Owens Chemistry Unit 10 - Radioactivity
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What are the 3 subatomic particles
protons, neutrons, electrons
Proton (p⁺)
Discovered by Rutherford
- Relative mass: about 1
- positively charged
Neutron (n⁰)
Discovered by Joliot-Curie/ James Chadwick
- Relative mass: about 1
- no charge
Electron (e⁻)
Discovered by JJ Thompson
- Relative mass: negligable\
- negatively charged
What keeps the nucleus together?
The strong nuclear force
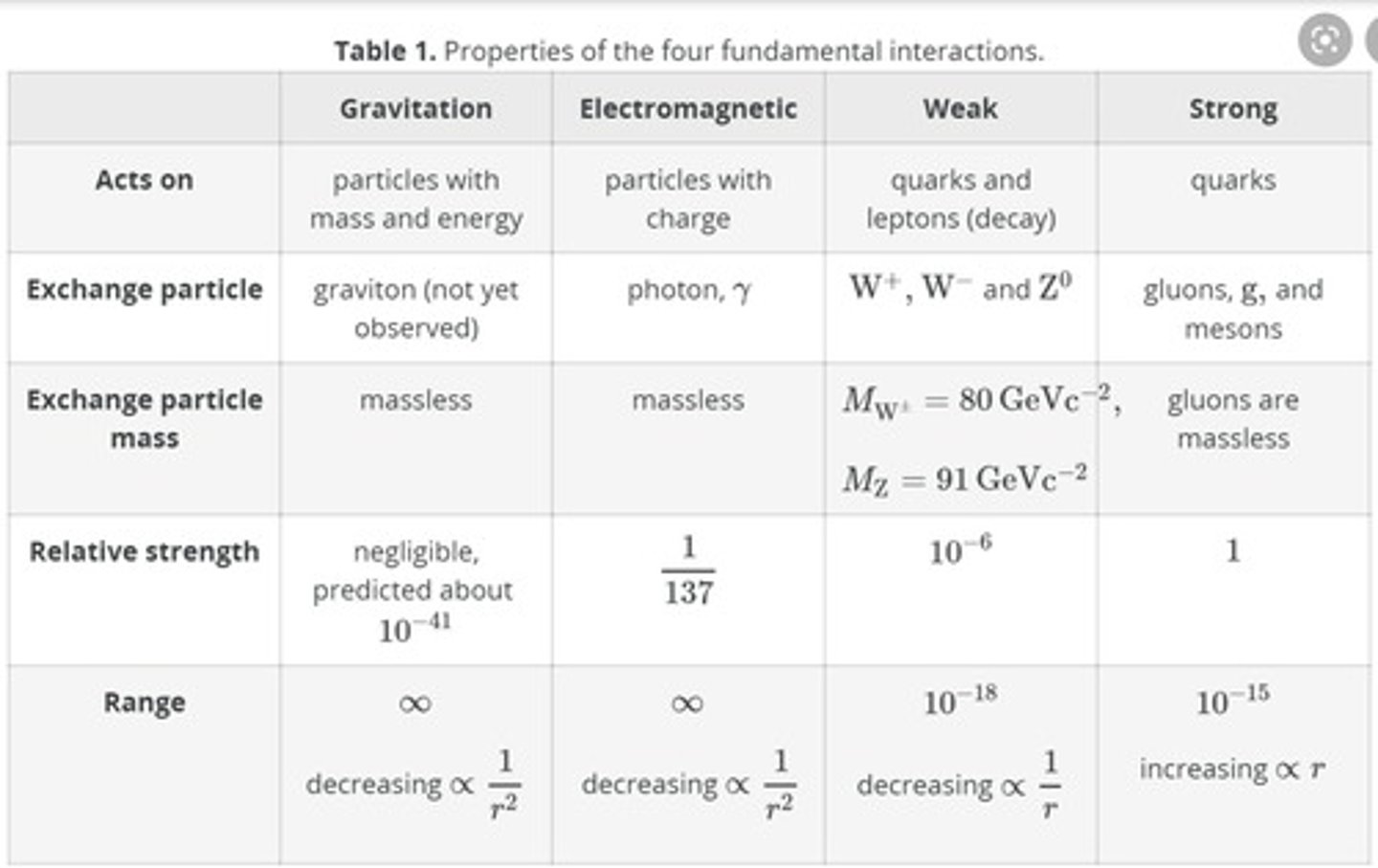
What are the four fundamental forces
gravity, electromagnetic, strong nuclear, weak nuclear
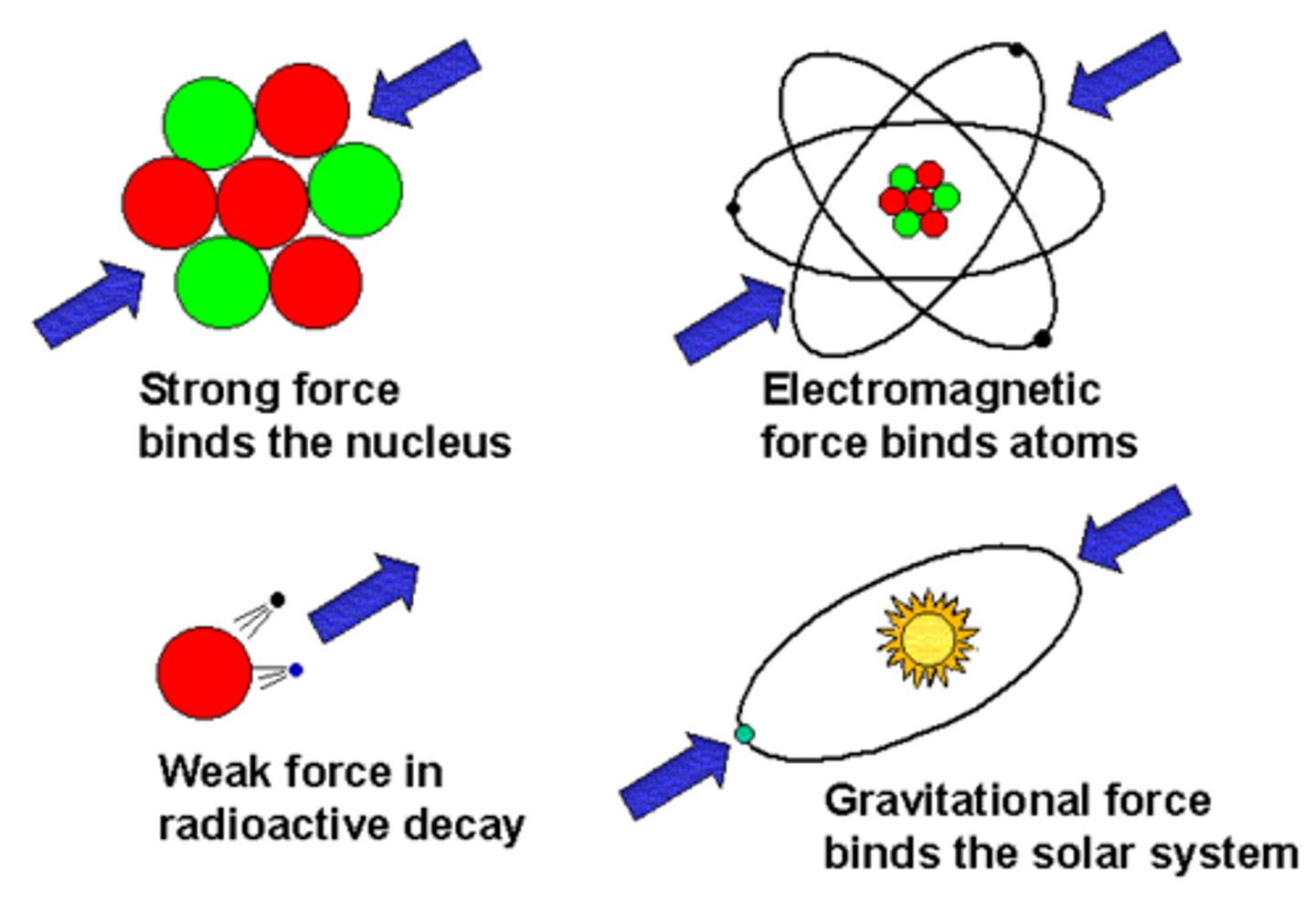
Carrier particles for the four forces
Gravity: gravitons
Electromagnetism: photons (γ)
Strong nuclear: gluon
Weak nuclear: W and Z
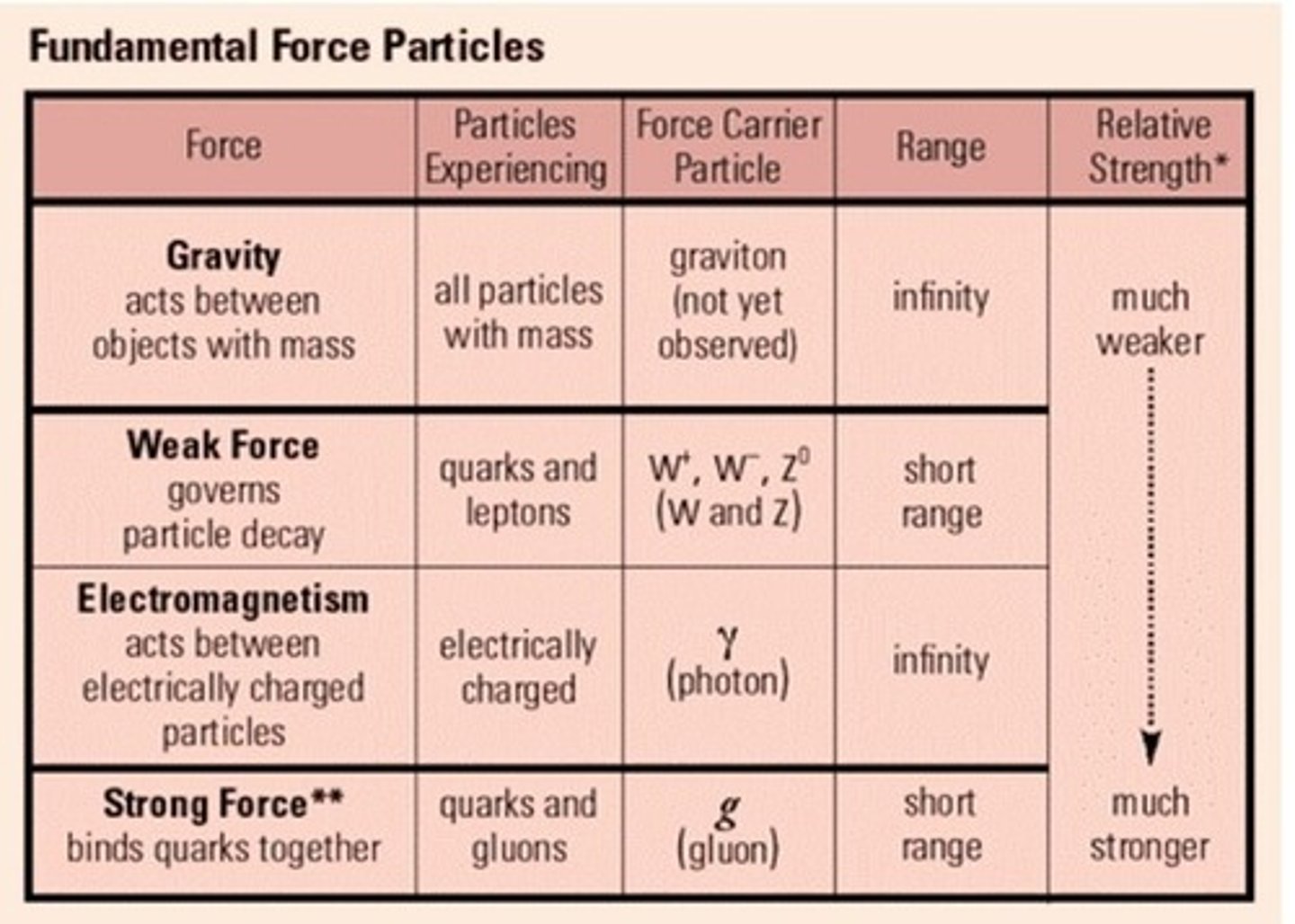
