Unit 6: Discharge Measurements and Weir Design (Exam 2)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
L = ?
length of the weir over which flow is occurring (L)
A = ?
area of the orifice (A)
Cd = ?
discharge coefficient (Cd)
H = ?
head over the orifice (H)
H = height from the center of the orifice to the liquid surface
As Cd decreases, H ___
increases
As H increases, V ___
increases
What are the components of the discharge coefficient?
Cc (contraction coefficient) and Cv (velocity coefficient)
Cd = Cc * Cv
Cc = ?
contraction coefficient (Cc)
Cd = Cc * Cv
Cv = ?
velocity coefficient (Cv)
Cd = Cc * Cv
What is the contraction coefficient (Cc)?
The contraction coefficient (Cc) allows us to use the area of the orifice (A) as opposed to the area of the Vena Contracta (VC).
What is the velocity coefficient (Cv)?
The velocity coefficient (Cv) takes into account all losses in the system.
Why do we need to differentiate between small orifice and large orifice?
For large orifice, the average velocity is NOT represented by the velocity at the center of the orifice.
For small orifice, the velocity at the center of the orifice represents average velocity.
W = ?
width of the channel (W)
L = ?
length of the weir (L)
P = ?
height of the weir (P)
V0 = ?
approach velocity (V0) = velocity in the river approaching the weir
If P (height of the weir) and W (width of channel) are known, we must use…
approach velocity (V0)
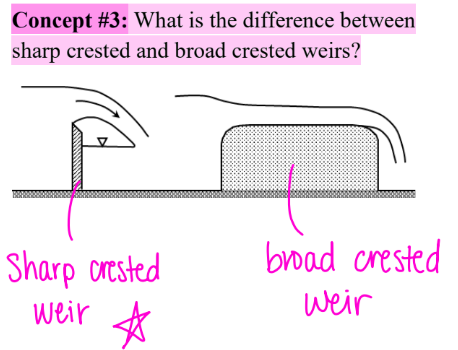
What is the difference between sharp crested and broad crested weirs?
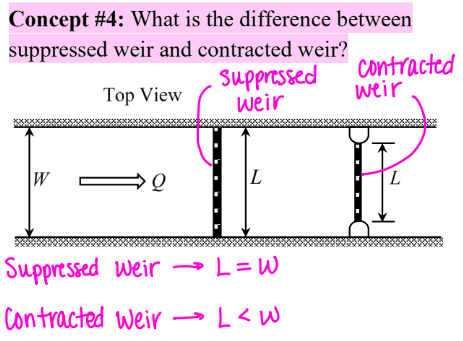
What is the difference between suppressed weir and contracted weir?
Piers
Located in the middle of flow on top of the weir
Abutments
Located at the end of a weir and are anchored to the channel bank
What is the difference between piers and abutments?

Each contraction reduces ___ by 0.1H
L (length of the weir over which flow is occurring)
Weir Contractions
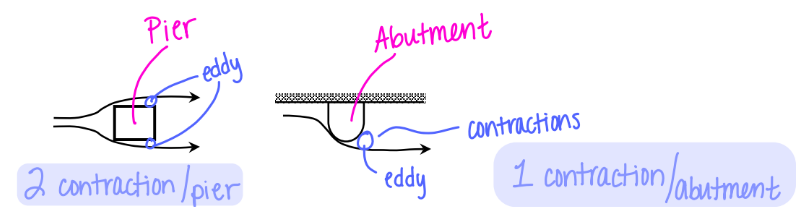
What are weir contractions?
Weir contractions occur when the flow has to curve around abutments or piers.
How are weir contractions accounted for?
