SNELL NEURO CHAPTER 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
1
New cards
Both CNS and PNS are covered with a sytem of membrane called?
Meninges
2
New cards
what are the process structures of neurons?
Axons or nerve fibers
3
New cards
specialized cells that support the neurons
Neuroglia
4
New cards
they are gray structures that consist of nerved fibers imbeded in neuroglia
Gray Matter
5
New cards
The CNS interior is organized into two main structures which are the?
gray and white matter
6
New cards
white matter is consist of nerve fibers embedded in neuroglia and is white in color because?
presence of “LIPID MATERIALS” in nerve fiber myelin sheath
7
New cards
In the PNS, the nerves are surrounded by what structure to help in protection?
Fibrous sheath
8
New cards
Part of the ANS that prepares the body for emergency
Sympathetic
9
New cards
part of the ANS that aims to conserve at restore energy
Parasympathetic
10
New cards
Suspends the brain and spinal cord
Cerebrospinal fluid
11
New cards
Cylindrical and begins superiorly at the foramen magnum where it is continuous w/ medulla oblongata of the brain
SPINAL CORD
12
New cards
What are the three meninges that protects the brain and spinal cord?
1\. Dura mater 2. Arachnoid mater 3. Pia mater
13
New cards
The spinal cord tapers of into??
conus medullaris
14
New cards
There are 32 pairs of spinal nerves that are attached by the anterior and posterior roots. (T or F)
False (there are 31 pairs)
15
New cards
Posterior and anterior roots possesses posterior and anterior root ganglion that give rise to the CNS and PNS nerve fibers. (T or F)
False (only the posterior roots have ganglia)
16
New cards
Explain the structural orientation of spinal cord in terms of its matter
Gray matter- inner core and in a H-shaped pillar, devides into ant and post columns
White matter- outer covering, divided in to anterior, lateral, posterior columns
White matter- outer covering, divided in to anterior, lateral, posterior columns
17
New cards
The brain is continuous with spinal chord through what strcuture?
foramen magnum
18
New cards
Collective term for medulla oblongata, pons, and midbrain
Brain stem
19
New cards
Surrouded by the 4th ventricle
Hindbrain
20
New cards
Conical in shape; connects pons above to spinal cord below
Medulla oblongata
21
New cards
Explain the orientation/relationship of the pons in the brain
Situated anterior to cerebellum; inferior to midbrain; superior to medulla oblongata
22
New cards
Name derives from large number of transverse fibers that connects 2 cerebellar hemispheres
Pons
23
New cards
Lies within posterior cranial fossa of the skull
Cerebellum
24
New cards
what connects the 2 hemisphere of the cerebellum
vermis
25
New cards
large bundles of nerve fibers connecting cerebellum to remainder of nervous system
Peduncles
26
New cards
Explain the 3 peduncles of the cerebellum
to the midbrain = superior cerebellar peduncles
pons = middle cerebellar peduncles
medulla = inferior cerebellar peduncles
pons = middle cerebellar peduncles
medulla = inferior cerebellar peduncles
27
New cards
The cortex is the surface layer of each cerebellar hemisphere and is composed of white matter. (T or F)
False (it is gray matter)
28
New cards
Cortex have folds cold gyri and fissures called sulci (t or f)
True
29
New cards
Largest mass of gray matter found inferior to cerebellum and is embedded in white matter
Dentate Nucleus
30
New cards
Narrow part of brain that connects forebrain to hindbrain
Midbrain
31
New cards
What connects the 4th and the 3rd ventricle?
cerebral aqueduct
32
New cards
central part of the forebrain
Diencephalon
33
New cards
Diencephalon consist of ventral thalamus and dorsal hypothalamus. (t or f)
False (dorsal thalamus and ventral hypothalamus)
34
New cards
Thalamus is large, egg-shaped mass of white matter that lies either side of lateral ventricle
False (gray matter, 3rd ventricle)
35
New cards
what forms the posterior boundary of interventricular foramen
anterior end of Thalamus
36
New cards
Hypothalamus forms the lower part of lat. wall and floor of 3rd ventricle (t or f)
True
37
New cards
– largest part of brain; consists of 2 cerebral
Cerebrum
38
New cards
Cerebrum is largest part of brain; consists of 2 cerebral hemispheres which are connected by white matter called
corpus callosum
39
New cards
Each hemispheres of the cerebrum extend from frontal to occipital bones of skull, superior to the anterior and middle cranial fossae, and posterior above the tentorium cerebelli. (t or f)
True
40
New cards
Fan-shaped collection of nerve fibers
Corona Radiata
41
New cards
Corona Radiata
Passes in white matter to and from the cerebral cortex to the brainstem
42
New cards
The corona Radiata converges basal nuclei and passes between them as what?
Internal capsule
43
New cards
The caudate nucleus tailed on what side of the internal capsule?
Medial Side
44
New cards
The lentiform nucleus is a lens-shaped structure that place on what side of the internal capsule?
Lateral side
45
New cards
Explain the structures of the brain base on the orientation of white and gray matter.