Relationship between range of force and strength of forces
Gravity:
- Range: infinite
- Strength: weakest
Electromagnetism
- Range: infinite
- Strength: pretty weak
Weak nuclear:
- Range: pretty far
- Strength pretty weak
Strong nuclear
- Range: shortest
- Strength: Strongest
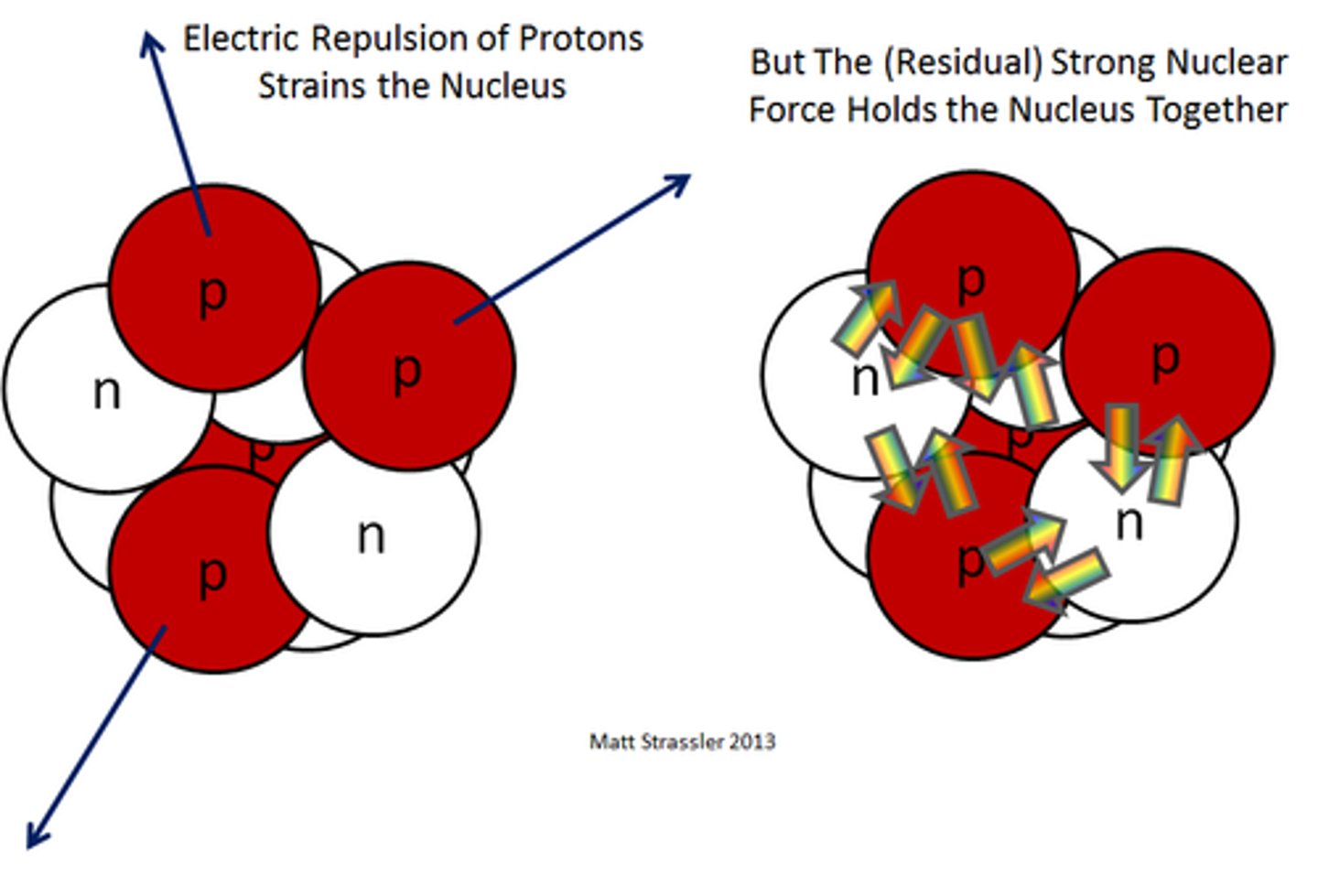
Strong Nuclear force
Force between protons and neutrons
- particle: gluons
