Introduce to Metabolism & Cellular Energy
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
What kind of system are you?
Living things are open system
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed but can only change form or be transform from one object to another
Entropy
Measure of disorder or Reduces the amount of usable energy available to do work
Second Law of Thermodynamics
Energy transfer increases the entropy of the universe
Is any energy transfer is completely efficient?
No, some energy is lost as heat
Internal Organization
Cells → Tissues → Organs → Organ Systems → Entire body
High degree of organization of living things is maintained by
Constant input of Energy
Energy
Capacity to caused change
Potential Energy
Energy that matter possesses because of its position, structure
Is chemical energy is potential energy?
Yes because its available for release in a chemical reaction
Kinetic Energy
Energy associated with motion
Why is Thermal energy is kinetic energy?
Because it associated with random movement of atoms or molecules
Metabolism
All the chemical reactions that are required to maintain cells
Catabolic
Breaking bonds between molecules (Hydrolysis)
Anabolic
Forming bonds between molecules (Dehydration Synthesis)
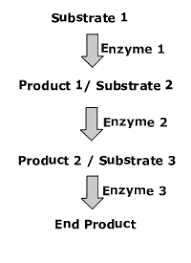
Metabolic Pathway
Begins with a specific molecule and ends with a product
Gibb’s Free Energy (G)
A measure of the amount of usable energy of a system
Exergonic Energy
Chemical reactions that released energy
Endergonic Energy
Chemical reactions that require input of energy
Spontaneously
Occuring naturally
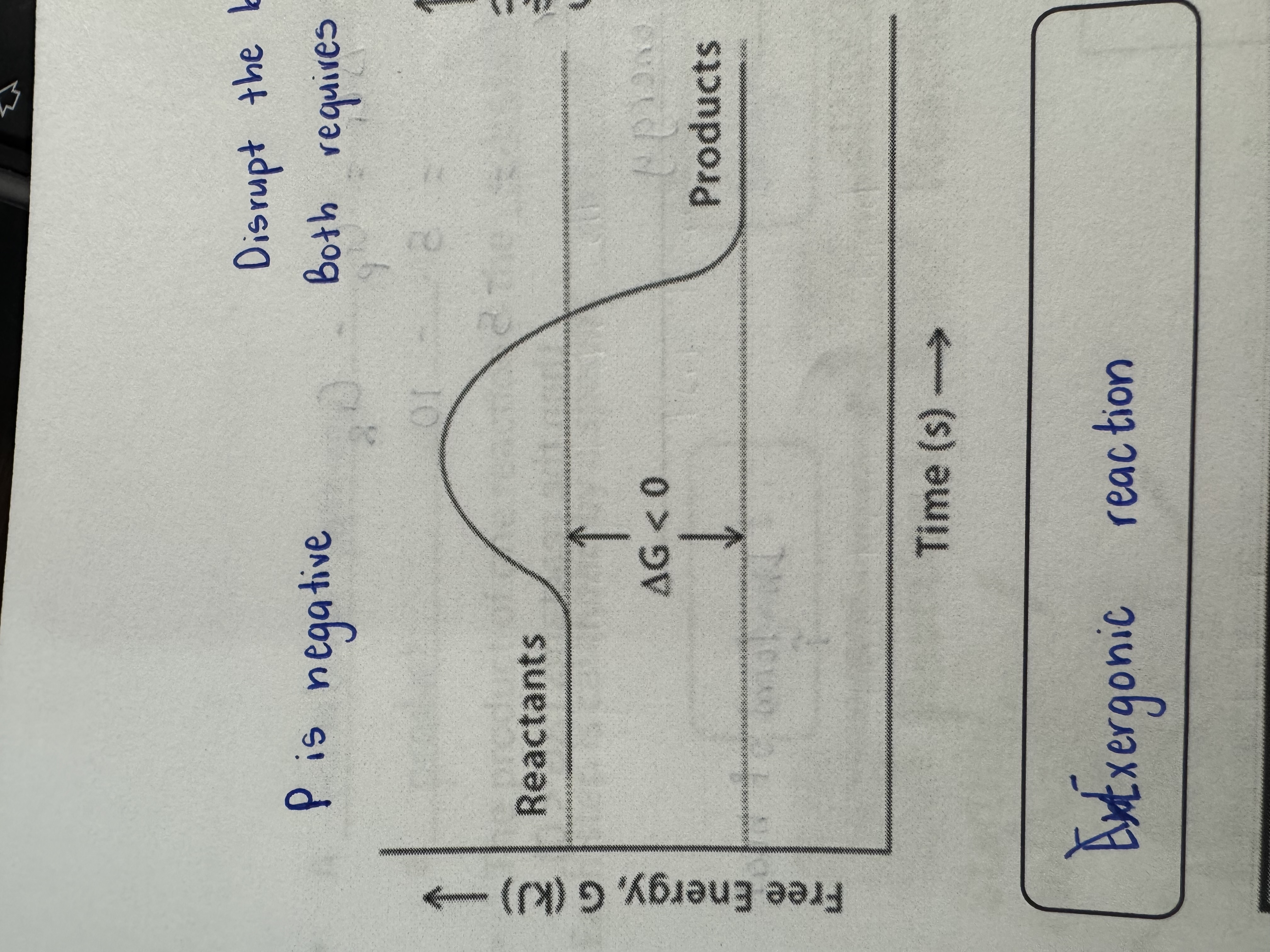
Exergonic Reaction
G < 0
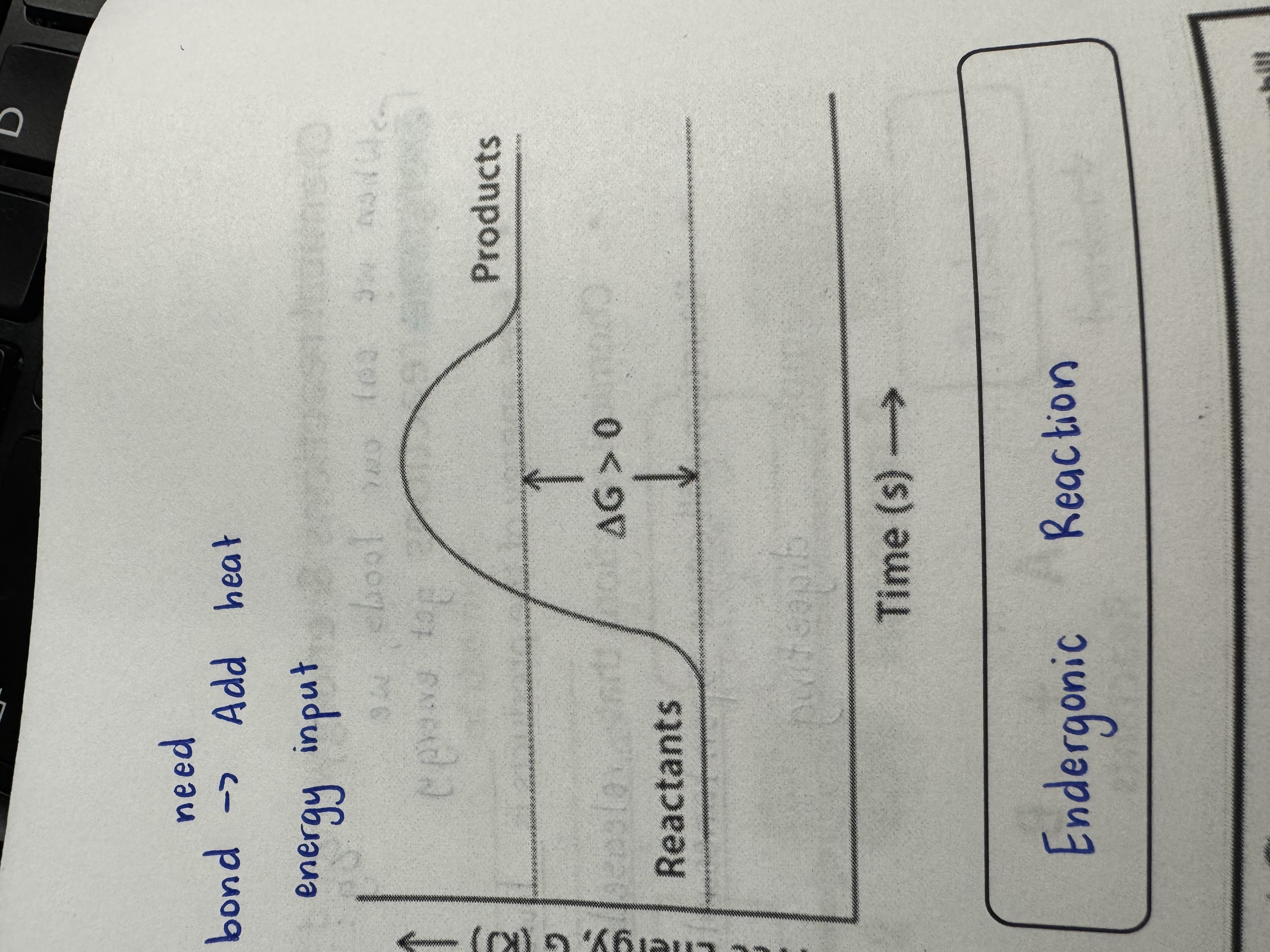
Endergonic Reaction
G > 0
Energy Coupling
Cells store chemical energy in biological molecules, digest it and harvest the energy for cellular work
