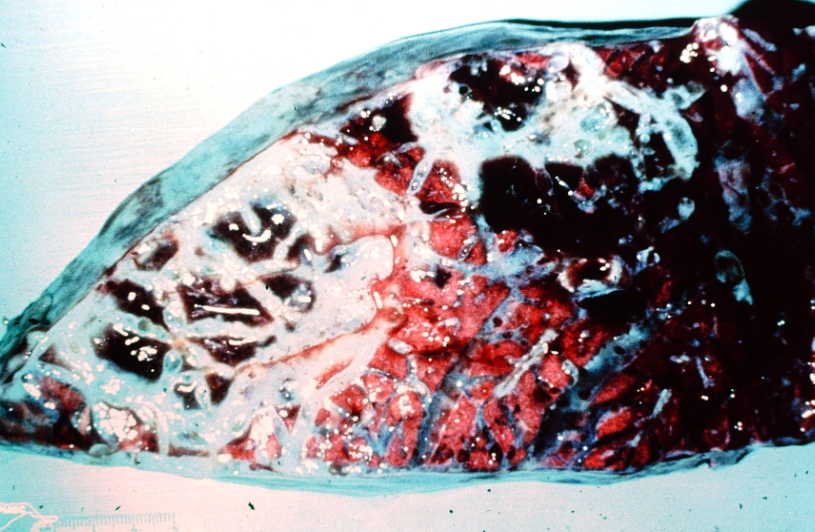
Ox. Cause and disease name?
Mycoplasma mycoides mycoides small type
Contagious bovine pleuropneumonia
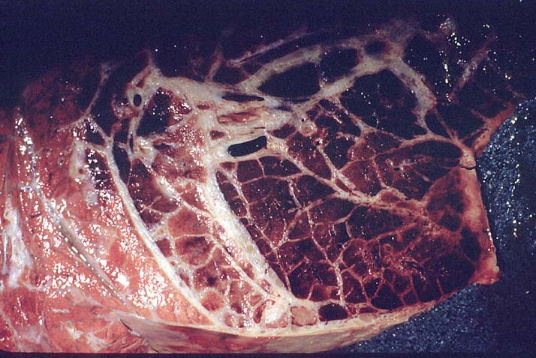
What is the main pathogenic mechanism of this disease?
Colonization of the airways and invasion of the vasculature causing vasculitis, thrombosis, and infarction leading to coagulative necrosis and marked interlobular edema (marbling)
There are early leashes of bovine tuberculosis seen in the lungs?
Subpleural and caudodorsal
What are the agents that cause atypical bovine pulmonary emphysema and edema (ABPEE)?
3-methylindole (L-tryptophan)
4-ipomeanol (fusarium solani)
Purple mint
Stinkwood
Brassica (rapeseed and kale)
What cells are the target of ABPEE?
Type II pneumocytes and bronchiolar cells
What cells in the lungs are critical to the pathogenesis of 3-methylindol?
Club cells
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis is seen in ______ cows in the (season) due to inhalation of ________ and a type ___ hypersensitivity reaction.
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis is seen in dairy cows in the winter due to inhalation of bacterial spores (Saccharopolyspora rectivigula) and a type III hypersensitivity reaction.
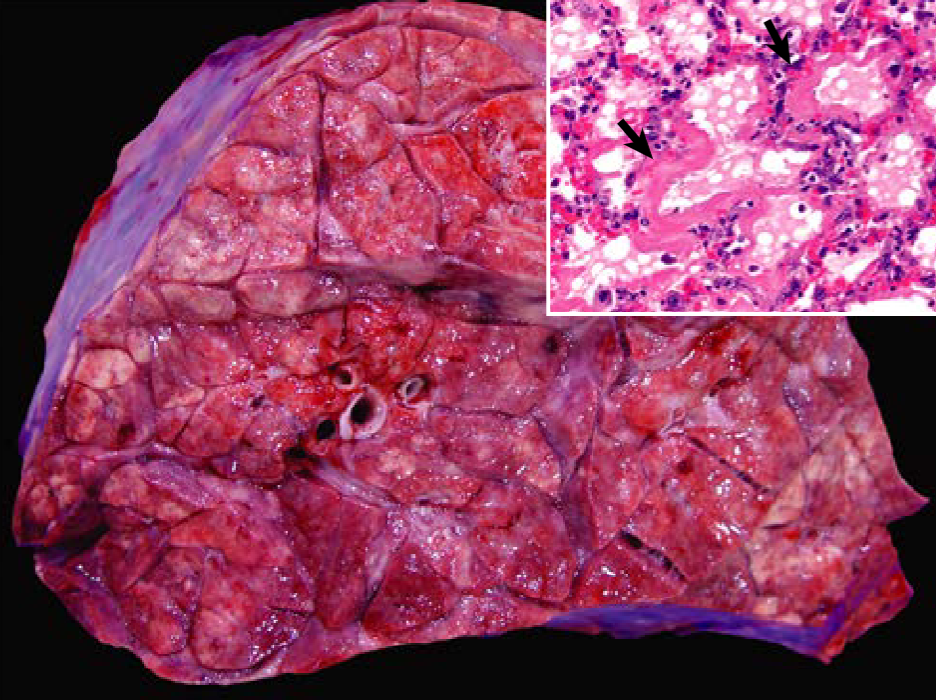
Dairy cow, winter. What type of hypersensitivity is this most likely?