- neutrons bring more strong force interactions to the nucleus
- you need the right amount of protons and neutrons to have a stable nucleus
Nucleons (N)
- total of protons and neutrons
- same as atomic mass/mass nimber
Atomic number (Z)
Equal to the number of protons found in an atom of an element
Mass number (A)
The total number of protons and neutrons in an atom (e.g. ¹²C)
Chemical symbol vs atomic symbol
Chemical symbol is just the element
- see picture for atomic symbol (picture doesnt include charge)
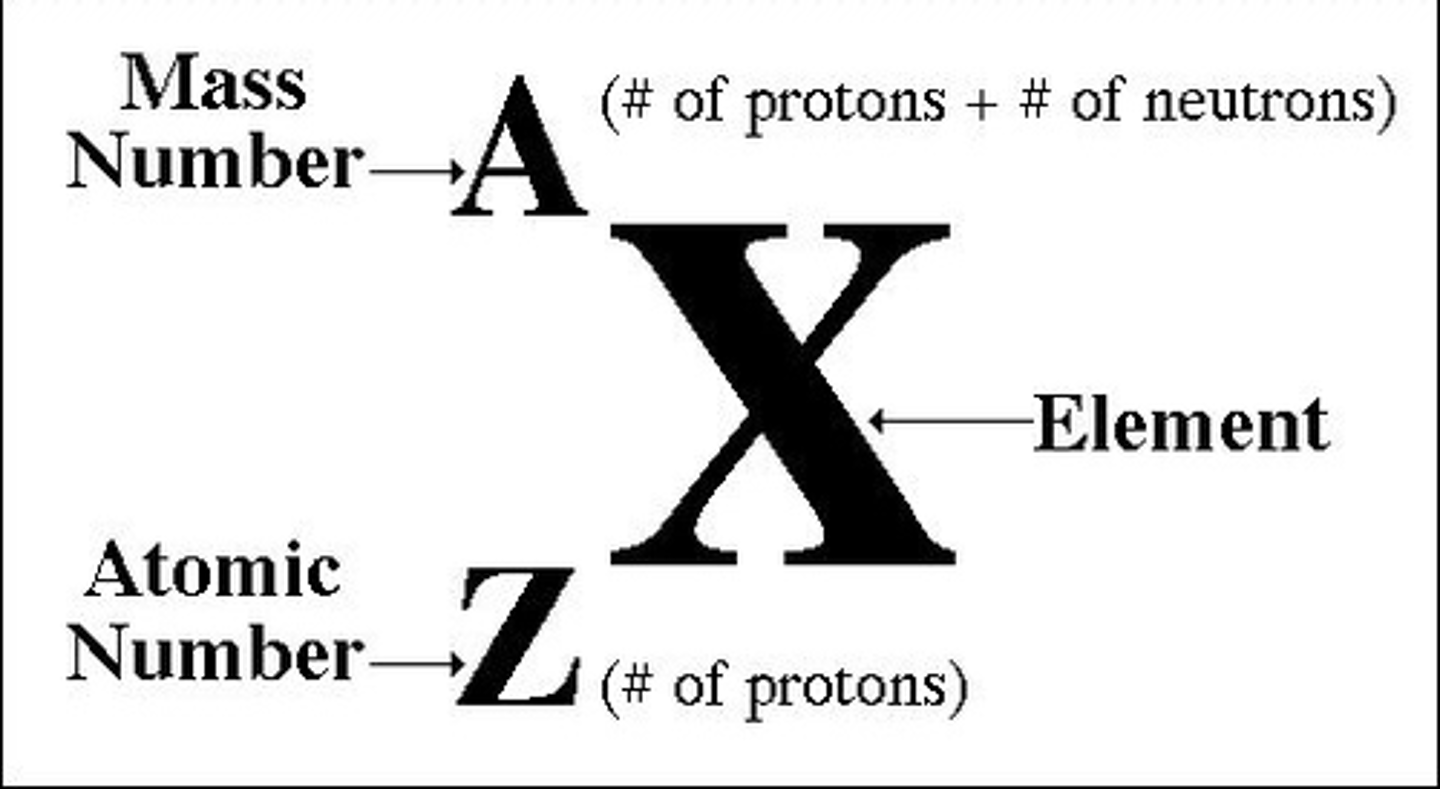
mass number vs average atomic mass
Mass number: total number of protons + neutrons in a nucleus
Average atomic mass: the weighted average of the masses of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element
What is the maximum amount of protons for a stable atom?
