Geology, Earth Resources, and Climate Change Overview
1/253
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
254 Terms
Crust
Outermost layer, least dense, brittle.
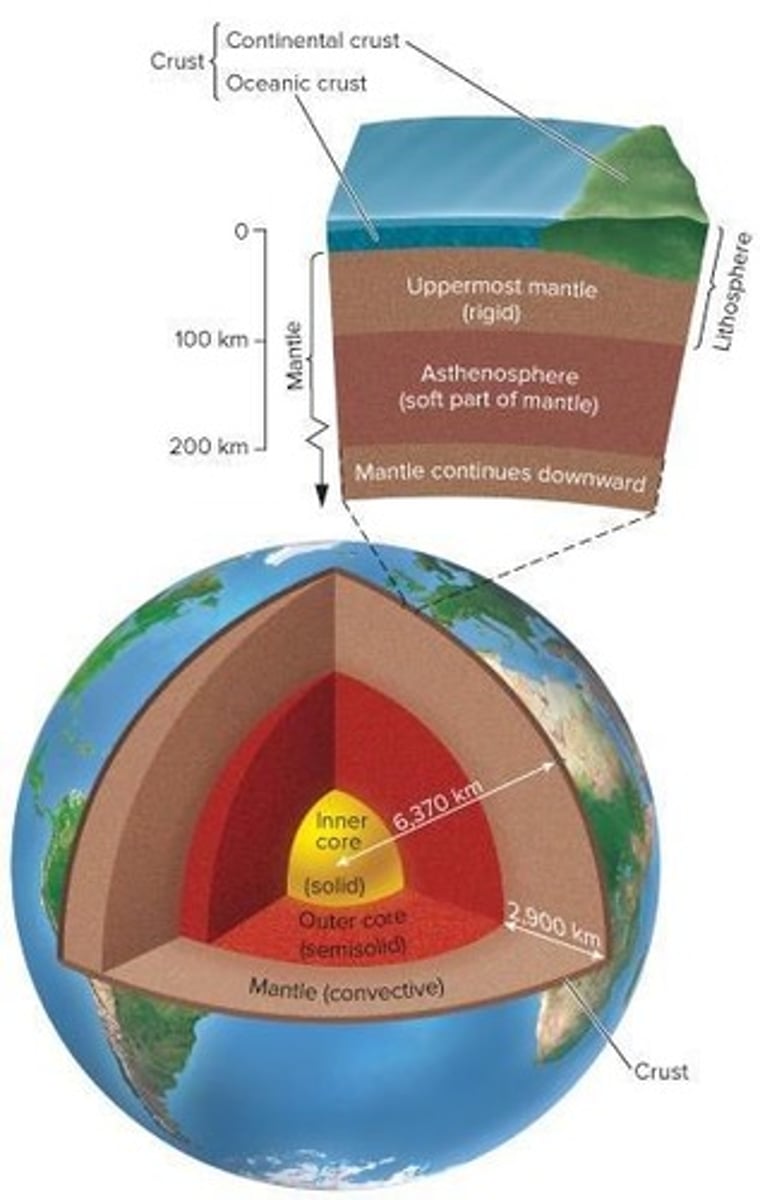
Oceanic Crust
Thinner, denser, recycled under 200 million years.
Continental Crust
Thicker, less dense, up to 3.8 billion years.
Outer Core
Hot, slowly moving liquid, generates magnetic field.
Inner Core
Solid state of iron and nickel under pressure.
Mantle
Hot, pliable rock layer, increases in density.
Asthenosphere
