AP Bio Unit 1: Chp 3: Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life (Intro and Carbohydrates)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Polymer
Long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
Monomers
Small building-block molecules
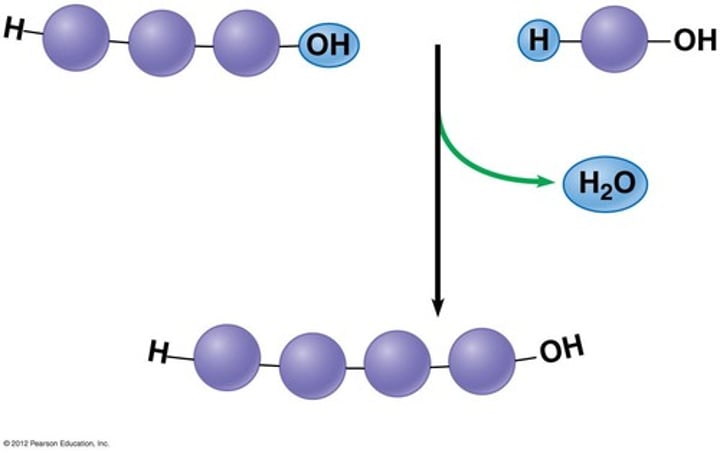
Dehydration reaction/synthesis
Creates a polymer; Short polymer is attached to an unlinked monomer to create a longer polymer by removing a water molecule to form a new bond. Facilitated by enzymes
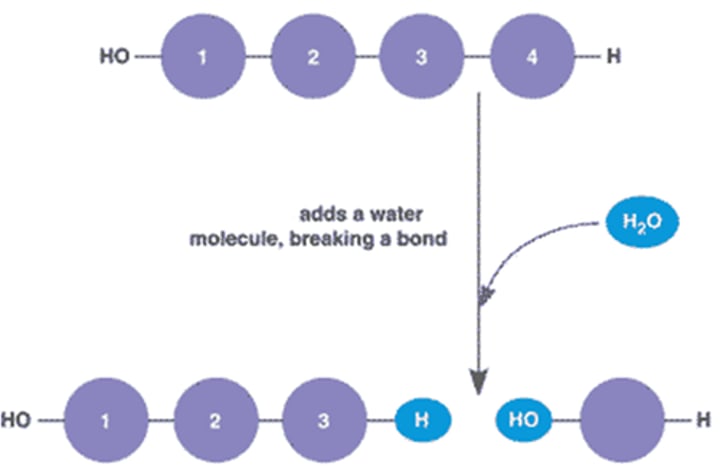
Hydrolysis
Breaking down a polymer to a monomer; Adds a water molecule, breaking a bond. Reverses dehydration reaction. Facilitated by enzymes
Biomolecules (Macromolecules/large molecules)
Molecules that make up EVERY LIVING THING; Ingredients of life: Essential energy sources, storage, and instructions
Carbohydrates
Source of all energy, includes sugars and the polymers of sugars (-saccharides)
Monosaccharides
Simplest sugar/carb, instant energy, major fuel for cells and raw material for building molecules, classified by # of carbons in carbon skeleton and the placement of the carboxyl group (C=O)
Examples of Monosaccharides
Glucose, Fructose
Ratio of elements found in carbohydrates
CH2O (1:2:1)
Glucose
C6H12O6
Fructose
Same molecular formula as glucose but arranged differently
Glycosidic Linkage
type of ether bond that joins a carbohydrate molecule to another group, which may or may not be another carbohydrate
Disaccharides
2 monosaccharides put together (dehydration synthesis)
Sucrose
Example of a disaccharide; glucose and fructose molecules joined by covalent bonds
Polysaccharides
Polymers of sugar, can contain 1,000s of simple sugar units; used for storage and structural roles, structure and function is determined by sugar monomers and positions of glycosidic linkages
Storage polysaccharides
Starch, Glycogen
Starch
Plants store glucose monomers in this, simplest form of this is amylose
Glycogen
Storage polysaccharide in animals, stored in liver and muscle cells (short term storage)
Polysaccharide cellulose
a major component of the tough wall of plant cells