82: lead
Of the 3000+ known isotopes how many are stable?
around 250
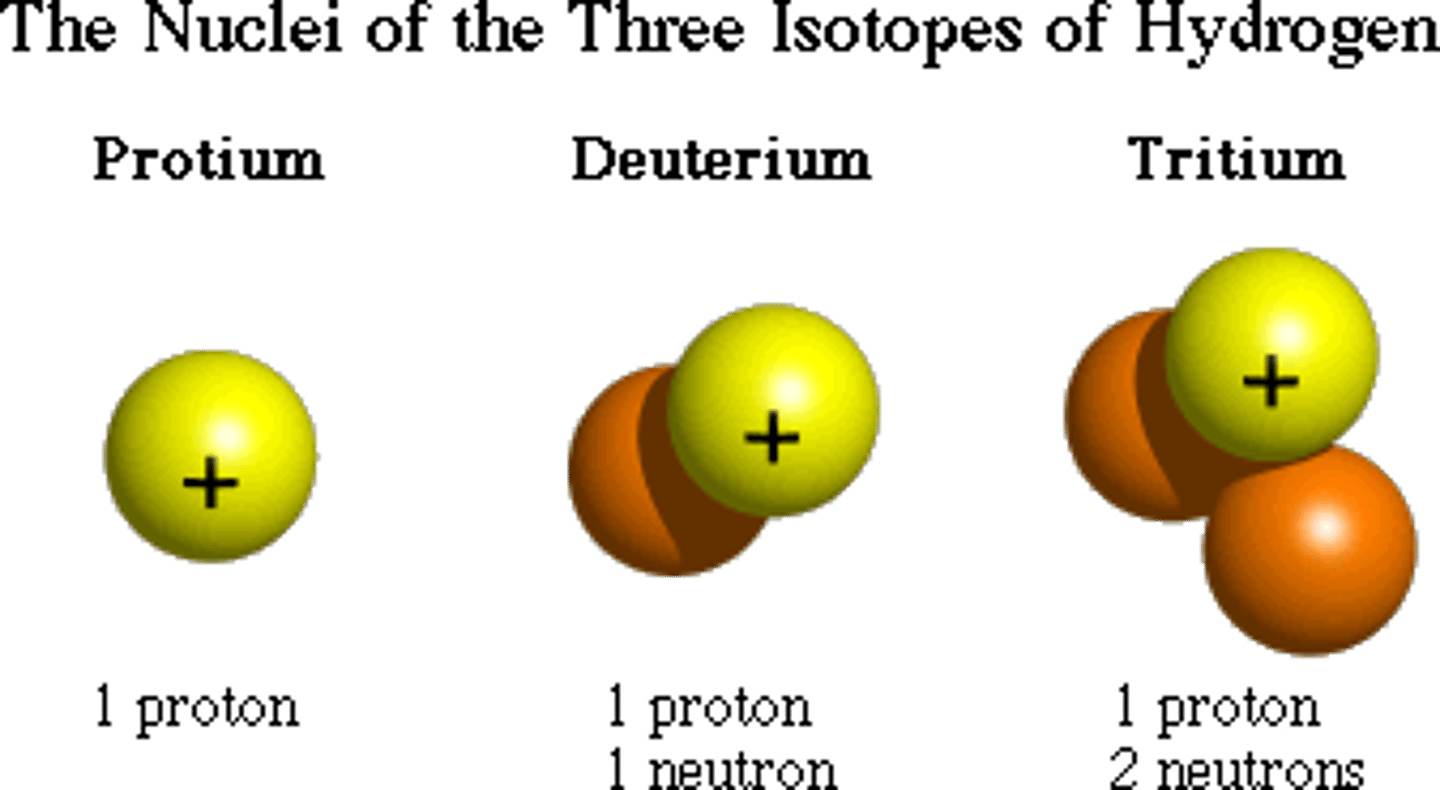
Isotopes of hydrogen
Protium ₁¹H
Deuterium ₁²H
Tritium ₁³H
Alpha emision (α)
Alpha particle: ₂⁴He (helium nucleus)
Occurs when the atom is just too big (ex: past element 82)
- nucleus emits 2 protons and 2 neutrons
Properties:
- Charge: positive
- Mass: basically 4 protons (2 protons + 2 neutrons) (heavy) (doesnt penetrate much)

Beta decay (β⁻)
Beta (minus) particle: −₁⁰e⁻ (electron)
Occurs when there are too many neutrons (weak force problem)
- nucleus converts a neutron into a proton, releasing an electron
Properties:
- Charge: negative
- Mass: negligable (electron basically)
Positron emission (β⁺)