Upper mantle part, less rigid, allows movement.
Tectonic Plates
Sections of crust floating on mantle.
Divergent Boundary
Plates move apart, creates new oceanic crust.
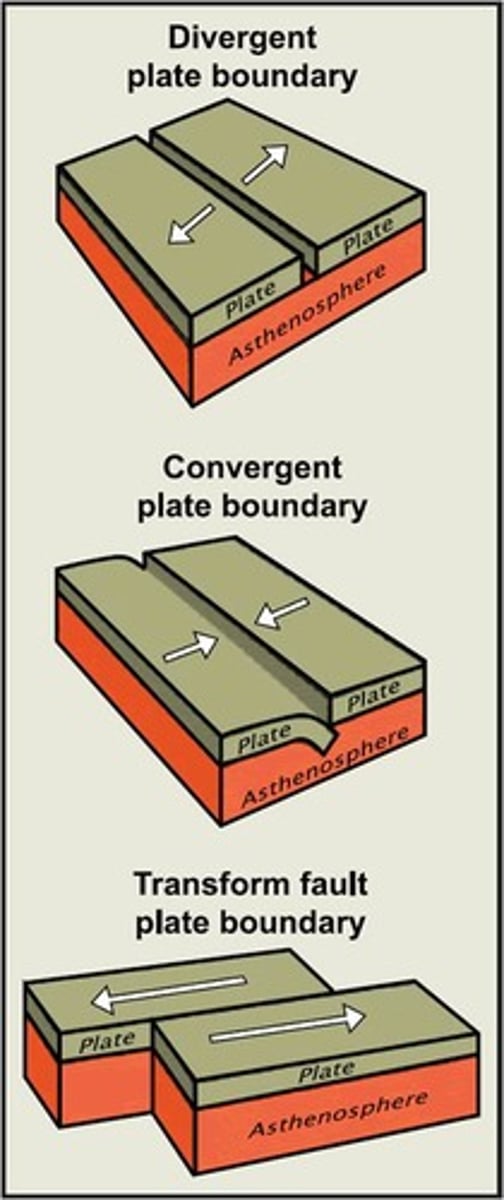
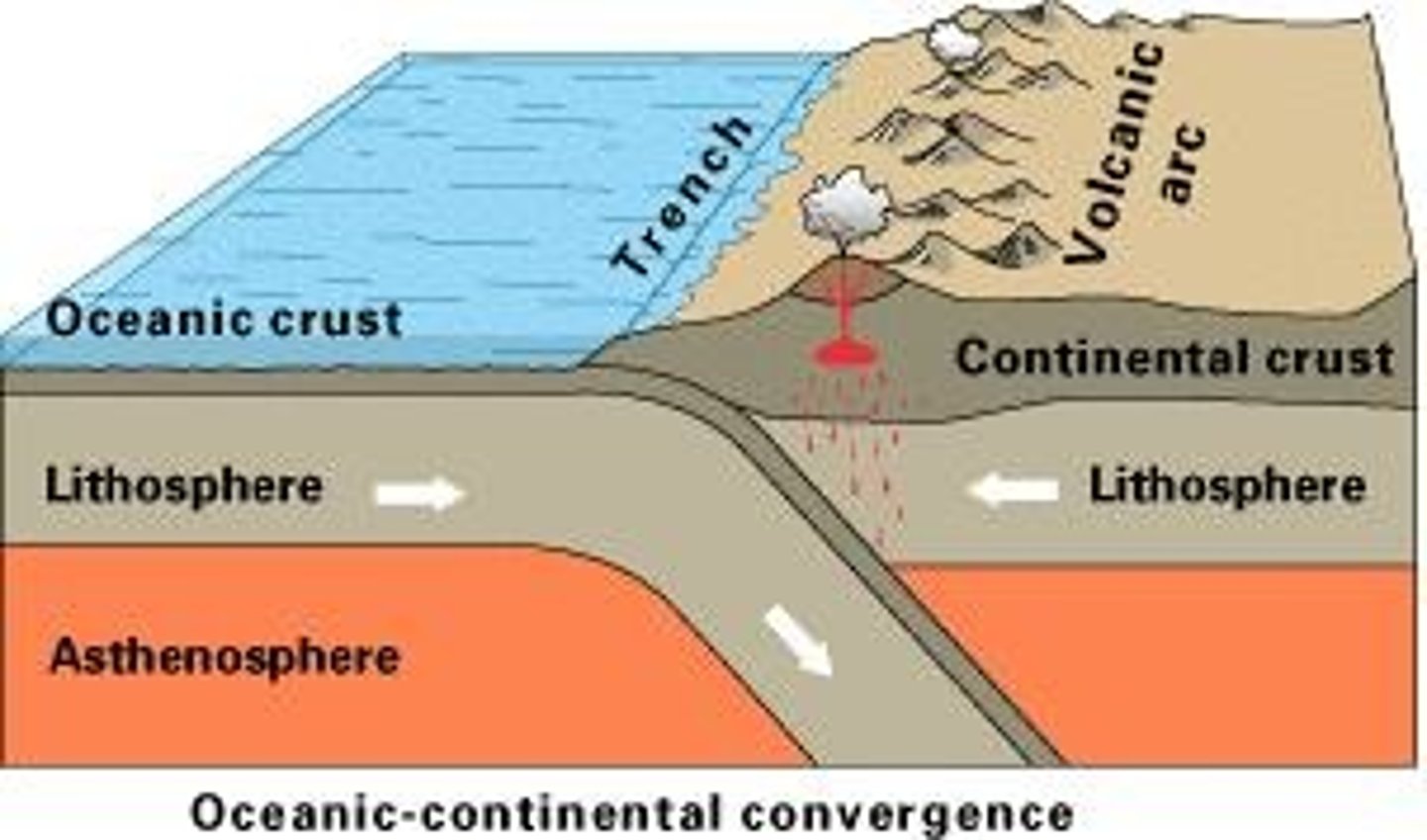
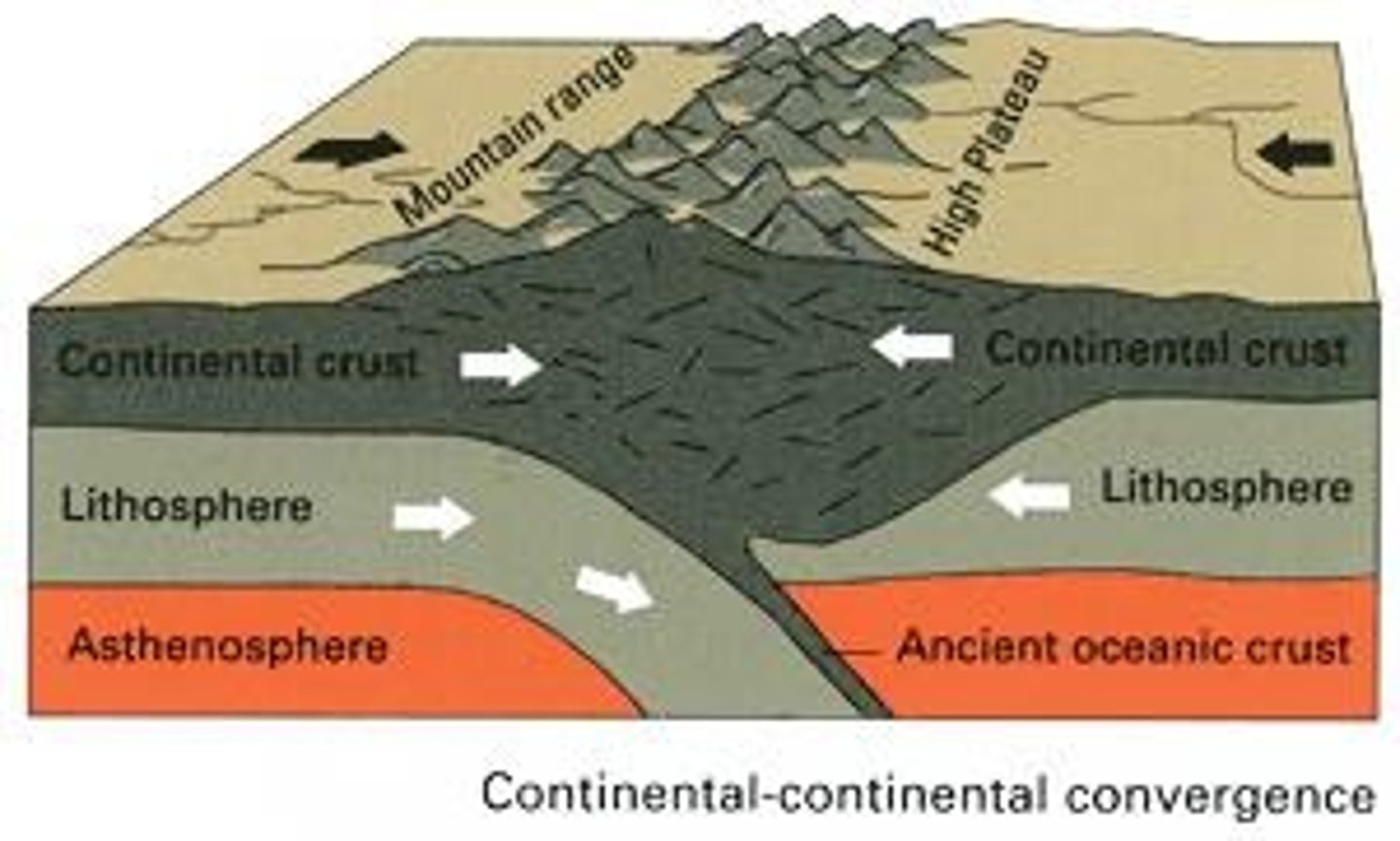
Convergent Boundary
Plates move together, destroys oceanic crust.
Transform Fault Boundary
Plates slide past, no crust created or destroyed.
Subduction
Denser oceanic plate descends into mantle.
Trenches
Formed at converging plate boundaries.
