1.3 organic molecules in living organisms
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
what is found in all organic molecules and forms a wide range of different compounds
carbon
what does every compound contain
2 or more carbon atoms
a carbon atom can form how many covalent bonds
4
wha forms all the basic molecules for all life
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
what is the most abundant group of biological molecule
carbohydrates
what elements do carbohydrates contain
carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
what elements do lipids contain
CHO but much less oxygen and with small amounts of other elements like phosphorus
what elements are proteins made up of
nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur, and other elements
what elements do nucleic acids contain
nitrogen and phosphorus
what role does carbohydrates play in animals
source of energy
what role does carbohydrates play in plants
source of energy and structural function
a single sugar that cannot be hydrolysed
monosaccharide
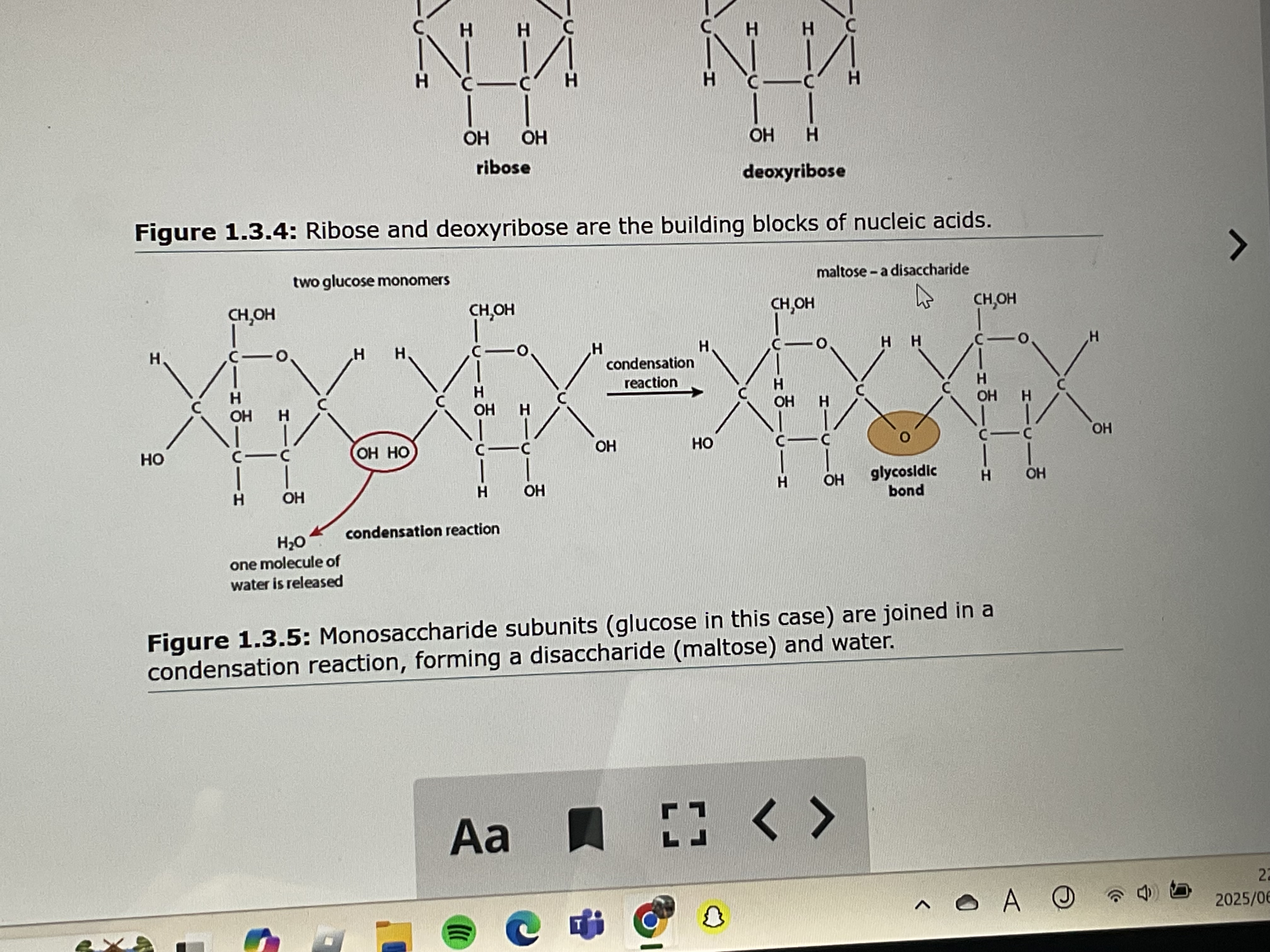
molecule composed of 2 monosaccharide molecules linked in a condensation reaction
disaccharide
large carbohydrate formed by condensation reactions between large numbers of monosaccharides
polysaccharides
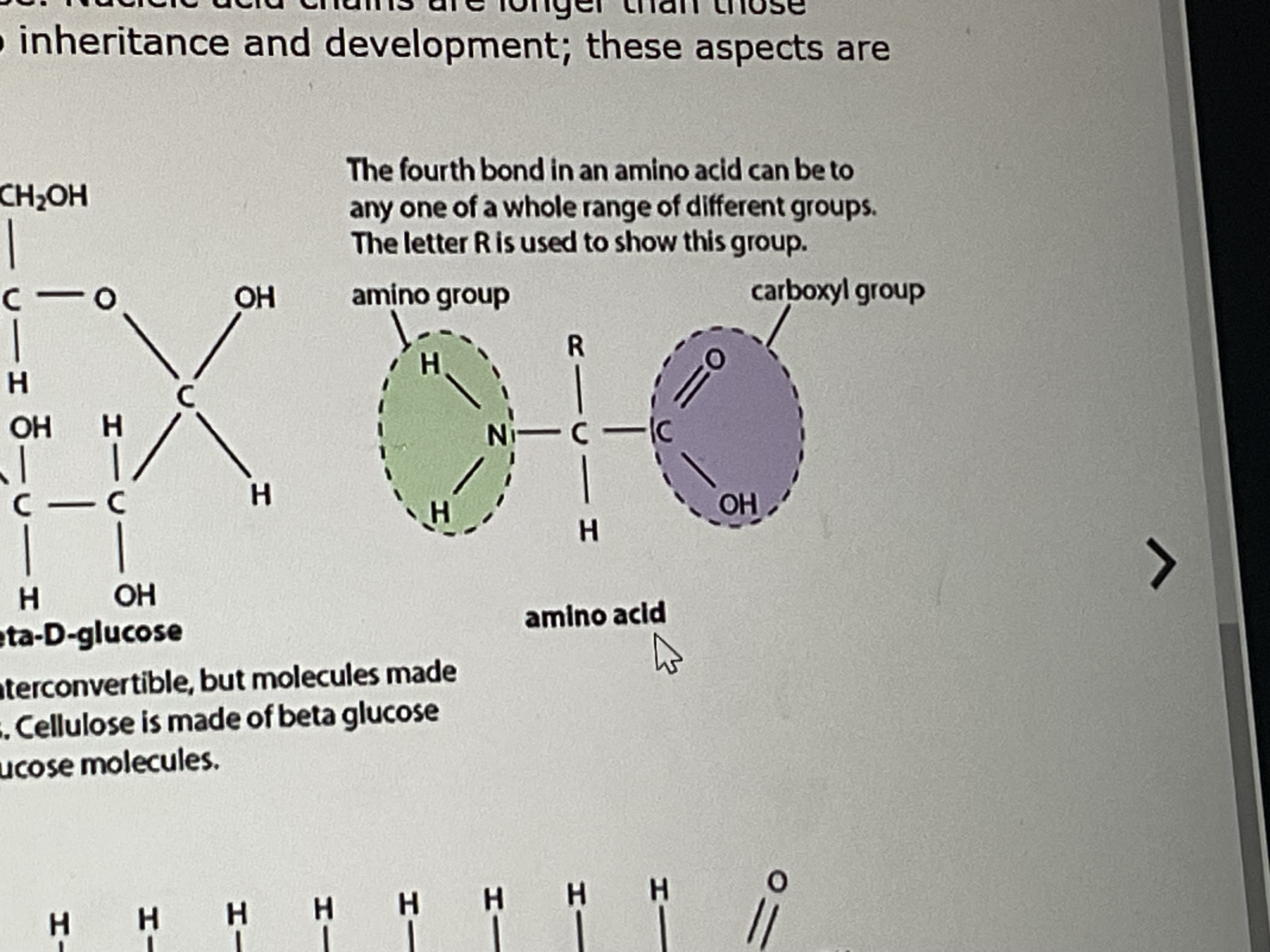
what is built up of units called amino acids
proteins
what part of the amino acids give each one its own properties
the R group
what is the simplist amino acid
glycine
out of 100, how many naturally occurring amino acids are used in the bodies of living things
20
amino acids bond together in condensation reactions and form what
polypeptide chains
fats, oils, waxes, steroids
lipids
what are lipids
organic compounds that are insoluble in water but dissolve in organic solvents