Beta (plus) particle: +₁⁰e⁺ (positron) (antimatter)
Occurs when there are too few electrons
- nucleus converts a proton into a neutron, releasing a positron
Properties:
- Charge: positive
- Mass: negligable
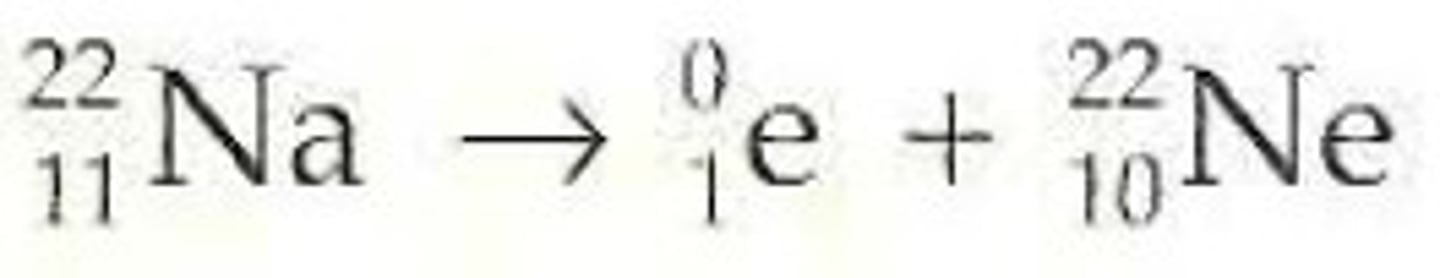
Gamma decay (γ)
Gamma ray: ₀⁰γ (light (really high energy))
Occurs when the nucleus is excited (indicated by *)
- nucleus releases a really high energy photon
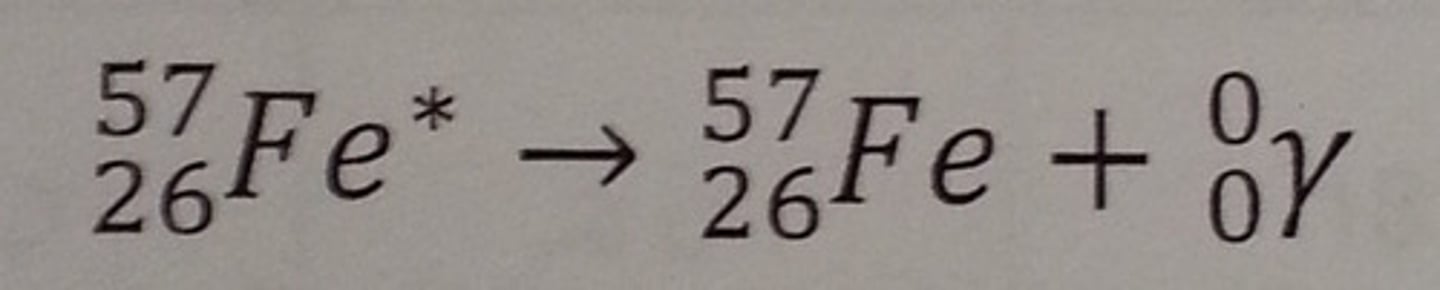
half life
definition: the time it takes for half of the radioactive atoms in a group of identical atoms to decay
Equation: Amount of isotope remaining / Original amount of isotope = (1/2)ⁿ (where n is the amount of 1/2 lives)
Methods of radiation damage (bonus)
rads: amount of radiation
REMs: damage
RBE: damage