Volcanic Arcs
Created at converging plate boundaries from magma.
Orogeny
Mountain formation at converging plate boundaries.
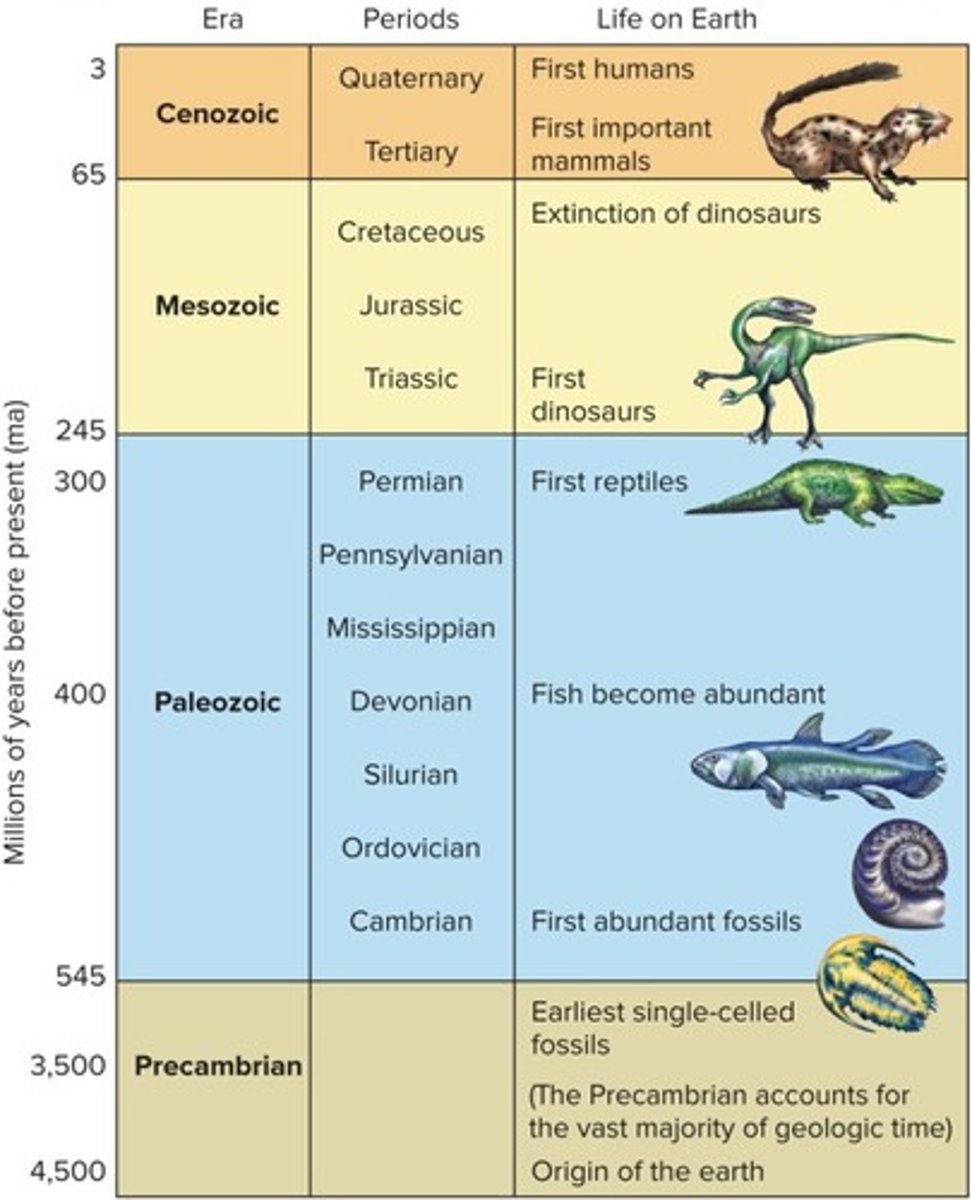
Precambrian Era
4.6 billion - 545 million years ago.
Great Oxygenation Event
2.4 billion years ago, atmosphere became oxygen-rich.
Paleozoic Era
545 - 245 million years ago, explosion of life.
Cambrian Period
Begins Paleozoic, abundant fossil record starts.
Mesozoic Era
Age of Dinosaurs, 245 - 65 million years ago.
Mass Extinction
Largest extinction at end of Permian period.
Converging Plate Boundaries
Denser plates subduct, lighter plates remain.
Earth Processes
Natural occurrences shaping Earth's structure and resources.
Plateosaurus
Oldest dinosaur fossil, 243 million years old.
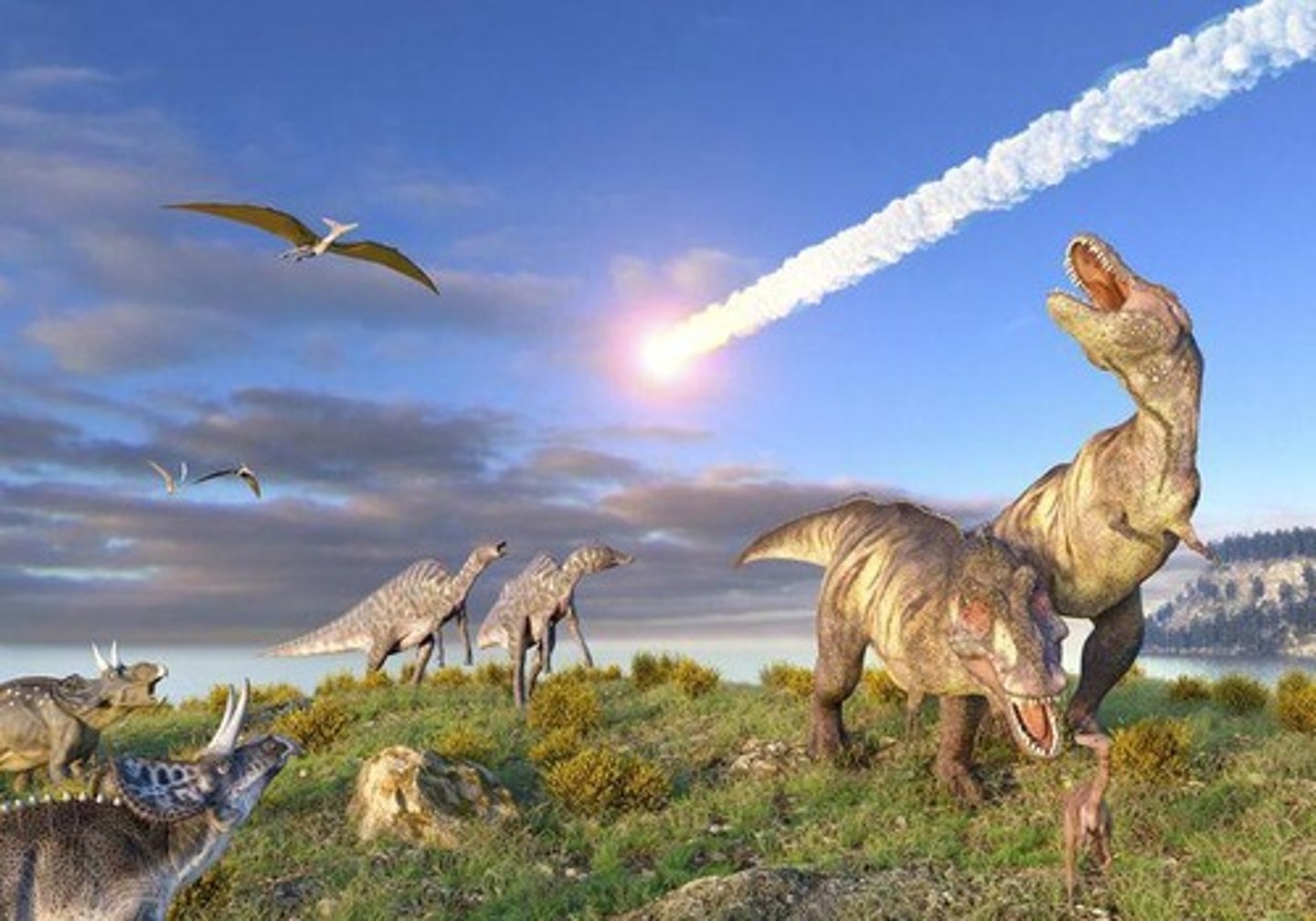
Meteor extinction theory
Meteor impact caused dinosaur extinction 66 million years ago.