an important role of lipids in living organisms
energy storage
solid lipids =
liquid lipids =
fat, oil
lipids contain _x the amount of energy per gram as carbohydrates
2
examples of steroids
vitamin d and cholesterol
small molecule that can bond to other similar small molecules, to make up repeating chains that form large polymers
monomer
large, complex molecule built up of a series of monomers, formed by condensation reactions in a process called polymerisation
polymers
found in all living cells and viruses
nucleic acids
2 types of nucleic acids found in cells
deoxyribonucleic (DNA) and ribonucleic (RNA)
where is the DNA found
nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts of eukaryotes
where is RNA found
the cytoplasm
condensation reaction of a carbohydrate
amino acid structure
2 molecules joined together by strong covalent bonds to form a larger molecule and water is released
condensation reaction
a reaction which builds up large molecules from smaller ones
anabolic reaction
what does each condensation reactions require
an enzyme to catalyze the process
monosaccharide + monosaccharide =
disaccharide
amino acid + amino acid =
dipeptide + water
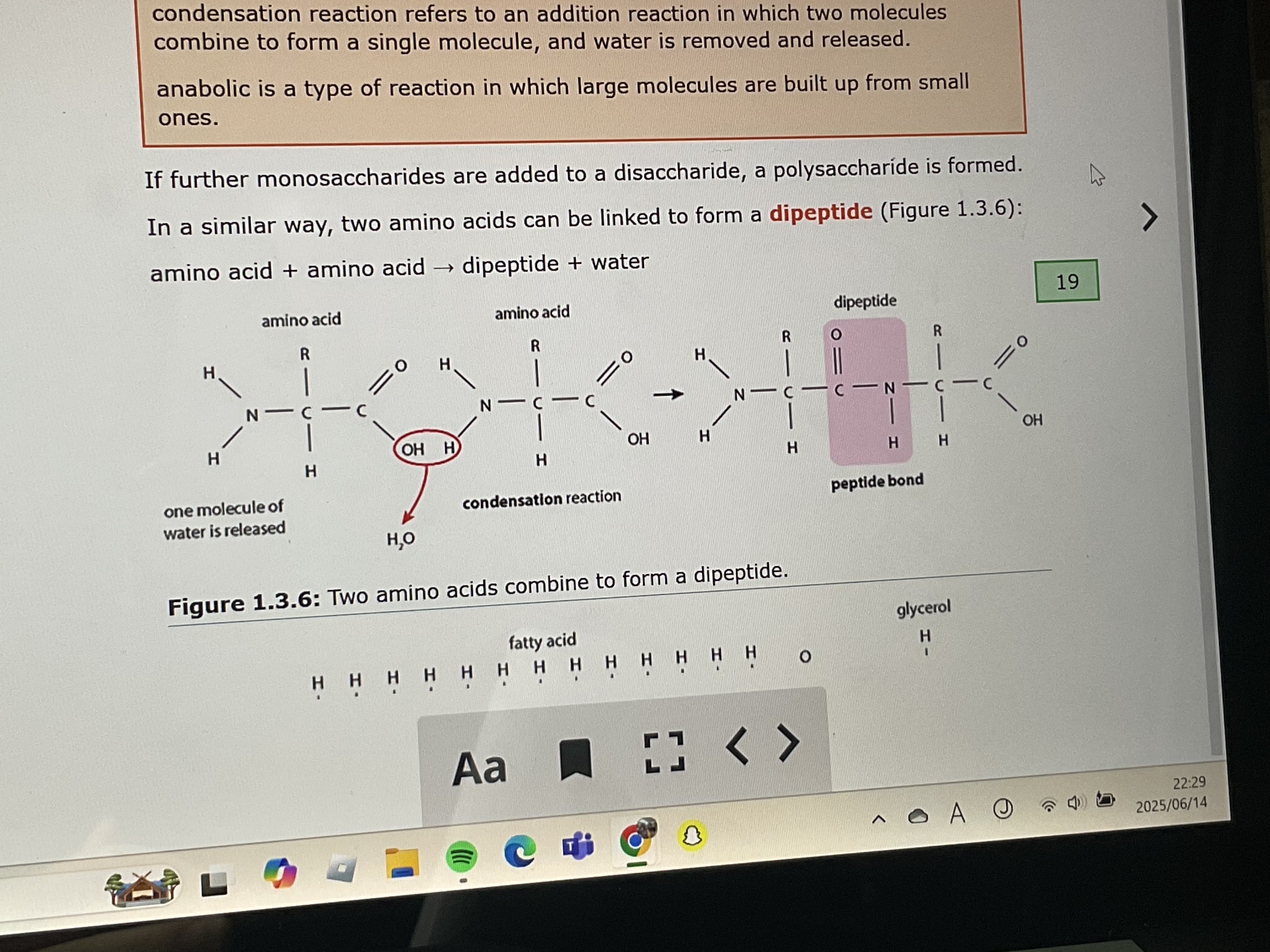
when more than 2 amino acids are joined they form a
polypeptide
glyceride + 3 fatty acids =
triglyceride lipid + water
what are large polymers that are essential to all forms of living organisms?
nucleic acids
_ are the building blocks of DNA
Nucleotides
DNA structure (make sure u can draw it bitch)
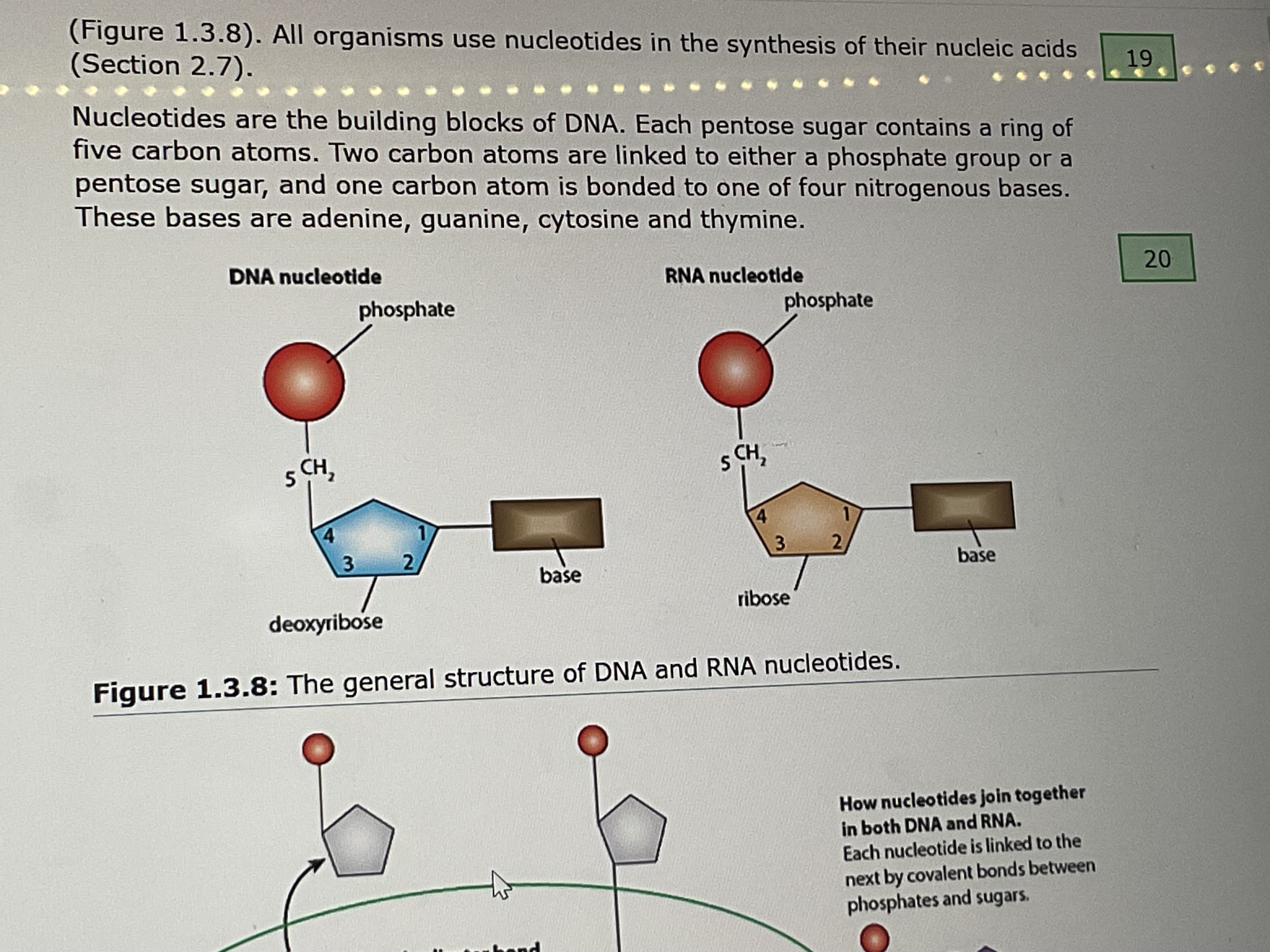
the 4 bases of DNA
adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine
4 bases of RNA
cytosine, guanine, uracil, adenine
3 parts of a DNA nucleotide
phosphate group, pentose sugar, base
the backbone of DNA and RNA molecules
sugar nd phosphate groups
break down polymers into smaller units
hydrolysis reactions
reverse of condensation reactions
hydrolysis reactions
3 important functional groups in living organisms
carboxyl group, amine, phosphate
a functional group that binds to larger molecules and gives them specific properties
carboxyl group
carboxyl group
-COOH
a group of atoms that has similar chemical properties in every compound in which it appears
functional group
relating to a molecule in which the distribution of electrons is not even
polar
every amino acid contains…
a carboxyl group and an amino group
functional groups that contain a nitrogen atom with a lone pair of electrons in their outer cell
amines
ion that contains one phosphorus and 4 oxygen atoms
phosphate
molecules that have the same molecular formula, but different molecular shapes.
isomers
2 major classes of isomers
structural isomers and stereoisomers