Organisms couple:
Exergonic Reactions with Endergonic Reactions
Full name of ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate
ATP meaning
Energy currency of the cell
Short term energy-storing molecule
ATP
Long term energy-storing molecule
Lipid
ATP Structure
Ribose Sugar (Pentose Sugar)
Adenine (Nitrogenous base)
Tri - phosphate group (3)AT
ATP Function
Releases energy when the bonds between the 2nd and 3rd groups are broken, forming ADP (Adenosine Diphosphate) and Inorganic Phosphate
Pi
Inorganic Phosphate and no carbon
Explain the ATP/ADP Cycle
Rechargeable Energy
Phosphorylation meaning
Kinase enzymes transfer phosphate groups from one molecule to another
Phosphatases remove phosphate group from proteins
What does Inorganic phosphate caused when it binds to another molecule?
Because it’s unstable, it causing a conformational change and becomes unstable
Conformational change
Change form, shape to new function
Phosphorylation is
Essential for controlling the activation of proteins involved in various cell functions
What is an enzyme?
An enzyme is a biological catalyst. They increase the rate of reaction without being consumed and reduce the activation energy.
What is activation energy?
Minimum amount of energy needed for a reaction to occur. It destabilizes bonds in reactants, and is required for all reactions, both exergonic and endergonic. |
What is a catalyst?
A substance that reduces the amount of energy that is needed to start a reaction.
What is metabolism?
All chemical reactions that are required to maintain cells.
What is a substrate?
A reactant that binds to an enzyme.
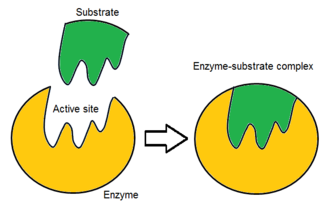
What is an active site of an enzyme?
An enzyme’s catalytic site, this is the place where a substrate fits into an active site.
What is a property of an enzyme?