a. Type I hypersensitivity
b. Type II hypersensitivity
c. Type III hypersensitivity
d. Type IV hypersensitivity
Dairy cow, winter. What type of hypersensitivity is this most likely?
a. Type I hypersensitivity
b. Type II hypersensitivity
c. Type III hypersensitivity
d. Type IV hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity pneumonitis is seen in dairy cows in the winter due to inhalation of bacterial spores (Saccharopolyspora rectivigula) and a type III hypersensitivity reaction.
Interstitial pneumonia due to reinfection syndrome is caused by what infectious agent?
Larvae of Dictyocaulus viviparus
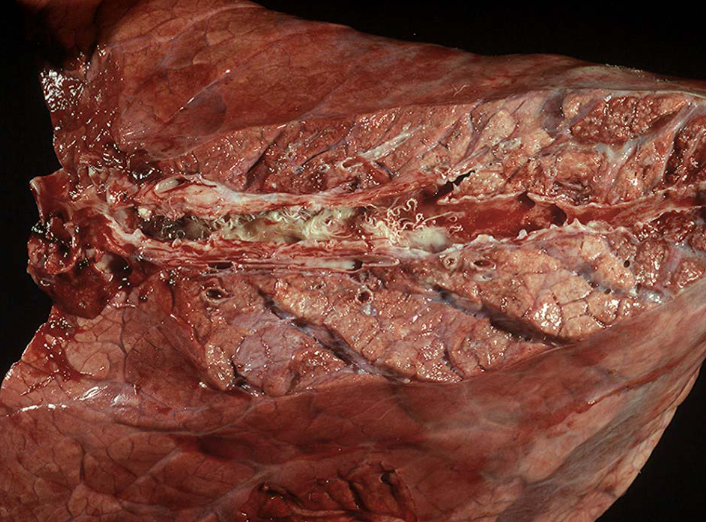
Ox. MDX and a cause.
Diffuse interstitial pneumonia
Dicytocaulus viviparus
What virus in cattle causes an interstitial pneumonia that is similar to ABPEE?
BRSV
What gasses cause interstitial pneumonia?
NO2 (nitrogen dioxide)
H2S (hydrogen sulfide)
NH3 (ammonia)
What is the most common source of gasses that cause interstitial pneumonia in cattle?
Silo gasses
Where are adult Dictyocaulus viviparus found in cattle lungs?
Caudal lobes mostly
What cattle are mostly likely to develop reinfection syndrome d/t Dictyocaulus viviparus?
a. calves exposed to large numbers of larvae during their first spring
b. naive adult cattle exposed to large numbers of larvae
c. previously exposed adult cattle exposed to few larvae
d. previously exposed adult cattle exposed to a large number of larvae
What cattle are mostly likely to develop reinfection syndrome d/t Dictyocaulus viviparus?
a. calves exposed to large numbers of larvae during their first spring
b. naive adult cattle exposed to large numbers of larvae
c. previously exposed adult cattle exposed to few larvae
d. previously exposed adult cattle exposed to a large number of larvae
What lobe is most severely affected in cattle with aspiration pneumonia?
Right cranial lung lobe because right cranial bronchus is the most cranial branch
What are the three most common infectious causes of pleuritis in adult cattle?
Mannheimia haemolytica
Histophilus somni
Mycoplasma mycoides spp. mycoides
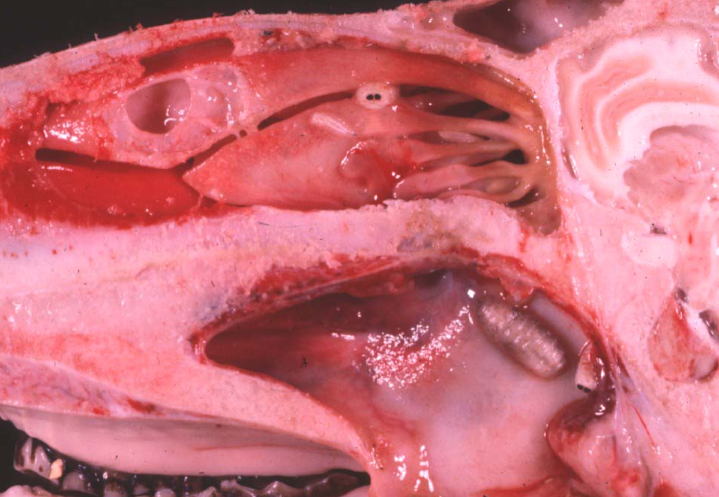
Sheep. Cause and most severe sequelae?