Cenozoic Era
Current geological era, began 65 million years ago.
Australopithecus afarensis
Early hominid species appeared 3.2 million years ago.
Homo sapiens
Modern humans appeared 315,000 years ago.
Igneous Rocks
Formed from magma cooling at surface or underground.
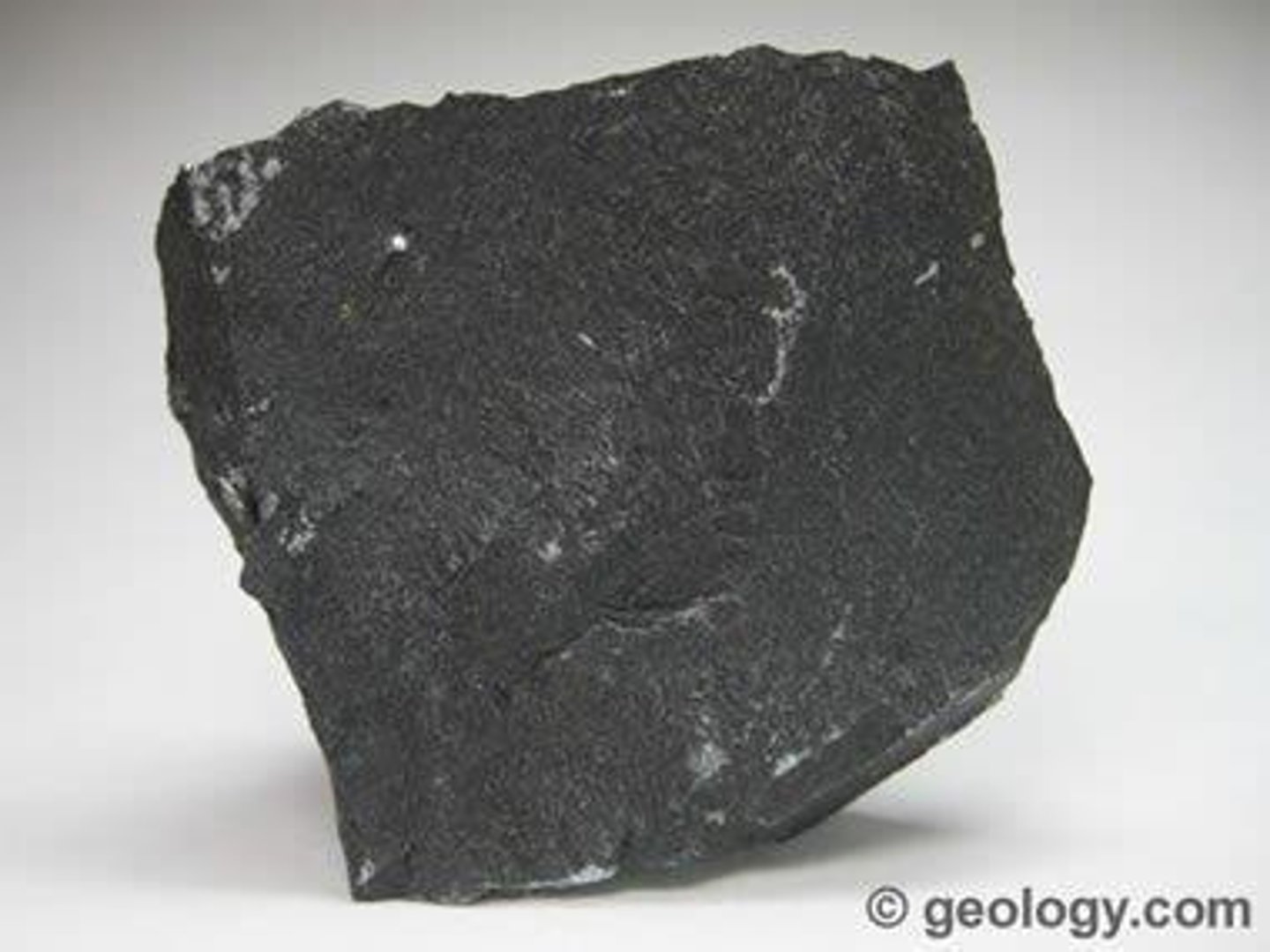

Extrusive igneous rocks
Form from lava, cool quickly, microscopic grains.
Basalt
Fine-grained rock formed from quickly cooled lava.
Intrusive igneous rocks
Form from magma underground, larger mineral grains.