Weir contractions reduce the length of the weir
Each contraction reduces L by 0.1H
Free vs Submerged Weir
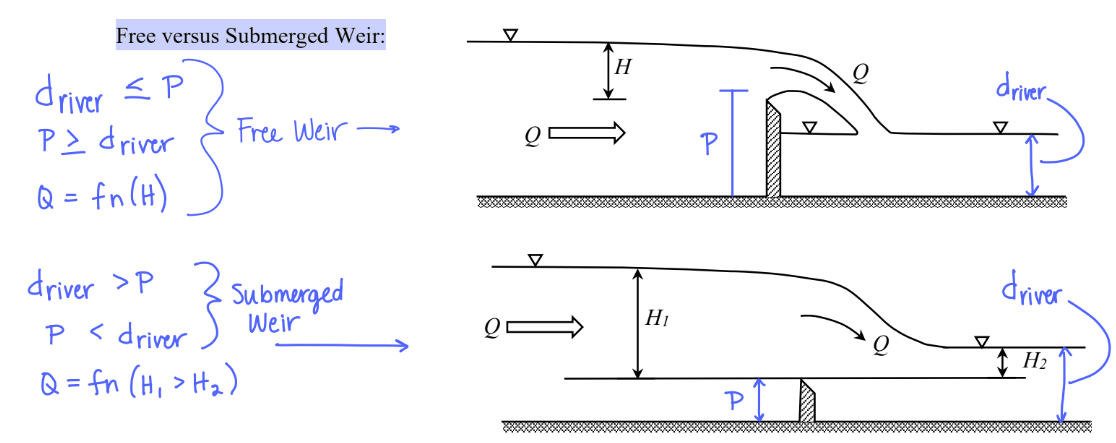
Free Weir
weir where the downstream water level is at or below the crest of the weir
P ≥ d
Submerged Weir
weir where the downstream water level is above the crest of the weir
P < d
n = ?
total # of contractions (n)
When do you include the approach velocity (v0)?
If P and W are known
If __ is known
Cd is a function of H and __?
θ (theta)
For a rectangular weir, n (number of contractions) is at least #?
2
If there are piers, n (number of contractions) will ___?
increase
There is only one ___ value for the whole weir.
Cd (discharge coefficient)
Submerged Weir diagram
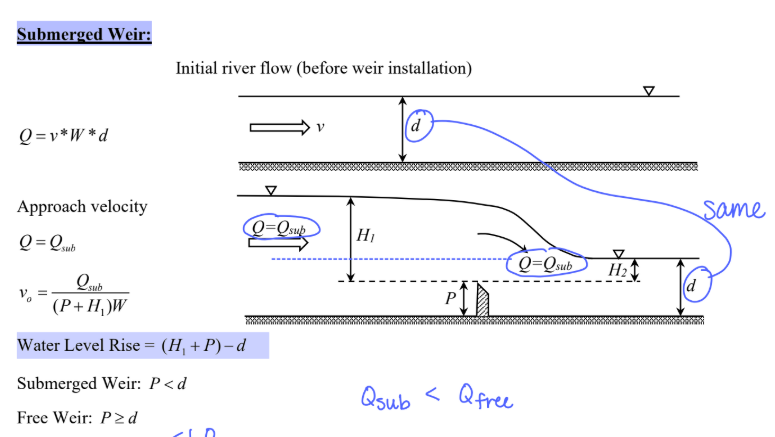
Steps to solve submerged weir:
Find Qfree
Find Qsub
v0 = Qsub / ((ρ+H)*w)
Triangular Weir - V-Notch diagram
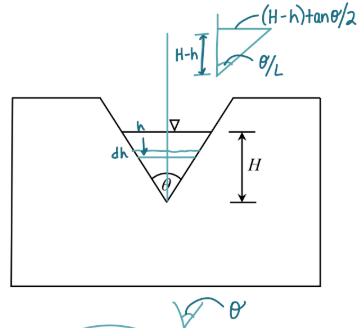
A Triangular Weir (V-Notch) is always a ___ weir.
free
A Triangular Weir (V-Notch) is ____ to approach velocity (v0).
insensitive
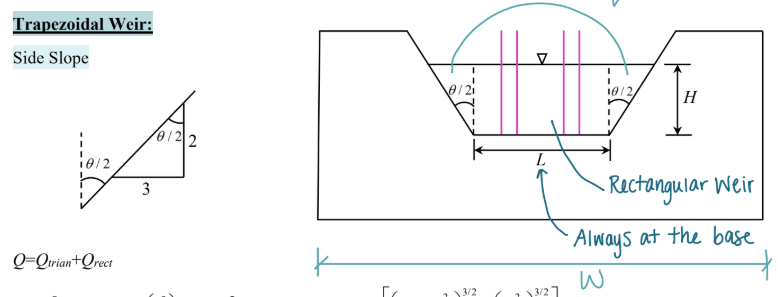
Trapezoidal Weir diagram