Enzymes are reaction specific, in that they can only bond with a specific substrate.
Enzymes bind with substrates through Hydrogen and Ionic bonds.
They can catalyze many reactions without being consumed in reaction
What functions does an enzyme perform?
Enzymes can perform digestion (breaking something apart into smaller parts) and synthesis (making one thing out of two or more)
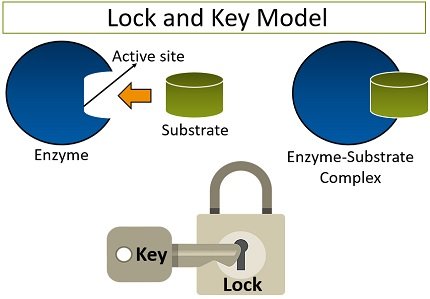
What is the lock and key model?
A simplistic model that shows how a substrate (key) and an enzyme (lock) fit together. An enzyme and a substrate have complimentary structures, which means that they are made to bond to each other.

What is the induced fit model?
A more accurate model of a substrate and an enzyme fitting together. Substrate binding causes enzymes to change shape leading to a tighter fit, called “conformational change”.
What is synthesis?
The active site orients substances in the correct position, the enzyme brings substrate closer together.
What is digestion?
The active site puts stress on the bonds between the molecules and breaks them.
Explain how the enzyme catalase works in breaking down hydrogen peroxide.
Catalase speeds up the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂) — a toxic byproduct of metabolism — into water (H₂O) and oxygen (O₂).
Reaction: 2H₂O₂ → 2H₂O + O₂

What is salinity:
Concentration of salt in an environment (like salinity of water)
What is a cofactor:
Non-protein, small inorganic compounds and ions, such as Mg, K, Ca, Zn, Fe, Cu. They are bound within enzyme molecules.
What is an activator:
A compound that activates an enzyme.
What is a coenzyme:
Non-protein, organic molecules. They bind temporarily or permanently to the enzyme's active site. (vitamins)
What is competitive inhibition:
Inhibitors and substrates “compete” for an active site.