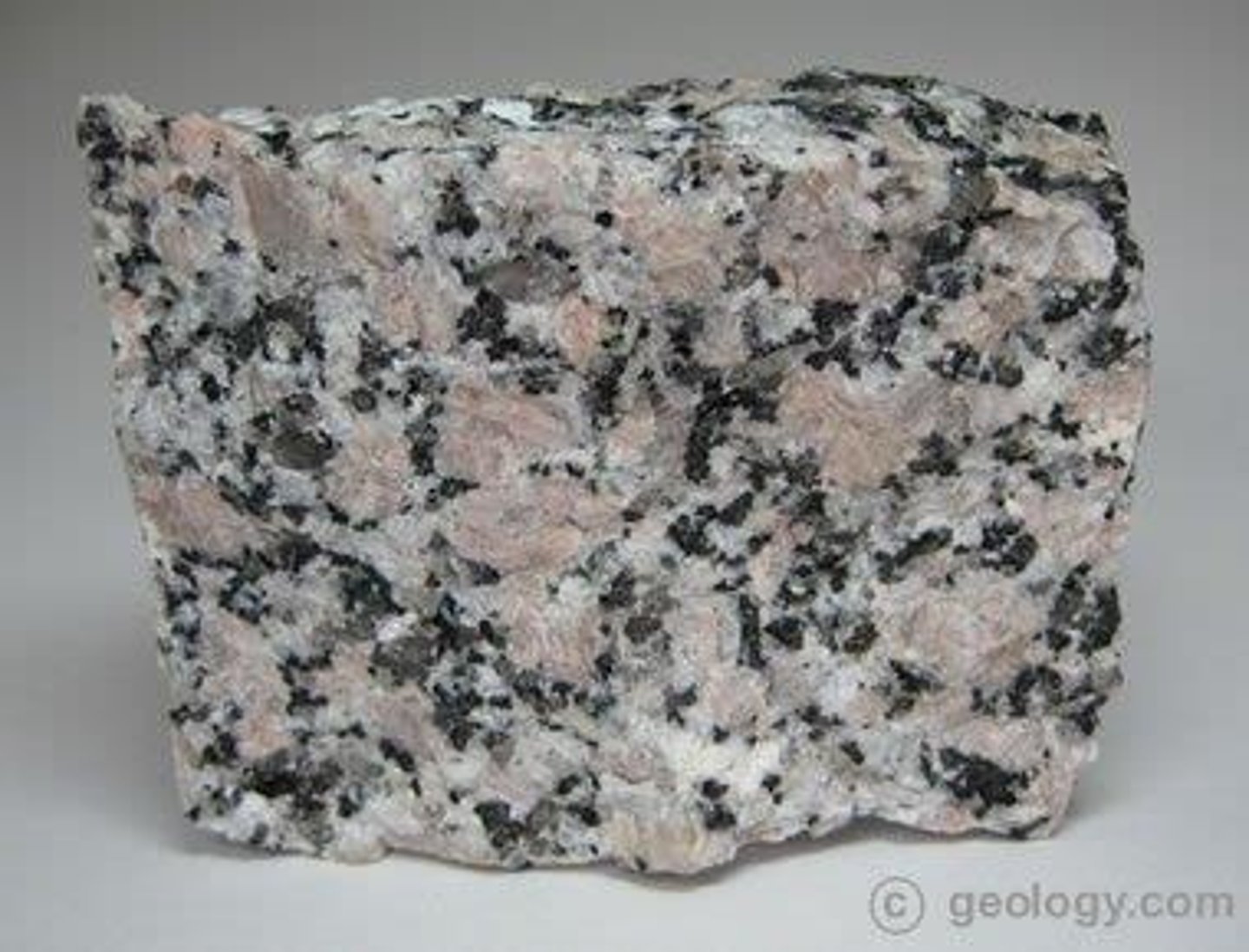

Granite
Slowly cooled rock with visible mineral grains.
Metamorphic Rocks
Formed under pressure and heat from existing rocks.
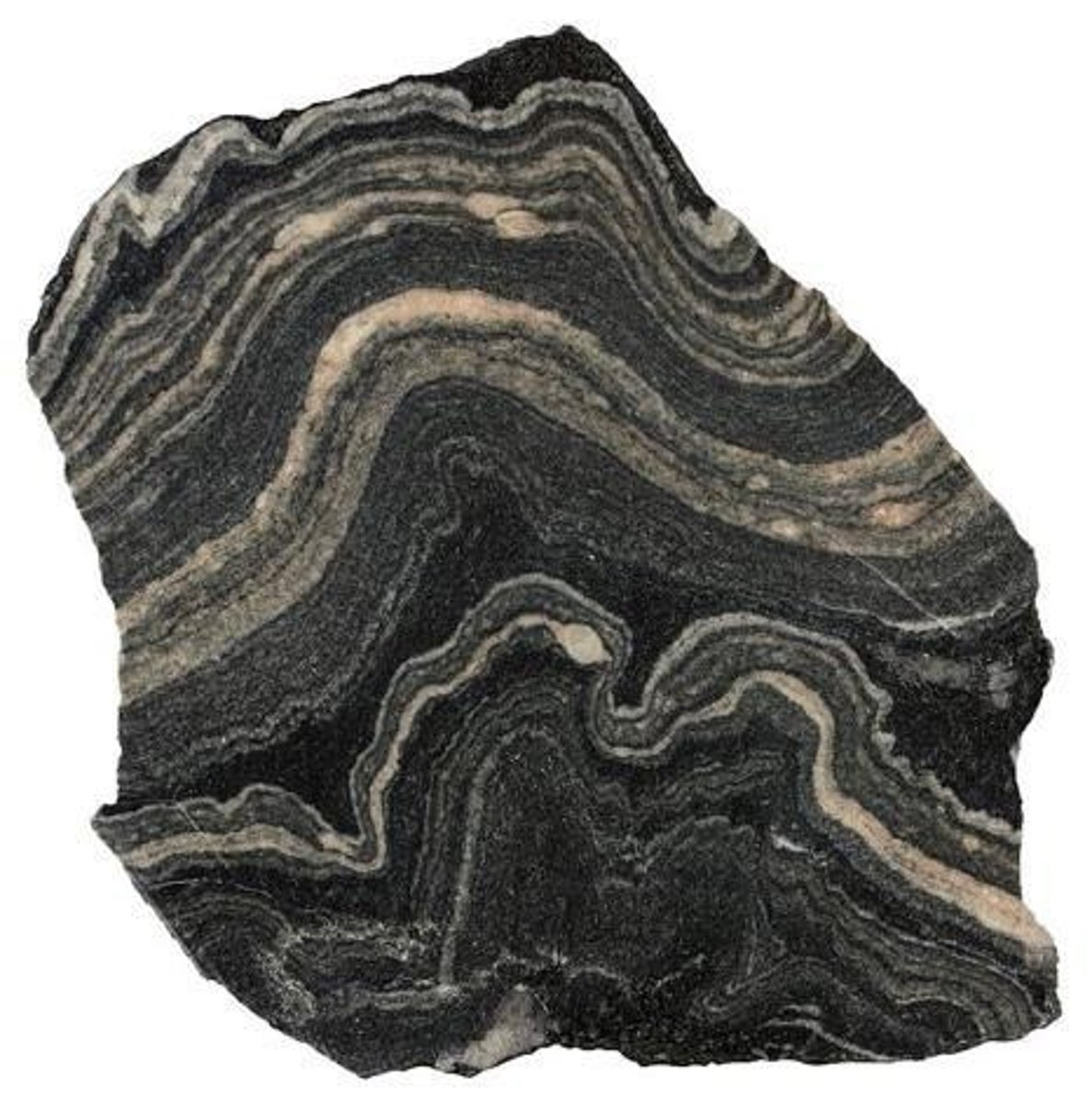

Foliated metamorphic rocks
Mineral grains align under directional pressure.
