Lecture 26: Mutation, Mutagens, Repair
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Transition
purine to purine or pyrimidine to pyrimidine
Transversion
pyrimidine to purine or purine to pyrimidine
Nonsynonymous
mutation alters the animo acid sequence of protein
missense and neutral
Missense
changes in amino acid that may alter protein function or protein is non-functional
Neutral
change in amino acid that doesn’t affect protein function
Nonsense
changes codon so it becomes a codon stop
ex) GAG mutates to UAG
Synonymous (Silent)
codes for the same amino acid
ex) AGG mutates to CGG but both are Arginine anyways
Readthrough
stop codon is changes to a codon that codes for amino acids resulting in a larger protein
Exact Reversion
causes normal codon to be put back into position
AAA —> GAA —> AAA
Lys Glu Lys
Equivalent Reversion
restores normal phenotype but the DNA sequence after the equivalent reversion isn’t exactly the same as normal
UCC —> UGC —> AGC
Ser Cys Ser
Intragenic
mutations that occur within the same gene
Intergenic
mutations that occur in different genes to restore normal phenotype
Depurination
results in a purinic site where the glycosidic bond is removed at either G or A bases
Wobble Base Pairing
mispairing because of flexibility in helix; results in transitions after replication
Frameshift Mutation
occurs when one or more base pairs of DNA are inserted into the gene which shifts the reading frame of all codons from one involved in the change and onwards, so this can alter start and stop sites
Intercalating Agents
agents like proflavine, ethidium bromide, and acridine orange can slide in between the base pairs of the DNA, distorting the helix and causing template slippage during replication
Pyrimidine Dimers
occur between two pyrimidines that are adjacent to each other on the same strand of double stranded DNA.
UV light can cause these to form.
Most of us have a repair mechanism that catch and repair a large proportion of these dimers.
Individuals with the disorder Xeroderma pigmentosum are lacking a repair mechanism for these dimers resulting in a high frequency of skin cancer among these individuals.
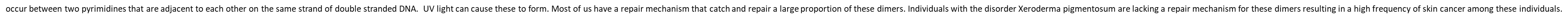
Direct Repair of Pyrimidine Dimers (in bacteria)
Corrects structure of abnormal nucleotide without replacing the nucleotide
Enzyme Photolyase absorbs light and clips dimer
Enzyme is released from the DNA, restoring the normal DNA sequence.
Mismatch Repair
identify improperly paired base pairs and to remove them
Exonucleases remove an area of the new strand from the methylated sequence to the mismatch.
fills in the gap and DNA polymerase ligase seals the nick
Nucleotide Excision Repair
repair many types of DNA damage and is found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
An enzyme complex (UVR Endonuclease) recognizes the distortion in the helix due to the abnormal situation
Strands of DNA are separated and held apart by SSB
Enzyme cleaves sugar phosphate bonds on both sides of lesion removing several nucleotides including the defective area
DNA polymerase fills in gap
DNA ligase seals nick
Base Excision Repair
Glycosylase recognizes and removes defective base resulting in an AP site
glycosylase/specific modified base (uracil, 7-methylguanine, etc.)
AP endonuclease cleaves the phosphodiester bond next to the missing base (causes a nick) and then removes the rest of the nucleotide
DNA polymerase fills in the gap
DNA ligase seals the nick
Double Stranded Break Repair
Homologous Recombination Repair
Uses the sister chromatid to repair the break
Uses the many of the same enzymes as homologous recombination in meiosis
BRCA1, BRCA2
Nonhomologous end joining
Often used in G1
Joins broken ends
often leads to translocations, deletions and insertions
Translesion DNA Repair
Specialized polymerases that can bypass lesions on the DNA during replication
polymerases often make errors and allow replication to proceed at the cost of introducing mutations
Point vs Frameshift Mutation
Frameshift mutations occur when one or more base pairs of DNA are inserted/deleted into the gene
Point mutation occurs when one base pair is substituted for another
Some chemicals that cause transitions are
base analogs
alkylating agents
deamination
hydroxylamine
Some chemicals that cause transversions are
aflatoxin
8-oxygaunine