What is an inhibitor:
A molecule that reduces enzyme activity.
What is non-competitive inhibition:
Inhibitor binds to another place on the enzyme, that is not an active site.
What is allosteric inhibition:
Inhibitor changes the shape of the enzyme, so it cannot bind to a substrate.
What is conformational change:
What causes enzymes to change shape.
What is allosteric regulation:
Conformational changes by regulatory molecules. (Regulatory molecules are activators and inhibitors. Activator makes an enzyme active, and an Inhibitor deactivates it)
What is irreversible inhibition:
Inhibitor binds to an enzyme and makes it permanently inactive.
What is feedback inhibition:
The final product is the allosteric inhibitor of an earlier/first step. (point E deactivates point A and stops it from making more product)
What is a metabolic pathway:
Chemical reactions are organized step by step. (From point A to point B, to point C and so on, like a relay race)
Why is a metabolic pathway important:
Allows for efficiency and control/regulation.
What factors affect enzyme function:
Enzyme concentration, substrate concentration, temperature, pH level, salinity.
How does the enzyme concentration affect reaction rate:
Enzyme concentration rate increases enzyme reaction rate, because more enzymes collide more frequently with the substrates.
What is the limiting factor of the enzyme concentration effect:
Substrate, because not all enzymes will be able to find it and bind to it.
How does the substrate concentration affect enzyme reaction rate:
If the substrate concentration increases, so does the reaction rate. More enzymes collide more frequently with substrates. (Like the enzyme concentration, but instead we’re adding substrates)