Inner core: white matter
Outer covering: gray matter
Certain important masses of gray matter are situated deeply within white matter
Outer covering: gray matter
Certain important masses of gray matter are situated deeply within white matter
46
New cards
Gray cerebellar nuclei is found in what structure of the brain?
Cerebellum
47
New cards
Give me the three gray matter masses you can found inside the cerebrum
Gray thalamic, caudate, and lentiform nuclei
48
New cards
Cranial nerves is 12 pairs of nerves that leaves the brain and pass through the foramina of the skull. (T or F)
True
49
New cards
The spinal nerves leaves and pass through to what structures of the vertebral column?
Intervertebral foramina
50
New cards
How many spinal nerves in the spinal region? Enumerate!!!
8 – cervical
12 – thoracic
5 – lumbar
5 – sacral
1 – coccygeal
12 – thoracic
5 – lumbar
5 – sacral
1 – coccygeal
51
New cards
Consists of bundles of nerve fibers carrying nerve impulses away from the CNS
Anterior roots
52
New cards
Motor fibers are said to be efferent and lies in the anterior gray horn of spinal cord. (T or F)
True
53
New cards
Posterior roots are both afferent and efferent. (T or F)
False (afferent only)
54
New cards
Cell bodies of posterior root fibers are situated in a swelling on posterior root called the?
posterior root ganglion
55
New cards
Level of termination of the spinal cord
1st Lumbar
56
New cards
Roots of lumbar and sacral nerves form vertical leash of nerves around filum terminale and are called
cauda equina
57
New cards
Upper cervical region, spinal nerve roots are short and run almost diagonally (T or F)
False (horizontally)
58
New cards
Continues anteriorly to supply the muscles and skin over the anterolateral body wall + muscles and skin of the limbs
Large Anterior Ramus of spinal nerves
59
New cards
Passes posteriorly around vertebral column to supply muscles and skin of the back
Small posterior ramus
60
New cards
The large anterior and small posterior ramus both contains afferent and efferent fibers. (T or F)
True
61
New cards
What rami forms the nerve plexuses of the limbs?
Large anterior ramus
62
New cards
Ganglia can be divided into?
1\.Sensory ganglia of spinal nerves (posterior root ganglia) and cranial nerves
2\. Autonomic ganglia
2\. Autonomic ganglia
63
New cards
Irregular in shape; situated along the course of efferent nerve fibers of the ANS
Autonomic Ganglia
64
New cards
Sensory ganglia can be found at what cranial nerve fibers?
CN 5,7-10
65
New cards
Explain the 3 main cell layers during gastrulation!
1\. Entoderm – GI tract, lungs, and liver
2\. Mesoderm – muscle, connective tissues, and vascular system
3. Ectoderm – entire nervous system, skin
2\. Mesoderm – muscle, connective tissues, and vascular system
3. Ectoderm – entire nervous system, skin
66
New cards
During the 3rd week of development, ectoderm thickens to form the ?
Neural plate
67
New cards
Neural plate is pear-shaped and wider caudally; develops longitudinal neural groove ( T or F)
False (wider cranially)
68
New cards
Wat closes first, the ant or post neuropores? Explain other infos you might find relevant hehe
Anterior neuropores – closes first o
Posterior neuropores – closes 2 days later
Posterior neuropores – closes 2 days later
69
New cards
Neural tube is complete within 40 days (T or F)
False (28 days)
70
New cards
Explain how the neural crest is form!
The cells forming the lateral margin of the plate do not become incorporated in the neural tube, instead form a strip of ectodermal cells that lie between the neural tube and the covering ectoderm, the Neural Cres
71
New cards
Neural crest cells will differentiate into the cells of? ENUMERATE!
1\. Posterior root ganglia
2\. Sensory ganglia of the cranial nerves
3\. Autonomic ganglia
4\. Cells of suprarenal medulla
5\. Melanocytes
2\. Sensory ganglia of the cranial nerves
3\. Autonomic ganglia
4\. Cells of suprarenal medulla
5\. Melanocytes
72
New cards
Excessive numbers of neurons and neuroglial cells develop, and many will be programmed to die by a process known as?
programmed cell death
73
New cards
Simplest progenitor cells will differentiate into neurons and neuroglial cells (T or F)
True
74
New cards
Kung magaling ka (explain the whole table of gastrulation :>)
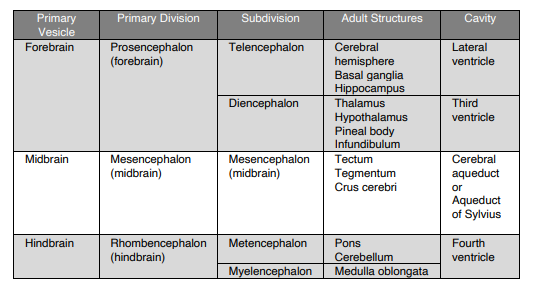
75
New cards
In what space can you fine the subarachnoid space?
Between the pia and arachnoid matter
76
New cards
The hemisphere of the cerebrum is separated by a deep cleft called?
Longitudinal fissure
77
New cards
A septum that is found in the separation of the two hemisphere of cerebrum
Falx Cerebri