Oestrus ovis
Migration through cribriform plate causing direct or secondary bacterial meningitis
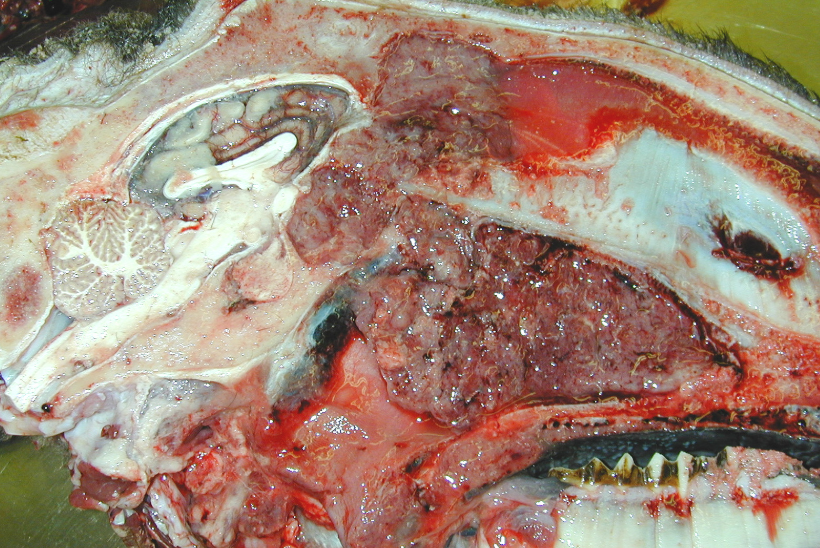
Sheep. MDX and a cause?
Nasal adenocarcinoma
Betaretroviruses
ENTV-1 (sheep) and ENTV-2 (goats)
What cell type does Maedi-Visna virus infect?
Monocytes and macrophages
In Maedi, are lymphocytes predominantly B, T, or mixed?
T lymphocytes
What are important histologic features of CAE that are not present in Maedi?
Type II pneumocyte hyperplasia and flooding of alveolar spaces with proteinaceous eosinophilic fluid (surfactant)
PdPR is caused by what etiologic agent and what are the three key histo features in lungs?
Morbillivirus
PIIP hyperplasia
Alveolar edema
Syncytia with INIB or ICIB
What is the multifactorial, mild form of respiratory disease called in sheep?
Chronic enzootic pneumonia
Septicemic Pasteurellosis in lambs >5 mo is caused by ____ and younger than 2 months is caused by ____.
Septicemic Pasteurellosis in lambs >5 mo is caused by Biebersteinia trehalosi and younger than 2 months is caused by Mannheimia haemolytica (biotype A).
What is the hallmark histologic lesion of septicemic pasteurellosis in lambs
Disseminated intravascular thrombosis with bacterial colonies
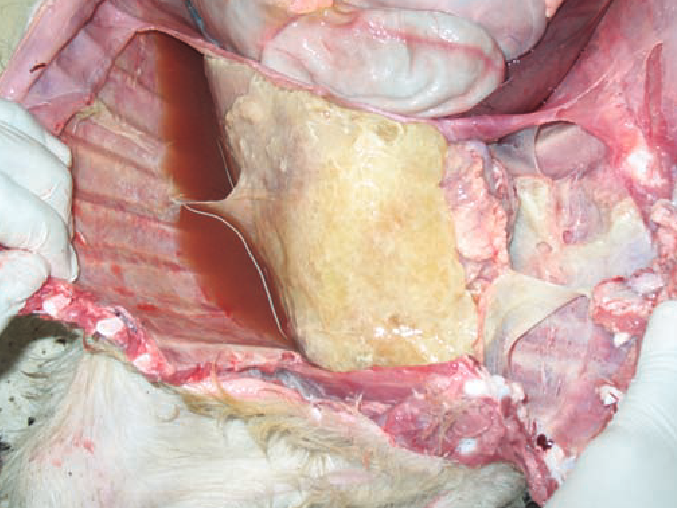
Goat. Most likely cause?
Mycoplasma capricolum subsp. capripneumonia
Contagious caprine pleuropneumonia
Besides S. aureus what other agent is involved in tick pyemia?
Anaplasma phagocytophilum
This decreases the the phagocytic capacity of neutrophils allowing S. aureus to run rampant
Dictyocaulus lives in the ______.
Muellerius lives in the _____.
Protosrongylus rufescens lives in the ___.
Dictyocaulus lives in the small bronchi.
Muellerius lives in the alveoli.
Protosrongylus rufescens lives in the bronchioles.
What is a unique presentation of Muellerius in goats?
Can present as a diffuse interstitial pneumonia and mimic CAEV.
In Jaagsiekte virus induced pulmonary neoplasms, what cells do the tumors originate from?
TIIP and club cells
What is a clinical feature of Jaaksiekte that can differentiate it from Maedi?
Abundant fluid pours from nostrils when hind legs are raised