What is the limiting factor of the substrate concentration effect:
Substrate is the limiting factor, eventually there will be too many substrates, and they won’t be able to find an enzyme to bind to. This makes the substrates wait for their turn.
What is optimum temperature:
The most favorable temperature, at which an enzyme functions most efficiently. (for human enzymes it’s between 35-40 ℃)
How does temperature affect enzyme reaction rate:
Optimum temperature makes the enzyme react the most. Heat increases their kinetic energy and disrupts the bonds in them and between an enzyme and a substrate. Makes the enzymes denaturate (stop working) Hydrogen and ionic bonds are affected. Colder temperature slows down enzymes, decreases collision between enzyme and a substrate. Will not denature the enzyme.
How does the pH level affect enzyme reaction rate:
If the pH level becomes acidic (adds H+) or basic (removes H+), it disrupts the bonds in the enzyme, denatures it.
How does salinity affect enzyme reaction rate:
Changes in salinity, adds or removes cations (+) and anions (-), disrupts bonds in the enzyme, and denatures it. (Enzymes can’t be in extreme salinity!)
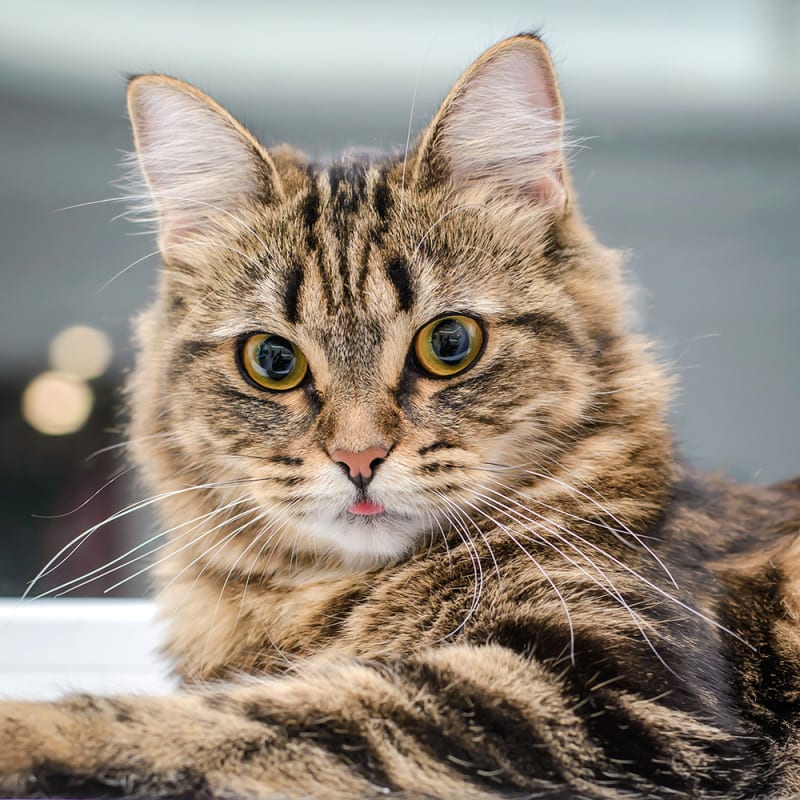

What is an endotherm:
An animal that maintains a constant body temperature, independent of the environment. Also known as “warm-blooded”, can be a cat, dog, horse, …
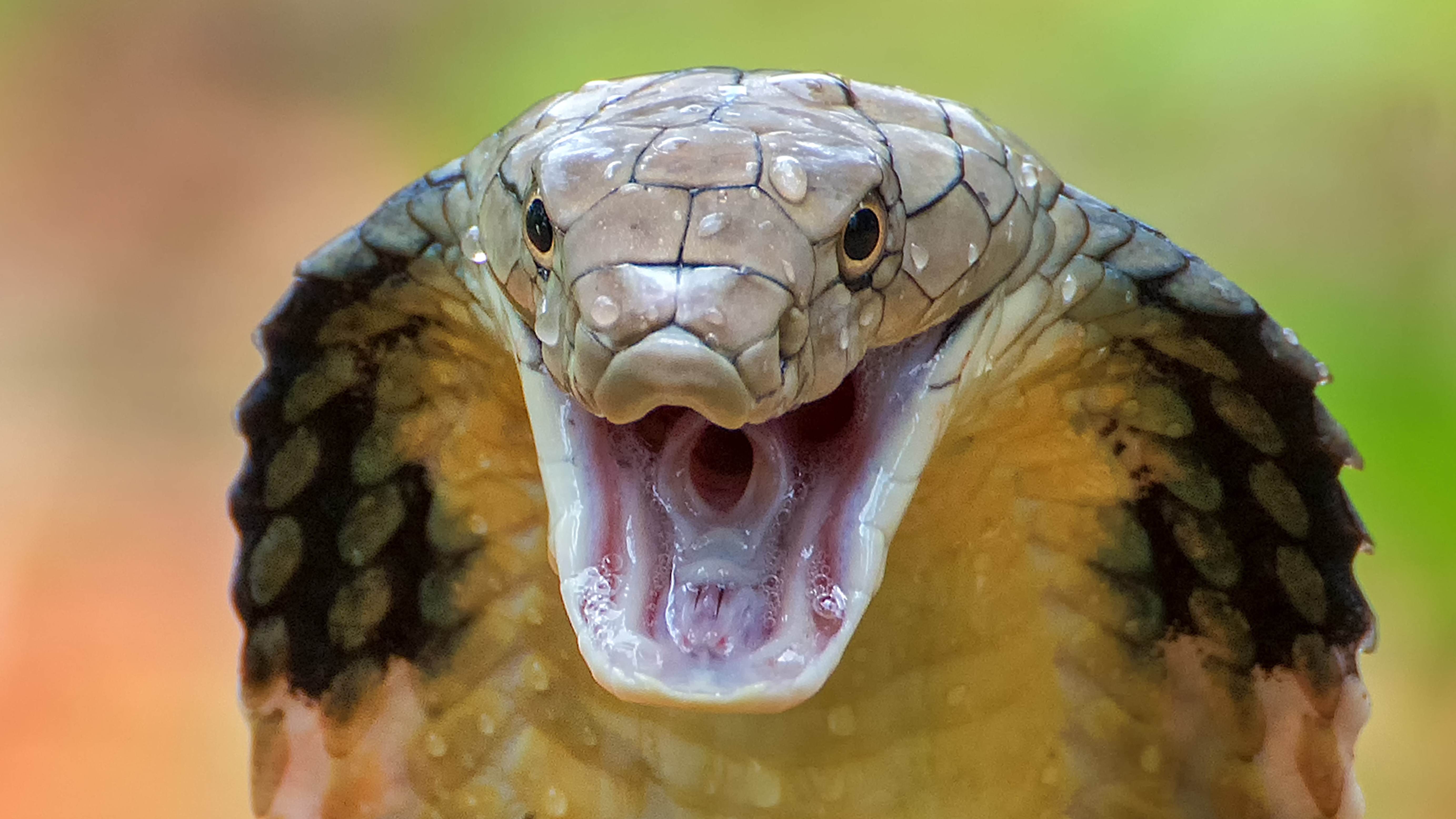

What is an ectotherm:
An animal that depends on external sources of body heat. Also known as “cold-blooded”, can be a snake, lizard, fish, etc.
What is the optimum pH for human enzymes:
6-8 pH level