Gneiss
Foliated rock formed from granite.
Non-foliated metamorphic rocks
Mineral grains not aligned due to omnidirectional pressure.
Marble
Non-foliated rock formed from limestone.
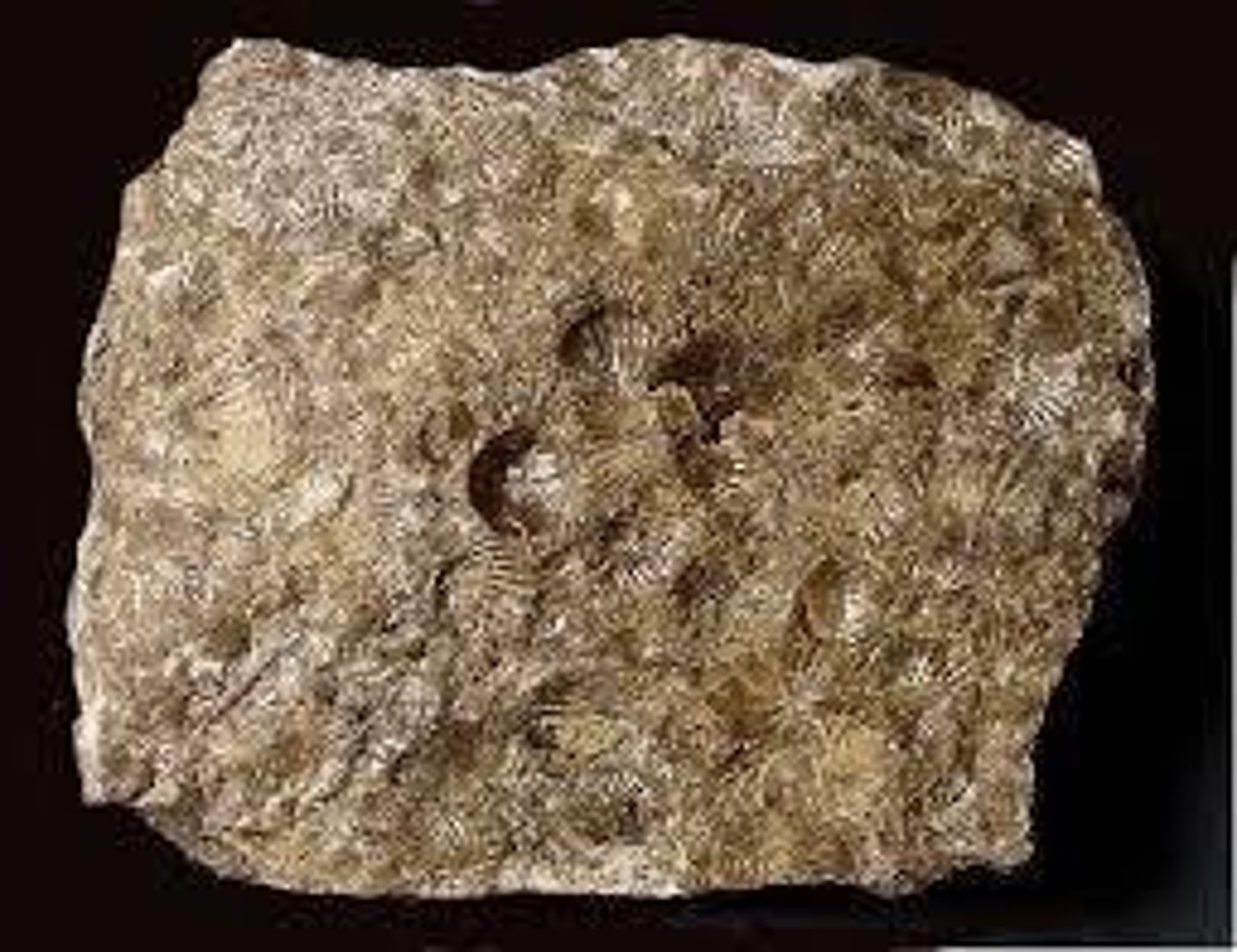

Sedimentary Rocks
Formed on Earth's surface from weathering and erosion.
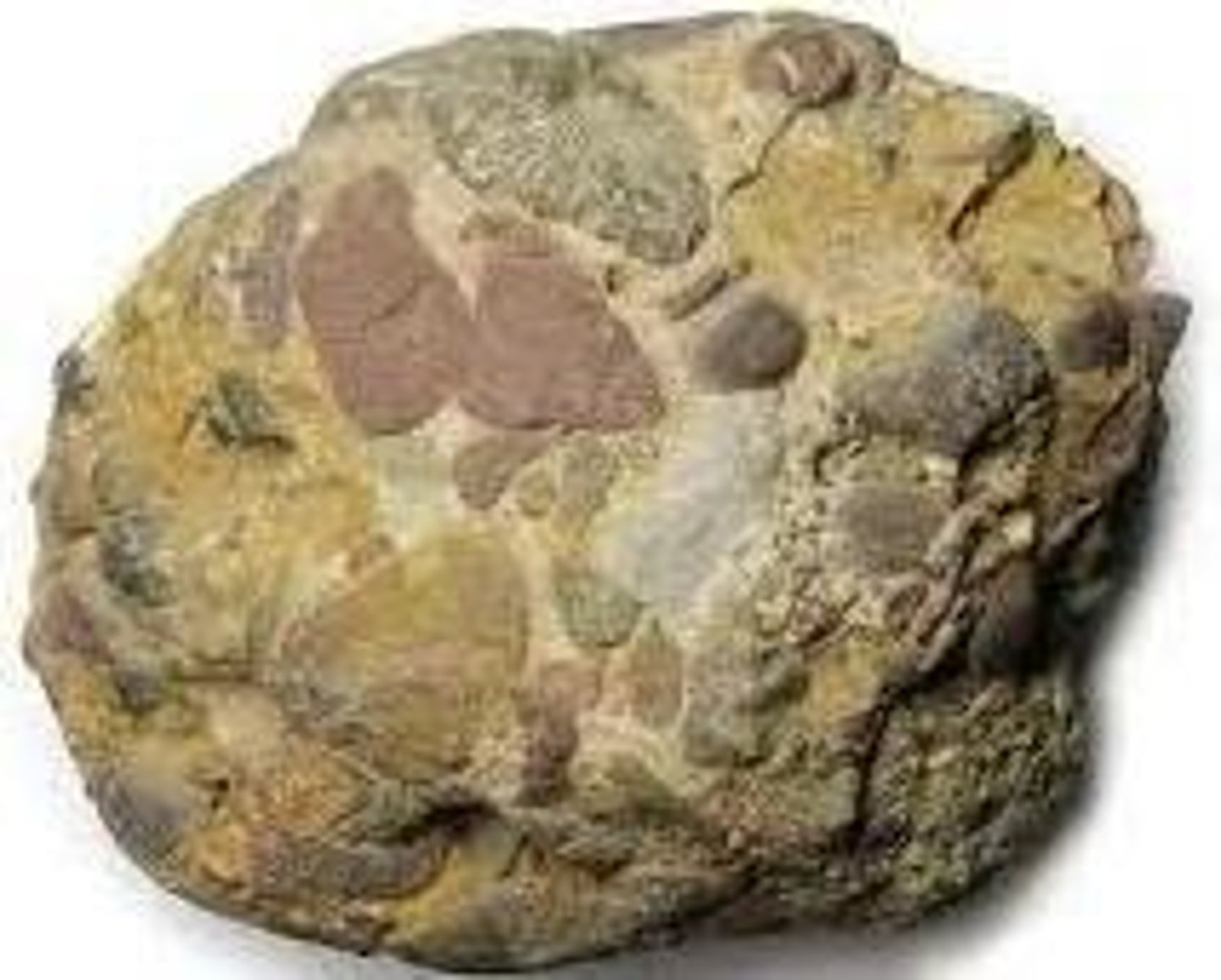

Clastic rocks
Formed from lithified smaller rocks.
Conglomerates
Large rocks lithified together.
Organic rocks
Formed from deposition of plant or animal materials.
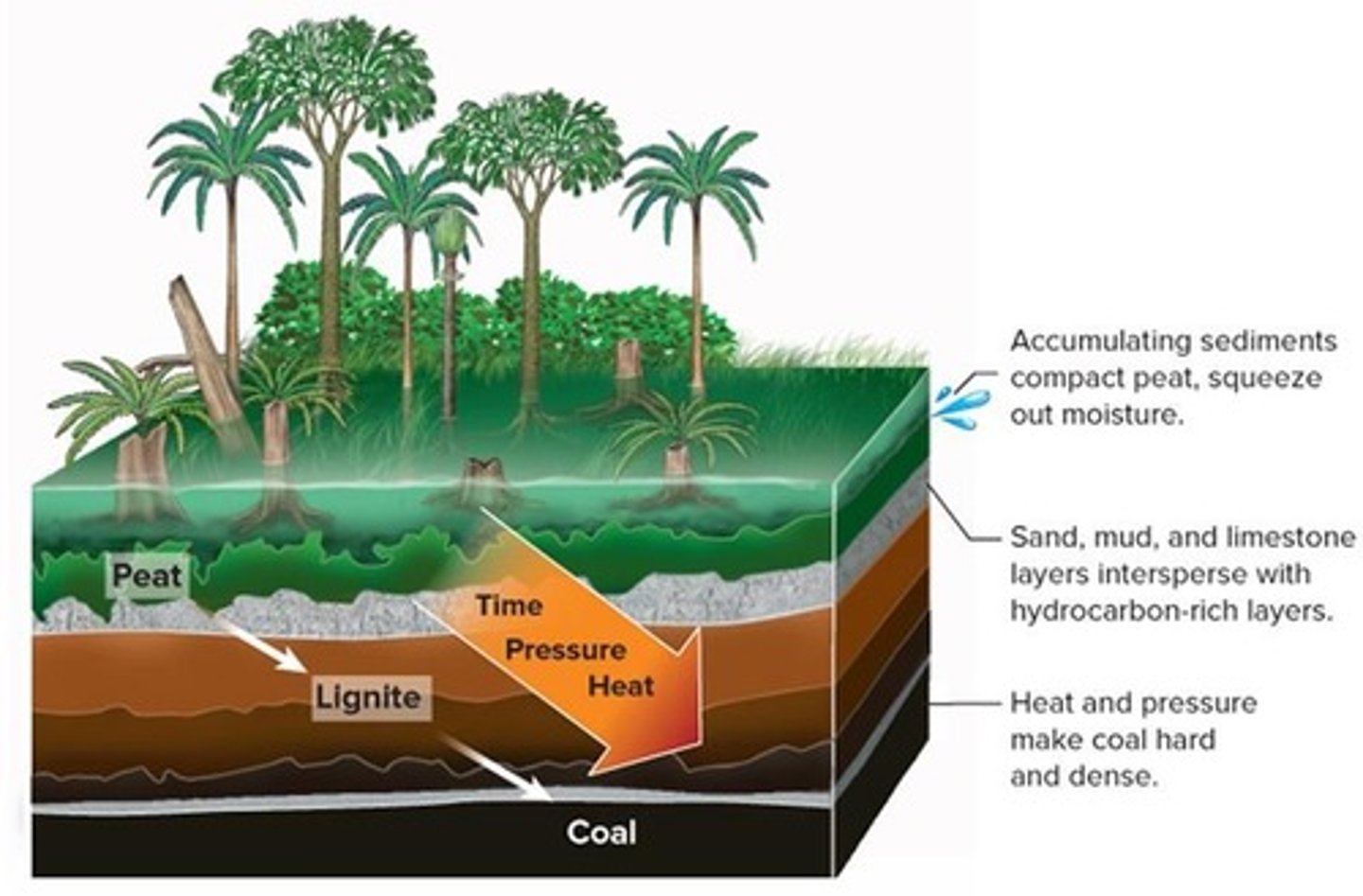
Coal
Organic rock formed from plant matter deposition.
Chemical rocks
Formed from minerals precipitating out of solution.
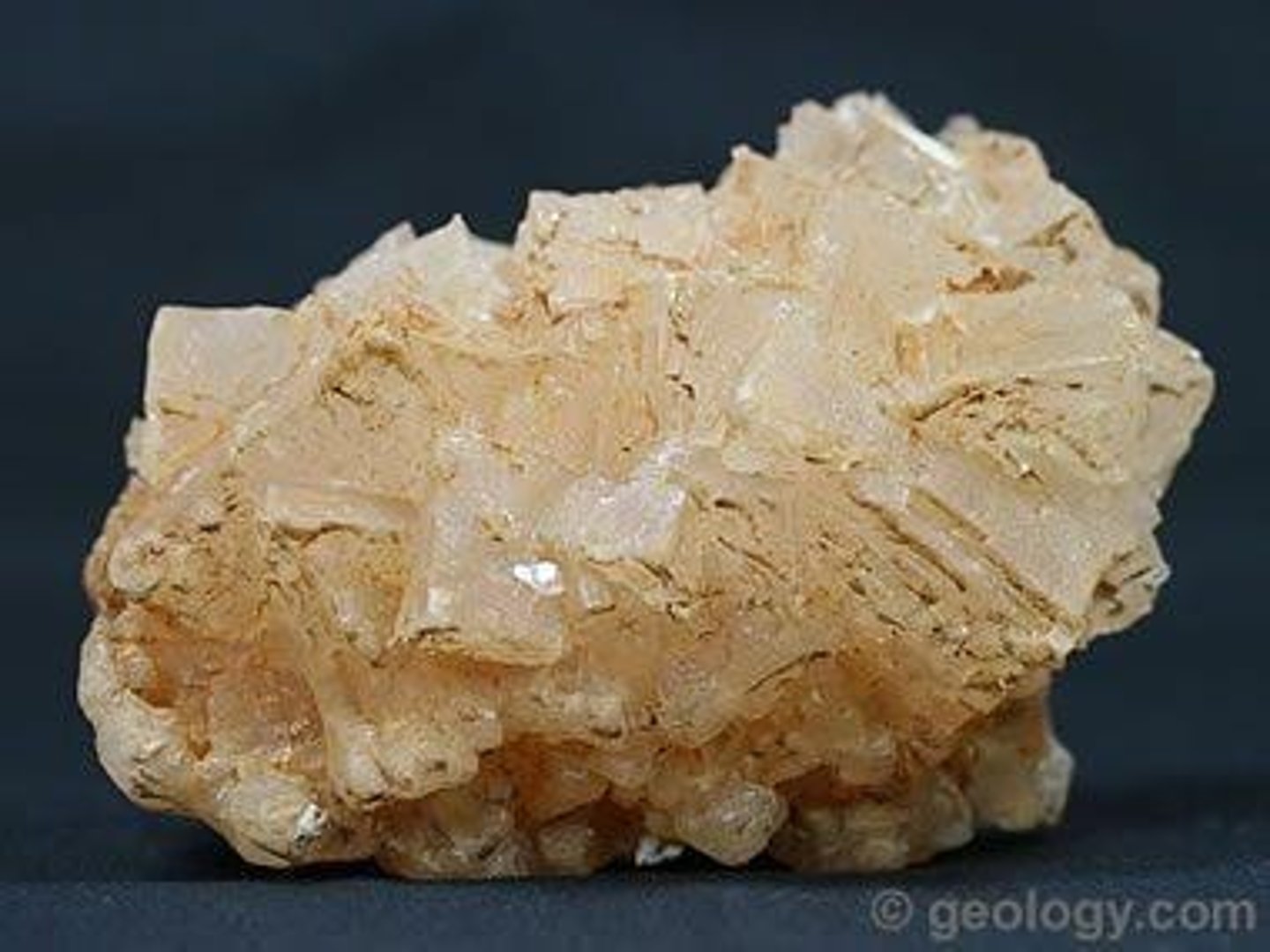

Halite
Rock salt formed from evaporated seawater.
Mechanical weathering
Physical break-up of rocks without chemical change.
Chemical weathering
Alters specific components, weakens rock structure.
Oxidation
Oxygen reacts with minerals, causing rusting.
Hydrolysis
Water dissolves minerals in rocks.
Carbonation
Acidic water breaks down limestone into carbon dioxide.
Sedimentation
Deposition of transported rock particles in new locations.
Peat
Organic matter that forms coal over time.
Coal Formation
Burial of peat under pressure and heat.
Energy Density
Amount of energy produced per unit mass.
Lignite Coal
Lowest grade coal, requires 60 million years burial.
Sub-bituminous Coal
Requires 250 million years burial for formation.
Bituminous Coal
Requires 300 million years burial for formation.
Anthracite Coal
Highest grade coal, requires 350 million years burial.
Carbon Dioxide Release
Anthracite releases most CO2 per BTU.
Mesozoic Era
Period when most oil reserves formed.
Kerogen
Organic matter in oil shale that generates oil.
Anoxic Environment
Lack of oxygen preventing decomposition of organic matter.
Oil Formation Temperature
Oil forms at 90°C to 160°C; above forms gas.
Confining Layer
Structure holding oil in place, resembles upside-down bowl.
Rare Earth Elements
China dominates market; U.S. has stricter laws.
Mountain Pass Mine
California mine closed due to competition and costs.
Recycling Benefits
Reduces demand for new ore and environmental impact.
Substitution
Using alternatives to reduce resource demand.
Open-Pit Mining
Surface mining method for various minerals and ores.
Toxic Lake
Water-filled open pits can become hazardous to wildlife.
Berkeley Pit Incident
Thousands of birds died from contaminated mine water.
Strip Mining
Removes vegetation and soil to access coal seams.
Spoil Banks
Debris piles from mining that can erode and contaminate.
Reclamation Measures
Efforts to restore land after mining activities.
Mountaintop Removal
Explosives remove mountains to access coal seams.
Buried Streams
900 km of streams buried in West Virginia.
Clean Water Act
EPA halted major mountaintop removal in 2011.
Underground Mining Risks
Includes tunnel collapses, explosions, and contamination.
Centralia Mine Fire
Burning since 1962, costing $40 million to control.
Coal Mine Fires in China
Some have burned for 400 years.
Ore Processing Pollution
Can be more polluting than mining itself.
Smelting
Heating ore to extract metals, causes air pollution.
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
Released from sulfide ores, contributes to acid rain.
Acid Rain
Forms from sulfuric acid, harms vegetation and aquatic life.
Heap Leach Extraction
Uses cyanide to dissolve gold from crushed ore.
Freshwater Usage
Rinsing ores consumes large amounts of water.
Contaminated Wastewater
Contains arsenic, heavy metals, and mercury.
Mine Site Reclamation Costs
Estimated $70 billion cleanup cost for U.S. abandoned mines.
Bonding Money Requirement
1977 law requires funds for site cleanup before mining.
Meridian Gold Beartrack Mine
$220 million gold extracted, only $2 million bonded.
Gold King Mine Incident
Toxic sludge leaked, killing aquatic life in Animas River.
General Mining Law of 1872
Allowed mining land sales at $2.50 to $5 per acre.
Land Use Abuse
Purchased land can be used for non-mining purposes.
Royalty Payments
Mining companies pay no royalties on federal land.
Potential Royalty Revenue
8% royalties could generate $320 million annually.
Current Bonding Issues
Existing bonds for cleanup are insufficient.
Environmental Regulations Debate
Should mining laws be revised for better protections?
Bonds for site cleanup
Higher bonds could save $320 million annually.
Meteor impact
Caused Mesozoic extinction through atmospheric soot.
Volcanic eruptions
Permian extinction caused by gases and cooling.